Climatology/Heat Budget
Concept of Heat Budget
[edit | edit source]the meaning of budget is an estimate of your income and the expenditure of the same over a certain period of time. Heat is a sort of energy which our earth receives from the sun. Therefore, the energy received (your income) from the sun and its utilization (your expenditure) by/in the atmosphere as well as the surface (land and water surface) of the earth is basically heat budget. In this context, the heat budget has two main components incoming shortwave solar radiation and outgoing long-wave terrestrial radiation. Let us study them in brief:-
Incoming Shortwave Solar Radiation
[edit | edit source]
the sun is the prime source of almost all energy on the earth. This energy coming from the sun is known as solar radiation.Since the sun is extremely hot, it emits shortwave radiation in the form of electromagnetic waves. different types of shortwaves like x-rays, ultraviolet, visible and near infrared . the shortwave energy from the sun is not directly absorbed by the atmosphere.
Processes Involved with Incoming Radiation
[edit | edit source]The uppermost atmosphere of earth receives about one part of energy out of two billion parts radiated from the entire sun’s surface.Processes Involved with energy is the cause of various interactions in the atmospheric systems.the processes involved with incoming radiations: There are three processes operating with the incoming solar radiation. They are:-
- Reflection
- Diffusion
- Scattering
- Absorption
Reflection
[edit | edit source]The meaning of reflection is returning something back from where something was coming. you bring a mirror to the sunlight, a bright beam of light is thrown away from the surface of the mirror. The angle of the reflection of light is dependent on the angle of the incidence. you find that the angle of incidence and angle of reflection is equal.The certain amount of incoming energy is lost and it does not participate in the heating process of atmosphere or the earth’s surface. It is generally expressed in percentage of the incident radiation reflected. It is also called as albedo or coefficient of reflection.

Diffusion and Scattering
[edit | edit source]The term diffusion refers to the spreading of something more widely from its centre to all directions. In scattering, sun energy or light is forced to deviate from the direction of propagation. When the sun energy passes through the atmosphere, it has to travel through numerous solid minute particles of aerosols and gases.In this process of passing through, the energy and light is diffused and scattered.The blue colour of the sky is due to selective scattering of sun light. Before dawn or after the sunset, the sky is red and it is due to diffusion and scattering of red visible light.
Absorption
[edit | edit source]The term absorption refers to a state of being engrossed or being captivated.It is a process by which something is absorbed by another thing. With reference to the absorption of solar radiation, it is done so by the atmosphere or the earth surface. Incoming solar radiation is absorbed by the different elements of atmosphere present at a particular point of time. These elements are gas molecules, water vapour, smoke and dust particles. They trap a part of solar energy during transmission through the atmosphere.

Outgoing Longwave Terrestrial Radiation
[edit | edit source]The received energy from the sun heats the earth surface. Heated earth surface is not that hot hence, it re-emits the energy. This returned energy is in the form of long-wave radiation. In this process, the longwave energy is absorbed by the atmosphere and the atmosphere is warmed up.
Processes Involved with Outgoing Radiation
[edit | edit source]The received energy by the earth as well as by the atmosphere is re-emitted back.It happens through different processes.The outgoing energy involves following processes:--
- Latent heat transfer
- Sensible heat transfer
- Emission by vapour and clouds
- Longwave radiation

Latent Heat Transfer
[edit | edit source]Latent heat is the energy absorbed or released from a substance due to changing phases. For example, when solid to liquid or from liquid to gas or even from solid to gas and vice versa. If a substance is changing from solid to liquid, it absorbs the energy from the surroundings so that its molecules are spread out. If the liquid is again changing its state to gas, it further requires more energy for the same reason.
Sensible Heat Transfer
[edit | edit source]Sensible heat is the energy needed to alter the temperature of a substance without any change in the state. It is possible by absorption of sunlight by the land surface or even the air is warmed up by gaining heat. Release of latent heat or the cool air coming in contact of warm air also cause the temperature to rise.
Emission by Vapour and Clouds
[edit | edit source]Emission means discharge or release of something. Huge amount of terrestrial energy is released through the vapour and clouds. In fact, the energy due to which the atmosphere was heated up, in general, is released through vapour and clouds as well.
Longwave Radiation
[edit | edit source]Little amount of energy is directly released to the space by direct longwave radiation.It means that this amount of energy is not trapped by the atmosphere.

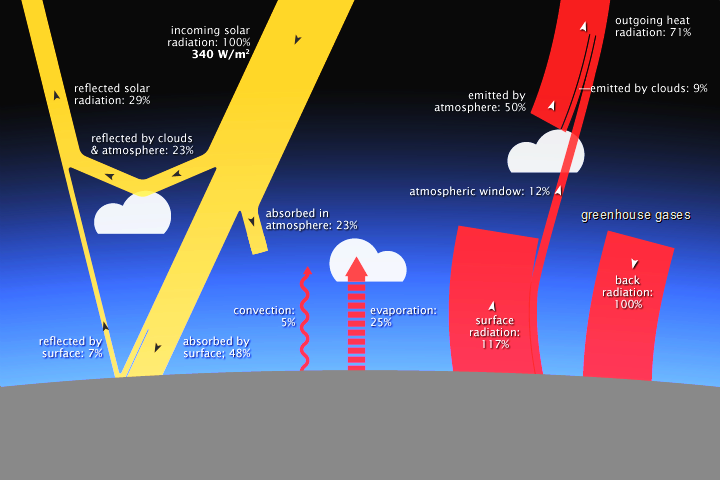
Heat Budget
[edit | edit source]The ideal heat budget of the earth is supposed to be a perfect balance between the incoming solar radiation and outgoing terrestrial radiation.It has to be a zero outcome of the incoming solar radiation and outgoing terrestrial radiation . The total incoming shortwave radiation reaching at the top of the atmosphere is considered to be 100 percent. The distributed and re-distributed of this 100% or 100 units energy is termed as heat budget of the earth. Out of these 100 units, 17 units are reflected back to the space by cloud cover. Air molecules scatter 8 units of the energy back to the space. Energy reached on earth surface is also reflected by some surfaces like snowcover, deserts or other bright surfaces. Their contribution in reflection is 6 units. Hence, the total reflection, from atmosphere (17 units), from air molecules (8 units) and from surface (6 units) is 31 units. This much of energy is not at all used in the heating of the atmosphere or the earth surface. Remaining 69 units are involved in heating of the atmosphere and the earth surface. Out of these 69 units, 19 units are trapped by the water vapour, dust particles and ozone and heats up the atmosphere. Four units are absorbed by clouds and the rest 46 units reach directly to the earth surface. The 31 units directly reflected back to space, 23 units utilized in the atmosphere and 46 units reaching the earth make the total 100 units of incoming solar radiation.
Out of 46 units received by the earth, 9 units are directly released back to space by longwave radiation without heating the atmosphere. Six units of the longwave radiation are absorbed by clouds, water vapour, carbon dioxide and ozone. The total energy used up in heating the atmosphere is 60 units; 37 units released by the earth surface (7 units –sensible heat; 24–units latent heat and 6 units absorbed by clouds, water vapour, carbon dioxide and ozone) and 23 units already absorbed during transmission of the solar energy (19–units absorbed by water vapour, dust particles and ozone and 4 units –absorbed by clouds).
Heat Balance
[edit | edit source]Heating is the process of transfer of energy from a body of higher temperature to another body of lower temperature. The distribution heat energy is not uniform over the earth surface. It has numerous factors to affect. the maximum energy is received near the equator throughout the year. The seasonal variations of energy received are considerable with increasing latitudes.
