History of video games/Esports
-
The Intel Extreme Masters 2013 in Poland.
Early History
[edit | edit source]First game tournament
[edit | edit source]The first video game tournament occurred at Stanford University in Palo Alto, California on October 19th, 1972 with the Spacewar! as the game being played.[1]
Other early events
[edit | edit source]A world championship was held in 1981.[2]
1990's
[edit | edit source]Nintendo World Championship
[edit | edit source]The 1990 Nintendo World Championships was a major event.[3][4]
Age of Fighting Games
[edit | edit source]A number of StreetFighter II versions were made.[5] Over the course of development, ideas from fan modifications were integrated with the official product to create a superior experience.[6]
Rise of competitive FPS
[edit | edit source]Many notable events like Quakecon first saw a start during the 1990's.[7]
Dennis Fong, known as the ace Quake and Doom player Thresh, helps popularize the control scheme WASD.[8][9]
-
Pro Quake gamer Thresh sitting in a Ferrari 328 he had just won from programmer John Carmack in 1997.
2000's
[edit | edit source]StarCraft
[edit | edit source]StarCraft becomes a hit in South Korea as an esport, with it's popularity lasting over a decade.[10] In 2000 World Cyber Games (WCG) is established.[11] StarCraft also gains popularity in China, especially in internet cafes.[11] Following Chinese players winning several gold medals at WGC Seoul 2003, the Ministry of Sports of the Chinese government recognizes esports as an official sport in November 2003,[12][11] becoming one of the first major governments to do so.
Important Developments
[edit | edit source]In 2001 Russia becomes the first nation to recognize Esports as a sport, though the government later retracts this recognition in 2006.[13]
In 2000 the first complete version of Counter Strike is released after Valve cooperation hires modders Jess Cliffe and Minh Le to turn their betas into a full experience.[11][14]
In 2003 the first version of Defense of the Ancients is released as a Warcraft III: The Frozen Throne mod.[15]
-
Televised South Korean Star Craft match in 2006.
-
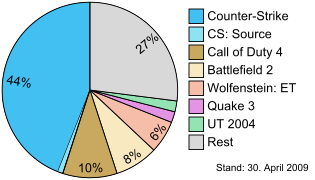
Marketshare of various FPS in America in 2009. Competitive FPS was very popular in the 2000's.
2010's
[edit | edit source]Major Competitions
[edit | edit source]The first DOTA 2 international was held in 2011.[16] Also in 2011 the first League of Legends championship hosted a $100,000 prize and attracted 1.69 million viewers.[17]
American Esports
[edit | edit source]In 2013 the United States government recognizes Esports as a sport.[18][19] This allowed foreign players to obtain professional P-1 visas visit the United States of America to attend competitions.[20][21] In 2019 Pennsylvania lawmakers declare February to be Esports month,[22] The "PA Cup" statewide eSports tournament is announced shortly afterwards.[23] In November 2018 the US Army Esports team is created.[24][25]
-
The International 2016, the Dota2 world championship.
-
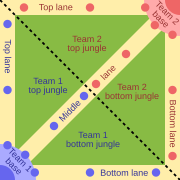
A typical map in a MOBA game, a genre that defined esports in the 2010s.
2020's
[edit | edit source]Collegiate Esports
[edit | edit source]
On June 10th, 2020 the Mid-American Conference for Collegiate Athletics creates the independent Esports Collegiate Conference.[26]
Esports during COVID-19
[edit | edit source]The initial closure of in person sporting events drew many people to esports during the COVID-19 pandemic.[27] Despite this, the cancelation of in person events affected many esports organizations, which then accepted out PPP relief loans.[28]
On November 19th, 2020 The Big House 10 Super Smash Brothers tournament was canceled after Nintendo sent the tournament organizers a cease and disist notice for using netcode needed to make the tournament an online, socially distanced experience.[29] An official Splatoon 2 tournament was canceled following many gamers using tags which supported the Smash Bros community, with an unofficial event The Squid House taking it's place.[30][31]
2020 Olympics
[edit | edit source]Beginning on May 13th, 2021 the International Olympic Committee hosted their first esports event, the Olympic Virtual Series, focusing on games based on real life sports.[32][33][34]
The first virtual motorsport event was won by Valerio Gallo who represented Italy, with Mikail Hizal of German taking second, and Baptiste Beauvois of France taking third.[35]
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ Farokhmanesh, Megan (20 October 2012). "First game tournament, ‘Intergalactic Spacewar Olympics,’ held 40 years ago" (in en). Polygon. https://www.polygon.com/2012/10/20/3529662/first-game-tournament-intergalactic-spacewar-olympics-held-40-years. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ↑ "VIDEO GAMES STAR WAR (Published 1981)". The New York Times. 25 October 1981. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ↑ Fern, Ricky; Conceição, es da (16 May 2015). "Looking back at the 1990 Nintendo World Championships". Goomba Stomp. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ↑ Pitcher, Jenna (5 February 2014). "Nintendo World Championships cartridge sells for $100K on eBay". Polygon. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ↑ Leone, Matt (23 November 2020). "Street Fighter Alpha: An oral history". Polygon.
- ↑ February 2008, David Houghton 14. "Why Street Fighter is still the most important fighting game series around". gamesradar.
- ↑ Statt, Nick (31 March 2020). "QuakeCon canceled for the first time in 25-year-history over coronavirus". The Verge.
- ↑ Wilde, Tyler (24 June 2016). "How WASD became the standard PC control scheme". PC Gamer.
- ↑ Edwards, Phil (18 October 2018). "Why gamers use WASD to move". Vox. Retrieved 24 November 2020.
- ↑ "StarCraft: Remastered hasn't changed how Korea feels about StarCraft".
- ↑ a b c d Yu, Haiqing (2018). "Game On: The Rise of the eSports Middle Kingdom[1]". Media Industries Journal. doi:10.3998/mij.15031809.0005.106. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ↑ Zhang, Chenglu (13 February 2019). "The Chinese government recognizes esports as a profession". Esports Insider. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ↑ "Gamma Law Why Isn't Russia an Esports Superpower?". Gamma Law. 30 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ↑ "The history of Counter-Strike". Red Bull. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ↑ "Gamasutra - Features - Postmortem: Defense of the Ancients". web.archive.org. 7 December 2010. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ↑ "Announcing "The International"} Dota 2". Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ↑ "League of Legends championship draws nearly 1.7 million viewers". Engadget. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ↑ Tassi, Paul. "The U.S. Now Recognizes eSports Players As Professional Athletes". Forbes. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ↑ Ligman, Kris. "U.S. recognizes eSports players as professional athletes". www.gamasutra.com. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ↑ "US Government Recognizes League of Legends' LSC as Sport - IGN". Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ↑ "Score! Professional video gamers awarded athletic visas". NBC News. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ↑ Fogel, Stefanie (5 February 2019). "PA Lawmakers Debate Video Game 'Sin Tax' During State's Esports Month". Variety. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
{{cite web}}: Missing|author1=(help) - ↑ "Harrisburg University announces statewide esports tournament on Pa.'s first annual Esports Day". pennlive. 6 February 2019. Retrieved 9 December 2020.
- ↑ "The U.S. Army Turns to Esports as It Fails to Meet Its Recruitment Targets - IGN" (in en). https://www.ign.com/articles/2018/11/15/the-us-army-turns-to-esports-as-it-fails-to-meet-its-recruitment-targets.
- ↑ "US Army launching esports team as recruiting effort" (in en). GamesIndustry.biz. https://www.gamesindustry.biz/articles/2018-11-14-us-army-launching-esports-team-as-recruiting-effort.
- ↑ "MAC Membership Unveils Esports Venture". getsomemaction.com. Retrieved 10 November 2020.
- ↑ "COVID-19 and the Rise of Esports". University of Nevada, Las Vegas.
- ↑ "Why Professional Gamers Are Getting Loans From the Government". www.vice.com. Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- ↑ Good, Owen S. (19 November 2020). "Smash Bros. tournament The Big House 10 canceled over netcode". Polygon.
- ↑ Hernandez, Patricia (7 December 2020). "Fans say Nintendo canceled tourney over Smash Bros. protest". Polygon. Retrieved 7 December 2020.
- ↑ "Smash Bros, Splatoon and Other Fan Communities Clash With Nintendo - IGN" (in en). https://www.ign.com/articles/nintendo-smash-bros-splatoon-etika-joy-cons-communities-freemelee-freesplatoon.
- ↑ Horiuchi, Junko (28 June 2021). "IOC weighs addition of pandemic-boosted virtual sports to Olympics". The Japan Times. https://www.japantimes.co.jp/sports/2021/06/28/olympics/ioc-esports-future-games/.
- ↑ Peters, Jay (2 June 2021). "The Olympics’ vision of gaming looks very different from the biggest esports" (in en). The Verge. https://www.theverge.com/2021/6/2/22464255/olympic-virtual-series-esports-most-popular-games.
- ↑ Note: Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the 2020 Olympic games were held in 2021.
- ↑ Evans, Andrew (23 June 2021). "Valerio Gallo Wins Gran Turismo Olympic Virtual Series". GTPlanet. https://www.gtplanet.net/valerio-gallo-wins-olympic-20210623/.