Introduction to Computer Information Systems/Print version
| This is the print version of Introduction to Computer Information Systems You won't see this message or any elements not part of the book's content when you print or preview this page. |
The current, editable version of this book is available in Wikibooks, the open-content textbooks collection, at
https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Introduction_to_Computer_Information_Systems
Computers in Your Life
Why Learn About Computers?
[edit | edit source]Today's world runs on computers. Nearly every aspect of modern life involves computers in some form or fashion. As technology is advancing, the scale of computer use is increasing. Computer users include both corporate companies and individuals. Computers are efficient and reliable; they ease people's onerous jobs through software and applications specific to their needs offering convenience. Moreover, computers allow users to generate correct information quickly, hold the information so it is available at any time. Computers and technology affect how we live, work and entertain ourselves. From voice-powered personal assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Cortana to more underlying and fundamental technologies such as behavioral algorithms, suggestive searches and autonomously-powered self-driving vehicles boasting powerful predictive capabilities.
Computers offer a quicker way to gain information which is by providing an internet access. Up to this moment, many internet browsers and applications have been invented. For instance, Google Chrome is one of the largest web based applications used by everyone in the world for reliable sources of information.
Computer skills are required to be hired in companies these days. Imagine if two candidates are interviewed, one of them knows nothing about computers while the other does. The employer will definitely hire the latter. Furthermore, with computer skills, one can build his own company and expand his business. He could perhaps work online and export his goods or service.

Not only have computers become more integrated in our lives. They are increasingly becoming more essential in any aspect of life. As computers become more essential, the skill to operate them also becomes more essential. They are no longer just an advantage but rather a requirement in today’s computer-oriented society. Those who have not had the opportunity to learn computer skills when computers were not as widespread have started to, or are forced to learn to use them as computer skills have become a necessity in order to be a productive and contributing person in not only the workplace but also in society.
Proof of the ever increasing integration in our lives comes from the fact that almost anything can be done with the use of computers. You can now order food, even groceries, through the computer, you can now watch almost anything on your computer, you can now work from home or you can play games to procrastinate at work through the help of computers, you can even conduct interviews through your computer, there are so many things that a computer is capable of that learning the skills to fully reach the potential of computers is a priority.[1]
Computers at Home
[edit | edit source]
A computer is a good product to have at home. There are so many benefits to owning your own computer. It allows you to be able to write letters, articles, stories, reports and other things easier and faster. If you own a printer, you can easily write a letter to a friend or family member, print it out and send it to them. You can save your written documents on your home computer and have easy access to them when you need them again.
Having a computer at home allows you to have access to work from home jobs such as research, data entry, writing and other work-from-home jobs. With a computer at home, you can easily communicate with friends and family through email, social networks and instant messaging. Using a computer to communicate is cheaper than calling friends and family long distance. You can also communicate with co-workers, your boss and anyone else you meet on the Internet through your own computer.
People usually go to the library for their research. If you have your own computer at home, you don't have to travel to the library when you need to research something. Log on to the Internet and research whatever you need with your computer at home. When you need to know something fast you can look it up on Google or your favorite search engine. Having a computer at home gives you access to learning all kinds of things through research. This will save you on gas charges instead of having to drive to the library.
Having a computer at home means your own personal entertainment source. There are literally thousands of games on the Internet which you can play anytime you want to. You can also watch movies and your favorite TV shows on DVDs. You can also join social networks and interact with your friends on a daily basis.
With a computer at home and the Internet, students can now get a college degree from home. There are a lot of different schools that allow students to take college classes online. Using a computer and the Internet can get you a degree at your own pace and faster than going to a college campus.
While almost every household has at least one personal computer within it, desktop and laptop computers are no longer the only computers found in the home. Many homes have numerous computers embedded throughout. Thermostats, appliances, entertainment systems and home security systems are just a few examples of things in a home that can be controlled by an internal computer. These smart homes are capable of so much. All of the devices work on a network and often communicate wirelessly. Home security systems can be monitored from an offsite location. Lights can be turned on and off remotely. Simple tasks, like watering the lawn or running the dishwasher, can be programmed to occur at the homeowners’ convenience, or specifically timed to conserve energy. Some thermostats can even learn and adapt to homeowner preferences.
Smart homes are becoming more and more common. Technology is advancing at a rapid rate and smart homes are expected to become the norm in the very near future. The smart devices and appliances can be controlled from personal computers, or other network devices like smart phones. Some people believe that these homes will eventually be smart enough to recognize the inhabitants and adapt to the needs,[2] giving the phrase computers in the home a whole new meaning.
Computers in Education
[edit | edit source]

At most colleges and universities, their students are familiar with blackboard,[3] a course management system that is used quite frequently in order to stay in touch with teachers, figure out homework assignments, and keep track of grades. While not all classes utilize this technology, it can be very helpful especially for online courses. With technology growing and advancing so far forward we now have the ability to learn and take classes from the comfort of our own home.
While many students still go on campus, there is no shortage of computers. Most colleges have at least one mega lab with nearly a hundred computers. But if you wish to bring your own laptop there are plenty of wireless hot spots where you could get a connection to the internet from anywhere on campus. Understandably lugging textbooks around campus may seem exhausting and tiring, you now have the option to get an electronic e-Book of most textbooks needed for class.
Most people are knowledgeable on the fact that computers are widely-used in colleges and at universities, but let's take a step back and take a look at the ways in which computers are used in elementary schools. The biggest benefit of a computer being used in a classroom is that it can provide many different study tools depending on the class. They can provide electronic flashcards, math games, and even things as simple as crossword puzzles. Although a computer cannot replace a teacher, it can help expand a students independent thinking skills by allowing activities to be taken as many times as needed. Most of the activities found in classrooms are very interactive which helps keep the student interested. Also, we must not forget that because modern day children are drawn towards electronics, they are more compelled to engage in study activities on a computer rather than a sheet of paper.
Working on a computer at an early age helps build fundamental skills needed later on in life. At a young age a child can learn how to fully operate the basic external hardware of a computer like the screen, keyboard, or mouse. With enough exposure to computers and their components, a student can become more efficient for the following years of school and even their future career.[4]
Computers on the Job
[edit | edit source]If you have seen any older movie (or SpongeBob) you have probably seen people getting to work grabbing their time card and getting it stamped to show what time they have arrived at work. This is called an authentication system or timesheet.[5] While now the authentication system is more digital than before, the concept still applies. This isn't the only use of computers on the job or at work in general. For instance say there is a presentation you must give to the board of directors, you might want to make a PowerPoint[6] to give visuals to help drive home your point. Or perhaps you work retail and the pair of pants a customer wants is out of stock, you could easily order it online for them, and minimize the headache of shopping for those who hardly shop. Whatever the case, computers can help.
Spectrum of Computers
[edit | edit source]Every industry has computers. These machines have been incorporated into the fabric of every workforce. Computers have even created many fields which did not exist prior to their existence.[7] Computers manifest themselves in different ways to perform unique tasks. One size does not fit all in the realm of computers, rather each has a purpose or assigned task. The computers that fulfill similar tasks can be classed together. The categories range from small scale to industrial. An embedded computer is something that allows somewhere like an office to have appliances that range from routers to printers. Then there are mobile devices such as smart phones, tablets, and smart watches that are, for example, able to keep a New York stock broker up-to-date on the latest stocks, or instantly keep in touch with investors. These devices have compressed, basic operating systems −although they are getting more advanced by the day. Personal computers are one order of magnitude up from mobile devices. Personal computers have the full and universal capabilities in order to have the capacity to access work from outside the workplace, as well as handle the software that might be used on the job. Midrange computers or midrange servers are yet another order of magnitude up on the spectrum. These machines are between 20 and 50 times larger than a traditional desktop computer, though their previous name was a "minicomputer" and has business and scientific applications. These computers are often referred to as servers due to the majority of them being used as such.[8] Next are Mainframe computers, which are primarily used by large corporations and governments to store and process massive amounts of information. This leads to the final class which is Supercomputers. As the name would suggest, this type of computer is quite powerful. It calculates enormous amounts of information with countless variables to get information. These are responsible for tasks such as weather prediction, security, simulating the moment the universe came into existence, as well as helping to create the next tier of computer - which is not yet fully operational - the quantum computer.
-
Embedded Computer
-
Personal Computers
-
Midrange Servers
-
Mainframe Computers
-
Supercomputers
Electronic Flight Bags
[edit | edit source]
Computers have been ubiquitous in most work places since the mid 1990’s. A notable exception, until recently, is the commercial airliner flight deck. In the last 5 years, electronic flight bags (EFB’s) have become more and more commonplace. Before the FAA approved EFB’s, pilots would have to carry paper charts, approach plates, and aircraft manuals and checklists for each flight. This paper system was cumbersome, heavy, and took up the space of an extra suitcase. Now, tablets are taking the place of this system. In 2012, United Airlines provided their pilots with mounting hardware, and iPads for use in the cockpit.[9] Southwest and American Airlines followed suit.[10] Now, most major airlines use EFB’s for their operations. This allows for more complex flight planning, greater precision and efficiency, and better organization. Airlines also save weight, as pilots no longer have to bring 45 pounds of paper with them on their flights. The use of a tablet brings the weight down to 1.5 pounds. Not only does this make the pilots life easier, but it also helps the airline save on jet fuel.[11] Future aircraft designs have tablet mounting and charging stations built into the flight deck, to make the integration of the system even more seamless.
Portable Computers
[edit | edit source]
Phablets, a portmanteau of "Phone" and "Tablet", were first pioneered in 2007 by HTC. The concept was an original hybridization, borrowing the large, touchscreen display from a tablet computer and the functionality and size from a mobile cellular phone. The idea was eventually adopted by other large manufacturers including LG (GW990) and Nokia (N810), and underwent several different phases. The early generations had, in addition to a touchscreen, physical keyboards whereas the later ones do not. The Verizon Streak, produced and carried by the network, was released in 2009. Unlike most others at the time, it was restricted to phone and internet use within the household only. The current style of phablets was not popularized until 2011, after the launch of the Samsung Galaxy Note, (Android) which featured a 5.3" inch display and a removable stylus.[12]

Portable computers are compact and fully functioning versions of a regular desktop computer that are designed to be mobile. While they rely on rechargeable batteries or an electrical outlet for power, they allow a person the freedom to move around while still being productive. Their mobility alongside their ability to operate similar to a desktop make them powerful tools for businessmen, students, and common individuals alike. Whether giving or preparing a project or presentation, taking notes or studying online, or simply connecting to the internet from a cafe, portable computers have become essential for individuals who wish to work, study, or play on the go. Portable computers come in three basic versions which include the laptop, tablet, and netbook.

Laptops are thin computers that contain a keyboard and monitor folded on top of each other so that the top half is the visual display and the bottom half is the input. Laptops are commonly called "notebooks" do to this folding feature and their thin appearance. Recently, touch screens have been introduced into some laptops allowing some operating systems like Windows 8 to open applications with the touch of a finger. While laptops are comparable to desktops in their use, their smaller size results in some small amounts of the computing power and functionality being lost. However, their compact size allows them to be stored when not in use and the familiar "nest" of wires associated with linking up a desktop is reduced to a single power cord. Laptops are also better at "creating" fully functional content when compared to a Tablet or Mobile Device (such as a cell phone). If you require the ability to write reports or long e-mails, to use a spreadsheet in order to crunch numbers, to create a "PowerPoint" presentation, to rearrange music libraries or photo albums, or to edit pictures then you will need a desktop, laptop or a netbook. Tablets and Mobile Devices are more designed to consume content than to create.[13]
Tablets are smaller than laptop PCs, very lightweight, and extremely easy to carry, but they lack the processing power of a laptop as well as a keyboard input. They rely, instead, on a stylus and touch screen. For those who are hardcore gamers, giving business presentations, or conducting heavy research a tablet doesn't offer the speed and efficiency that is needed to complete these tasks. However, if a person is more of a casual internet surfer or "lightweight" game player then a tablet can handle what computing is needed to do this. They can browse the web relatively easy and stream movies or Youtube videos too. It should also be noted that tablets have become handy for other lightweight tasks involved with simple music/DJ production like FX and mixing as well as live sequencing. Some artists and designers are now using their tablets for preliminary sketches that they transfer into design software and programs on a full powered laptop later on as well.[14]
Netbooks are similar to laptops but differ in size as well as processing. While netbooks are smaller versions of laptops, they have been designed, to the best of their ability, to have the same functionality as laptops and PCs. A netbook's computer display will rarely reach above 10" or 12", and are more commonly smaller than this, whereas some laptops can contain up to 15.5" of display screen. Netbooks have been around since 2008, roughly, and have revolved around their ability to connect to mobile networks such as the wifi at your local cafe or restaurant. Because of this feature, it has changed the laptop industry and has been heralded as a revolutionary and pivotal focal point in the production of laptops and netbooks. Since then this capability has now become a standard among both. Even though they don't maintain some of the functionality and computing power as their desktop and laptop counterparts, they are still capable of word processing, mathematical computation, and other productivity programs that businessmen and students use. On top of that, they are also extremely durable and affordable which make them perfect for educational tools. Students will find them easy to manage, organize, and carry around as well as a "distraction free" resource because of their minimalistic capabilities. Couple these advantages with internet access to mobile hotspots such as school libraries and it can be easily seen why this device had dominated the market for so long. It has only been a recent trend for individuals to pick up the tablet despite it's rudimentary processing power and it has been speculated that this is due to the tablet's sleek design and effective marketing strategy toward the younger generation.[15]
Smartphones are mobile personal computers that use advanced mobile operating systems that allow mobile, handheld usage. A smartphone is much smaller than a tablet making it easy to fit one in a pocket. Not only can a smartphone make voice calls it can also send and receive text messages. Smartphones have digital personal assistants, event calendars, media players, video games, GPS navigation, and the ability to take digital photos and videos. A smartphone can also access the internet by either connecting to Wi-Fi or using cellular data. The user may also download many helpful apps to a smartphone.[16]
-
Netbook
-
Laptop vs. Netbook
-
smartphones
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://www.pixuffle.net/the-importance-of-computers-in-our-daily-lives/
- ↑ http://www.wired.com/insights/2014/10/smart-homes-of-the-future/
- ↑ http://www.blackboard.com
- ↑ http://everydaylife.globalpost.com/should-computers-used-early-elementary-schools-3986.html
- ↑ Wikipedia: Timesheet
- ↑ http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/powerpoint/
- ↑ http://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/index.html?nbId=7345&nbNodeId=1013914#!&parentId=1013918
- ↑ http://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia/term/47026/midrange-computer
- ↑ http://www.apple.com/ipad/business/profiles/united-airlines/
- ↑ http://www.cnn.com/2012/09/14/travel/ipads-in-airline-cockpits/index.html
- ↑ http://www.apple.com/ipad/business/profiles/united-airlines/
- ↑ http://www.verizonwireless.com/mobile-living/tech-smarts/what-is-a-phablet-verizon-samsung/
- ↑ http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2364302,00.asp
- ↑ http://www.lenovo.com/us/en/faqs/laptop-vs-tablet/
- ↑ http://www.lenovo.com/us/en/faqs/what-is-a-netbook/#eventbody1
- ↑ Wikipedia: Smartphone
What is a Computer?
Data vs. Information
[edit | edit source]

Data is calculated and processed on a daily basis through computers in business, at home, and in education. Data is essentially the raw facts that are usually typed into a computer. We call these "raw" facts due to them being unorganized. They can come in any form from audio and visual, to text and numerical. When the data is entered into the computer, it is considered input. The computer calculates the data and spits out the information. Since this information is the output, it becomes the organized version of what used to be raw facts. This system is considered information processing. Data can also come in other forms including figures, experiments, and surveys. Most everything that is entered into a computer becomes data, which is why this term is so vital to understanding computers and how they operate.[1] Information is produced by the data; it is form of knowledge, and computers calculate detailed information.[2]
When most people think of information, the first source that comes to mind is Google. Google allows you to access a lot of information in a short amount of time. What most do not know is that is exactly what a computer does behind the scenes every time you are entering data into a computer, most of the time without even considering it to be "data." Information is a way to get answers to questions, because they are the output of the data you have put in to process. Many online sources provide endless amounts of information. Without information, people will not have reliable sources for school and their career. Work can be made much easier with information, including jobs which need to calculate employee's total hours worked, or any "total data" that needs to be found or calculated. Data and information are very valuable, and is most certainly the backbone of a computer. These two components may help your computer to be user-friendly by working behind what you are typing to make data useful and organized.[3]

Computers Then and Now
[edit | edit source]The Industrial Age: First general mechanical computer was proposed and partially built by the English inventor Charles Babbage in 1837. It was an Analytical Engine which contained an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and permitted basic programmatic flow control. It was programmed using punch cards, and also featured integrated memory. Historians consider it to be the first design concept of a general-purpose computer. Unfortunately, because of funding issues the Analytical Engine was never built while Babbage was alive. It wasn't until 1910 that Henry Babbage, Charles Babbage's youngest son, was able to complete a portion of this machine which was able to perform basic calculations. The Analytical Engine was to be a general-purpose, fully program-controlled, automatic mechanical digital computer. It was designed to consist of four components: the mill, the store, the reader, and the printer- which are all essential components of every computer today.[4]
The Information Age (beginning in 1950 until current): Also known as the Computer Age, Digital Age, or New Media Age. Digital computing was invented by Claude Shannon in late 1950's. What he envisioned was a computer built from electrical circuits instead of motors. By drawing on Boolean algebra — which assigns the value of “1” to “true” statements and the value of “0” to “false” statements — he applied the value of “1” to circuits turned on, and the value of “0” to circuits that were off. Shannon also pioneered the field of information theory, which addresses the issue of how to quantify information, as in “bits” and “bytes.” To express information in a “bit,” one uses a binary digit, either a “1” or a “0.” These binary digits can describe everything from words to pictures to songs to videos to the most sophisticated gaming software.[5]
Today, it is difficult for any student to imagine life without a computer. However, computers have only been around since the mid 1900's. The computer industry went from making computers that took up an entire classroom to currently being able to fit into a student's backpack. Also, computers used to be much more expensive and required a greater amount of energy than today's computers. Finally, in the 1980s, people began placing these foreign objects into their home. During this time, people had to really study and be patient with this handy device.[6] People have seen the drastic changes that have been made to computers in a span of only forty years. Computers today are much smaller, lighter, require less energy, and cheaper. However, in today's generation, computers are second nature to most people, and one could not imagine life without them.

Computers in our generation seem to be integrated in our every day life to assist in multiple tasks related to our many needs. So much so, it is difficult to picture our world without them. However, with great success comes great patience. In the first computer model (1946-1957) for example, the machine required certain inputs, referred to as punch cards, and physical work to reprogram the computer. The computer itself was nowhere near as helpful, simple, nor convenient as it is today.
The first generation computers were built with thousands of vacuum tubes, required physical effort to re-wire the computer, and could only solve one problem at a time. The second generation of computers (1958-1963) introduced transistors, which replaced the vacuum tubes. Transistors simply acted as a light switch, allowing the electronic circuits to either open or close. Both first generation computers, and second generation computers continued to use punch cards for their input. Second generation computers also introduced hard drives (hardware), and programming languages (FORTAN & COBOL). Soon after, (1964-1970), the third generation used a system of integrated circuits, which incorporated many transistors and electronic circuits on a single silicon chip. The third generation of computers started the innovative trend of smaller and more reliable computers. Keyboards and monitors were now considered the computer’s input/output. Finally, the development of our current computers, used by practically everyone in society, began. The fourth generation of computers began in 1971, when it was possible to place far more transistors onto a single chip- the microprocessor. This discovery led within the decade to the creation of IBM's personal computers, as well as the popular Apple Macintosh. Consumers currently use inputs, outputs, and storage that consist of: keyboards, mice, monitors, printers, speakers, hard drives, flash memory media, and optical disks. Fifth generation computing devices, based on artificial intelligence, are still in development, though there are some applications, such as voice recognition, that are being used today. The use of parallel processing and superconductors is helping to make artificial intelligence a reality. Quantum computation and molecular and nanotechnology will radically change the face of computers in years to come. The goal of fifth-generation computing is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization.[7]
Although the movement from vacuum tubes to microprocessors seemed to take a while, compared to the beginning of civilization thousands of years ago, this advancement happened very quickly. However, it also opens the human mind to realize that innovation takes trial, error, and patience.[8]
Hardware
[edit | edit source]The term hardware refers to the components used to build a computer. Breaking down the components into categories, you will find four main groups:
- Input
- Output
- storage
- processing
Although these are the four main categories, there are three more components to consider that do not fit into those main four:
- Case
- Power Supply
- Expansion Cards
Case
[edit | edit source]A computer case is used to put the essential components of a computer in. This provides an enclosed space and easier organization for the components to go.
Power Supply
[edit | edit source]A power supply unit (PSU) is used to power all components inside the case. It does this by converting AC power to DC power that is regulated by the PSU. What this means is that each component needs a certain amount of volts to work and the power supply will regulate the volts accordingly.
Expansion Cards
[edit | edit source]An expansion card is used to enhance certain attributes of the system. For example, a sound card can enhance sound by giving you surround sound capability. Another example is a video card, this will enhance the graphics of your system.
-
Sound Card
-
Video Card
Input/Output
[edit | edit source]This category refers to the components a computer uses that receive data and send information. Input devices do the receiving and the output devices do the sending. Some examples of input devices are a keyboard, mouse, and a gaming controller. Examples of output devices are a printer, monitor, and speakers.
-
Keyboard
-
Mouse
-
Controller
-
Printer
-
Monitor
-
Speakers
Memory
[edit | edit source]The memory within a computer can be broken down into two categories: short term memory and long term memory. Short term memory is the random access memory (RAM) while the long term is either your hard disk drive (HDD) or compact disk drive (CDD). RAM can be tapped into immediately by programs on a computer allowing it to compute faster, but if the user needs to save information for later use, using the HDD or CDD is required.
-
RAM
-
HDD
-
CDD
CPU
[edit | edit source]The central processing unit (CPU) is used to calculate the commands sent to it by the programs used on the system. It performs all the arithmetic and logical operations. This comes in the form of a small chip that is connected into the computer motherboard. The motherboard is where all other devices are connected so they can speak with each other.
-
CPU Chip
-
Motherboard
Communications Hardware
[edit | edit source]
Communications hardware is important when it comes to letting computer users access information from the Internet, put information onto the Internet, or interact with other computer users on a network. This type of hardware includes modems, routers, and network adapters. Modems and routers are the devices that connect computer users to the Internet: Signals go from the Internet service provider to the modem, which then converts them into an appropriate form and sends them through the router to the computer (or, when the computer user is sending information to the Internet, signals are sent via the router to the modem, which converts them and sends them to the Internet service provider.)[9] Modems and routers can be either wired or, increasingly commonly, wireless, communicating with the computer via signals rather than a physical connection. Network adapters are what allow computers to communicate on a small, local network. Sometimes, however, a computer may have a network adapter that consists entirely of software, called a virtual adapter. If this is in use, such as on a virtual private network (VPN), then no hardware component is needed.[10]
Software
[edit | edit source]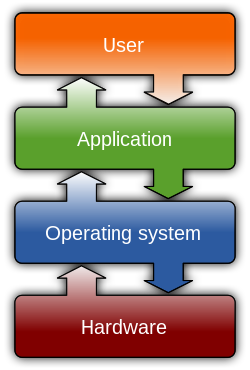
Computer software is used to communicate with the computer processor to direct certain operations to be performed. This is done through computer programming languages. Software can be broken into two parts: System Software and Application Software.
System Software
[edit | edit source]System software refers to the software used to operate the computer components. This also provides a foundation for application software, giving it the ability to carry out the desired functions. System software commonly comes on a system CD, for example a Windows 7 CD. This CD provides the operating system, drivers, Windows system, and utility software. The operating system allows the parts of the computer to communicate. This is done by transferring data. This is also the specific component of system software that allows for the running of application software. Utility software maintains the computer systems. Device drivers set up the ability for the hardware connected to the computer to function. Windows systems is the part that gives you a graphical interface on your monitor and allows the user to configure all connected devices.
-
BIOS Menu
Application Software
[edit | edit source]Application software are the programs and applications that are developed to carry out desired functions by the user. The way an application works is through programming software. Programming software is the middle man between the system and the actual application the user wants to run. Some examples of programming languages are Java, C++, and Visual Basic. Some examples of application software are web browsers and video games.
-
Repeat loop for Mint
-
Firefox logo

Computer Users and Professionals
[edit | edit source]Computers are nothing without the people that use them, the common user and the professional. The common user is anyone that uses the computer for general purposes. This includes checking emails, playing computer games, typing up a paper, and the list goes on. What distinguishes a common user from a professional is that a professional works in the field of computer information technology. Examples of professions in this field are a computer programmer, web designer, network administrator, and software engineer. These are but a few of the many jobs involved in the field of computer information technology. These are the people that design the hardware to build computers, they keep business networks secure, they program software to communicate effectively with the user and hardware, and develop the latest and greatest software for the common user to enjoy.
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://otec.uoregon.edu/data-wisdom.htm
- ↑ http://www.huridocs.org/information-systems/
- ↑ Understanding Computer Today and Tomorrow 14th Edition Comprehensive
- ↑ Technology/Analytical-Engine
- ↑ Claude Shannon: The Juggling Unicyclist Who Pedaled Us Into the Digital Age
- ↑ http://www.youngzine.org/article-u-write/first-computers
- ↑ The Five Generations of Computers
- ↑ Understanding Computer Today and Tomorrow 14th Edition Comprehensive
- ↑ http://www.pcmag.com/encyclopedia/term/63628/modem-vs-router
- ↑ http://compnetworking.about.com/od/hardwarenetworkgear/a/networkadapter.htm
Computers to Fit Every Need
Phablets
[edit | edit source]Phablets, a portmanteau of "Phone" and "Tablet", were first pioneered in 2007 by HTC. The concept was an original hybridization, borrowing the large, touchscreen display from a tablet computer and the functionality and size from a mobile cellular phone. The idea was eventually adopted by other large manufacturers including LG (GW990) and Nokia (N810), and underwent several different phases. The early generations had, in addition to a touchscreen, physical keyboards whereas the later ones do not. The Verizon Streak, produced and carried by the network, was released in 2009. Unlike most others at the time, it was restricted to phone and internet use within the household only. The current style of phablets was not popularized until 2011, after the launch of the Samsung Galaxy Note, (Android) which featured a 5.3" inch display and a removable stylus.[1]

Embedded Computers
[edit | edit source]

An embedded computer is a mini computer with a specific function within a product that completes detailed tasks or jobs for that product. Often times, individuals do not realize how many objects have embedded computers enclosed in them. Some examples of embedded computers used in households include, remote controls, heating pads, digital clocks, washing machines, and microwaves. Others include Bluetooth capabilities in cars, camera traffic lights, and Red Box machines. Surprisingly, a pregnancy test is also considered a simple, yet complicated embedded computer.[2] Embedded computers are developed to do one particular duty, and therefore a regular computer cannot act as an embedded computer.
So how does an embedded computer work? To put it into simple terms, an embedded computer is a computing chip rooted directly onto its motherboard or logic board. Before embedded computers were invented, a computing chip would be connected via wires to the motherboard, which would then be connected via more wires to the RAM and other peripherals. This not only made the interior of any computing device look like an absolute mess, but it was incredibly inefficient and performance was never what it could have been given the capacities of the components involved. With the advent of “embedded” or “integrated” components, the interior is free of all these transferring wires, and data only needs to bridge a small gap, rather than travel through tons of cables. The advantages of the embedded computers are that the bussing speed for data has greatly improved over externally transported components due to the minimal amount of physical distance data needs to travel.[3] Today, there are specialized jobs just for programming embedded computers.[4] The first embedded system used was the Apollo Guidance Computer created by Charles Stark Draper. It was considered to be one of the highest risks in the Apollo project since it was newly developed, but since then it has been proven to be more efficient.[5] Embedding computer technology has continued to develop and the “gaps” that needed to be covered have become smaller and smaller. A great example of this is the cell phone, which has evolved from the first “portable” bag phones into today’s iPhone5s that can fit in the palm of one’s hand. These embedded computer systems are used in all areas of life, and can be found anywhere from cooking and consumer functions to medical and military tasks.[6]
Mobile Devices
[edit | edit source]A mobile device is a handheld tablet or other device that is made for portability, and is therefore both compact and lightweight. New data storage, processing and display technologies have allowed these small devices to do nearly anything that had previously been traditionally done with larger personal computers.[7] These mobile devices are capable of numerous tasks including making phone calls, sending text messages, viewing Web pages, playing games, downloading music, taking digital photos, and watching TV shows and movies. With our ever-growing world of technology, mobile devices are at the tips of our fingers. Questions can be answered, maps can be observed, and weather can be checked. Of the many mobile devices used today, smartphones are the most common form of device. They have Internet capabilities along with the extensive list above. Tablet devices do not have all the capabilities smartphones have, but they are used for Web browsing, gaming, taking digital photos, and playing movies as well as TV shows. Mobile devices are now a big part of people’s everyday lives. Google stated, “The mobile phone might be the world’s most ubiquitous device…” (www.thinkwithgoogle.com/insights/uploads/940910.pdf/download/). This shows how technology will keep improving, to become the some of the most widely used devices around.
One of the drawbacks to some of the newer mobile devices is their use of non removable batteries. These batteries are designed to make the device more light weight. Although they are made to last for the duration of the computers life, there are instances when they fail. If this happens, it can be pricy and difficult for them to be replaced. Because of this, it is not uncommon for a user to simply throw the device away rather than spend the time or money to fix it. This has resulted in a big increase in what is known as e-trash, or electronic trash. Adding to this problem is the fact that these devices often contain toxic and harmful chemicals and eventually end up in landfills that are not able to dispose of them properly. Much of these devices make their way to countries with less standards and regulations for waste management, giving way to environmentally unfriendly and dangerous practices. This leads to toxic and lethal chemicals entering the air and water. Certain organizations such as Clean Production Action and Greenpeace have developed programs to attempt to persuade manufactures to stop using hazardous chemicals in their products. Unfortunately it may already be too late to reverse the damages done from e-waste. It is essential for the well being of this planet that mobile devices and other computer equipment are disposed of properly.[8]
Personal Computers
[edit | edit source]
A personal computer is a computer that is mainly for individual use. Before personal computers, computers were designed for companies who would then attach terminals that would allow for more than one user to a single large computer and the resources were shared among all users. The first personal computers came out around the 1970s. The most popular of the time was the Apple II, which came out in 1977 from Apple Computer. In 1981, IBM came out with its first personal computer. IBM PC took over the market and it was what most people bought. Personal computers use single-user systems and are based on microprocessors.[9] Many people do link their personal computers together to create a network. Most personal computers are made up of a central processing unit, control circuitry on an integrated circuit, and various input/output devices. It also contains two types of memory; main memory and auxiliary memory. The sales of personal computers has grown tremendously over the years, according to Michael Dell in 2005 there were 240 million personal computers sold worldwide.[10] The sale of personal computers will, likely, continue to increase.
Midrange Servers
[edit | edit source]

Midrange servers were also known as midrange computers or minicomputers in 1960s and were mostly sold to small and medium-sized businesses. However, midrange servers started to become popular in the 1990s. Midrange servers are used to host data and programs for networks, such as in hospitals or school computer labs. Midrange servers stand in between entry-level servers and mainframe computers. The big difference between midrange servers and mainframe computers is that the midrange servers function as stand-alone personal computers where mainframes are a network hosts. Midrange servers tend to have more memory capacity, such as random access memory (RAM), processing power (have multiple processors), room for expansion (have comparably large hard drives), and are more expensive than desktop computers.[11] Midrange servers are not limited for business use only. Another type of midrange servers is a special home server that can be build or purchase when personal computer is not enough. Special home server links all the content from all the computers onto one network.[12] Moreover, something that is happening more frequently with midrange servers is called virtualization. It involves splitting hard drives and creating two separate hard drives. It can also involve server virtualization which is splitting the physical server into smaller virtual servers. Each virtual server can run multiple operating system requests at the same time. Virtualizing servers is the best solution for small and medium-scale applications.[13] Virtualization helps companies to use fewer servers and that leads them to reduced costs and less server management.[14]
Mainframe Computers
[edit | edit source]

Mainframe Computers are much larger computers that consolidate the needs of large organizations like universities, hospitals, banks, government offices, etc. These much more powerful and expensive computers are usually stored in data centers where they connect to all the other computers using a computer network. From this room a single mainframe can serve thousands of users on the same network. Early mainframe computers were first produced in the 1950s due to the increasing processing demands of growing businesses. From then on, these mainframes have increased in power and improved in size.[15] However, with more processing power, this requires more energy consumption, leading computer manufacturers to focus more on energy efficiency in these new computers. Manufacturers also began bundling free software with their mainframe computers as an incentive to help compete against other computer manufacturers. Eventually, a lot of these programs and several new ones were offered as separate products that they could sell rather than just giving them away for free.[16] Today, mainframe manufacturers use advances in technology to further improve the power and efficiency of their computers, one important being virtualization, creating several virtual servers rather than physical ones that take up space.
Mainframe computers may be good for having one space to collect data for a company. They are also known as high end servers, or enterprise class servers. The mainframe computer at IBM has 100,000 virtual servers and is actually very economically efficient, and more and more of businesses are trying to make them the most energy efficient as possible. The mainframe computers need a large enough space to be located for one, since they are used for large business responsibilities, such as computing data for a census, statistics, and economic processing. They are also used for payroll and billing but are constantly running day and night with different tasks to complete all the time. The type of tasks this computer does allow for them to operate for a long time with no interruptions. Mainframe computers are also very expensive. Having to find a way to cool a mainframe computer is difficult just because of their size alone. The other problem with the computers is that they are also expensive to even run, again because of their size. The amount of electricity to cool and run the mainframe computers makes them not the most energy efficient machine to have in a business.
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://www.verizonwireless.com/mobile-living/tech-smarts/what-is-a-phablet-verizon-samsung/
- ↑ http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2379383,00.asp
- ↑ Understanding Computer Today and Tomorrow 14th Edition Comprehensive
- ↑ http://searchenterpriselinux.techtarget.com/definition/embedded-system
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embedded_system
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Embedded_system
- ↑ http://www.techopedia.com/definition/23586/mobile-device
- ↑ Understanding Computer Today and Tomorrow 14th Edition Comprehensive
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/P/personal_computer.html
- ↑ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/personal-computer-PC
- ↑ http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-a-midrange-computer.htm
- ↑ http://www.techopedia.com/definition/14471/midrange
- ↑ http://www.techopedia.com/definition/719/virtualization
- ↑ http://searchservervirtualization.techtarget.com/definition/virtualization
- ↑ http://www.computerhistory.org/revolution/mainframe-computers/7/172
- ↑ http://www.computerhistory.org/revolution/mainframe-computers/7/172
Computer Networks and the Internet
The History of the Internet
[edit | edit source]The history of the internet begins in 1962 with J.C.R. Licklider’s memos about an Intergalactic Network idea, in which users around the world are connected and can access programs and data. With colleagues, he forms a research program called Information Processing Techniques Office (IPTO). After an experiment with an air travel reservation system, the first communication satellite is launched that can allow machines to exchange data. Soon, IBM introduces System 360 computers into the market which becomes remarkably popular. American Airlines debuts IBM’s SABRE air travel reservation system to process on-line transactions, which links over 50 cities through telephone lines (1964).

[1] By 1965 the first wide-area network connection is established by Larry Roberts and Thomas Marill. Over the next four years, the Network Working Group works diligently, creating a router, a modem, and even experimenting with monitors. On October 29, 1969 the first host-to-host connection was made! Then, over 3 years, memory, speed, processing, and communication capabilities are tested and refined and protocols are made. By 1973, 30 institutions are connected to the network called ARPANET.[2] In 1977 Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak announced the Apple II computer, opening the consumer and small business market for computers. This led to the creation of more modems for dial up services. A computer science research network called USENET sets up a server where newsgroups can post to, in 1979. A year later an email only service opens. Less than a decade later, 30,000 networks are on the internet due to the advances with computers, including the new Macintosh computer and the use of Ethernet. [3] Within 2 years the number of hosts jumps to over 160,000! By 1991 over 600,000 hosts are connected in over 100 countries! [4] In just 30 years the hypothetical concept J.C.R. Licklider once toyed with has become a part of everyday life! A lot of experimenting and funding went into the creation of this remarkable "cyberspace."
From ISP to URL
[edit | edit source]Now that you know the history of how the internet came to be, it's time to start exploring. You double-click your browser of choice, the screen opens up... and you start drawing blanks. 'Where do I go from here?' you might start asking yourself. Just take a deep breath; using the internet isn't as complicated as you might think. The most important thing to understand before you start browsing through the cornucopia of online resources is the URL, (Uniform Resource Locator.) The URL uniquely identifies a specific Web page. The URL is composed of a communication protocol, (typically HTTP or HTTPS,) a domain, and a page. If you want to have your own website, you have to buy the domain name and then build upon your address. [5] The most interesting tidbit about domain names is that, just like fingerprints, no two can ever be the same. Unfortunately, this means you can't ever own the domain name www.apetit.com.
Internet Communication
[edit | edit source]

In today's technologically booming society, there are hundreds of ways we are connected to computers and the Internet every day. We use computer networks (collections of computers and other devices that are connected together to enable users to share multiple forms of information)[6] on a daily basis. While it is not always free to do so, such as having to pay an Internet service provider (ISP), there are many places that offer free wifi to people in their area. Today, we mostly use networks for social media, communication, and spreading of information. Think of the networks in your life. I'm guessing something like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, or LinkedIn came to mind along with many others[7]. These are all networks that allow us to share information whether it be personal, images, news stories, surveys, information on new products, etc., these networks have become engrained into our daily lives and most people see them as helpful devices for distance communication and spreading of ideas. Another way we use the Internet for communication is through email. Most people today have an email address because they are required for registration for many different things we use on a daily basis (such as the networks previously listed)[8]. Usernames for e-mails have to be unique to ensure that every person in the world that wants to be on the Internet can have e-mail. E-mails consist of a username (something to identify it specifically), followed by the @ symbol, and finally a domain name like “yahoo”, “gmail”, and many others. Many usernames just incorporate a person’s name, but you can also use periods, underscores, numbers and other symbols to make it unique. In the past, blank spaces were not allowed in a username but some companies do allow it now. One symbol that is still not allowed in a username is the @ symbol, because it could be confused with the same symbol that separates the username and domain name. An example of this is Drupal. It is each company’s responsibility to make sure that each username attached to their domain name is unique. Today's evolving technology is making it easier to access things like networks and email through all of the mobile devices available and the use of apps or condensed mobile versions of the full desktop websites. Besides the obvious social uses of e-mail communication, they are now being used to help college campuses communicate with their students to help alert the students of an emergency like a tornado, dangerous lightning storm, flood warning, or if an intruder is on the campus. All in all, the Internet and computer have changed our world in forms of communication. [9] [10]
Searching the Internet
[edit | edit source]
Searching the internet for a specific page or phrase has become easier than ever through the help of online search engines. Certain webpages, most popularly Google, have specific programs and algorithms that sort through the vast expanse of information available on the web. These websites work by processing keywords that are typed into the search bar and displaying a large list of webpages matching the keywords. Even in the early days of the internet there were programs such as “Gopher” that could help search the net, although the scale of these searches has risen exponentially since then. [11] Using special programs called “spiders”, the search engine compiles a list of results by crawling through the internet starting with the most popular websites and servers for the keywords searched. Through these processes an index is created by the spiders that is constantly being updated regarding the most popular and relevant results of all searches being completed, which on Google is over 3.5 billion per day and 1.2 trillion per year [12]. The more that people use these search engines, the faster and more efficient they become. Other websites may search for more specific information on webpages such as phone numbers, addresses, and maps. The websites where this information is kept are called reference pages.
TCP/IP
[edit | edit source]

TCP/IP - Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol –the most prevalent protocol stack used to connect hosts to the network and networks to each other. The suite of communication protocols has been developed due the request of the Department of Defense as a protocol of an interconnection the experimental “ARPANET” and diverse computing networks. A great contribution to the development of TCP / IP stack has made by the University of Berkeley, implementing protocols stack in its version of OS UNIX which has led to widespread IP protocol. Moreover, the Internet, the biggest global information network, runs on TCP/IP suite and Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is a major contributor to the improvement of the standards of the stack, published in the form of specification RFC. Since the TCP / IP stack was designed before the OSI – Open System Interconnection, his 4 layered structure also corresponds to 7 layered OSI model is rather arbitrary. The lowest (level 4) corresponds to the physical and data link layer model OSI. This level in the TCP / IP protocols is not regulated, but it supports all popular standards of physical and data link layer both LAN (Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, Fast Ethernet, 100VG-AnyLAN0 and WAN - communication protocols, ("Point to Point" SLIP, PPP X.25, Frame Relay). The next level (level 3) - is the level of interconnection, which is engaged in the transmission of packets using a variety of transport technologies of local networks, regional networks, special communication lines, and so on. As the main network layer protocol (in terms of the model OSI) IP, which was originally designed to transmit packets through the many numbers of networks, combined both local and global protocols. Therefore, the IP protocol works well in networks with complex topologies using rationally presence of subsystems and economically consuming bandwidth low-speed communication lines. The IP protocol is a datagram protocol, which means it does not guarantee delivery of packets to the destination node, but trying to do it. Besides the IP protocol, internet layer is represented by some other protocols such as RIP (Routing Internet Protocol), OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol). The last protocol is designed to share information about errors between routers and network node. Level 2 is called the primary. This level is a field of a functioning TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). TCP provides the guaranteed delivering of the information and usually is being used by applications if data integrity and accuracy are critical. The UDP is being used for a non-guaranteed transmitting. The upper level 1 is the application level. Over the years, TCP / IP stack has accumulated a large number of protocols and application-level services. These include such widely used protocols as protocol to copy files FTP, TFTP, telnet, SMTP, HTTP, DNS and etc. [13]
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://www.computerhistory.org/internet_history/
- ↑ http://www.computerhistory.org/internet_history/internet_history_70s.html
- ↑ http://www.computerhistory.org/internet_history/internet_history_80s.html
- ↑ http://www.computerhistory.org/internet_history/internet_history_90s.html
- ↑ https://www.nationalserviceresources.org/understanding%20-urls-and-domain%20-names
- ↑ http://www.techopedia.com/definition/25597/computer-network
- ↑ http://socialmediatoday.com/soravjain/195917/40-most-popular-social-networking-sites-world
- ↑ http://www.email-brokers.com/en/emailing-business-strategy
- ↑ https://www.drupal.org/node/56487
- ↑ http://dmv.ny.gov/transaction-message/information-about-email-addresses
- ↑ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/internet/basics/search-engine1.htm
- ↑ http://www.internetlivestats.com/google-search-statistics/
- ↑ http://www.w3schools.com/website/web_tcpip.asp
Computers and Society
Benefits of a Computer-Oriented Society
[edit | edit source]
Our generation strives to be the quick paced society which we are known to be. To do so, our generation uses computers to their full potential in order to do more tasks and to do them at a faster pace. Computers benefit the business and personal world by being able to do the following more efficiently: buying and selling products, communicating throughout the world, enhancing our knowledge, job influences, entertainment, research, and paying bills. We’re now capable of creating new, more and better quality tasks via computer technology. Computers also benefit society with the enhancement of knowledge of medicine which creates more effective treatments for a healthier and longer life. Computers are improving healthcare through robotics and research. We communicate operation results and any surgical problems easily and immediately between healthcare providers all over the world. Using robotics, surgeons can now perform surgeries in remote and/or distant countries without ever leaving their resident hospital. education, computers have changed the way we are able to acquire knowledge and attend school. In the past, school was a physical building we had to attend. Today, we can "attend" school completely online, never having to step foot outside of our homes, or attend both online and on a college campus in what is known as a blended course. We are able to invest our time differently and accomplish more. The convenience of computers is that we are able to access the computer 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, and 365 days a year. This also gives our society time to expand our knowledge and create new opportunities for our selves.[1]

Being crucially important to the human race, computers have ultimately altered the way today’s society works, communicates, entertains, and educates. There is hardly any field of career left where technology isn’t essential; every small action performed in a job ultimately goes through some kind of a computer. In the end, being able to communicate and engage in this fast-paced manner enhances productivity levels by a great amount. One area this advancement of computers has immensely impacted is the business field. All businesses use computers to keep track of accounts, money, or make transactions. No longer will it take days, or even weeks, to communicate with someone that might not be located in one’s vicinity, as a computer allows one to easily send and receive emails with just a click of a button.
Another field that has come a long way since the production of computers is the entertainment area. Without the exceptional special effects put into an action movie with the help of our advanced technology, the audience would most likely not enjoy the show, resulting in the potential collapse of the entertainment business. For example, imagine watching the epic science fiction film, Avatar, but without any special effects put into it…it certainly would not be as entertaining as the power of computers transformed it to be. Hence, computers are able to keep both consumers and sellers satisfied, while still continuing to integrate into the everyday lives of average individuals.[2]
Disadvantages of a Computer-Oriented Society
[edit | edit source]
With any benefits, there comes a disadvantage. As for computers, there have been problems with excessive use, security and privacy issues and the problem with a dominant culture. With any product, any excessive use is bad; in this case the excessive use of the computer may result in a lack of human communication for face to face conversation and more communication through the computer. This affects our society’s confidence for when they are in in-personal conversation. To further add, people have the accessibility to abuse their time whereas people tend to be more attentive to their internet accesses and making the computer a time-consuming product. Many of the security and privacy concerns stem from the lace online. One example of a security risk today is malware. Malware can be accfact that a lot of our personal business takes pidentally installed onto your computer by clicking on a link on a Web page or e-mail message that contains a malware program, such as a computer virus. Once a malware program is successfully installed, it will typically erase data or bog down the computer, but it can also a steal sensitive data from the computer such as passwords or credit card numbers. To fight against malware, a wide variety of security software can be installed which will notify and block any attempts of malware trying to gain access to a computer. Another very common security risk is identity theft. Identity theft is when someone else gains access to your personal information and uses your identity to purchase goods or services. A popular way for identity thieves to steal personal information is phishing, a fraudulent e-mail or website that appears like a legitimate business in order to obtain Social Security numbers or other information needed for identity theft.
Lastly, societies throughout the world compete with one another for the latest technology, pitting countries against each other, While competition can be a good thing, tension and competition. computer use influences our society is that there dominant culture crisis that the cultures, globally, compete with one another for the latest technology enhancements which create a stronger ethnocentrism to the countries. As computers become more accessible and create new ways to be more effective, these disadvantages increase and/or new ones are created.[3]
Differences in Online Communications
[edit | edit source]
It is obvious that, as the computer has evolved, our communication processes through it have as well. Emails and social networks have quickly become the telephone of the past; these tools are not only used in the personal world, but in the business world as well. However, though computers make it easy and drastically more convenient to communicate with people, it is important to follow a few simple guidelines and watch the tone while talking. These guidelines have come to be known as netiquette. Netiquette simply establishes what is and what is not acceptable when involved in online communications. One needs to remember that though it may not be face-to-face, they are still interacting with a human being. Act kind, courteously, professionally, and respectfully. Be sure to adjust your spelling, grammar, and tone of voice depending on the situation you are in; it may be okay to be casual when in a personal conversation, but emoticons and abbreviations don’t look to impressive within the business world. And how can you adjust your tone of voice when communicating by typing? Simply remember to NOT use all caps, which denotes yelling, and watch your use of exclamation points. Too often exclamation points are used when a simple period is best.[4]
The Anonymity Factor
[edit | edit source]

It is an inevitable fact that, with increasing online communications, there is almost always going to be a sense of anonymity. Like almost anything in the world, this can be used for both good and bad purposes. Online, one can be who they want to be. They can have a secret identity, they can make unknown usernames, and they can say the things they want without feeling the judgment of others upon them. This can be used for good if it is for true, honest, and legitimate opinions. Examples of this are reviews, discussions, blogs, and important emails. The freedom of being a faceless commentator makes the individual feel comfortable expressing how they truly feel. However, it is important not to abuse this anonymity. People often use it to insult, harm, or coerce others into fraud. It is essential that one learns how to properly and respectfully use this gift of obscurity without abusing it.[5]
Diving deeper into the aspect of anonymity on the Internet, we see the need for anonymity and accountability. Users need to be anonymous in regards to personal information, such as credit card information but need to be accountable for what they say online. Accountability means that anyone that partakes in misconduct online will be identified and be responsible for the consequences. David Davenport, an assistant professor in the Computer Engineering department at Bilkent University, explains that allowing anonymous communication online ensures that users of the Internet become unaccountable for what they say. He believes that free speech is not hindered if users are identifiable online. One reason for anonymity is the need for information privacy, which refers to the rights of individuals and companies to control how information about them is collected and used. If everyone online could see the credit card number or the physical address of individual Internet users then no one would be safe. Professor Davenport explains the need for anonymity in protecting personal information and for accountability in identifying users that partake in criminal acts online. Perhaps, in the future, as technology improves and is increasingly able to identity persons of malicious intent then anonymity will not be such a concern.[6]
Integrity Factor
[edit | edit source]
Due to the relative ease of accessing virtually any sort of information on the internet, every user will encounter the scenario of verifying the credibility of that piece of information. It is estimated that there are over 200 billion web pages, yet search engines cover less than a quarter of that figure. This leads to the fact that the internet is bound to provide both accurate and inaccurate information, which therefore places the responsibility of validating what was found on the user. For example, because Wikipedia provides such an extensive database of human knowledge freely and the ability for any person to edit many of the articles, it became apparent early on that there was a sort of “vandalism” taking place. Users would purposefully make false claims relating to that article for entertainment, and this constant abuse of the system inevitably led to a somewhat damaged reputation for the reliability of the site. However, over the years, Wikipedia has improved itself with updated methods of deterring vandalism to provide for more accurate information.
Wikipedia is only one site of billions, though. To obtain reliable information means for a user of the internet to question literally every site. According to Virginia Tech, this “questioning” is composed of five fundamental aspects: authority, coverage, objectivity, accuracy, and currency. Authority relates directly to the source of the information on that page. A user must take into consideration who is creating the information and the associations of the author(s) to other persons or groups (e.g. URL, reputation, expertise). Next, coverage questions the depth of the relevant information. This requires the user to examine the page and determine whether the information is actually useful or not. Objectivity is another crucial component because it examines inherent bias that authors use to further their goals. The information must be factual instead of distorted to persuade the user into taking a side. Accuracy is arguably the most important because it tests the validity of the information. For example, if the page contains a claim that completely contradicts the scientific community, it might be good reason to determine that everything else be read with a skeptical mindset. Lastly, currency examines how up-to-date the page is compared to the present time. If there are multiple updates frequently with links that are still alive (that is, they do not redirect the user to a dead page) then the user can feel confident that the author is providing information that is relevant to today.[7]
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://riogietoledo.blogspot.com/2012/03/nowadaysour-society-depends-on.html
- ↑ http://www.insidetechnology360.com/index.php/how-computers-benefit-society-6-30949/
- ↑ http://www.studymode.com/subjects/benefits-of-computer-oriented-society-page2.html
- ↑ http://www.albion.com/netiquette/corerules.html
- ↑ http://people.dsv.su.se/~jpalme/society/anonymity.html
- ↑ http://www.csl.mtu.edu/cs6461/www/Reading/Davenport02.pdf
- ↑ http://www.lib.vt.edu/instruct/evaluate/
Review
Key Terms
[edit | edit source]- Application software
- Application software is all of the programs on a computer that is developed to do a specific task. i.e. playing video games, or typing a paper.[1]
- Boot
- Booting up a computer is the process where you first turn it on after a time where the computer is off. The computer does a system check to ensure everything is operational between the OS, Bios, and hardware.[2]
- Computer
- A computer is any electronic device that is programmable, accepts input, processes that data, and produces an output.[3]
- Domain name
- A domain name is a text based name that is unique to each computer on the internet.[4]
- Email or electronic mail is a digital message sent from one user to another through a network or the internet.[5]
- Embedded computer
- An embedded computer is a small computing device that does a specific function for that device.[6]
- Hardware
- Hardware is the physical, tangible parts of a computer.[7]
- Input
- Input is where you would enter data to the computer, usually be means of peripherals. Such as keyboard and mouse.[8]
- Internet
- Simply put the internet is a network of networks, connecting millions of computers together.[9]
- Internet service provider
- The internet being a network of networks, you must be able to connect to said network and the only way is through an internet service provider(ISP). Generally, the ISP is a large company that you would pay monthly for this service.[10]
- Operating system
- An operating system (OS) is the major system software that controls all other system applications and manages the computer hardware. All PC's need an OS.[11]
- Output
- Output occurs after the computer processes the data you inputted and displays said data.[12]
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]1. An object or device outside the computer, that one would plug into a port to control the functions of a computer are ________.
2. A calculator and Excel are are both an example of _________?
3. A public program and/or website available free of charge that encourages its users to contribute and develop it’s code.
4. Adobe reader is an example of ________?
5. The structure that fits all the computer components for a computer to function is a ___________.
6. A language sent to computers to read, also called bits, that is deciphered using only 1s and 0s is also called____?
7. A Storage device that uses flash and has no moving parts _____, also often referred to as a USB drive?
8. A computer that has limited amounts of functions and has a fixed purpose is a ______?
9. A ___________ is an Internal storage device that spins magnetically coated disks to store and retrieve data.
10. A ______ is a machine that is programmable.
11. A computer first needs to process ________ to produce information.
12. A component in the computer that transmits signals through copper wires to all the components in the computer.
13. . The _____ is also known as the “brains” of the computer.
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ Wikipedia: Application software
- ↑ Wikipedia: Boot up
- ↑ Wikipedia: Computer
- ↑ Wikipedia: Domain name
- ↑ Wikipedia: Electronic mail
- ↑ Wikipedia: Embedded system
- ↑ Wikipedia: Computer hardware
- ↑ Wikipedia: Input device
- ↑ Wikipedia: Internet
- ↑ Wikipedia: Internet service provider
- ↑ Wikipedia: Operating system
- ↑ Wikipedia: Input/output
Answers
[edit | edit source]1. Input Devices 2. Application Software 3. Open Source Software 4. Freeware 5. Computer Case 6. Binary Code 7. Solid State Drives (SSD) 8. Embedded Computers 9. Hard Drive Disks 10. Computer 11. Data 12. MotherBoard 13. CPU
The System Unit
Data and Program Representation
[edit | edit source]Digital data and numerical data
[edit | edit source]Most computers are digital computers which use a specific language to communicate within itself in order to process information. If there are programs running in the background or a person is typing up a word document for example, the computer needs to be able to interpret the data that is being put into it by the human as well as communicate to working components within itself. This language that digital computers use is called binary code and is a very basic form of language composed of only two figures; 1 and 0. Whereas the English language is composed of 26 figures which we commonly call the alphabet, computers use a language composed of only two figures, hence its name "binary code". These 1's and 0's are referred to as "bits" - which are known as the smallest unit of data that a binary computer can recognize. They are found through every action, memory, storage, or computation that is done through a computer, such as creating a document, opening a web browser, or downloading media. In order to comply with more actions memory or storage, bits must compound together to form a larger unit referred to as "bytes".
Bytes are commonly used when referring to the size of the information being provided. For example, a song that is downloaded may contain several kilobytes or perhaps even a few megabytes if it is a whole c.d. and not just a single track. Likewise, pictures and all other documents in general are stored on the computer based on their size or amount of bytes they contain. The amount of information that can be stored onto a computer is also shown or displayed in bytes as is the amount left on a computer after certain programs or documents have been stored. Since bytes can be extremely long, we have come up with prefixes that signify how large they are. These prefixes increase by three units of ten so that a Kilobyte represents around 1,000 bytes, a Megabyte represents around one million bytes (1,000,000 bytes), a Gigabyte represents around one billion bytes (1,000,000,000 bytes), etc. Computers components have become so small that we can now store larger and larger amounts of data bytes in the same size computers resulting in the use of other larger prefixes such as Tera, Peta, Exa, Zetta, and Yotta. Below is a chart outlining the name of the prefix used and powers of ten they symbolize.[7]

Digital Data Representation, otherwise known as how the computer interprets data, is a key concept to understanding computer data processing, as well as overall functioning. Data is represented by particular coding systems. The computer recognizes coding systems- rather than letters or phrases that the user of a computer views. The actual process of the computer understanding coding systems is called digital data representation. A digital computer operates by understanding two different states, on or off. This means that the data is represented by numbers- 0’s and 1’s, and is known as a binary computer. The binary code is a very basic coding system for computers to comprehend. An advantage to digital data computing lies behind the binary coding systems. Although the binary code has become decreasingly popular in the professional, recreational fields due to an increase in technology, they still provide a use in programming. Digital data creates a simple way to duplicate and transfer information accurately from computer to computer, which is why it is still used today.[1] The terminology for the smallest unit of data is a bit, which consists of a single numeric value,0 or 1. Bytes, on the other hand, consist of groupings of multiple groupings of bits. Bytes allow the computer hardware to work more quickly and efficiently.[2]
(from the SI page on Wikipedia):
| SI Prefixes | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | yotta | zetta | exa | peta | tera | giga | mega | kilo | hecto | deca |
| Symbol | Y | Z | E | P | T | G | M | k | h | da |
| Factor | 1024 | 1021 | 1018 | 1015 | 1012 | 109 | 106 | 103 | 102 | 101 |
| Name | deci | centi | milli | micro | nano | pico | femto | atto | zepto | yocto |
| Symbol | d | c | m | µ | n | p | f | a | z | y |
| Factor | 10-1 | 10-2 | 10-3 | 10-6 | 10-9 | 10-12 | 10-15 | 10-18 | 10-21 | 10-24 |
Representing data in a way that can be understood by a digital computer is called Digital Representation and Binary Code is the most commonly used form of this. Binary Code is a Numerical Representation of data that uses only 1 and 0 to represent every possible number. Mathematics uses 10 symbols ranging from 1 TO 0 and include 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 as well. This Numerical Representation of data is called the decimal numbering system because it uses ten symbols. As shown on the chart, the prefix deci symbolizes ten. In both systems, the position of each digit determines to which power that number is raised. In the decimal system each digit is raised by ten so that the first column equals 1 (10^1) or ten raised to the first power, the second column equals 10 (10^2) or ten raised to the second power, the third column equals 100 (10^3) or ten raised to the third power and so on. However, since Binary Code only operates with two symbols, each digit is a power of two instead of ten. In binary the first column equals 1 (2^0) or two raised to the zero power, the second column equals 2 (2^1) or two raised to the first power, the third column equals 4 (2^2) or two raised to the second power, the fourth column equals 8 (2^3) or two raised to the third power, and so forth. Because the Binary system takes advantage of so few symbols, the result is that more positions for digits are used to express the same number than in decimal form, leaving long lines of information for even the simplest expressions.
Coding systems
[edit | edit source]

There are a few different coding systems, EBCDIC, ASCII and Unicode. EBCDIC (extended binary coded decimal interchange code) was created for use in mainframes, developed by IBM. The code uses a unique combination of 0’s and 1’s, 8-bits in length, which allows for 256 different combinations. ASCII ( American standard code for information interchange) was created for a more personal use. ASCII uses a 7 bit code, though there is an extended code which adds an extra bit, which nearly doubles the amount of unique characters the code can represent. However Unicode is a much longer string of code, between 8 and 32 bits. With over one million different possibilities, every language can be represented with this code, every mathematical symbol can be represented, every punctuation mark, and every symbol or sign from any culture.

Unicode is universal. With using 0’s and 1’s to represent different data, it has become fit for any language used all over the world. This code is replacing ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) because the characters in this code can be transformed into Unicode, a much more practical system for data. ASCII is known as the alphabet code, and its numbering codes range from 0 all the way to 127 considered to be a 7 bit code. Alphabets vary from language to langue, but 0’s and 1’s can be understood worldwide. The problem with Unicode is that it is not compatible with each computer system used today. Windows 95/98 does not have the ability to run Unicode while other Windows such as NT and 2000 are closer to being able to. There is a program Sun Microsystem’s Java Software Development Kit which allows you to convert files in ASCII format into Unicode. While Unicode is a huge improvement for coding systems today, it cannot process all symbols that are possible, leaving room for new systems to one day take its place.[3]
Graphics Data
[edit | edit source]
One type of multimedia data is graphics data. These data are of still images, and can be stored in the form of a bitmap image file. A bitmap image is a type of graphic that contains pixels, or picture elements, that are arranged in a grid-like pattern.[4] Each pixel is made up of a specific group of numbers which corresponds to the color, and the color’s intensity. Although there are a few other key factors when determining the detail quality of an image, pixels play an important role. An image with many pixels allows there to be more potential of higher quality in that image. However, this doesn’t mean that more pixels in an image definitely results in a higher quality picture.[5] When shopping for digital cameras consumers must be aware of the amount of megapixels, or pixels by the million, the cameras in front of them have. Today, an average person wishing to take decent and basic everyday pictures will be satisfied with about an 8 megapixel camera. In fact, many new smartphone cameras use 16 megapixels, like the HTC Titan 2, a popular smartphone released in April, 2012. Someone with different intentions of using images, perhaps for making high definition prints, will require a camera with more megapixels. This would allow for their prints to be large, but with appropriate and exceptional quality.[6]
Audio Data
[edit | edit source]Audio Data is very similar to graphics data in that it is understood in pieces. Instead of using pixels, however, audio data uses samples. Audio data is usually recorded with an input device such as a microphone or a MIDI controller. Samples are then taken from the recording thousands of times every second and when they are played back in the same order, they create the original audio file. Because there are so many samples within each sound file, files are often compressed into formats such as MP3 or MP4 so that they take up less storage space. This makes them easier to download, send over the internet, or even store on your MP3 player.
Video Data
[edit | edit source]Video data is also similar to graphic and audio data, but instead of using pixels or samples, video data is recorded with the use of frames. Frames are still images that are taken numerous times per second and that when played simultaneously, create a video (most films are recorded using twenty-four frames per second).[7] Similar to audio data, because video data contains so much information, the files can be compressed, making it possible for full length movies containing thousands of frames to be stored on optical discs.
The System Unit - The Motherboard and CPU
[edit | edit source]Motherboard
[edit | edit source]
"The motherboard can be thought of as the "back bone" of the computer." This quote is from the article Motherboard. Inside the system unit contains the motherboard. The motherboard is the "glue" of the computer. It connects the CPU, memory, hard drive, optical drives, video card, and sound card together. The front of the motherboard are peripheral card slots. The slots contain different types of cards which are connected to the motherboard. The left side of the motherboard contain ports. The ports connect to the monitor, printer, keyboard, mouse, speakers, phone line, and network cables.[8]
Like many of the components of computers, motherboards have not always been as advanced as they are today. Motherboards on early PCs did not have many integrated parts located directly on the board. Instead, most of the devices, such as display adapters and hard disk controllers, were connected through expansion slots. As technology advanced, more and more devices were built in directly to the board itself. At first, this began to create problems as manufacturers began to find that if one of the devices on the motherboard was faulty or in some way damaged, that the entire motherboard must be replaced. This led manufactures to change the design in a way that allowed them to remove faulty parts easily and replace them, especially parts that are growing and changing so quickly, such as the RAM or CPU. Today, a motherboard comes equipped with many parts working in conjunction with each other. One can find anything, from back up batteries, keyboard and mouse connectors, to cache memory chips, in close proximity to the CPU. The computer is able to do tasks faster as its components continue to be closer to one another. The advancement of technology has allowed for these parts to become smaller and more powerful, allowing more surface area on the motherboard to fit more devices. It is common today to find even audio and video components built into it as well. With technology moving as fast as it is, one may wonder what a motherboard will be capable of containing in the near future.[9]
-
RepRap Motherboard v1.1
-
Motherboard Diagram
-
Motherboard
-
Real-time clock on a motherboard
Expansion Cards
[edit | edit source]
An expansion card, also known as an expansion board, adapter card, or accessory board, is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an expansion slot on the motherboard to add functionality to a computer system. [10] The three most common expansion cards are the audio card, graphics card, and network card. Each type of expansion card has a self-explanatory name and all serve the same purpose of adding functionality to the computer. The audio card is responsible for producing sound that is then transferred to speakers or headphones. Commonly audio cards are built onto the motherboard, however, they can be purchased separately. The graphics card turns the data produced by a CPU to an image that is able to be seen on a computer's display. Along with the audio card, graphics cards are commonly built onto the motherboard, yet graphics card that produce higher resolution images can be bought separately. Lastly, the network card is an expansion card that connects the computer to a computer network. This allows for a computer to exchange data with the computer network through a commonly used number of protocols called IEEE 802.11, popularly known as wireless LAN or Wi-Fi. [11]
CPU
[edit | edit source]The central processing unit, also known as the CPU, is responsible for executing a sequence of instructions called a program. The computer needs the CPU in order to function correctly. It is known as the brains of the computer where the calculations occur. The microprocessor and the processor are two other names for the central processing unit. The Central processing unit attaches to a CPU socket on the motherboard. A multi-core CPU contains more than one processor chips. This specific type of CPU is efficient because it allows computers to work on more than one task at a time because the singular processor can run multiple instructions on the different cores at the same time. Also, these multi core CPU's experience less over heating than the original CPU which causes much less problems to the computer.
-
Intel i7 940
-
AMD Dual Core
History of the CPU
[edit | edit source]
The first CPU ever made was the Intel 4004, which was designed by Federico Faggin. After ten months of Faggin and his colleagues working on the chip, it was released by Intel Corporation in January 1971. Even though this first generation, 4-bit microprocessor could only add and subtract, it was a major breakthrough in technology. The amazing quality was that all of the processing was done on one chip, as opposed to prior computers which had a collection of chips wired together. This invention lead to the first portable electronic calculator.[12]
While technology has advanced quite a bit since 1971, old technology is not as “out-of-date” as one thinks. There are still CPU chips made in the 1970’s and 1980’s that are still being used today. Personal computers, such as PC’s and Mac’s, use faster, more up-to-date CPU’s because the users run many programs at the same time. However, the more simple computers embedded in cars, printers, and microwaves can still use the older forms of microprocessors. For example, one famous CPU was the MOS 6502, made in 1975, and it was still being used in many appliances up until 2009. Control processing units are the key component in any computer, and thus sometimes the simpler styles work best.[13]
The System Unit - Memory, Buses, Ports
[edit | edit source]Memory
[edit | edit source]
Memory identifies data storage that comes in the form of chips and is used to store data and programs on a temporary or permanent basis. There are two main types of memory storage which are random- access memory (RAM) and read-only memory (ROM). Inside the system unit, ROM is attached to the motherboard. Random-access memory can read data from RAM and write data into RAM in the same amount of time. RAM capacity is measured in bytes. It is volatile which means that it loses the information/data stored on it when the power is turned off. In order to retrieve an important file at a later date, one needs to store it on a separate, non-volatile, storage medium (such as a flash drive or hard-drive) so that, even though the information is erased from RAM, it is stored elsewhere. RAM has different slots where it stores data and keeps track of addresses. Read-only memory cannot be written to and is non-volatile which means it keeps its contents regardless of whether the power is turned off or not. Flash memory (solid-state) is starting to replace ROM. It is also a non-volatile memory chip that is used for storage on devices, like mobile phones, tablets, digital cameras, etc. This type of memory can often be found in the form of flash drives, SD cards, and Solid-State hard drives. The reason for this is so that the data can be quickly updated over time while taking up a smaller amount of physical space in comparison to its precursors. Flash memory is also more resistant to outside forces, such as electro-magnetic fields or shock, than other memory alternatives such as traditional hard-drives.

Cache memory and Registers are special types of volatile memory that allows a computer to perform certain tasks much more quickly. The cache memory is a high speed circuitry that can either be built right into the CPU or very close to the CPU. Registers are built into the CPU to store intermediary results during processing. A good analogy from HowStuffWorks compares the computer to a librarian, data to books, and cache to a backpack.[14] Suppose somebody walks into a library and asks the librarian for a copy of the book Moby Dick. The librarian goes back into the room full of books, grabs that book, and gives it to the reader. Later that day, the reader returns, having finished the book, and gives it back to the librarian, who returns it to the same storage room. Then, a second reader walks in asking for the same book, Moby Dick. The librarian has to get up and go all the way back to the room in order to get the book he was just handling, which is a waste of time. Instead, suppose the librarian had a backpack that could store up to 10 books. When the first person returns Moby Dick, the librarian puts it into his backpack instead (after making sure the backpack doesn't have 10 books in it already.) Then, when the second person comes in requesting that same book, the librarian can just check his bag, get the book out, and hand it to the second person without having to walk all the way back into the other room. Cache memory functions like that backpack, it stores previously accessed data in a specific area with a limited amount of memory so that the processor can get this data much more quickly.
Ports
[edit | edit source]
Ports are on the outside of the system unit and they are used to connect hardware devices. There are physical ports and virtual ports. A physical port is a physical connection to a computer where data is transferred. It is when something is physically plugged into the computer or some other device. Virtual ports allow software applications to share hardware resources without having to physically connect to each other or to interfere with one another.[15] Parallel ports are most often used with a keyboard, printer or mouse, but these are more commonly known as legacy ports instead. Each port has a certain connector to plug it into the computer. Different type of ports would be power connectors, VGA monitor port, USB ports, Firewire port, HDMI port, Network port, audio ports, and empty slots. The connectors would be Monitor (VGA, HDMI), USB, Firewire, network, and audio connector. Each port also has a different purpose and connector. Almost all PCs come with a serial RS-232C port or a RS-4222 port and they are used for connecting a modem, mouse, or keyboard. They also have parallel ports that are used to connect printers. These are also considered USB ports because they are physical ports and which standardize communications between computers and peripheral. USB ports were created in the mid 1990’s; USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. There are also network ports used to connect a computer to a network. Ethernet was developed in the 1980s and it is a system for connecting a number of computer systems to form a local area network (LAN).
A serial port is used to connect modems to personal computers. The term “serial” signifies that data sent in one direction always travels over a single wire within the cable. The last main kind of port is the FireWire, which are used to connect FireWire devices to the computer via a FireWire connector. These are used with mostly digital video cameras and other multimedia devices.
Thunderbolt port
[edit | edit source]
A Thunderbolt port connects peripheral devices through that cable. These ports allow you to connect more devices to your computer and are very fast. Thunderbolt ports support hardware controller I/0 protocols with the use of a single cable. I/O technology is input and output, and is a device that transfers the data to the computer peripherally (a CD-ROM would be an example of an I/O technology). This port supports full bandwidth for both directions of the port, thus allowing the user to be faster and more efficient with the connected devices. This type of technology allows people to plug in as many devices as they can use on their computer while not slowing any of those devices down. The thunderbolt port is also small, so it is easy to travel with as well.[16]
Power supply unit
[edit | edit source]
Computers need power and there are two main functions the power supply unit, also commonly referred to as the PSU, is responsible for. The first is to convert the type of electrical power available at the wall outlet such as 110 V 60 Hz AC (alternating current) or 230 V 50 Hz AC to the type the computer circuits can use. The other crucial task is to deliver low voltages to each device due their requirements. The converting currents could be represented either by built in PSU (desktops, servers, mainframes) or by the separate power supply adapters for computers with rechargeable batteries inside (laptops, tablets). Three main voltages are used to power computer : +3.3 V, +5 V, and +12 V DC, Usually, the +3.3 or +5 voltages are being used by logic circuits and some digital electronic components (motherboard, adapter cards, and disk drive logic boards) while the motors (disk drive motors and any fans) use the +12 V power. The power supply must provide a good, steady supply of DC power for the proper system operation. Devices that run on voltages other than these must be powered by onboard voltage regulators. For example the CPUs operate 1.5 V and 2 V and require very stable power with high power consumption. [17]
Ethernet Cable in Theatre
[edit | edit source]
A commonly used cable today is Ethernet cable. You are probably most familiar with its use involving the internet in your home, mostly going from your modem, to another computer of to a Wi-Fi router. However, the use of Ethernet cable has been instrumental in the changing would of technical theatre. Before its introduction, the most common computer cables used in theatre were DMX and XLR, for lighting and sound respectively. The issue with this is that each cable can only carry the information for one device, be that a microphone or light. In addition, if these cables are stored improperly, they can corrupt the information being transmitted. Ethernet is much smaller, and can transmit far more data. Also, there is less of a danger regarding storing cable. Ethernet, combined with new operating system and equipment, has made things far more efficient. For example, an analog board must have one XLR cable go to each microphone, so if you wanted to run 40 microphones, you must have 40 channels available on your soundboard. Also, the size of a cable with 40 smaller lines inside it can reach a one-inch diameter, and can weigh several hundred pounds. Now, a digital soundboard can control up to 100 microphones on a single Ethernet cable.

How the CPU Works
[edit | edit source]CPU Architecture and Components
[edit | edit source]

As previously discussed on this page, the CPU is a complex piece of the computer made up of many parts. The way these parts all fit together inside the CPU is different in each processor but they mainly contain the same parts from device to device. The most abundant part in the CPU would be the transistor. Modern CPU's typically hold several hundred million transistors with some of the more high-end computers holding over a billion, and for good reason. Calculations in a computer can be performed thanks to the combination of transistors turning off or on. Besides these transistors, there are several parts that make up the CPU. Some of these include the arithmetic/logic unit (ALU) and floating point unit (FPU), the control unit, and the prefetch unit. The ALU is the part of the CPU that deals with the mathematics involving whole numbers and any functions done with those numbers. The FPU takes care of the mathematics with other numbers like fractions, or numbers with decimal places.[18] These two parts work hand in hand, using arithmetic and logical processes, to allow you to perform basically any function you perform on your computer. The control unit takes charge in controlling where and when information is transferred to and from the CPU. When information leaves the control unit, it is usually sent to the ALU/FPU where it can be converted into a process. The prefetch unit, as its name implies, fetches data before it is needed. It uses a sequence of processes to guess what information will be needed next, and have it readily available before the time it needed. Other components of the CPU include the cache, the decode unit, and the bus interface unit. The cache serves as high-speed memory for instructions that the CPU would like to access faster, in other words instructions that the CPU would rather avoid retrieving from RAM or the hard drive. The decode unit, just as it sounds, decodes instructions. Once the prefetch unit fetches data, the data goes through the decode unit so the instructions can be understood by the control unit. The bus interface unit allows communication between the core and other CPU components. Think of it as literally a bus, taking information from one place and transporting it somewhere else. [19]
The Internal Clock
[edit | edit source]Every computer actually has two different clocks. One is the virtual or system clock that runs and is displayed whenever the computer is on and running.[20] The other is a real-time clock or hardware clock that runs continuously, and is responsible for tracking the correct time and day. This device does not count time in days and hours for example. Instead it just runs a counter at times per second. As far as the century goes, it is the job of the BIOS, the Basic Input-Output System, to track this and save it in the non-volatile memory of the hardware clock. These two clocks run independently on each other. The system clock is physically a small quartz crystal that can be found on the motherboard. It also helps synchronize all computer functions by sending out signals- or cycles- on a regular basis to all parts, much like a person’s heartbeat. Hertz is the unit of measure used to count the number of cycles per second. For example, one megahertz is one million ticks of the system clock. This clock is very important to the CPU because the higher the CPU clock speed, the more instructions per second it could process. Since the entire system is tied to the speed of the system clock, increasing the system clock speed is usually more important than increasing the processor speed.
PCs in the past only had one unified system clock with a single clock, which drove the processor, memory, and input/output bus. However, as technology advanced, the need for a higher speed, and thus multiple clocks, arose. Therefore, a typical modern PC now has multiple clocks, all running at different speeds to enable any data to “travel” around the PC. Furthermore, two CPUs with the same clock speed will not necessarily perform equally. For instance, if an old microprocessor required 20 cycles to perform a simple arithmetic equation, a newer microprocessor can perform the same calculation in a single clock tick. Therefore, even if both processors had the same clock speed, the newer processor would be a lot faster than the old.

As mentioned previously, a CPU serves as a great example for the synchronization that the system clock performs. To synchronize, most CPUs start an operation on either the falling edge, when the clock goes from one to zero, or the rising edge, when the clock goes from zero to one. All devices, such as a CPU, synchronized with the system clocks run at either the system clock speed or at a fraction of the system clock speed; therefore, the CPU is unable to perform tasks any faster than the clock. For example, during each system clock tick, a CPU clock speed of 2 GHz allows the CPU clock to “tick” 10 times, executing one or more pieces of microcode. This ability to process multiple pieces of microcode at one time is known as superscalar. [21]
The Machine Cycle
[edit | edit source]
A machine cycle is a term often used when discussing the clock. It has four main parts- fetch, decode, execute, and store. The machine cycle occurs whenever a CPU processes a single piece of microcode. The fetch operation requires the program instruction to be fetched from either the cache or RAM, respectively. Next, the instructions are decoded so that the ALU or FPU can understand it, known as the decode operation. Then, the execute operation occurs when the instructions are carried out. Finally, the data or result from the ALU or FPU operations is stored in the CPU’s registers for later retrieval, known as the store operation. A fifth possible step in the cycle is the register write back operation, which occurs in certain CPUs. The RISC CPU, which stands for reduced instruction set computer processing unit, is an example that uses the fifth step of the machine cycle. Machine cycles can only process a single piece of microcode, which forces simple instructions, like addition or multiplication, to require more than one machine cycle. In order to make computers faster, a system known as pipelining has been created. Originally, one machine cycle would have to finish processing a single instruction before another instruction could be carried out through a second machine cycle. With pipelining, as soon as an instruction passes through one operation of the machine cycle, a second instruction can start that operation. For example, after one instruction is fetched and moves on to decoding, the CPU can fetch a second instruction. This invention allows for multiple machine cycles to be carried out at the same time, which boosts the performance of the computer. Also, because of how fast the CPU can work with pipelining, it can be measured in millions of instructions per second.[22]
Typical CPU Components (continued)
[edit | edit source]

To round up the simplified inventory of a CPU's guts, we have the decode unit, the registers and internal cache memory, and the bus interface unit. Of the remaining three sections of a CPU, the decode unit is easiest to understand because its job immediately follows the job of the prefetch unit. After the prefetch unit collects the data, the decode unit decodes the data into a language that is easier for the ALU/FPU to understand. It does that by consulting a ROM memory that exists inside the CPU, called microcode.[23] The registers are used during processing; they're groups of high-speed memory located within the CPU that can be accessed by the ALU and FPU, or for other assorted optimization purposes. While the registers provide the fastest speed of memory, their space is extremely limited. In the cases where the small register space isn't good enough, there are the caches to save the day. The cache is used by the CPU for memory which is being accessed repeatedly, speeding up the access time and having a slightly larger storage than the register.[24] The bus interface unit does exactly what it sounds like; it buses the data back and forth, connecting the core of the CPU to interact with other components.[25]
Another aspect of the CPU is improving processing performance. In the past most CPUs designed for desktop computers had only one single core, so the only way to improve performance was to increase the speed of the CPU; however, increasing the speed also caused the CPU to heat up. So now a days CPU have multiple cores in order to increase the performance. The new iPhone XS, for example, will have six CPU cores. In an article by Stephen Shankland from CNET on September 12, 2018, he explains how the new Apple iPhone XS CPU will be able to perform faster. The new Apple iPhone is going to have a new A12 Bioinic chip. It is going to have more transistors, which if you recall, are small devices made of semiconductor material that acts like a switch to open and close electrical circuits. This new A12 chip will have about 7 billion transistors according to the article Mr. Shankland wrote. Mr. Shankland states in his article that that the new A12 will be 15 percent faster than 2017’s iPhone X, and consume 40 percent less power. As of now, this information is coming from graphs and information that Apple has shared. The thing to know and realize is that companies are constantly striving to improve performance and reworking the architecture of the CPU can improve the performance.[26]
Improving the Performance of Your Computer
[edit | edit source]
Add More Memory and Buy a Separate Hard Drive
[edit | edit source]When it comes to technology, there is no question that newer is better. New systems are able to process faster, store more, and run more applications at one time. However, it is obviously not within everybody’s means to just run out and purchase the newest technology the minute it hits the market. Technology is expensive, and therefore it is important to know your options. For example, if you have a computer that is a couple of years old, it is not unreasonable to assume that the hard drive and memory on the system are starting to slow down. However, what many people may not know is that buying a new computer is not the only solution to the problem. You can add memory to your old system simply by purchasing a new memory card and installing it into the computer hardware. By doing this, you are saving money and buying yourself a little bit more time with the computer.[27] Another way to speed up your computer with out having to invest in a whole new one is by buying a second hard drive. When the original hard drive starts to fill up, one can simply purchase either an internal or external hard drive for the computer and drastically increase the operating speed.[28]
Upgrade To A Solid-State Drive
[edit | edit source]
Since solid-state drives (SSDs) are hard drives that use flash memory technology instead of hard disk platters they have no moving parts. They also no longer make noise, consume less power thus generating less heat, and are much faster than hard drives. Since they are much faster than hard drives, the performance of the computer would also be improved. Running programs, opening files, saving things to the disk, even browsing the web will be much faster. Also with a mechanical hard drive, physical heads have to move around to read data from the disk while in a solid-state drive data can be read and written on any location thus there is no penalty in performance. Not only are solid-state drives faster but they have also become less expensive that upgrading to them is much more affordable and reasonable. Even further, installing solid-state drives is not too difficult or complex. It is basically the same as installing regular hard drives. Also if the decision of upgrading to solid-state drives seems a little too final, it is possible to just add a solid-state drive alongside the hard drive. Thus not only having more space, but also having the ability to keep the old mechanical drive.[29]
Upgrade Your Internet Connection
[edit | edit source]If your system seems to be running poorly while using the internet, you may have to upgrade your internet connection. Upgrading your internet connection may become more costly but there is a significant change in the processor. Your first step would be to discuss any upgrades or check if the provider needs to be enhanced in any way. Then find a browser that is suitable for your connection type. With that being stated, you can change the settings on the router in order to speed up the internet connection. In order to prevent your internet connection becoming slower, it’s highly suggested to have a password in order to access the internet. In addition, every computer owner should provide maintenance to their computer in order to prevent viruses or any bugs the computer may receive but it also prevents an internet connection from being slow. In order to do so, keep up with upgrading and cleaning the computer because the more the computer is trying to maintain, the slower the internet connection may become.[30]

System Maintenance
[edit | edit source]In order for computers to operate at their maximum efficiency, users must be aware of the importance of system maintenance because, over a period of time, one may notice a reduction in system performance. This can be attributed to a number of common factors that lead to the degradation in performance. One major reason is hard drive fragmentation. As more programs are installed onto the hard drive, the pieces of the files that are on those programs take longer to be located. The longer pieces of the program become shorter and fragmented, leading to a longer waiting period for the user as the computer searches for these scattered pieces. Related to this, although not nearly as detrimental to system performance as fragmentation, is the cluttering of pieces and references to uninstalled programs in the operating system. For Windows users, this occurs in the Registry. After the user uninstalls a program, there are references to that program left behind in the Registry that can possibly impact performance. However, performance is not necessarily the issue here. For example if the user is going to update the system by switching from an Nvidia graphics card to an AMD one, it might be a good idea to not only uninstall all drivers and related programs but also to clean the Registry of any references to the Nvidia drivers and software (in order to avoid possible conflicts when the AMD card is installed). This will ensure a “clean” install of both the hardware and software components. A free registry cleaner utility one can use is CCleaner.[31]
Temporary files (e.g. from web browsers and installation programs) can take up valuable storage space if they are not removed after extended periods of times. Also, users should be aware of the programs they are installing and decide which specific programs are to run at startup. Too many programs can slow down the initial startup time of the computer because it must launch program after program. Only those programs that are necessary should be included, and to check for this, click Start (in the lower-left Windows icon) and enter the command msconfig in the search tab. This will open the System Configuration window. Programs that run at startup are listed under the Startup tab. Here the user can enable or disable programs, which can affect startup time.
Another important factor in determining system performance is the corruption of system files by malware. Viruses, worms, trojans, spyware, and other forms of malware can infect a system by various means, so it is important for the user to be aware and defensive. Anti-virus programs and other security software provide protection from malware, so it is recommended that a user has some sort of program installed and regularly scans the system for any traces.
Lastly, dust can accumulate in and on heatsink fans (e.g. processor and graphics card), case fans, ports, power supplies, and motherboards. Every internal component can accumulate dust, and this can be a major issue for system integrity because dust acts as an insulator by trapping heat. Fans with too much dust do not operate efficiently because the fins do not spin quickly, which further exacerbates the heating problem. Not only that, but dust can also cause electrical shorting of the circuits, which can irreversibly damage components.[32] To clean the computer, power off the system, which includes turning off the power supply. It should not be connected to any source. Then open the case and use a can of compressed air to blow out the dust wherever it may be. The goal is to rid the case of any remnants of dust. Following this and the other tips listed above will help ensure reliable performance and a longer lifespan for the computer.
Future Trends
[edit | edit source]
The challenge of making computers faster and more efficient has brought new ideas to the table of technology. One such idea is nanotechnology, which uses microscopic components only nanometers in length. Carbon nanotubes are already being used in technology today in products such as lithium ion batteries because of their great performance conducting electricity. Other nanotechnology includes nanoparticles and nanosensors. Another idea that has received increased recent attention is quantum computing. These computer’s go beyond regular computers’ binary system using qubits, which can be either a 1, a 0, or both simultaneously.[33] Although these computers are only able to perform seemingly simple tasks like sudoku puzzles as of recently, their potential is outrageous for tasks such as encryption. Optical computing is another form of future technology which uses light waves to transfer data. Since the in fared beams do not interfere with each other, optical computers can be much smaller and more efficient that electronic computers. In fact, once optical computers have been mastered the computers will be able to process information at the speed of light using very little power at all.[34] In years to come, the extraordinary power of supercomputers is predicted to be available in more common computers using technology like terascale computing to process at incredible speeds.
Review Definitions
[edit | edit source]Application Software: Programs that enable users to perform specific tasks on a computer, such as writing letters or playing games.
Computer: A programmable, electronic device that accepts data input, performs processing operations on that data, and outputs and stores the results.
Data: Raw, unorganized facts.
Information: Data that has been processed into a meaningful form.
Computer Network: A collection of computers and other hardware devices that are connected together to share hardware, software, and data, as well as to communicate electronically with one another.
Hardware: The physical parts of a computer system, such as the keyboard, monitor, printer, and so forth.
Internet Appliance: A specialized network computer designed primarily for Internet access and/or e-mail exchange.
Operating System: The main component of system software that enables a computer to operate, manage its activities and the resources under its control, run application programs, and interface with the user.
Output: The process of presenting the results of processing; can also refer to the results themselves.
Software: The instructions, also called computer programs, that are used to tell a computer what it should do.
Storage: The operation of saving data, programs, or output for future use.
URL: An Internet address (usually beginning with http://) that uniquely identifies a Web page.
Web browser: A program used to view Web pages.
World Wide Web (WWW): The collection of Web pages available through the Internet.
Web server: A computer that is continually connected to the Internet and hosts Web pages that are accessible through the Internet.[35]
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]1) What is the key element of the CPU?
2) What are the connectors located on the exterior of the system unit that are used to connect external hardware devices?
3) What is an electronic path over which data travels?
4) _________ are locations on the motherboard into which _________ can be inserted to connect those cards to the motherboard.
5) What is used to store the essential parts of the operating system while the computer is running?
6) The ______________________ consists of a variety of circuitry and components that are packaged together and connected directly to the motherboard
7) A _________ is a thin board containing computer chips and other electronic components.
8) The main circuit board inside the system unit is called the ___________ .
9) Before a computer can execute any program instruction, such as requesting input from the user, moving a file from one storage device to another, or opening a new window on the screen, it must convert the instruction into a binary code known as ____________.
10) In order to synchronize all of a computer's operations, a __________ is used.[36]
Review Answers
[edit | edit source]1) Transistor 2) Ports 3) Bus 4) Expansion slots, Expansion cards 5) RAM 6) Central Processing Unit 7) Circuit Board 8) Motherboard 9) Machine Language 10) System Clock
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse100/99au/FIT100-99.L5.pdf
- ↑ http://compnetworking.about.com/cs/basicnetworking/f/bitsandbytes.htm
- ↑ http://www.peachpit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=31286&seqNum=16
- ↑ http://desktoppub.about.com/od/glossary/g/bitmap.htm
- ↑ http://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/digital-camera-pixel.htm
- ↑ http://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/digital-camera-pixel.htm
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Frame_rate
- ↑ http://pcsupport.about.com/od/componentprofiles/p/p_mobo.htm
- ↑ http://www.pctechguide.com/motherboards/evolution-of-the-motherboard
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Expansion_card
- ↑ https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_card
- ↑ http://www.howstuffworks.com/microprocessor.htm
- ↑ http://www.cpushack.com/life-cycle-of-cpu.html
- ↑ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/cache2.htm
- ↑ http://www.computerports.net/
- ↑ http://www.tomshardware.com/reviews/thunderbolt-performance-z77a-gd80,3205.html
- ↑ http://www.instructables.com/id/Power-Supply-For-Arduino-power-and-breadboard
- ↑ http://www.techterms.com/definition/alu
- ↑ http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/central-processing-unit-cpu-parts-definition-function.html#lesson
- ↑ http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/vtpubs/spectrum/sp970911/3b.html
- ↑ https://courses.engr.illinois.edu/ece390/books/artofasm/CH03/CH03-2.html
- ↑ http://www.jegsworks.com/lessons/lesson4/lesson4-4.htm
- ↑ http://www.hardwaresecrets.com/printpage/How-a-CPU-Works/209
- ↑ http://www.moreprocess.com/devices/computer-memory-hierarchy-internal-register-cache-ram-hard-disk-magnetic-tape
- ↑ http://www.electronics.dit.ie/staff/tscarff/BIU/bus_interface_unit.htm
- ↑ https://www.cnet.com/news/iphone-xs-a12-bionic-chip-is-industry-first-7nm-cpu/
- ↑ http://www.pcworld.com/article/129177/article.html
- ↑ http://windows.microsoft.com/en-us/windows7/install-or-remove-a-hard-disk-drive
- ↑ http://www.howtogeek.com/194750/its-time-why-you-need-to-upgrade-to-an-ssd-right-now/
- ↑ http://www.auslogics.com/en/articles/speed-up-internet/
- ↑ http://www.piriform.com/ccleaner
- ↑ http://www.computerdust.com/downloads/special_report_on_the_effect_of_dust_on_electronics.pdf
- ↑ http://www.dwavesys.com/quantum-computing
- ↑ http://www.extremetech.com/extreme/187746-by-2020-you-could-have-an-exascale-speed-of-light-optical-computer-on-your-desk
- ↑ http://coursemate.cengage.com/CPReader/View/9781133114598/default.aspx?eISBN=9781133114598#70a7d313-0a5d-4ddc-ba5c-766e5fb0dc77
- ↑ http://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/index.html?nbId=7345&nbNodeId=1013914#!&parentId=1013922
Storage
Storage System
[edit | edit source]As the demand for technology and technology itself continues to excel throughout history, so does user's wants and needs. The user's lifestyle pertaining to computers may revolve around publishing documents, creating presentations, media management, networking on the internet, and much more. In correlation with their wants and needs, there's the need to be able to have access to storage of the data being produced. Storage is also referred to as 'memory', as it can be any type of hardware that's functionality includes, storing data, maintaining downloaded files along with extracting files as well. This can be performed through both permanent and temporary storage along with being internal to a device, or external.
As the spectrum of technology storage is a wide-range and continues to grow, benefits of storage included today are:
- Cost-efficient
- Speed
- Enhanced efficiency
Examples of storage includes:
- Hard Disk Drives / Solid State Drives
- Storage Area Networks
- Network Attached Storage
- Computer Disks
- USB
- Cloud Computing
Storage Media, Storage Technology, and Volatility
[edit | edit source]
Storage media is the hardware in which information is physically stored. This differs from the storage device which is usually the docking bay for the storage medium. One example of a storage device would be your CD/DVD drive in which you place your disks when inserting them into your computer or your USB flash drive reader. Storage media would be the actual CD/DVD disk itself or the memory within your computer known as RAM (Random Access Memory). Storage media can be internal or external meaning that it can be either hard-wired to the computer (ex. hard drive) or it can be a separate physical storage facility thats meant to be more mobile, (ex USB Flash Drive). Internal storage media is usually faster since it is hard-wired to the desktop or laptop and does not requires any extra space outside of the computer. On the other hand, external media is very mobile, can be transferred from one computer to another rather quickly, and is easily secured in a safe place separate from your main working station.[9] On top of this the Non-Volatility of these storage medias have made them very valuable. Normally when a computer is shut down, any unsaved information is wiped clean from the RAM. Or if the information isn't being used, while the computer is still on, the RAM may delete it to make room for processes being recalled more frequently. Storage media on the other hand, saves data despite the computer being powered down and can only be deleted by the user. From this, storage media such as flash drives and data CD's are more commonly used for the user's wants and needs.


Storage Technology usually comes in three forms; magnetic, optic, and solid state. Some common magnetic storage systems are hard drives, floppy disks, and cassette tapes. Though cassette tapes don't work with computers, they use the same technology. This type of technology stores binary code using polar alignments on the magnetic medium and can change those alignments as needed when information is altered, deleted, or rewritten. The magnet does this by converting the binary code from 1's and 0's to positive and negative charges, respectively, which are recorded on an iron oxide film inside the media. Optics use laser beams which rely on marking the media. In this case, lasers burn in lines of data which represent the binary code it is converting. "Rewritable" media has also become a popular choice for those who want to reuse the same disk. Rewritable media relies on changing the reflectivity of the media instead of scarring it. When the binary number 1 is recognized, the laser alters the reflection of the discs surface in certain spots. Data is then separated by the pits in between reflectivity which represent the binary number 0 so that 1's alter the reflection and 0's leave the reflection of the media as is. This creates a "bouncing-wave" like appearance on the surface of the disk called an Amplified Spontaneous Emission or ASE for short. Solid State Drives, or SSD's as they are called, do not contain any moving parts such as lasers or magnetic heads. They operate electronically by storing the binary code as electrons which are either trapped or not trapped inside the flash memory cells within the unit. These types of media tend to be faster than the other two since they rely on electrical polarity within a cell instead of electronic motors to be read or rewritten. This also makes them more resistant to shock, allows them to run more quietly, and reduces the latency of the media. Typical storage media of this kind are "jump" drives or "thumb" drives, but some computers use this technology in their hardware as well.
Clusters, Sectors, and Tracks
[edit | edit source]
Hard disks have many circular pieces called platters inside them. These platters have two sides are made up of tracks, sectors, and clusters. A cluster is a group of sectors, and a sector divides tracks into pie shaped sections. Each cluster, sector, and track is numbered in order to help the computer quickly locate where specific stored data is. For example, data can be saved to side 2, sector 1, track 5. A track can be compared to the grooves on a music record, because there are physical indents where the data is actually stored. Data is read and written by a read/write head, also commonly referred to as a “head.” Each platter has a head. When data is to be stored on a hard disk, the heads will align with the same track on every platter, and write the data across each one. There are a few measurements you can take to see how well a hard disk preforms. The most important measurement is calculating seek time. Seek time will tell you how long it takes for a head to move from one track to another. The quicker the seek time the better because that would mean data can be reached faster.[1]
Random vs. Sequential
[edit | edit source]
When thinking of storage systems, one could presume that all of your data in one folder is located next to each other within the hard drive. This is false when talking about random access. With random access your information can be pulled from any location on the disk. Meaning, your one folder could have its data scattered about the physical hard drive. The benefit of this type of storage is that you could access data in any order. Think of it as your CD player, your favorite song ends and you want to hear it again just hit back and you instantly hear it again. It’s fast and nearly instantaneous, unlike sequential. You could think of sequential access like a cassette within a cassette player. When a song finishes and you want to listen to it again, you must rewind the cassette, or if you want to skip a song you must fast forward the tape.[2] This is used with magnetic tape drives which, are used for backup purposes. Even though in random access media devices may seem like data could be misplaced or somehow lost in the sea of data. When created, every file is given a unique name by the computer system, other wise called addressable media, in order to keep tabs on all the data.


Random access and sequential access of data are two separate ways a computer can access data. Random access is the ability to access data in any given location within the hard drive, quickly and efficiently. Most computers use random access today, because it saves the user time, as well as avoids confusion. Sequential access requires data being accessed in a sequence. Examples of sequential access would be: data on a disk file, or magnetic tape data storage. This can be useful to some users, if they are purposely attempting to process a sequence of data elements in order. However, this can also be time consuming for users who are trying to find a certain file on a disk or tape, which requires skimming through all of the data in a sequence. An example of a comparison between random access and sequential access would be the A-Z method. Sequential access would inquire the user to go through letters A-Z to achieve the goal of meeting point” Z”; whereas with random access, the user is able to jump directly to point “Z”.
Storage Devices and Storage Media
[edit | edit source]
The storage medium is a part of the storage system where the actual data is stored, such as on a DVD or a memory card. This medium can then be put into a storage device like a DVD player or phone to read this data. You usually find these two parts to be separate pieces, making the storage medium removable. Some storage devices can be found inside of the system unit, while others are plugged into an external port. There are letters on the storage device that go along with this that helps the unit to identify them. These letters or words describe where these are and what they are used for. For example, when you plug in a USB into the USB port on the computer, while viewing this USB in “My Computer” you will see a letter next to it verifying what it is used for in the system unit. Storage devices contain primary and secondary memory. Primary memory is volatile memory, which means that when the device is shut off, the information is lost. Secondary is the exact opposite, being non-volatile in that the memory remains even if the computer is turned off.[3] The problem with these devices is you must be cautious with how they are treated, especially if they have important information. Misplacing or mistreating can result in a loss of important data that could be impossible to get back depending on the circumstances.
Hard Drives
[edit | edit source]

Every computer contains one, if not two, hard drives. There are internal and external hard drives. The internal hard drive is located inside the system unit, and the external hard drive is connected to the computer for extra storage. It is vital that an owner of a computer purchases an external hard drive to backup his or her computer in case it crashed. An external hard drive is extremely convenient to store information; however, one must be cautious of the possibility of "hard drive theft" because it is easy for someone to access a random, external hard drive into their own computer. Many people today use a finger print or password to access to their hard drive because of this reason. Without a hard drive, one could not store the countless amount of information contained to a computer. The hard drive holds a port to connect to the motherboard.[4] There are a wide range of capacity for hard drives, depending on the computer owner's preference.[5] Magnetic hard drives and solid-state hard drives are two common hard drives used for computers. A magnetic hard drive is the term computer users mean when they say hard drive, and solid-state hard drives cause flash memory technology. Without hard drives, many information and data would be lost and forgotten.
Hard drives are used as primary storage units to store most data and computer programs to operate on a computer. The two types of hard drives available for purchase are: internal hard drives, and external hard drives. There are many things to consider if you are a consumer seeking these storage devices. The internal hard drive, which can be included in the computer before purchase, is directly connected to the motherboard, (A.K.A the brain of the computer), as well as other components inside the tower or casing of the computer/laptop. An external hard drive is commonly used among users who are either portably transporting data/programs from device to device, or seeking extra storage space for their files. External hard drives can be very small, and convenient for traveling with data. There are multiple different options to explore while considering a hard drive: speed, consistency, and durability. The types of hard drives offered include either of the following: magnetic storage, optical storage, and electrons which use flash memory media.[6]
-
Magnetic hard drive
-
Solid-state hard drive
Hard drive interface standards
[edit | edit source]
A hard drive interface (or hard disk interface) refers to "the logical and physical means by which the hard disk connects to the PC."[7] For over a decade, the most common hard drive interface was by a wide margin AT Attachment/ATA, also known as Parallel ATA or PATA. ATA is still used in modern PCs, but it is not as significant as the more modern interface, Serial ATA, or SATA. The more modern SATA uses smaller cables, is more reliable, and possesses greater bandwidth than the now-obsolete PATA. SATA and ATA are not compatible, but there exist adapters to connect ATA interfaces with SATA drives (or SATA interfaces with ATA drives). Another common interface is SCSI (or Small Computer System Interface), which is especially useful for multitasking where multiple hard drives are used, such as in a workplace environment.[8] Essentially, the difference between these three interfaces can be summarized as follows:
- ATA interfaces are cheaper and are still fairly common, but they are slower and outdated.
- SATA interfaces are the most useful: the only problem is that you need to buy additional adapters for them to interact with older systems, but they are still relatively cheap, they have high speed, and their wires are small, which frees up more room in the computer and helps prevent overheating.
- SCSI interfaces are very fast and can handle a wide range of applications and amount of data, but they are quite inexpensive and impractical for home use; SCSI is used more for networks than personal use.[9]
"The Cloud"
[edit | edit source]Cloud storage, also referred to as "The Cloud", is simply the use of a remote storage device that is accessed by means of the internet. Cloud storage has seen a massive increase in popularity over the last few years, and the industry for it has grown substantially to the point where there are now hundreds of companies that offer a variety of cloud storage services. More specifically, some cloud services focus only on digital pictures or email messages, while other systems store all kinds of digital data. Some services, like Google Drive, allow users to save their files in one of many massive data centers Google operates where, for instance, multiple users can collaborate on projects by having access to the same file.[10]
As the cloud’s popularity is growing, more and more businesses are transferring over to its storage capabilities. Many businesses are using the application as a back up program for their software and documents. By scheduling a set time for the computer to automatically transfer documents over, businesses can be sure that their information lies safely in the hands of the Internet without having to spend the tedious amount of time and cost of backing it up manually. Though the different applications of the cloud do sometimes have a monthly fee to pay, it is a small price to pay for the time and convenience it lends you. By utilizing these applications, anybody is able to access their documents anywhere worldwide. An individual is no longer tied down to just one electronic device in one set area, but can instead revise a version of a document on their laptop and then pull it up at work for a presentation the next day. This is just one example of the hundreds of ways that the application can be used conveniently to meet your day-to-day needs. The cloud is connecting electronic devices all across the globe and making every day processes just a little bit easier. [11]
Despite of the fact, that a Cloud storage term has appeared in use quite recently, people and businesses actuality use online storages for a long time. For example saving copies of letters on mail server or retrieving network configuration files from TFTP server. These days Cloud storage term should be considered is one of many other Cloud computing services. It could be provided as separate product – “Storage-as-a-Service”, and also be a part of others, for example: Infrastructure-as-a-service, Platform-as-a-service or Software-as-a-service.
As was mentioned above, the rapidly growing popularity is primarily due to quite low cost for a service itself (Storage-as-a-Service) when users pay only for the volume of data they stored, and if we are talking about the Infrastructure or Platform services which are great opportunity for business to reduce an IT expenses as well. With all advantages are given by online storing, there are few things users should be aware deciding entrust the care of their data to the provider. It might be as purely technical concerns (reliable internet connectivity, provider’s backup algorithm, disaster recovery, security of access, etc.) and legal aspects as well (ownership of data, jurisdiction, rights to audit).
[12]
Disk Access Time
[edit | edit source]
Disk access time is a measurement that calculates the amount of time it takes before for a drive to read and write data. Disk access time involves three major steps: seek time, rotational delay (or rotational latency), data movement time. Seek time is the amount of time it takes for the head to move to the disk to prepare for reading. Rotational delay is the delay that occurs when waiting for the disk to begin rotating. Data movement time involves the movement of data from the disk to memory of the computer or the movement of data from the memory of the computer to the disk. Maximum rotational latency is the time it takes for the disk to perform a full rotation excluding any acceleration time. There are two types of ways in which a disk rotates: constant linear velocity and constant angular velocity. Constant linear velocity occurs when the rotational speed of the disk is dependent upon the location of the head. Constant angular velocity occurs when the disk is spun at the same speed regardless of the location of the head, like vinyl records. Certain low-noise disks utilize a slower disk access time to reduce noise created by the hard drive. Slower rotational speeds and seek speeds are purposefully installed to make sure that audible clicks and crunching sounds don’t interfere with recordings.
Flash Memory
[edit | edit source]Flash Memory and How It Works
[edit | edit source]
Flash memory is a type of storage device that uses electronic memory. Flash memory comes in a variety of ways and is known as a solid state storage device, meaning “there are not moving parts – everything is electronic instead of mechanical.” Flash memory is used in many different devices, such as, computers, digital cameras, and mobile phones. Flash memory is a type of EEPROM chip. EEPROM stands for Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. Inside of a flash memory chip is a grid of columns and rows with a cell. There are two transistors at each intersection and a thin oxide layer separates them. One transistor is known as a floating gate and the other one is known as the control gate. An electrical charge comes through the columns to the floating gate, which is called tunneling. The electrical charge causes the floating gate transistor to act like an electron gun. When the electrons get trapped on the other side of the thin oxide layer, closer to the control gate transistor, they act like a barrier between the two transistors. A cell sensor monitors the level of the charge. If the flow is above the 50% threshold, it has a value of 1 and if it is less, the value changes to 0. This is how information/data is being read on the flash memory device. Nowadays, flash memory has become the “dominant memory type wherever a system requires a significant amount of non-volatile, solid state storage.” [13]
Embedded Memory
[edit | edit source]Embedded memory is becoming an increasingly popular type of flash memory due to its small, convenient size. In today's society these types of memory can be found in phones, cameras, gaming devices, and even handheld devices like a GPS.[14] In July 2013, Samsung announced that they developed the world's fastest embedded memory. These new products will be available in the 16, 32, and 64 GB sizes and feature an interface speed of 400 MB/s. This will increase user's abilities to multitask and perform tasks such as file transferring, browsing, and gaming. It also decreases the amount of time it takes to boot and load applications. This is a key factor in mobile devices where the physical space for additional storage or memory is limited. Memory cards are being used less and less when manufacturing mobile devices and smartphones. One limitation of the chip is the amount of memory it could store. The larger the chip, the more expensive the device is going to cost. Something else to consider is the problem that arises if the device breaks. Any valuable information that was stored on it is virtually irretrievable. That is one advantage of having a removable memory as discussed below.
Flash Memory Cards and Readers
[edit | edit source]

If you want a fast and easy method of storing various types of media, you can't get much better than a flash memory card. Most modern portable devices contain a flash memory card because of its versatility and ease of use; cellphones, mp3 players, and digital cameras are but just a few examples of products that benefit from flash memory cards. However, just like how not all electronic devices can use the same type of battery, not all flash memory cards are compatible with every electronic portable device.[15] That's why it's always important to read your user manual for instructions on the right card to purchase if you ever need a replacement.
Although the devices themselves can only use a specific flash memory card model, most modern desktop and notebook computers come with a flash memory card reader. The reader typically supports a number of different cards so you're able to organize and transfer the data from card to computer. If you aren't one of the fortunate few to have this reader built in to your computer, external models are sold at most stores that sell computer components and they're inexpensive.
Although a general-purpose flash memory card is used for most applications, there are other special memory cards that are made only for one unique purpose. For example, a professional compact flash memory card is designed for professional photographers for improved speed, quality, and storage capacities, taking telling a story through a picture to the next level. Also, special gaming flash memory cards are used for all game consoles, like Nintendo Wii and Sony PlayStation, to hold saved game data. Other special flash memory cards include HD memory cards for capturing high-definition videos; netbook memory cards to expand the storage of a netbook computer; and Wi-Fi enabled flash memory cards used to wirelessly upload photos from a camera. [16]
USB Flash Drives
[edit | edit source]
The USB storage device is one that has been growing rapidly in popularity. It is a very user friendly form of storage. To save information to a USB flash drive, one simply must plug in the USB drive into the USB port (usually on the side or back of the computer), click the "save as" option on their project, then select the drive on their computer which represents the USB. Then one can eject the USB and take the saved information anywhere they need. USBs are quickly advancing as well. There are now ways that you can create an entire mobile computer, a fingerprint enabled secure file, and secure the use of your computer all with the use of a single USB flash drive. These new advances are sure to be hot on the market. USBs are high in demand right now, not just because of their technical abilities but also because of how you can choose a USB to fit into any lifestyle or match any personality. There are thousands of custom USBs available in stores and online. These range in colors, sizes, amounts of memory, and even shapes.[17] USB flash drives are something that will definitely be here to stay for a while longer, even with the ever emerging cloud. USB flash drives are also very secure ways to store information. Since they are not connected to the Internet, they cannot be hacked, and some can be encrypted to prevent unauthorized access. The one down side to this use is the possibility of the flash drive being lost or stolen, but with proper precautions and organization, this can be avoided. Flash drives also preserve data and documents in a non-volatile state. As some specialized computers (such as theatre control boards) are prone to crashes and glitches, saving information on a flash drives prevents is from being corrupted or lost in the event of a system crash or other glitch. In simpler systems, flash drives can be used as the central storage point for a computer. While this may be inefficient on most machines, those that are single use and do not require large amounts of memory can benefit from this, as the system is flexible, and more memory space can be added as needed. However, the primary benefit of flash drives remains the mobility. Flash drives are an inexpensive and more secure alternative to the cloud and other means of Internet storage.

USB drives are the perfect devices for transporting data and files. They are easy to use and their portability makes them incredibly convenient. In addition to storing files, they can also be used to run portable apps. Certain applications can be turned into portable versions of themselves. You can have access to various software applications to use on any computer. Free programs exist to convert applications to portable ones to, in essence, create a portable PC on a thumb drive. USB drives range in storage capacity from 2 GB to 4 TB. With 4 TB of storage in such a portable size, the limits to their use are virtually endless.
USB drives can be password protected, or some can even be secured using biometric features, like a finger print. There are some concern related to USB drive security. They can contain large amounts of information, and given their portability, they can be used for transporting files secretly. Anyone with access can simply plug a USB drive into a computer, copy files onto it, and remove them from the premises. USB drives carry an additional security risk in that they can contain malware that can be automatically launched using AutoPlay (which can be disabled) as soon as they are plugged in.[18]
Solid State Drives
[edit | edit source]
SSDs serve the same purpose as HDDs: they store data and files for long-term use. The difference is that SSDs use a type of memory called “flash memory,” which is similar to RAM—but unlike RAM, which clears its data whenever the computer powers down, the data on an SSD persists even when it loses power. SSDs use a grid of electrical cells to quickly send and receive data. These grids are separated into sections called “pages,” and these pages are where data is stored. Pages are clumped together to form “blocks.” SSDs are called “solid-state” because they have no moving parts. SSD's are much faster than traditional hard disks (especially during random reads/writes) as they do not rely on mechanics to locate data (which becomes slow when data is located at different ends of a hard drive).[19]
However, as with flash memory, SSD's can last only a finite amount of writes. As an SSD is used, the electrical charges within each of its data cells must be periodically reset. Unfortunately, the electrical resistance of each cell increases slightly with every reset, which increases the voltage necessary to write into that cell. Eventually, the required voltage becomes so high that the particular cell becomes impossible to write to. While SSD's include extra capacity (which cannot be seen by the user) solely to replace cells which become damaged this way, after a lot of writes (usually over 150 TB), the drive will fail. However the volumes of writes (reading alone isn't affected) required to do so is far out of the reach for most users.
The main drawback of a SSD as compared to a HDD is price; SSD's cost significantly more than a HDD, but the price difference is rapidly falling, and more and more computers now include a SSD by default.

Remote Storage
[edit | edit source]Remote storage is there to expand the disk space without hard disks and isn’t connected to the computer directly but accessed through internet. That way you can access your files wherever you are, whenever you want, on your laptop or Smartphone or even a different computer. This is the basic concept of cloud storage. When you need to access a file, you open the file as usual but if the data isn’t on your local volume, Remote Storage retrieves the information from a media library. When data is removed from a file, the logical size of the file remains but the physical size is reduced. [20]
Being much faster and reliable than storage devices like CDs, DVDs, hard disks, and flash drives, an online remote storage provides protection against system errors like viruses, and enables one to recover lost data from any potential system crashes. Being critical to not only businesses, but home computer users as well, an online storage provides low-cost and easily accessible security for data management and storage. To assure maximum security, many online companies automatically backup systems on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis, to an “electronic vault.” Also, unlike CDs or DVDs, using remote storage diminishes its vulnerability to damage and data loss. Living in today’s high-tech society, the online remote storage system is definitely a very essential, yet affordable tool to assure that the countless amounts of data being saved on devices is still remediable after a computer failure. [21]
Floppy Disk
[edit | edit source]The floppy disk drive was invented at IBM by Alan Shugart in 1967. The first floppy drives used an 8-inch disk that was later called a "diskette" as it got smaller, which evolved into the 5.25-inch disk that was used on the first IBM Personal Computer in August 1981. The 5.25-inch disks were dubbed "floppy" because the diskette packaging was a very flexible plastic envelope, unlike the rigid case used to hold today's 3.5-inch diskettes.[22]
The floppy disk is an archaic physical external storage device that is now obsolete. There might be some banks that still use this storage medium, but any business or person who is considered computer literate does not use this system to store information. The down sides to floppy disks are that they are not compatible with any device that is contemporary, their security is non-existent, and the storage capacity is low - usually with a maximum of 1.44MB. The last version of a floppy disk was released in 1987 by IBM.
Holographic Storage
[edit | edit source]
Holographic storage utilizes photo-sensitive media and innovative laser beam technology as a means of computer storage. This new storage method has the ability to store 1,000 DVD's into this 4 square inch storage device. This is unlike previous methods of data recording, such as magnetic and optical hard drives, which involve a rotating disk or simple 2D lasers. Instead, holographic storage begins with a single laser that is split into two separate parts -- the signal beam (carries data), and the reference beam (reconstructs hologram when prompted). A spatial light modulator is used to encode data for the signal beam, followed by a conversion of electronic data into binary code. It is then arranged into a specific pattern of dark and light pixels (representing zeros and ones), consisting of >1 million bits each. The signal and reference beams intersect, and a holographic image is created through a 3D refraction that is etched into the media. Advantages include a safe, fast, reliable, and portable system of storage. Disadvantages include expense, limited capacity, and recording fails. UV rays can also erase the data, which makes this method unstable in the long-term. Since the concept is still in its infancy, however, problems are expected to diminish greatly over time.[23]
Storage area network
[edit | edit source]
Storage area networks are clusters of high performance computers used to transfer huge amounts of data. SANs are also used for distributed processing applications requiring fast local network performance and designed specifically for data management. SANs move storage resources off the common user network and into an independent network. What this does is allow each server too access any shared storage extremely quickly, as if it was already attached to the server. Typically, a SAN is assembled using three components: cabling, host bus adaptors, and switches. [24] [25]
What makes a good storage area network? A SAN definitely needs to be indestructible and have a built-in protection against any potential harmful failure. If a SAN is vulnerable to failures and is unable to recover lost data, an enterprise may even go out of business! Secondly, a vast amount of storage capacity is another essential to a valuable storage network; since the number of devices connected to one host system may increase by time, the organization’s storage and processing also needs to expand accordingly. A big advantage of using a good storage area network is the fact that even if all of one’s system servers crash, the SAN remains online and provides disaster recovery. [26]
Network Attached Storage
[edit | edit source]
NAS is a type of dedicated file storage device typically connected by a wired networking connection, therefore only providing local area network users with storage. NAS supports file transfers, in which it will back up any data that appears in the form of files, such as email boxes, web content, remote system backups. The main advantage of a network attached storage is that network storage is no longer limited to the amount the computing device can hold. NAS devices typically look very box-like, without a keyboard or display. NAS products come in levels of capable storage space, drive capacity and drive scalability, often placed into one of 3 categories: Desktop NAS, devices aimed at small businesses and home users; Mid-market NAS, devices capable of running several hundred terabytes but not clustering; Enterprise NAS, devices that can store huge amounts of files, including virtual images, and being able to NAS cluster. [27] [28]
NAS vs SAN
[edit | edit source]
Both systems of storage serve different purposes for their clients. The main difference between SAN storage and NAS storage is the way that the systems interact with the network. A NAS network will behave in a way that makes it similar to any other network component. In contrast, the storage devices of a SAN network are found in a separate network but connected to the main one. Overall though, both systems are used for storage and over time the performance offered by both is becoming harder to distinguish. For example a SAN uses Fibre Channel interconnects while NAS makes Ethernet and TCP/IP connects, but now many SAN systems are switching over to those connection routes NAS systems use.[29]
Optical Discs
[edit | edit source]Characteristics
[edit | edit source]
An optical disc is a flat, circular disc that stores data and is made out of a very strong plastic called polycarbonate substrate. This helps to protect the disc with many layers of coating. Data on these discs are read optically, which means that they store data using laser beams. Data can be stored on one or both sides of the disc. The track, which is a single spiral around the disc, spins from inside the center track (or groove) to the outermost track for the data to be read. Most people today have already switched from VHS movies to DVD movies, and now to Blu-ray DVDs. The advancement in technology has made viewing and burning capabilities for DVDs and CDs much more beneficial. These optical discs do not degrade, like VHS and magnetic media do. Optical discs are used in our every day lives for storage, backing up, photos, movies, music, and much more.
Read only discs are molded and stamped to show the data so that it can only be read (and not over written). This happens with most CDs for music and software, and DVDs for movies. A recordable or rewritable optical disc with a CD or DVD uses a laser to represent the data. An example of this would be burning a CD for music, or an iMovie project to a DVD. There is a complex process that takes place when writing the data on the optical disc. To mold or stamp the discs, bumps (called pits) are formed on the disc’s surface. The places that are not changed on the optical discs are called lands. Switching from a pit to a land represents a 1 (like discussed in the system unit). CD discs use infrared lasers, DVDs use red lasers, and Blu-ray discs use blue-violet lasers. These different types of lasers are used to store different amounts of data at a more compact size.
Optical drives are the machines that read the discs of CDs, DVDs, and BD drives. Many households have switched to Blu-ray DVD players. However, users are upset because only BD discs can be played on BD drives which is considered a hassle to some. These drives are also used to burn data on the discs.
History
[edit | edit source]
Optical disks were invented in 1958 by David Paul Gregg, he patented them. James T. Russell was then the first person to have made a recording audio digitally to an optical disk. Later Sony and Phillips research physicists made the CD’s we know today that can store large amounts of data. For this first generation of CD’s they could hold up to 75 minutes of audio with 650Mb of storage. The purpose of the first generation was only for audio and computer software. They were capable of making a CD video but the VHS cassette was more popular at the time and it cost too much to produce them. These CD’s were read with an infrared laser. Later the second generation could store even more data and was used for video. They were read with a visible laser light which allowed the lands a pits to be smaller thus creating more space to for more data. They allowed 4.7 GB of storage on a standard single disc. The third generations are being developed to create even more storage available, like a Blu-ray disc. The Blu-ray disc use blue-violet lasers. There is even a fourth generation to be discovered that could hold up to one terabyte of storage.
CDs, DVDs, and BDs
[edit | edit source]
Read-only optical discs include CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, and BD-ROM discs. These are CDs or DVDs that come with something already prerecorded on them and they cannot be cleared. This is because the pits that are molded into the surface of the disc are permanent. There are also read-only discs for video games and different software.[30]
Recordable optical discs are also sometimes referred to as write-once discs. This means that these can be written to but the discs cannot be reused or erased. These include CD-R, DVD-R, DVD+R, and BD-R discs. The difference between the DVD-R and the DVD+R is the standard being used. There is also a DVD-R DL and a DVD+R DL, which indicates whether or not it is dual layer. Using DVD+R will allow you to instantly eject the DVD without having to wait for the finalized version. It also allows you to record some of the DVD on a personal computer and some of it on the TV. Another feature is that is it 100% compatible with all DVD players. Recordable CDs are often used for backing up files, making music CDs, or sending large files to other people. BD-R discs are used for even larger back ups that need even more storage and they are used for high-definition multimedia files.[31]
Rewritable optical discs include CD-RW, DVD-RW, DVD+RW, and BD-RE discs. These can be written on and then erased and rewritten on. To rewrite on these types of discs they use phase change technology. So basically the rewriteable disc is coated with a metal alloy compound. They then use heating and cooling to write on the disc without making it permanent. These are used for backing up files but they are more convenient than recordable optical discs because they can be used multiple times.
Details about CDs
[edit | edit source]
Compact Disc (CD) is used to store video, audio, and data in different formats classified in the Rainbow Books. It includes formats like CD-ROM (Compact Disc Read-Only Memory), CD-R (Compact Disc- Recordable), CD-RW (Compact Disc-ReWritable), VCD (Video Compact Disc), photo CD, and Enhanced Music CD. Compact Disc comes in standard 12 cm (120mm) or 8 cm (80mm) in diameter. The most popular is the 12 cm type with a 74- or 80-minute audio capacity and a 650 or 700 MB (737,280,000 bytes) data capacity. The 8 cm type is used in electronic devices like portable compressed digital audio players or data storage products like miniature CD recorders.[32] CD-Rs were invented by Philips and Sony and together with CD-ROM there were about 30 billion CDs sold worldwide in 2004. The high-capacity recordable CDs can hold 90 or 99 min of audio on a 12 cm disc and 30 minutes of audio on a smaller disc (8 cm). The ability to write beyond the manufacturer’s declared capacity on a CD-R or CD-RW disc is called oversizing or overburning. However, Overburning might affect product warranties and result in lost data so it is not recommended. However, it might affect product warranties and result in lost data so it is not recommended.[33] These days, more and more compact discs are being replaced by flash drives or downloading.
Details about BDs
[edit | edit source]
The newest form of optical disk is the Blu-ray disk (BD), which was officially announced on February 19, 2002, and was first available to consumers on April 10, 2003. Blu-ray gets its name from the blue laser that reads it (as opposed to the red laser that reads DVDs). BDs have more storage capability than its predecessor and also has a variety of new functions that DVDs did not have, such as the following: record high-definition television without losing quality, record one program while watching another at the same time, automatically search for an empty space on the disc to avoid recording over a program, and access the Web to download subtitles and other features. The way BDs achieve this is by having smaller pits, so more data can be stored, and having a laser with a shorter wavelength, a blue laser, that can read more precisely. DVDs could not fit more information because a red laser is not precise enough to read pits that are packed together as close as the pits on a BD. Pits on a DVD could be a minimum of 0.4 microns, while BDs pit minimum is 0.15 microns. Also, the track pitch on BDs has been reduced from 0.74 microns to 0.32 microns. Because of all these improvements, a BD can hold more than 25 GB of information, which is five times the amount that a DVD can hold.[34]
How to Repair a Scratched CD or DVD
[edit | edit source]
Compact Discs (CDs) and Digital Video Discs (DVDs) both store their data externally on a disk. Unfortunately, as we all have experienced, these disks often times get scratched, making the CD or DVD skip, or sometimes not work at all. Depending on where the scratch is located, the disc may or may not be able to be repaired. It seems scratches on the top, shiny part of the disc are harder to repair than if the scratch is on the lower plastic part of the disc. Although some companies are developing scratch resistant discs, their efforts may be in vain due to technology moving fast past these forms of storage. For those people still utilizing CDs and DVDs, scratches on them can be annoying and frustrating. There are a few simple remedies consumers can try to repair their discs and attempt to get more life out of them. The first step is to clean the disc with a mild soap and water. This can help by removing any finger prints that may be hindering the disks’ functionality. Users then want to dry the disc with lint free cloth, as even the smallest fibers can scratch and damage the disc further. After the disc is dry, the user can then apply toothpaste to it, smoothing it out in a straight direction from the disc’s center. After this, the disc should be rewashed to remove any excess paste. If this procedure is successful, the toothpaste will fill in the scratches so the disc can again be played with little or no skipping. Often times, scratches to these discs are too severe for this method to help. If that is the case, companies advise consumers to discard the disc altogether. Luckily, as technology continues to advance, the reliance on these forms of storage is decreasing, and with it, the annoyance and frustration that comes from their malfunctioning.[35]
Are Optical Discs Becoming Obsolete?
[edit | edit source]
While Optical Discs may be excellent media of storage, their necessity has now come into question with the ever advancing of technology. Floppy disks used to be what everyone used to store information and that soon became obsolete. As the cycle of technology inevitably catches up to optical discs, they may no longer be as useful as before. First, there’s the rise of technologies that no longer make use of optical discs because of the size. Most tablets and laptops no longer having optical drives because they take up space and may make the device less portable. Next is the fact that there are many more storage options that have become available that are much more convenient. Cloud storage has been on the rise as well as regular flash drives have had an increase in storage capacity as compared to optical discs. Then there’s the fact that many media companies have moved to a disc free environment. Streaming services have made renting CDs and DVDs obsolete. Gamers no longer buy physical discs but rather just download a digital copy. Even music has moved to a streaming service that makes buying physical albums and LPs more of a novelty. Finally, there is the fact that consumers want what’s convenient and optical discs are no longer as convenient as they used to be. However which way you look at it, the advancement of technology will eventually make anything obsolete. The future holds many possibilities for other forms of storage and that too will eventually become obsolete.[36]
Smart Cards
[edit | edit source]
A smart card is a credit card-sized piece of plastic that contains computer circuitry, like a processor, memory, and storage. Smart cards can only store low amounts of data, around 8 kilobytes of RAM or 346 kilobytes of ROM. The processor is actually a microprocessor, and it is situated under a gold contact pad on one side of the card. The processor in the card has the capability to encrypt the data so that only authorized access is allowed. The purpose of a smart card is to store sensitive data securely, usually identification or digital cash. Unlike a credit card where all of the information on it can be read easily and identity theft is more common, the smart card cannot be physically read and it puts up a difficult fight against a hacker trying to access the data. To make it even more secure, some smart cards actually store biometric data to even further ensure that only the correct user can use it. A smart card is used by sliding it through, placing it in, or placing it in front of a smart card reader. This allows for the smart card reader to interact with the smart card by transferring the data on the card. An example of this is having a smart card reader on a locked door. The authorized user, a government official, places their smart card in front of the smart card reader on the door and the data on the card would be read by the reader. Once the reader acknowledges that the government official is allowed in, the reader would unlock the door and the official could walk in. All in all, the smart card is a great new technology that is making transactions and equipment safer.[37]
Large Computer Storage Systems
[edit | edit source]
Major companies and organizations require large computer systems that can store their massive amounts of data. The amount of data that the world needs to store is growing at a phenomenal rate, predicted to increase by half in 2014 alone. Regulations have been put in place by the government to make companies keep data and information about clients and customers. This information is stored in the same types of hardware that everyday consumers would use but on a much larger scale. Many hard drives are connected and used together to increase the amount of data that can be saved. A leader in the industry, IBM, is currently at work on the largest storage server ever with an incredible 120 petabytes of space. This server is going to be comprised of over 200,000 standard hard drives connected in a large warehouse.[38] Some companies may also use a system called RAID, or redundant arrays of independent disks. This method uses two or more hard drives which contain redundant copies of the same data in order to process and access it faster. This can be done one of two ways. The first method, disk striping, actually separates and spreads the files out over multiple hard drives while the second method, disk mirroring, has an exact duplicate of the information on the first.
Review
[edit | edit source]Review Questions
[edit | edit source]- True or False; A magnetic hard drive uses flash memory.
- True or False; A Blu-ray disc offers a larger storage capacity than a DVD disc.
- True or False; Folders are places on a storage medium that hold files.
- True or False; Holographic storage uses lasers to produce three dimensional representations of data.
- True or False; NAS and SAN technologies refer to the same type of storage setup.
- A _____ is anything that is stored on a storage medium.
- A _____ _____ _____ is a type of flash memory device that is inserted into a USB port.
- Music and software typically use a _____ disc.
- Most computers use a _____ _____ as the primary storage system.
- A drive that uses optical discs is known as an _____ _____.
Answers
[edit | edit source]- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
- file
- USB flash drive
- CD
- hard drive
- optical drive
Glossary
[edit | edit source]- BD-R a Blu-ray disc that is recordable
- BD-RE a Blu-ray disc that is rewritable
- BD (Blu-Ray disc) a disc with a high storage capacity of approximately 25 or 50 GB. Commonly used in HD movies
- CD a disc with a low storage capacity of approximately 650 MB. Commonly used in music and software
- CD-R a CD disc that is recordable
- CD-ROM a CD that can only be read from but not able to write over
- CD-RW a CD that is rewritable
- cluster a sector that is the smallest addressable area of a disk
- cylinder a collection of hard drive tracks
- disk access time how long it takes to locate and read data from some storage medium
- disk cache memory that improves the time it takes to read from or write to a hard disk
- DVD a disc with a medium storage capacity of approximately 4.7 GB or 8.5 GB. Commonly used in software, movies and games
- DVD-R/DVD+R a DVD that is recordable
- DVD-ROM a DVD that can only be read from but not able to write over
- DVD-RW/DVD+RW a DVD that is rewritable
- embedded flash memory flash memory chips used in products
- file anything stored on a storage medium
- filename the name given to the file
- flash memory nonvolatile memory that can be found in a computer or used in a storage medium
- flash memory card a flash memory medium often found in digital cameras and other small devices
- folder a named place on a storage medium where files are kept
- hard drive a storage system found in most computers
- holographic storage a medium that stores data in three dimensions using multiple blue laser beams
- hybrid hard drive a hard drive with both flash memory and magnetic components
- magnetic hard drive a hard drive with one or more metal magnetic disks, an access mechanism and read/write heads
- magnetic tape storage media that stores data as a series of magnetic spots
- network attached storage (NAS) a high-performance storage device individually connected to a network to provide storage for computers on that network
- online storage remote storage devices accessed via the internet (i.e. cloud storage)
- optical disc a storage medium that reads and writes using a laser beam
- optical drive a drive used with optical discs (e.g. CD, DVD, BR)
- RAID (redundant arrays of independent disks) the configuration of several hard drives working together to improve performance and/or reliability
- remote storage a storage device that not directly connected to the computer that uses it (e.g. cloud storage)
- sector a small piece of a track
- smart card a small card-sized circuit piece that can store data
- solid-state drive (SSD) a hard drive that uses flash memory (rather than metal magnetic hard disks)
- storage area network a network of hard drives or other devices that provide storage for a computer network
- storage device hardware in which a storage medium is inserted to be read from or written to
- storage medium the part of a storage system where the data is stored (e.g. CD)
- track a circular path on the surface of a disk where data is recorded
- USB flash drive a storage device, that uses flash memory, that is inserted in a USB port
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ https://www.inkling.com/read/dummies-comptia-aplus-clarke-tetz-3rd/chapter-5/understanding-hard-drive
- ↑ http://kb.sandisk.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/8150/~/difference-between-sequential-and-random-access-operations
- ↑ http://www.dineshbakshi.com/igcse-gcse-ict/storage-devices-and-media>
- ↑ http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/h/harddriv.htm
- ↑ http://it.med.miami.edu/x929.xml
- ↑ http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2404258,00.asp
- ↑ https://www.ifixit.com/Wiki/Hard_Drive_Interfaces
- ↑ http://www.newegg.com/product/CategoryIntelligenceArticle.aspx?articleId=209
- ↑ http://www.adrc.com/interfaces.html
- ↑ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/cloud-computing/cloud-storage1.htm
- ↑ http://www.theguardian.com/media-network/media-network-blog/2013/jun/19/how-businesses-using-cloud
- ↑ http://www.thesecurityadvocate.com/2013/03/20/cloud-service-contracts-breaking-down-the-all-important-service-level-agreement-sla/
- ↑ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/flash-memory1.htm
- ↑ http://smithsonianchips.si.edu/ice/cd/MEMORY97/SEC11.PDF
- ↑ http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2388408,00.asp
- ↑ http://www.newegg.com/product/CategoryIntelligenceArticle.aspx?articleId=220
- ↑ http://www.usbgeek.com/search?q=USB&search-button.x=0&search-button.y=0
- ↑ http://www.howtogeek.com/203061/don%E2%80%99t-panic-but-all-usb-devices-have-a-massive-security-problem
- ↑ https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/solidstate-drives-work-makeuseof-explains/
- ↑ https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-server-2003/cc759742(v=ws.10)
- ↑ http://www.spamlaws.com/online-remote-storage.html
- ↑ https://computer.howstuffworks.com/floppy-disk-drive1.htm
- ↑ http://www.vibrant.com/blog/holographic-storage-101.html
- ↑ http://searchstorage.techtarget.com/definition/storage-area-network-SAN
- ↑ http://compnetworking.about.com/od/networkstorage/g/storage_san.htm
- ↑ http://www.snia.org/education/storage_networking_primer/san/what_san
- ↑ http://compnetworking.about.com/od/itinformationtechnology/l/aa070101a.htm
- ↑ http://searchstorage.techtarget.com/definition/network-attached-storage
- ↑ http://compnetworking.about.com/od/networkstorage/f/san-vs-nas.htm
- ↑ http://www.thefreedictionary.com/compact+disc+read-only+memory
- ↑ http://netforbeginners.about.com/cs/multimedia/a/DVD_explained_3.htm
- ↑ http://www.osta.org/technology/cdqa7.htm
- ↑ http://www.osta.org/technology/cdqa7.htm
- ↑ http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/blu-ray1.htm
- ↑ http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/how-to-fix-scratched-dvd.htm
- ↑ http://compreviews.about.com/od/cddvd/a/Death-of-PC-Optical-Drives.htm
- ↑ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/question332.htm
- ↑ http://phys.org/news/2011-08-petabytes-ibm-largest-storage-array.html
- Wikipedia Computer Data Storage [10]
Input and Output
Keyboards, Pointing, and Touch Devices
[edit | edit source]Keyboards
[edit | edit source]Keyboards are one of the many different types of input devices, and one of the most common. Most, if not all, keyboards are set up in an alphanumeric key arrangement, also referred to as a qwerty keyboard.[1] There are a few different ways a keyboard can connect to a computer, either wired or wireless, via USB or Bluetooth respectively. For the most part all keyboards are similar to one another, some may have extra keys for games and others may have a numerical keypad built into the board itself.

While not all computing devices have keyboards they do have supplements, such as a on-screen touch keyboard. Many phones used to have a slide out keyboard for those who prefer an actual physical keyboard. But technology has moved toward touch screen phones which don't require the slide out keyboard. Examples include the Apple iPhone and the Samsung Galaxy. Furthermore, you can purchase physical keyboards to connect into tablets. All of these additional keyboards that you could add to devices are most likely membrane keyboards. Membrane keyboards are the cheapest and most common types of keyboards. The other growing type of keyboards are mechanical keyboards. When you type on a membrane keyboard you complete a circuit which produces the data on screen, which generally makes little to no sound and gives no tactile feedback. For many gamers and avid typist, they would use a mechanical keyboard, which has the point of contact directly beneath the each key. This gives a better tactile feedback along with a faster typing speed, but generally cost much more than membrane keyboards.[2]
The keyboard is one of the most important parts of a computer!
Different Types of Keyboards
[edit | edit source]The purpose of all keyboards is to input data, however, there are as many different types of keyboards as there are variations of devices that need one. At first, there was only one design for a keyboard, but just as all other technology has progressed with time, so has the keyboard. The “original” keyboard, known as the standard keyboard, is the QWERTY keyboard, which is probably the most familiar to people. This keyboard has an average 105 keys, and while minor changes have been made to the design, its overall format has stayed the same.[3]

Due to the stress put on the wrist and hand muscles from typing, the ergonomic keyboard was invented. This keyboard has the keys split so that the angle of the user’s wrist is in a more comfortable and less-straining position. By improving posture, the Ergonomic Keyboard is supposed to prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. It comes either as one separate board with pre-angled keys, or as two separate boards so the user can angle them any way he/she prefers.[4]
The other types of keyboards that have come along have been produced to fit very specific uses. For example, a gaming keyboard, as the name suggests, is made specifically for gamers and has special designs such as built-in joysticks. Another example is the internet keyboard, which have “hot keys” related directly to browsing the internet. These hot keys include bookmarks list, e-mail inbox, Google search, and YouTube.[5]
Lastly, there are keyboards made simply to be more convenient for the consumer. These include the wireless keyboard, which connects to a computer via Bluetooth, the compact keyboard, made for laptops and other portable devices, and the virtual (or touch screen) keyboard which is found mostly on mobile devices and tablets.[6] The last one is the most recently developed and will most likely come to be the only type of keyboard in the future.

The History of Keyboards
[edit | edit source]The first keyboards were called QWERTY keyboards named after the six letters in sequential order on the top left hand side of the keyboard. Surprisingly, the keyboard was actually designed to make typing as slow and difficult as possible. This is due to the fact that the very first design of the first typing machine developed by a man named Christopher Latham Scholes back in 1873 was originally set up in alphabetical order. After some time, it was typical for keys to get jammed together due to fast typing. This prompted Scholes to redesign the machine with the letters most commonly used as far away from each other as possible to avoid jamming. By making the user slow down, his new design became a success. It wasn’t until the 1960’s that a couple by the name of Bob and Joan Crozier came up with the idea that there was a need to integrate computer technology into business. At that time, there were only large mainframe computers available. The couple came up with a device that had keyboard switches, which led to more understanding about the growing need for such a device. By the 1970’s, the first keyboards were born. They had to be put together one switch at a time which was a lengthy process. Later in this decade, the first ever personal computers were developed. The keyboard was not attached to these computers so they required an IBM electric typewriter to be attached. By the 1980’s, IBM launched its first personal computers with their famous model M keyboards attached. This model came with some problems as it was criticized for its Enter and Shift keys being too small. IBM came up with keyboard expanders to fit the keyboard and enlarge the keys. By the 1990’s, Membrane switches became available to replace individual keys. This was also the decade that the laptop computer became available, making Membrane Switches to increase in popularity. The last decade has seen advancement in the design of the keyboard with the release of ergonomic keyboards that lessen the chance for a user to be injured due to overuse. Today, the modern keyboard faces extinction as the use of touch screen devices and voice recognition are taking the center stage of computer input.[7]
Point and Clicks
[edit | edit source]
Pointing devices are inputs that connect to a desktop or laptop and are used to move an on-screen pointer, usually an arrow, to allow the user to select objects on the screen. The most common of these is the "mouse" which derives its name from its size, shape, and "tail", or thin wire, which connects it to the computer. It's usually connected via a USB port and it often rests next to the keyboard for easy access. Recently, laser "mice" have become popular due their added mobility as these connect via Bluetooth or other wireless connection and no longer need their "tails" for support to the system. Older mice have a ball at their base and use this to move the pointer on screen as the user's hand moves the mouse across the desktop surface. Once the pointer is over the desired icon, link, or image, etc. the mouse is used to interact with it by clicking one of the two buttons on its surface. A wheel may also be found on some and is commonly used to scroll up or down a page or zoom in and out of a window. Optical mice use a laser on the bottom which track movement with light instead of a ball. Three dimensional mice may also be used to interact with three dimensional programs. These programs tend to recognize more complex movements and the mouse may be lifted to simulate flying or angled to simulate a visual tilt within the program.
Stylus
[edit | edit source]
In addition to using a mouse, many computing devices allow for the use of a pen or stylus. The pens input could be drawing, writing, or tapping on the screen. The stylus is often just a piece of plastic solely used to touch the screen, and that’s it. However, other stylus pens can detect the amount of pressure that is applied to the screen allowing you to have a more precise input. The stylus has a smooth rounded tip so it would not harm the screen it is used with, and may also contain buttons so it could be similar to a mouse and execute similar functions. The stylus is used in a way similar to using pen and paper. It is used in areas like photography, graphic design, animation, industrial design, and healthcare. There are even certain gestures that a pen can read to complete a task. Flicking the pen up, for instance, could delete something, print, or copy. Stylus pens are beneficial for people with long nails, or are wearing gloves; there's nothing more annoying than having to take off gloves in the winter to have to use a touch screen device. Many smartphones like the Samsung Galaxy Note 3 have a pen stylus included. These phones allow the user to use the screen to its fullest since the screen is so large, the phone embraces being able to use two hands while doing something on the phone.[8]
Touch Screens
[edit | edit source]
Touch screens are electronic visual displays which allow a user to interact with programs by using simple touch-based movements. Through the use of a special stylus/pen and/or one or multiple fingers, the user can interact with the content being displayed in multiple ways allowing actions such as scrolling, zooming, rotating, dragging, and dropping items to be handled with ease without the need for a pointer or mouse. Because the touch screen interface can be used with practically any PC software and is useful in a variety of applications, mobile phones, tablets, desktops, laptops, and surface computers have taken advantage of this technology. It can be found in museums, consumer kiosks, newsrooms, automated teller machines (ATMs), medical field, etc. There are many touch screen technologies that have different methods of sensing touch, such as resistive, surface acoustic wave (SAW), capacitive, infrared grid, infrared acrylic projection, optical imaging, dispersive signal, and acoustic pulse recognition. They can recognize multiple inputs allowing for more than one person to operate the device at the same time as well as verify and pinpoint multiple objects that are place on them or near. Systems that use a stylus can recognize the differences in pressure applied to the screen and may even contain buttons to aid in "right-clicking" on an object.[9] The stylus is one of the most popular accessories in the touch-screen age.[10]
Fingerprint Scanners
[edit | edit source]A popular security option, which is now becoming standard on laptops and certain external hard drives, is fingerprint scanners. Small "touch screens" are placed adjacent to keyboards (or in the case of hard drives, on top of the hard drive) to prompt users to use their finger print as a means of secure login. Until recently, such hardware was expensive and unreliable. This means of input has been adapted by certain companies to increase security measures and provide peace of mind to clients (often in the case of physical cloud security). This technology was science fiction until recently and it has caught on in government use all the way down to the individual.
Other Pointing Devices
[edit | edit source]
Examples of other pointing devices can be seen in gaming. A popular pointing device in video games is the joystick. Joysticks are moved by hand to point to an on-screen object, such as a character, and then a button or buttons are pressed to execute an action, for example jumping. Gamepads are also examples of pointing devices, performing similar functions to the joystick but held fully in hand instead. Another example of a pointing gaming device is a proprietary controller, such as the Wii remote. These devices are motion sensitive and require the controller to point into a sensor, which will move accordingly with an on-screen pointer. A trackball is a pointing device consisting of a ball in a socket, similar to an upside-down mouse, that the user rolls with the thumb, fingers, or palm. Trackballs are commonly seen on CAD workstations for ease of use. Control buttons and wheels are pointing devices commonly found on handheld gaming devices or portable digital media players. For instance, on an ipod, the user can spin the wheel to scroll through songs, and then click on the desired track. Touch pads are generally rectangular pads that a user can slide a thumb or fingertips across. Tapping the touchpad executes the same action clicking a mouse would. Touch pads are typically found on laptops and notebook computers. [11]
Specialized Pointing Devices
[edit | edit source]
Depending on the device and applications being used, pointing devices can become quite specialized. Theater lighting boards have several different ways to input information due to the vast amount of equipment they can control. These can vary from joysticks to the more common control wheels. These wheels tell the lighting fixture to cycle between colors, change effects, and move on at x/y axis graph displayed on a screen. Besides lighting boards, flight simulators can have numerous input devices, most of which are customized to do a certain task. A number of manufacturers build throttle quadrants and aircraft yokes for use in home simulators. These devices can be set up in minutes, and mimic the movements of the actual aircraft controls. Airlines and colleges take this a step further, using immersive simulator that enclose the operator and mimic the movements of an aircraft in flight. In these simulators, the entire enclosure is one large input device, with each button and knob controlling some function. In addition, an instructor has a workstation where they can input commands and load scenarios to test the person flying the simulator. The full motion simulators used by airlines to train flight crews are perhaps the most complicated computer input devices.
-
A Saitek control yoke is being used to control the aircraft in the simulator.
-
This type of enclosed simulator is fairly common in flight schools, and collegiate aviation programs.
-
This is the flight deck of a full motion simulator, used by airlines for testing and emergency training.
Scanners, Readers, Digital Cameras
[edit | edit source]
Scanners
[edit | edit source]A scanner is a device that copies a picture in digital form. After capturing the image, the data is transferred to the computer. People use scanners to store their hand held pictures in their computer, and one might scan a document for business, school, etc. The two main types of scanners are flatbed and portable scanners. A flatbed scanner is the most common type of scanner which is designed to scan flat objects. A portable scanner is designed for travel purposes.[12]

A sheet fed scanner is much like the flatbed scanner, only this may now be immobile and be used in stores to scan items on shelves. Optical scanners capture the image of a usually flat object and transfer it to a computer, much like flatbed scanners. In order to produce a better quality image, as most people strive for in their printing, you need a higher resolution scanner. The resolution of a scanner is measured in dots per 12-inches, which makes sense because the more dots you have, the more color that shows up, producing higher quality scans. Along with the resolution of a scanner comes the quality, which can be edited and improved once the image is scanned. If the user wants an extremely detailed scan, the drum scanner is a great tool to make this possible. It uses a photomultiplier tube to scan on a glass cylinder and send light rays in three beams, making light and color change and producing greatly detailed images.[13] There are even apps on our phone that we can personally scan documents to have on-the-go. The problem with this, however, is privacy issues and the crisis of having your phone or any other device stolen which has scanned any personal information. While scanners are a tremendous help especially in businesses, it is important users be aware of the risks and use with caution.
Although digital cameras are considered standard today, many individuals still have negatives from their days of using a film camera. This traditional film can easily be digitized using a specialized film scanner. Increasing the resolution will allow for higher quality reproductions of the images. [14]
Readers
[edit | edit source]Readers are designed to read the coding of different products. Readers are also called a "price scanner." It is usually a hand held device that captures the barcode on a certain tag, sticker, or twitter/facebook code. UPC (Universal Product Code) and ISBN (International Standard Book Number) are the two most famous barcodes. Barcodes are essential for efficiency in different businesses.[15]
-
An example of a barcode scanner
-
UPC barcode
-
ISBN barcode
Barcodes use lines to represent the numbers 0-9. They can be quite long, signifying a long string of numbers. These unique number combinations represent a variety information. Barcode readers interpret the bars in the code using reflected light or imaging technology. Once the bars are interpreted, the information that is tied to the number can be retrieved. The scanners can be stationary, like those found in stores, or portable, like those used by delivery services to scan packages.
-
Portable Scanner


QR Codes and RFID tags
[edit | edit source]QR codes, otherwise known as quick response codes, are pattern display bar codes read by an imaging device, that enable a user to automatically scan and open to an encoded hyperlink by using their “smart device”. QR reader applications on devices enable the user to access the hyperlink. The hyperlink opens up to a URL on the user’s device, displaying an image, or website. QR codes are often used by companies to allow the most efficient, least expensive way of advertisement for their product, company, event, website, etc. These codes enable a potential customer or user to access their information with convenience. QR codes are also used in other aspects to identify time tracking, item identification product tracking, as well as document management.[16]
QR Codes are an expansion on traditional barcodes. Traditional barcodes are one dimensional, while QR codes are two-dimensional. Storing data both horizontally and vertically allows for a significant increase in combinations of information.

"QR Code" is a type of matrix bar code originally created in 1994 by the Toyota Automobile Company. They were used during the manufacturing process in place of traditional bar code labels, which offer significantly less room to store data and were frequently damaged. Since the rise of smartphones (and downloadable QR scanning applications), they have experienced unprecedented growth in popularity and success from advertising/marketing, and have in a sense revolutionized these industries. QRCs save businesses money by offering an affordable and personalized way to promote their goods or services. Perhaps most importantly, however, is that they provided a new way for customers everywhere to access information quickly and easily. [17]
RFID codes, otherwise known as the Universal Product Code, in which the barcode is replaced by radio frequency identification tags, which allows communication between network systems that can track certain data or information. RFID codes are commonly used in our economy today in multiple different ways. Similar to QR codes, RFID codes allow users to gain efficiency in terms of time and convenience. Ways that RFID codes are used in our society consist of the following: inventory tracking, ticketing applications, mobile payments, as well as border security.[18]


Digital Cameras
[edit | edit source]Almost every American owns a digital camera to save their memories! Digital cameras are used to take a picture, and these pictures are usually stored in a memory card. When purchasing a camera, it is important to know how many mega pixels the camera contains. For example, the higher the megapixels, the better the quality of the picture will be. However, usually, the higher the mega pixels, the more expensive the camera will cost. People enjoy cameras because the pictures are almost immediately accessible.[19]

Today, digital cameras are often found integrated into various mobile devices.[20] When it comes to smartphones, the camera is often one of the most marketed features of the device. For instance, when shopping for a smartphone online, a website will often have an image that compares a picture taken by various competitor’s phones. The reason these cameras on smartphones are marketed to this extent is because they offer so many advantages to an average everyday consumer. A camera with the capability of snapping nice pictures allows someone to easily share daily activities to social media, scan barcodes at the grocery store, provide post-accident evidence for insurance, and so much more.[21]
While a digital camera can snap still images, a digital video camera can record videos. Although portable digital camcorders are slowly becoming unpopular in the market, other types of these cameras are used every day.[22] For example, these cameras are often used by buildings for surveillance, television networks for broadcasting, and companies for video conferences.[23] However, each type of camera used in these situations are different. Cameras used for security purposes are usually able to operate remotely, and are often found to be smaller than other cameras so that they are more inconspicuous. Television networks use expensive professional cameras which have many different function and are very high performance. Cameras used for video conferencing are often webcam cameras. These cameras are small, usually portable, and can be integrated with a laptop.[24] Overall, the digital video camera is a useful tool in today’s society.
One of the main appeals of digital cameras is the instant gratification of seeing the image immediately upon taking it. The instant gratification comes at a small price, however, because there is a slight delay between the pressing of the button and the actual taking of the photograph.
Biometric Readers
[edit | edit source]
Biometrics are objective, measurable, biological traits that can be used to identify somebody.[25] Biometric identification is becoming more and more common, and individuals can be recognized by a computer based on everything from their eyes to their fingerprints, from their voice to their face, from their unique body odor to the shape of their ear. Some uses of biometrics include fingerprint scanners to protect sensitive information stored in databases at places like nuclear power plants, biometric identification at borders and on passports, identification at nightclubs to ensure people who have been banned can't enter, and even at public schools to have stronger records of attendance and library book borrowing.[26] While biometric authentication is incredibly useful, there can also, obviously, be strong privacy concerns if their use is becoming too common. However, an organization called the Biometrics Institute is seeking to not only advance the use of biometrics but also ensure that all privacy concerns are addressed as this kind of technology becomes more and more common, with a set list of privacy guidelines that should be met whenever and wherever biometric identification is being employed.
Audio Input and Output
[edit | edit source]Audio Input
[edit | edit source]
Audio input is when audio data is put into a computer. Usually the audio that people put into computers is voice or music. Voice input is when words are spoken into a microphone on the computer and they are translated into the digital form via the microphone. Many people will use a sound recorder software to store the voice in a file. One thing that is becoming better known is speech recognition systems. An example of speech recognition being used is when you call a company and an automated voice recording answers and you speak to them and answer their questions and the computer is able to recognize what you are saying and take you where you need to go.[27] Many phones have speech recognition software that allows the user to speak their text message or anything else into their phone and the phone can type the text for them. However these programs are not perfect and they usually require the speaker to talk slowly and clearly. One new technology that is being developed has to do with computers picking up noises the hard drive is making and detecting if there are any problems. One way to input music into a computer is to input it from a CD. They also have keyboards that can be plugged into the computer and the sound can be inputted into the computer. With that technology they can also show the sheet music that was played.[28]
Speech Recognition
[edit | edit source]There are many different ways in which speech recognition systems work. One type of system is a speaker-independent speech recognition software which works no matter the user. Another type of system is a speaker-dependent system in which uses training to analyze a specific users voice. The system is then able to adjust to nuances in a persons voice and fine-tune the speech recognition. Another system is voice-recognition systems which are very similar to speaker-dependent systems in that they are dependent upon the speaker, but instead, they mostly focus on who is speaking rather than what they are saying. These types of systems are primarily used in personal security systems. Speech-recognition software is used to ease the users use of the computer and allow users the freedom of not having to use a keyboard or mouse to navigate through a computer system. Speech-recognition software can be used to perform many tasks including opening applications, making calls, calculating the amount of teaspoons in a cup, and even finding the nearest Chipotle. Today, the use of speech recognition systems are greatly advancing due to their incorporation in mobile devices such as Apple’s Siri and Windows Cortana. Also, speech recognition software has been included within the makings of cars due to regulations that require drivers to use hands-free devices to avoid distraction from the road.[29]

Speech detection and speech analysis are being used in robotics and automatic translation, access control systems and education, but not only a human speech is a subject of recognition. The created sound recognition software has a great scientific and practical value. A broken window, dolphin’s talks, faulty machinery unit, even flowing blood could be recognize due the sounds they make. Growing sound libraries and improving electronic equipment allows actively apply sound recognition technologies in areas such as industrial automation, home improvement, animal bioacoustics, medical bioacoustics and others. People use speech recognition to let computers understand them and use computers for sound recognition to better understand the world. [30]
Audio Output
[edit | edit source]
Audio Output is exactly how it sounds. These are the sounds heard while working on a computer, that incorporates voice, music, and other audio sounds. The most common type of audio output device are speakers. These are used to hear video games, music from iTunes [31] or YouTube,[32] TV shows on Netflix,[33] Web conferencing, and other types of programs. Most computers have the capability to add additional speakers for better sound quality. The speakers are usually included when the computer is bought. Other speakers vary in a broad span of prices. A subwoofer can be added to amplify the computer’s audio output. Subwoofer’s have low-pitched audio frequencies known as bass and are intended to strengthen the low frequency range of loudspeakers covering higher frequency bands.[34] They can be installed in automobiles and computers. For portable laptops and mobile devices, the speakers are built into the device. Some desktop computers have speakers permanently installed to the monitor. A unique example of audio output is a treadmill. Some treadmills have the ability to play music from an iPod or MP3 dock, which makes working out more enjoyable. With our rapidly growing and expanding market, recently many car companies have included headphone jacks, dock connections, or USB ports to connect an iPod or mobile device. These connections make it easier for the driver to listen to their own music from their iPod, instead of the radio or CD’s. Headphones can be used as audio outputs as well, instead of using speakers. Using headphones helps users not to disturb others around them (in a library or school).
Display Devices
[edit | edit source]Display Device Characteristics
[edit | edit source]

There are many different characteristics of display devices. These include display colors, monitor styles, resolutions, video compatibilities, and the extra abilities these devices may have. Most devices today have color displays but there are a few which still follow a monochromatic color scheme. The Nook eReader is one of these devices. There is also a difference in the type of monitor in the way it is illuminated. The older style devices such as the large, clunky, heavy tv's and computer screens are lot with cathode-ray tubes (CRT) and because the tubes take up so much room, the devices needed to be much larger. Today most of our devices are flat-panel displays. These displays use a chemical or gas reaction between two thin clear pieces of material to create their display; this is why they are able to be much thinner and lighter than CRT devices.[35]
Buyer beware, when buying a new device keep in mind that the monitors are measured diagonally. So that new 7" tablet you are looking at on Amazon is 7" diagonally from corner to corner. If you expect the 7" to be the width, you will be sorely disappointed by the smaller device you receive.[36] Keep in mind also that resolution is important. The more information that can be shown in less space, the clearer the image and higher the resolution will be. Video is input through a video card which holds the GPU inside of it. The video card is used to translate the video datas into an images that will appear on your monitor. It uses a fairly large amount of RAM to do so. There are many ways of connecting video devices to computers, and one of those actually allows the addition of extra monitors to an existing computer allowing for double the screen space. Other interesting features of display devices include the ability to hold a charge (temporarily) on their own and become known as wireless, display images in 2D or 3D format, become much more mobile and even wearable (such as a virtual reality simulator headset), as well as register commands based on touch and motion (e.g. iPhone, iPad, Android phone, and most other "smart" devices today).
Data Projectors
[edit | edit source]
While your computer has many talents and uses, sometimes it might seem as if there's not enough of it to go around. Let's say that there's a hilarious cat video on Youtube that you'd like to share among thirty of your best friends but there's not enough room for them all to huddle close before your glowing monitor. Instead of splitting the viewing party up in groups, you can use a data projector. A data projector lets you display what's on your computer monitor onto a wall or projection screen.[37] The image is blown up so all your friends can now laugh in unison as the Youtube cat extends its paws in surprise. Even if you didn't know the name for it, chances are that you've encountered a data projector sometime in your life, especially if you attend public school. They can transfer data from computer to projection screen either with a cord or through a wireless connection. For those of you who like to share on the go, there are even portable projectors called pico projectors that can provide a lesser quality but more accessible presentation.[38] Introduction to Computer Information Systems/Input and Output
Flat Display Devices
[edit | edit source]Flat display devices have become increasingly popular over the years because of their slim design and accessibility. Monitors today must be able to provide full color and gray scale, high efficiency and brightness, the ability to display full-motion video, wide viewing angle, and a wide range of operating conditions.[39] Consumers today want these devices to be thin and light weight, be insensitive to magnetic fields, and not produce any x-rays. All of these attributes are not possible with the cathode ray tubes that are generally found in older televisions or monitors. There are electroluminescent displays, plasma display panels, vacuum fluorescent displays, and field-emission displays all being sold today. The first are used in industries and medical fields because of how durable they are under many temperatures. Plasma displays are usually used in televisions. Vacuum fluorescent displays are used for low information displays like on appliances or small electronics. Liquid-Crystal Displays (LCDS)are the most commonly manufactured displays at this time.

Without even realizing it, we are constantly surrounded by items containing an LCD since they are much thinner and lighter than other displays. Laptop computers, digital clocks, microwave ovens, watches, and many other everyday items all have an LCD. A liquid crystal display works by blocking light as it uses charged liquid crystals that are located between two glass sheets to light up the appropriate pixels using a backlight provided by fluorescent lamps. Conveniently, LCD panels typically already contain those lamps at the rear of the display, hence the term backlight. However, to preserve more energy, today’s new technology has invented light emitting diode displays (LEDs), which are now replacing the fluorescent lamps that were previously used.
LEDs are another flat-panel technology seen in many objects around us like alarm clocks, Christmas lights, and car headlights, etc. An advantage of an LED over an LCD is that they are a lot thinner, have brighter images, color, and quality than an LCD, or even Plasma. Also, since an LED does not require backlighting from fluorescent bulbs, which have a relatively short lifespan, it tends to have a much longer lifespan. As fluorescent lamps burn out more quickly, LEDs are better to use for applications that require turning on and off frequently. Another benefit of LED monitors is the fact that they consume much less power compared to LCDs; LEDs actually consume almost half as much power than an LCD consumes! [40]

A new flat-panel display technology is the interferometric modulator display. This display uses a reflective membrane and a thin-film stack, which sit on a transparent substrate, to reflect external light onto the display. The device uses the interference of light wavelengths to create the different colors necessary for color images. This new display technology is meant to be used for portable devices and new mobile phones. The reason for this is because the display consumes a very little amount of power. By only using external light, the device would not need to continually backlight the display. In fact, the only time the display would need to consume power is when changing the image. This allows for the image to stay open without losing any power for the device, something we all have to deal with everyday on our mobile phones. Another plus for the IMOD display is that the images will stay clear even when in direct sunlight, because it is actually using that sunlight for the image. This is definitely an advantage for anyone who has noticed how hard it is to use a portable device or mobile phone outside when it is sunny. The IMOD display technology is a very energy efficient technology that needs to be utilized in mobile phones and portable devices to help consumers with their issue over battery consumption.[41]
Video Adapters, Interfaces, and Ports
[edit | edit source]
The graphics processing unit (GPU) is the chip devoted to rendering images on a display device. Devices either have a video card or an integrated graphics component built directly into the motherboard or the CPU. The GPU is located in the video card or the graphics component of the computing device. This is what determines the quality of the image that can be shown on a monitor. Video cards will usually contain a fan to cool the card. Video cards will either have a memory chip or they are designed to use a portion of the computer’s regular RAM as video RAM instead. Video cards contain between 256 MB and 2 GB of video RAM. The two most common types of interfaces used to connect a monitor to a computer are HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) and DP (DisplayPort). However, there are still the use of older connectors which include VGA (Video Graphics Array), and DVI (Digital Visual Interface). These are the ports that can be found on a computer to connect it another device, such as a TV screen or a projector. Today, HDMI and DP are widely used not only by large companies, but also by the general public. This allows for high quality connections and single wire capability for interconnect devices, regardless of who makes the computer.[42]
Virtual/Augmented Reality Devices
[edit | edit source]
One of the recent advancements is that of Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality devices. These devices display information by immersion rather than by just displaying it on a screen. First, the distinction between Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality is that the former completely immerses the user in a different “virtual” environment while the latter adds or displays information to the current and existing environment. So while virtual reality brings you into a theatre, augmented reality brings the movie to your wall. Both of these are implemented through various devices. There are head-mounted displays. These are displays that are usually worn by the user and are seen through in order to experience either virtual or augmented reality. Those that do virtual reality usually cover the eyes so that the user is completely blocked out of the real world and can be fully immersed in virtual reality. Those that make use of augmented reality are usually see through since the objects are displayed in the real world environment. Then there are hand-held displays which usually only do augmented reality. These usually make use of the devices camera and screen in order to show virtual objects in the real world.[43]
Printers
[edit | edit source]

Printers today can be divided into two main categories: impact printers and nonimpact printers. Impact printers (known as dot matrix printers) are the traditional printers that actually strike the paper with ink. Their primary uses are for the production of business forms like packing slips and receipts. On the other side are nonimpact printers. These printers do not touch the paper like impact printers, and there are two common types: laser and inkjet. Laser printers use ink powder or toner and inkjet printers use liquid ink, which both create the images with dots (similar to pixels on a monitor). These dots make up the print resolution, which is known as the dpi (dots per inch). The higher the resolution the sharper the image. General ranges for a dot matrix printer are 60-90 dpi, an inkjet 300-720 dpi, and a laser printer 600-2400 dpi.[44] With that, color printers and black-and-white printers are two standards found in either the home or office setting. Typically for home-use color printers are more common than offices, which will use black-and-white printers due to costs (unless the company needs color for specific materials and products like reports or brochures).
Advantages of laser printers include higher resolutions of the image, faster printing speed, and no smearing. However laser printers are more expensive than inkjet printers, which many people use because they are lower in cost yet still produce high quality images and remain relatively fast in operation. Besides these two types, the advantages of impact printers are their low printing cost per page, their ability to print on multi-part forms and their reliability. However these printers are much louder as well as slower than inkjet and laser printers.[45]
Personal printers and network printers are distinguishable by their connection to either a single computer or a home/office network. Network printers allow multiple computers to print from the same printer, which is why they are a standard in the business setting. Typically personal printers have a rate of 20 to 35 ppm (pages per minute) whereas network printers can print from 30 to 65 ppm.
Printers can connect via USB, wired or wireless networks, or connections from other devices such as memory cards or cameras. It is not uncommon to see printers that have multiple capabilities like copying, scanning and faxing. These inkjet or laser printers are known as multifunction devices and they can come in color or black-and-white options.

Laser printers
[edit | edit source]Why choose laser printer over any other printer? Well, Laser Printers are known to be good for their speed, precision and economy. Since it uses a laser, it can print one page at a time so it’s known to be significantly faster than the ink-jet printers. Although they are more expensive than ink-jet, they seem to be more cost-efficient considering ink is more expensive than toner powder, which is used for laser printers. Laser printers are more reliable with their prints because ink-jet printers tend to leave ink smears. Static electricity is the primary principle in making the printer work, which is an electrical charge built up on an insulated object. It uses objects with opposite static electricity forcing the fields to cling together.
Laser printers can work in either black-and-white or in color. To print on a page, a piece of paper must be first be inserted into the loading tray of the printer. A laser beam electrically charges the drum in the necessary locations that the microprocessor in the computer has decoded based on the image being printed. The ink used is a fine powdered ink known as toner, which is applied while the paper rolls over the drum. The paper finally goes through a fusing unit which permanently binds the toner to the paper. [46] [47]

Ink jet printers: Why choose Ink-jet printers? Well, ink-jet printers create pictures by spraying ink from the printhead onto the page. Depending on the printer there’s different sized ink droplets, nozzles and electrical charges for more precise printing. They are typically slower than laser printers because of the back and forth motion of the ink tray. Ink-jet printers have grown in popularity and performance while dropping significantly in price. These dots are thinner than a strand of hair and when different colors combined together to create photo-quality images. [48]

Special-Purpose Printers: Though almost every household has some sort of either ink jet printer or laser printer, there are also numerous special purpose printers out there that are made to perform a specific task. Many companies invest in these products to improve time and cost efficiency. Some examples of these printers are photo printers, bar code, label and postage printers, portable and integrated printers, and 3D printers. -Photo printers, as the name quite obviously gives it away, are used for the purpose of printing merely pictures. Often times, people invest in these printers because they produce a better quality picture than just a typical everyday printer would. They also have certain capabilities and apps that one would not just find on any printer. -Businesses are also often found using bar code, label, and postage printers for their products. Every sellable item needs a product label, and having a printer that is designed just for that saves both time and money. They are also useful for the electronic postage capabilities, saving companies time on the mass amount of envelops that they send out on a daily basis. -If you are an on the go businessman or woman, a portable or integrated printer is the way to go. With so much travel and back and forth, it is easy to pull out these commutable printers and print the documents or images you need on the fly. -Finally, possibly the newest and most up and coming printer is the 3D printer. This useful tool can be utilized for printing models and samples. It prints using plastic, and literally produces a finalized 3D prototype of what you want. With technology rapidly improving, more and more products are being designed for the purpose of cost and time efficiency. Depending on what you do on an every day basis, it may be a very wise choice to invest in one of these printers to save you valuable time and money in the long run. [49] -3D Printers

3D printers use virtual designs created in advanced programs such as CAD (Computer Aided Design) or scanned using a 3D scanner to print out physical models and parts. In order to do this, the software must “slice” the model into thousands of layers that the printer lays down one at at time. There are various kinds of manufacturing methods, such as FDM where material is melted into layers or SLS printing where powdered material is sintered into layers.[50] 3D printing has many applications, especially in design. Even manufacturers now use the printers to create rapid prototypes for research. This saves companies both money and time since changes only need to be made the design file on the computer.[51]
There are different 3d printing methods that were developed to build 3D structures and objects. Some of them are very popular nowadays, others have been dominated by competitors. Most of popular types of 3d printers are:
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM) - 3D printing machines that use FDM Technology build objects layer by layer from the very bottom up by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament.
- Stereolithography (SLA) - SLA 3D printers work with excess of liquid plastic that after some time hardens and forms into solid object.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) - Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a technique that uses laser as power source to form solid 3D objects. The main difference between SLS and SLA is that it uses powdered material in the vat instead of liquid resin as stereolithography does.
- Selective laser melting (SLM) - Selective laser melting (SLM) is a technique that also uses 3D CAD data as a source and forms 3D object by means of a high-power laser beam that fuses and melts metallic powders together.
- Electronic Beam Melting (EBM) - The same as SLM, this 3d printing method is a powder bed fusion technique. While SLM uses high-power laser beam as its power source, EBM uses an electron beam instead, which is the main difference between these two methods. The rest of the processes is pretty similar.
- Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) - During the LOM process, layers of adhesive-coated paper, plastic or metal laminates are fused together using heat and pressure and then cut to shape with a computer controlled laser or knife. [52]
There are different 3d printing methods that were developed to build 3D structures and objects. Some of them are very popular nowadays, others have been dominated by competitors. Most of popular types of 3d printers are:
- Fused deposition modeling (FDM) - 3D printing machines that use FDM Technology build objects layer by layer from the very bottom up by heating and extruding thermoplastic filament.
- Stereolithography (SLA) - SLA 3D printers work with excess of liquid plastic that after some time hardens and forms into solid object.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) - Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a technique that uses laser as power source to form solid 3D objects. The main difference between SLS and SLA is that it uses powdered material in the vat instead of liquid resin as stereolithography does.
Review
[edit | edit source]-Glossary
barcode A machine-readable code that represents data as a set of bars.
computer speakers Output devices connected to computers that provide audio output.
CRT monitor A type of display device that projects images onto a display screen using a technology similar to the one used with conventional TVs.
data projector A display device that projects all computer output to a wall or projection screen.
graphics tablet A flat, rectangular input device that is used in conjunction with a stylus to transfer drawings, sketches, and anything written on the device to a computer.
handwriting recognition The ability of a device to identify handwritten characters.
headphones A personal audio output device used by an individual so only he or she can hear the sound
ink-jet printer An output device that sprays droplets of ink to produce images on paper.
keyboard An input device containing numerous keys that can be used to input letters, numbers, and other symbols.
laser printer An output device that uses toner powder and technology similar to that of a photocopier to produce images on paper.
liquid crystal display (LCD) A type of flat-panel display that uses charged liquid crystals to display images.
monitor A display device for a desktop computer.
mouse A common pointing device that the user slides along a flat surface to move a pointer around the screen and clicks its buttons to make selections.
multifunction device (MFD) A device that offers multiple functions (such as printing, scanning, and faxing) in a single unit.
optical character recognition (OCR) The ability of a computer to recognize scanned text characters and convert them to electronic form as text, not images.
organic light emitting diode (OLED) display A type of flat-panel display that uses emissive organic material to display brighter and sharper images. See organic light emitting diode (OLED) display
photo printer An output device designed for printing digital photographs.
pixel The smallest colorable area in an electronic image, such as a scanned image, a digital photograph, or an image displayed on a display screen.
pointing device An input device that moves an on-screen pointer, such as an arrow, to allow the user to select objects on the screen.
printer An output device that produces output on paper.
radio frequency identification (RFID) A technology used to store and transmit data located in RFID tags.
scanner An input device that reads printed text and graphics and transfers them to a computer in digital form.
speech recognition system A system, consisting of appropriate hardware and software, used to recognize voice input, such as dictation or audio computer commands.
stylus An input device that is used to write electronically on the display screen.
touch pad A small rectangular-shaped input device, often found on notebook and netbook computers, that is touched with the finger or thumb to control an on-screen pointer and make selections.
touch screen A display device that is touched with the finger to issue commands or otherwise provide input to the connected device.
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]The vocabulary may or may not be listed above. What am i?
1. The smallest area of an image in which makes up a whole image.
2. Two of the most familiar_____are UPC and ISBN.
3. A device that is designed to convert physical form to data.
4. With a typical ____________ the sounds are broken into digit representation of Phonemes.
5. An output device that uses toner powder and technology similar to that of a photocopier to produce images on paper.
6. The device that shares the information on a screen.
7. The ability of a device to identify handwritten characters.
8. A personal audio output device heard by an individual.
9. A display device that projects all computer output to a wall or projection screen.
10. An input device that moves an on-screen pointer, such as an arrow, to allow the user to select objects on the screen.
Answers
[edit | edit source]1. Pixel 2. Barcodes 3. Scanner and Camera 4. Speech Recognition System 5. Laser Printer 6. Monitor 7. Handwriting Recognition 8. Headphones 9. Data Projector 10. Pointing Device
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/QWERTY
- ↑ http://www.pcworld.com/article/242037/mechanical_keyboard_faq_pick_the_right_switch.html
- ↑ http://www.buzzle.com/articles/different-types-of-keyboards.html
- ↑ http://www.buzzle.com/articles/different-types-of-keyboards.html
- ↑ http://www.buzzle.com/articles/different-types-of-keyboards.html
- ↑ http://www.buzzle.com/articles/different-types-of-keyboards.html
- ↑ http://www.computer-hardware-explained.com/history-of-computer-keyboards.html
- ↑ http://www.gizmag.com/galaxy-note-3-vs-iphone-6-plus/33905/
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Touchscreen
- ↑ http://www.nytimes.com/2012/08/02/technology/personaltech/on-touch-screens-rest-your-finger-by-using-a-stylus-state-of-the-art.html?pagewanted=all&_r=0
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pointing_device
- ↑ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/scanner
- ↑ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/scanner.htm
- ↑ http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/how-to-understand-film-scan-resolution.htm
- ↑ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/barcode-reader-POS-scanner-bar-code-reader-price-scanner
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/QR_code
- ↑ http://www.freeqrcodes.org/
- ↑ http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gadgets/high-tech-gadgets/rfid.htm
- ↑ https://www.google.com/search?q=digital+cameras&oq=digital+cameras&aqs=chrome..69i57j0l3.2852j0&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8#q=information+on+cameras
- ↑ Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow Comprehensive 14th ed. by Morley & Parker
- ↑ Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow Comprehensive 14th ed. by Morley & Parker
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_camera
- ↑ Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow Comprehensive 14th ed. by Morley & Parker
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Video_camera
- ↑ http://www.fbi.gov/about-us/cjis/fingerprints_biometrics
- ↑ http://www.biometricsinstitute.org/pages/faq-3.html
- ↑ http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gadgets/high-tech-gadgets/speech-recognition.htm
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/V/voice_recognition.html
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Speech_recognition
- ↑ http://publications.rafa-elayyan.ca/27.pdf
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ITunes
- ↑ https://www.youtube.com/
- ↑ https://signup.netflix.com/
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Subwoofer
- ↑ http://www.displaymate.com/crtvslcd.html
- ↑ http://www.necdisplay.com/Documents/WhitePapers/Measuring_Screen_Size.pdf
- ↑ http://www.northcanton.sparcc.org/~technology/Tutorials/Files/Using_a_Data_Projector.pdf
- ↑ http://popsci.typepad.com/popsci/2007/09/dont-publish-a-.html
- ↑ http://www.accessscience.com/content.aspx?id=757559
- ↑ http://www.supercircuits.com/resources/learn/top-7-benefits-of-an-led-monitor
- ↑ https://www.qualcomm.com/media/documents/files/mirasol-imod-tech-overview.pdf
- ↑ http://www.bestbuy.com/site/electronics-promotions/hdmi-cables/pcmcat210800050015.c?id=pcmcat210800050015
- ↑ http://www.nextgeninteractions.com/virtual-and-augmented-reality/
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dots_per_inch
- ↑ http://wiki.pcworld.com/index.php/Different_Types_of_printers_-_pc_world_tutorial
- ↑ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/laser-printer.htm
- ↑ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/laser-printer12.htm
- ↑ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/inkjet-printer.htm
- ↑ http://printscan.about.com/od/printerscannerreviews/u/Reviews.htm
- ↑ http://www.3dprinter.net/reference/what-is-3d-printing
- ↑ http://3dprinting.com/what-is-3d-printing/
- ↑ http://3dprintingfromscratch.com/common/types-of-3d-printers-or-3d-printing-technologies-overview/
System Software
Systems Software Overview
[edit | edit source]
System software can be separated into two different categories, utility programs and operating systems. Operating systems are the foundation of your computer and almost every electronic device. The OS boots up the computer and makes sure everything is operational. The OS is also what runs your cell phone and most of your electronic devices. In most cases, the OS is the GUI (graphical user interface) that displays all your applications. Without the operating system, you can't use your computer. There are many different types of OS’s which are discussed later. Utility programs perform a very specific task, to either enhance or manage your computer. For example your virus protection program, like Norton[1], is an example of a utility program along with the install/uninstall program that comes standard with Windows.
Systems Software vs Application Software
[edit | edit source]Systems Software
[edit | edit source]The operating system is a type of system software kernel that sits between computer hardware and end user.[2] Systems Software are applications that are designed specifically for running the hardware on a personal computer and are used to maintain a platform for Application Software to be used. This means that systems software is designed to communicate with the internal parts of your computer such as the hard drive, RAM, ROM, cache, microprocessors, etc. so that the user doesn't have to. It contains all of the drivers necessary for this type of communication and, in the simplest sense, it is the interface between the user and the hardware.[3] The Operating System (OS) is not only one of the most important systems software on a computer, but is also the most frequently used. It is the software that runs in the background and brings the separate physical parts of the computer together in order to provide the seamless stream of activity that a user experiences. Some of its responsibilities include the transfer of data between the memory and disks (on the hard drive) as well as providing the information needed to display icons, text, cursors and other visible necessities on the display screen. This display is called the graphical user interface (GUI) and is entirely the result of the OS on the computer. This can be compared by viewing the differences between the Ubuntu OS and the Mac Snow Leopard OS. The icons between the two are positioned differently and they look different too. The Mac OS and GUI tends to have a more three dimensional aspect to it where Windows tends to appear more flat. It is worth noting that the operating system behaves independently of the user and any applications being used. Some other systems software would include BIOS and other device firmware. These help the user interact with other utilities such as diagnostic tools, language translators, data communication programs, as well as data management programs. [4]
-
Ubuntu GUI
-
Mac GUI
Application Software
[edit | edit source]Application Software are the most common programs that run in the foreground of the computer. They tend to perform useful tasks which are not associated with computer maintenance, system boot-up, or hardware communication. Application software is directly reliant on the Systems Software to communicate to the physical components of the computer and cannot operate without it. If you were to visualize this, the application software will run on top of the system software, most interactive to the user, while the system software will remain unnoticed in the background. The system software communicates with the hardware, passing any information from the application software to it, and vice versa. Application Software are the most familiar forms of software and come in a variety of types. In most cases, they can be accessed through the GUI of the operating system used, by double-clicking on an icon. Some of the common include word processors, spreadsheets, photo-editing programs, database programs, and accounting programs to name a few. This list is by no means exhaustive of the possible uses of applications, and many more programs are constantly being created to help individuals with their daily activities.[5]
The Operating System
[edit | edit source]A computer would not be able to function correctly without an operating system. An operating system is a software program that empowers the computer hardware to communicate and operate with the computer software.[6] An operating system is one of the most important parts of a computer. The operating system is able to do basic tasks as well as complex tasks. An operating system can be classified as a multiuser, multiprocessing, multitasking, multithreading, and real time. The operating system makes sure that different programs, and users running at the same time, do not interfere with one another. The owner or owners of a computer interacts with the operating system through a set of commands. All application programs need an operating system. Also, operating systems optimizes one’s computer performance. Most of the work that is involved in the operating system is unnoticed because it does the work behind the scenes. This system is in charge of managing one’s network connections. Considering all the new technology out, operating systems must be uploaded in order to support the new technology being uploaded to computers. All in all, the operating system is the core of all computers.
-
Operating system architecture
Multitasking and Multithreading
[edit | edit source]Multitasking is a computer's ability to seemingly run multiple tasks or processes at the same time. For example, you might have an Internet browser open to read this page while also having a word processor open to take notes and a media player open to stream music. In reality, however, the computer is not actually able to process multiple tasks simultaneously; rather, it switches between them at incredibly quick speeds to give the appearance of working on them simultaneously. CPUs have become faster over time, which allows computers to increasingly run more applications at the same time and switch between them more quickly and seamlessly. If computers could not do this, a user would have to painstakingly close an application any time he or she wanted to do anything in another application.
Continuity is a new form of multitasking. Continuity was a new feature that came together with Apple’s iOS 8 and OS X Yosemite. It lets you seamlessly move between your compatible Apple devices or use them all simultaneously. Continuity includes features such as Handoff, Phone Calling, Instant Hotspot, and SMS. Handoff is a feature wherein you can start work from one device then continue on another. For example, you may be working on a document on your Mac but then suddenly you have to leave the desktop. With Handoff, you can simply continue your work on the iPad while you are away from the desktop. Phone Calling is simply phone calls on your computer or tablet when they are connected to your phone through the same Wi-Fi network. This allows for instant responses to calls without having the need to use your phone. Instant Hotspot is where your iPhone can provide internet access to your other devices. Finally, SMS allows you to send and receive text messages to and from your computer or tablet. This allows for you to seamlessly answer messages without even lifting your phone. Continuity is basically taking the concept of multitasking and simplifying it by using multiple devices instead of using multiple CPUS.[7]
Multithreading, on the other hand, is a computer's ability to perform multiple operations within a given task at seemingly the same time. Again, the processor is not actually able to do multiple things simultaneously, but it is able to switch between different actions so quickly that, for all intents and purposes as far as the user is concerned, it is doing them simultaneously.[8] As programs work on behalf of the initial request for that thread and are interrupted by other requests, the status of work on behalf of that thread is kept track of until the work is completed[9]
Functions of the Operating System
[edit | edit source]Some of the primary functions of the operating system include creating an interface for the user and the computer to interact, booting up the computer, configuring devices, managing network connections, and managing the jobs of the computer.
Process Management
[edit | edit source]A process is a program that is being executed. A process requires certain resources, including CPU time, memory, files, and I/O devices, to complete its task. The operating system is responsible for the creation/deletion, suspension/resumption, and providing communication mechanisms for processes.[10]
Main-Memory Management
[edit | edit source]Memory management is the process of controlling and coordinating computer memory, assigning portions called blocks to various running programs to optimize overall system performance.[11] The Operating System is responsible for maintaining bookkeeping information, mapping processes to memory locations, and allocating memory space as required.[12]
User Interface
[edit | edit source]
In order for computers and users to interact, some sort of user interface must be provided. User interfaces can be based on text, such as the original DOS that was used in the 1980s and 1990s, or it can be based on graphics. Most personal computers and mobile devices today use a graphical user interface, also known as GUI, which uses visuals such as icons, desktops, pointers, and menus for users to utilize. Basic forms of graphical user interface include the use of checkboxes, lists, and other fundamental forms of input. Examples of graphical user interfaces include Windows, Mac OS, and many other modern operating systems. The user interface ("UI") refers to the part of an operating system, program, or device that allows a user to enter and receive information. [13]
Booting the Computer
[edit | edit source]
Another function of the operating system involves booting up the computer. This process occurs when a CPU containing a bootstrap processor (BSP) (or a specifying one if in a multi-core processor) boots the basic input/output system (BIOS), which contains a set of instructions that tell the computer how to boot. The BIOS chip tells the computer to look for a boot loader. The boot loader's job is to start the operating system by finding the kernel containing it and loading it into memory. The BIOS also performs a power-on self-test (POST). The power-on self-test ensures that all of the computer's functions and components are working properly before booting.
Operating Systems for Personal Computers
[edit | edit source]
Buffering and Spooling
[edit | edit source]The part of the operating system used mostly with printers is buffering. This part can be in the RAM (Random Access Memory) or the hard drive. This area is meant to hold the input and the output during their way out of the system[14]. Although many people are familiar with buffering having to do with loading while streaming videos and music, it can also be referred to as a temporary form of memory[15]. While a buffer is doing its job, the CPU can change data before relocating to any other devices. When items are placed into a buffer waiting to be regained, this is called spooling. Along with buffers being used with printers, spooling often refers to print spooling. Many college campuses have print spooling, which enables one printer to have multiple print jobs sent to it at one time. These multiple documents can be sent all from the same computer or more than one. While this spooling occurs, there is a print queue that all documents waiting can be stored until they are printed. Spooling is a very useful tool because while one device may not run as fast, it provides documents with a waiting area in the meantime.
DOS
[edit | edit source]DOS (Disk Operating System) was the dominant operating system for microcomputers in the 1980s and the early 1990s. The first version of DOS was developed for IBM. DOS is a rather simple operating system but it does not utilize a graphical user interface and it does not support modern processors, which is why it is no longer used[16]. Some computers can still run the DOS commands but the user needs to know how to input the commands using the Command Prompt window.
This non-graphical operating system was originally written by Tim Paterson and was introduced in August 1981. The last DOS system to be released was the MS-DOS 6.22 in 1994. The DOS system used a command line, instead of a GUI (graphical user interface), to allow the user to navigate, open files, and perform other functions[17]. Today, people use a mouse to navigate the computer and carry out commands, but with the DOS there was a command-line interface which had specific commands put in a prompt, which then brought up whatever file or program was prompted. Later, software programs with menu-based or icon-based interfaces were created for convenience. While the DOS systems are not used anymore, the command shell, now called the Windows command line, is still used today[18]. It is expected that as these operating systems gain market share, DOS will eventually disappear. In the meantime, Caldera, Inc. markets a version of DOS called DR-OpenDOSthat extends MS-DOS in significant ways[19].
-
Part of a DOS code page
-
A Command Line Interface Page
Windows
[edit | edit source]Windows is a series of operating systems that is designed by Microsoft. The first two versions of the Windows operating system, introduced in 1985 and 1987 respectively, were primitive. Windows 1.0 had only basic functions such as MS Paint and a word processor and Windows 2.0 had very rudimentary versions of Word and Excel. Windows did not become popular until its third release in 1990. Windows 3.0 had enhanced graphics, the ability to “multi-task”, and (for the first time) virtual memory. This version was so popular that it stayed on the market for eleven years. The next big improvement came with Windows 95, which expanded from 16-bit to 32-bit (short for binary digit). Windows 2000 was known for its increase in plug-in devices that were congruent with the operating system. Windows XP, or Windows 2001, included a comprehensive help center to allow users to utilize different types of media and was designed mostly for user ease and convenience[20]. The main feature of Windows Vista is the Instant Search at the bottom of the start menu. Then Windows 7 came out and the improvements were mainly to make it faster and easier to use. The most recent version of Windows is Windows 10. Windows 10 came out late July 2015. The new Windows will allow you do to more than one thing at once. It also allows for a new way to search and there is a way to open the Windows store from your home page.[21]. Windows is the most commonly used operating system and is used on about 90% of all personal computers.
-
Screenshot of Microsoft Windows 1.0
-
A Presentation of Windows 8
Mac OS
[edit | edit source]Apple Corporation’s registered operating system is called Mac OS. There are many different branches stemming from the Mac OS X family. It was primarily based off of UNIX because of its standard interface and graphics look. Mac OS X Snow Leopard was the primary operating system, followed by the making of Mac OS X Mountain Lion, which is the newest and greatest version of Mac Operating Systems. Mac OS has capabilities of multithreading and multitasking. It also has a 64-bit processor that runs with applications used with 64-bit software. The many great features of Mac OS X creates an easy working environment for students, teachers, and parents to easily access many files. Mac OS is also known for its great graphic features that are popular to artsy users. The Launchpad and Mission Control with the bird’s-eye view of the Dashboard and desktop make opening applications easier for users. Apple launched a new operating system in 2014 titled OS X Yosemite, which features a redesigned interface as well as multiple ways for users to perform activities across their Apple devices[22]. In 2015 El Capitan was released, followed by Sierra in 2016 and High Sierra in 2017.
UNIX
[edit | edit source]
UNIX was trademarked in 1969 by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs as a multitasking, and multi-user computer operating system. UNIX can support systems ranging from microcomputers to mainframes, along with various devices. Because UNIX is used for an assortment of categories of computers, this is a great advantage. However, it is more expensive than most operating systems, and is very difficult to maintain upgrades. UNIX is widely known for its simplicity and ease while working on the computer, therefore different companies use a spin off of UNIX as their operating system, like Mac OS X. UNIX has just celebrated their 40th anniversary of being a business Unix combines the worldwide single Unix specification with X/open company’s XPG4, IEEE’s POSIX standards and ISO C. Single UNIX Specification defines this product in four parts specification, product, trademark, and technology allowing it to still be successful even though it was separated from AT&T and found its own angle. It allowed for one open consensus specification that is the requirement for the UNIX systems. UNIX was one of the first operating systems to be written in a high-level programming language and could possibly be installed on any computer. This high-level programming language was also developed by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Labs, which allows a more flexible language to be used in various applications thus being very beneficial for businesses. It being inexpensive allowed for many people to be a big fan of UNIX and actually many universities use it for that reason. It never really took off in the home computer business but for workstations it tends to be the number one choice. The source language was open so if anyone got a hold of it they could change it to fit their own needs the best.
-
Unix OS
Linux
[edit | edit source]
Linux is an open- source, portable, multi-user (multiple users can access system resources like memory/ ram/ application programs at same time), multiprogramming, operating system that was first released by Linus Torvalds in October 1991. It is very similar to other operating systems, such as Windows and OS X [23]and a source is available to the public, to which users can download Linux via the Internet and have the capability to run another operating system on their PC or Mac. No other company has done this before. The system has primary three components: Kernel (the core part of Linux), system library (special functions or programs), and system utility (responsible to do specialized, individual level tasks). Linux is one of the leading operating system on servers, mainframe computers and supercomputers. > Linux is used on a lot of popular electronic devices, such as mobile phones, tablet computers, network routers, facility automation controls, televisions and video game consoles. The system is widely used by local and national governments. The US Navy’s newest warship that is armed with missiles and robot guns is powered by Linux,[24] Spain is using Linux in education, and China uses Linux to achieve technology independence. Collaborators of Linux are continually making improvements to the system.
Chrome OS
[edit | edit source]
Chrome OS is an open-source operating system created by Google to create a better computing experience for people who spend most of their time on the web. [General referenced 1]On June 15, 2011, Chrome OS was launched to the public with the first Chromebooks, notebooks using the Chrome OS, created by Samsung and Acer. Today, Chromebooks are created by a number of other computer companies including HP, Toshiba, Asus, and Dell. The main reason the Chrome OS differs from other operating systems is that it allows for user data and applications to reside in the cloud, taking up less space on the computer hardware. By not storing files and data on the system it allows the Chromebooks to boot up faster. Which in return helps prevent viruses; making it an overall more secure and efficient laptop. Because of this, many Chromebooks only contain the same amount of memory and RAM as the average smartphone, Google, however, supplies each user with one-hundred gigabytes of Google Drive cloud storage for up to two years.

There are many things one should consider when purchasing a computer. One of the biggest factors one should be aware of is what operating system the computer uses. Different operating systems have different features to suit the user’s needs. If one is looking into a smaller laptop computer, they might consider a Google Chromebook, which uses Chrome OS. It is a good idea to look into the pros and cons of a computer’s operating system before making a purchase. Like all operating systems, Chrome OS has both advantages and disadvantages. One positive feature is that Chrome OS is based on Linux, which is virtually virus free, which means users will be safer from threats. Another great feature is its ability for fast boot times, generally loading in just under ten seconds. It also allows for different users to configure it differently according to their needs, and saves each person’s data separately, creating privacy for each user. One of the cons of this operating system is that it does not allow installation of new apps. Users must use web-based apps instead, which they can get in the Chrome Web store. Another feature that the Chromebook is lacking is a user friendly printing option. In order to print something, one must have a Cloud Print Ready Printer. It lacks the convenience to simply plug it in to an existing printer and print, which could become an annoyance. Another feature that may seem inconvenient is that Chromebooks require internet access to do most of its work. Users that have tasks such as editing video or making movies may find that a Chromebook is not for them. It seems there are advantages and disadvantages for Chrome OS, and one should take them into consideration when deciding which operating system will suit their needs best.
Operating Systems for Mobile Phones
[edit | edit source]There are many different operating systems for mobile phones and devices but most six stand out as being most used. These are Android, Asha, Blackberry, iOS, Windows Phone, and Windows RT.

Android
[edit | edit source]One of the most widely used mobile OS these days is Android. Android Inc was founded in Palo Alto of California, U.S. by Andy Rubin, Rich miner, Nick sears and Chris White in 2003. Later Android Inc. was acquired by Google in 2005.[25] It is a Linux based operating system that is designed primarily for touch screen mobile devices such as smart phones and tablet computers. The operating system has developed a lot in the last 15 years starting from black and white phones to recent smart phones or mini computers. After original release there have been number of updates in the original version of Android. The android is a powerful operating system and supports a large number of applications in Smartphones. These applications are more comfortable and advanced for the users. The hardware that supports android software is based on ARM architecture platform. The android is an open source operating system which means that it’s free and any one can use it. The android has millions of apps available that can help you managing your life in one way or another and it is available at low cost market making android very popular to its consumers. Android's worldwide market rose significantly and now reaches 87.9% of the global smartphone market share as of 2017.
Asha
[edit | edit source]Asha is used by Nokia phones. These smartphones are on the lower end when it comes to software and component capability. Because of the low capability, Nokia smartphones are usually the cheapest which makes them able to compete with higher end smartphones.
Blackberry
[edit | edit source]
Blackberry's operating system is called BlackBerry 10. This is a closed source operating system for smartphone and tablet devices. The newest operating system developed by Blackberry for tablet devices is BlackBerry Tablet OS. The BlackBerry operating system has all of the same features a smart phone does: email access, web browsing, phone calls, play music and video, and send and receive text messages. Most models are not touch screen, with the exception of the Storm and the Torch. Instead of a touch screen, a trackball or track pad is the hardware used for navigation. Because there is no touch screen, the operating system does not require that much battery life to process so the phone stays on longer than others. [26] The BlackBerry also has multiple buttons (similar to the image on the right) including a BlackBerry button, back button, call and end button, 1 or 2 convenience keys, and a full keyboard. The BlackBerry button is designed for easy integration, such as sharing a photo via email. This system is geared toward communications rather than games and apps. It features an email software that “pushes” email directly to the user’s phone, which saves battery and provides the most current information. One drawback to this type of smart phone is how limited the customization is. Only the wallpaper and the function of a few buttons can be changed. It also does not feature “widgets” or a wide selection of apps like the android phones do. Overall this operating system is easy for productivity, but falls behind its competitors in a wide selection of applications.
iOS
[edit | edit source]iOS is Apple's operating system for Apple's iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad and second-generation Apple TVs. This operating system is closed source and not until iOS 2.0 were third-party applications officially supported. Prior to this update, jailbreaking was the only way to allow third party applications access to a user's iOS device. As of September 2015, iOS is in its 9th iteration. It was introduced at Apple’s product convention in the fall of 2015 in conjunction with the new iPad. iOS is known for a colorful graphics, and an easy to understand user interface. This being said, it was created as an OS for mobile devices, and thus was designed primarily for consuming content as opposed to creating content. As Apple’s new iPad is designed for both consuming and creating content, iOS needed to be upgraded accordingly. The latest version includes the ability to split screen multi task on to applications at the same time, similar to a laptop. In addition, it includes new built application as well as upgrades to existing applications. Apple Maps now includes public transportation, and more apps can integrate with the cloud. Siri, a “personal assistant” has also been upgraded to do more tasks, and to integrate with additional apps, such as Pictures. Finally, there are new multi touch gestures built in to the system. These assist the user in typing, editing projects, taking notes, emailing and other tasks typically associated with a laptop computer. Generally, iOS 9 is built to create content rather than simply consuming[27].

Windows Phone
[edit | edit source]Windows Phone is developed by Microsoft as a closed source operating system for mobile phones. It allows users to access Microsoft SkyDrive, Office, Xbox, and other Microsoft programs remotely. Windows Phone devices are made mostly by Nokia, HTC, Samsung, and Huawei. On April 14, 2014, Microsoft released its newest mobile operating system, Phone 8.1. The new operating system contained new features including Cortana, a personal assistant similar to Apple’s Siri. The OS also featured upgrades in security, performance, and boot time.
Windows RT
[edit | edit source]
Windows RT was also developed by Microsoft but was designed for mobile devices and tablets. This close sourced operating system closely resembled Windows 8, an OS developed by Microsoft for desktop computers and laptops. Windows RT was discontinued in 2015[28].
Symbian OS
[edit | edit source]
There was one OS that used to tower above all the rest, before recently falling completely out of the race thanks to increasingly competitive and more simplistic operating systems. The name of this OS is Symbian, and between 2000-10 it ruled supreme thanks to its partnership with Nokia, a company that excelled in moving large units of inexpensive cellphones. The Symbian company had risen from the ashes of a failing PDA company named Psion, changing its focus to mobile OS development with funding from entities such as Motorola and Ericsson, while the largest funding share always came from Nokia. Unfortunately, between the more complex code (which contributed to development periods that were unthinkable in comparison to what Windows and Mac were developing) and Nokia changing their allegiance to Windows, Symbian said its final goodbye in mid-2013. Any individuals or companies still attached to the Symbian OS will be offered support for a few more years, but they will need to consider their options now instead of waiting for the last minute. Luckily, as can be seen from the plethora of options above, Symbian users can surely pick an OS that is the closest to the quality programming to which they had grown attached.[29]
Mobile Device Systems
[edit | edit source]Below are three very popular mobile phone/device providers today. They are Windows, Android, and Apple. The three use different operating systems.
Windows is full of change. Most people have used Windows on their personal computers, but did you know it is also integrated into our GPS systems, ATMs, and even robots? Windows mobile devices include things called tiles which are icons for different things stored in the device itself. Related tiles can be put together in hubs. Windows devices also offer integration with windows office software (Word, Excel, PowerPoint, etc.). They also include integration with Xbox Live. [30]
Android: Android was created by a group of 30+ mobile technology companies and is based on the Linux operating system. These devices offer the ability to multitask with a split thing (doing two things on the same screen verses switching between tasks). The screen will contain multiple applications that can be bought and downloaded (some for free) from the Android Market.[31] Android software will update regularly and is intended to fix any potential bugs, as well as loading any new features.
iOS (Apple): This system is based on Apple's Mac OS X. Similar to the apps of the android system, apple products also contain apps but they are downloaded and purchased from the App Store. There are over 900,000 apps currently available. These devices are also synced to your iTunes account allowing you to upload your music to their devices as well. Some things that are specific to these devices are their Safari web browser, FaceTime, and the ability to track your device through the "Find my iPhone" app. [32]
Utility Programs
[edit | edit source]
In general, the utility program is defined as special software written to take care of the operating system maintenance and management to keep the performance of a computer system at the appropriate level. The utility programs could be a part of operating system or a product of third party developers. Whether you want to install programs or move file to a different folder, search for a document or set the connection to the network, you are using the utility program tools. Another important improvement the utilities can help you with is your hard drive performance. Disc check, disc clean up and disc defragmentation programs alone with a files compression utility will let you keep your storage organized and reduce the time of the searching, retrieving and displaying information you requested. The last but not least task the utility programs are being applied for is the operating system and your data protection. The backup and recovery programs let us be sure that we will not lose all data in case of system malfunctions and will be able to return back to restore point, when the system was working properly, while the antivirus, antispyware and firewalls – utility programs – will protect the computer from data theft.

File Management Program
[edit | edit source]They organize files and are available for the user to access them. There are 6 important concepts that the file management programs have. To start off, it has a navigation system that gives the user access to the file hierarchy and be able to find their work. The actions to proceed are using the “up” and “down” to navigate through the folders and “go to” to reach their data. Another function is the operations functions which allow the user to interact with the files. The common functions along with this are as follows: open, save, close, copy, move, delete, rename, new and share. The user would obviously be concerned about the security of their files. With this being said, the files can be blocked with a login procedure which will only give people that know the username and password access to the file. To keep your file program organized, it is necessary to maintain the storage on the program in which you should delete any unneeded files. For the conveyance to the user, there is a communications function in which there are links available in order to send out a file to a given location. Lastly, there’s a search function in which you can find a particular file you are looking for.

Specifically, the Search Tool is very useful for the user. As explained previously, it will find a particular file by simply using the file's name. There are programs that will search the data by key words but it seems to be more beneficial to know the username instead of the program searching all the documents for key words, which may lead to a longer search than intended. [33] Also, a file can be searched based on other reasons, including if it is kept in a certain folder, if it has certain characters in its file name, if it has metadata tags, or if it is a specific type of file. If you do not know, a metadata tag includes information about the file, like its author, artist, or keyword. The program being used can set this automatically or it can be manually set to fit your needs. Also, the types of files that can be searched are documents, spreadsheets, videos, or songs. These search tools can be integrated into the operating systems that your computer is designed to run, or you can download them off the Internet for free or at a low charge. Some Internet based search tools, called desktop search tools, can find certain Web pages, messages sent over the Internet, or certain e-mails. A few of the websites that provide these services are Google, Yahoo!, and Bing. Other search tools that you can download off the Internet serve specific purposes, like finding duplicate files on your hard drive. This can come in handy when your computer’s hard drive storage is running high. In conclusion, the search tool utility program provides you with great accessibility to your files and documents when you don’t have time to spare. [34]
Diagnostic and Disc Management Programs
[edit | edit source]With technology playing such an important role in our everyday life, it is important to make sure that it is maintaining itself and running properly. Instead of having to go through and check every aspect of the computer ourselves, computers come with built in diagnostic management program and disc management programs. Diagnostic management programs deal with making sure that everything on the system is working the way it should be, while disc management systems programs worry about the hard drive operating correctly. Most computers come with the basics of this software already built in, however some people prefer to go outside of what they already have and purchase more protection and security for their computer. These programs keep your computer running quickly, optimally, and effectively on a daily basis.[35]

Uninstall and Cleanup Utilities
[edit | edit source]You would think that once a program or application is deleted, no trace of it would be left behind; however, this is very often not the case. In many instances, traces of that file, program, or application are still left embedded into your hard drive. In order to fully get rid of them, people often use something called uninstall utilities. These programs go through your hard drive and remove any unneeded space, memory, or left over remnants from that application that once existed. Many computers come with this option already installed, which makes keeping your computer updated and up to speed an easy task. Clean up utilities are very similar to uninstall utilities; however, instead of going through and deleting old applications and programs, they go through and clean up your computer by deleting temporary files.[36]

File Compression Programs
[edit | edit source]File compression programs are designed to reduce the size of files, which allows the user more storage space. For Windows users, these compressed files usually have the .zip or .zipx file extension. The most popular programs are Winrar, Winzip and 7-Zip.[37] For Mac users, these files usually have the .sit or .sitx format. Programs that are commonly used are RAR Expander, StuffIt Expander and MacZip. Some programs have the option of encrypting the zipped files, meaning that a password is required to open the file. This can help those who want to protect their files for themselves or specific users who are granted access. Overall using file compression programs is an efficient way to free up storage space for other computer tasks. The gzip program is a popular file compression program that compresses and decompresses files using Lempel-Ziv coding (LZ77). [38]
Backup and Recovery Utilities
[edit | edit source]Over time one might experience the unfortunate event of a power outage or some other event that leads to the corruption of important system files. For example a storm can cut the power in an instant, which turns off the computer in an unsafe manner thereby leading to the corruption of the operating system and possibly even hardware. The system now is damaged, and this is an important reason why backing up is necessary. Businesses understand this, so it is extremely unlikely for a one to not backup its data on a regular basis because the possibility of losing just a segment can be catastrophic. The Windows Backup program (Windows) and Time Machine program (Mac) are included with their respective operating systems, but software programs exist that can be used for free or a price.
Antivirus, Antispyware, Firewalls, and Other Security Programs
[edit | edit source]Malware consists of viruses, trojans, worms, spyware and other forms that disrupt computer operation. As mentioned, malware can infect computers in many ways, whereas the affected suffers while the infector gains. To protect against these threats, it is highly recommended to take advantage of the utility programs offered by the operating system as well as software programs. Popular antivirus programs for Windows include AVG, Norton 360,Kaspersky and Microsoft Security Essentials. A firewall is used to monitor network ports by controlling inbound and outbound traffic to the network.[39] Its primary purpose is to defend the computer from malware and hackers, but it can also interfere with programs that must access the Internet. It will also not remove malware if it has infected the computer; it only blocks the malware from entering.[40] Spyware is software that tracks personal information unknowingly from the user, which can lead to serious problems.[41] It is important to know the software one is downloading and to understand its license agreement and privacy statement (to see if unwanted software is included).
Review
[edit | edit source]Review: Key Terms
[edit | edit source]Android: A Linux-based operating system designed for mobile phones and developed by the Open Handset Alliance, which is a group of companies led by Google.
application software: Programs that enable users to perform specific tasks on a computer, such as writing a letter or playing a game.
BlackBerry OS: The operating system designed for BlackBerry devices.
command line interface: A user interface that requires the user to communicate instructions to the computer via typed commands.
buffer: An area in RAM or on the hard drive designated to hold input and output on their way in and out of the system.
device driver: A program that enables an operating system to communicate with a specific hardware device; often referred to simply as a driver.
file compression program: A program that reduces the size of files, typically to be stored or transmitted more efficiently.
graphical user interface (GUI): A graphically based interface that allows a user to communicate instructions to the computer easily.
kernel: The essential portion, or core, of an operating system.
Linux: An open source operating system that is available without charge over the Internet and is increasingly being used with mobile devices, personal computers, servers, mainframes, and supercomputers.
mobile operating system: A type of operating system used with mobile phones and other mobile devices.
server operating system: A type of operating system designed to be installed on a network server.
Symbian OS: An operating system historically used with mobile phones, primarily outside North America.
system software: Programs, such as the operating system, that control the operation of a computer and its devices, as well as enable application software to run on the computer.
utility program: A type of software that performs a specific task, usually related to managing or maintaining a computer system.
virtual memory: A memory-management technique that uses hard drive space as additional RAM.
Windows: The primary personal computer operating system developed by Microsoft Corporation; the most recent version is Windows 7, with Windows 8 expected to be released in 2012.
Windows Embedded: A family of operating systems based on Windows that is designed for nonpersonal computer devices, such as cash registers and consumer electronic devices.
Windows Phone: The version of Windows designed for mobile phones; the current version is Windows Phone 7.
Windows Server: The version of Windows designed for server use; the current version is Windows Server 2008 R2.
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]1. A computer's __________ is a collection of programs that manage and coordinate the activities taking place within the computer and it is the most critical piece of software installed on the computer.
2. _______ refers to the ability of an operating system to have more than one programs open at one time.
3. A _______ is an area in RAM or on the hard drive designed to hold input and output on their way in or out of the system.
4. The process of placing items in a buffer so they can be retrieved by the appropriate device when needed is called _______.
5. The older DOS operating system and some versions of the UNIX and Linux operating systems use a __________, although versions of UNIX and Linux are available with GUIs.
6. Operating systems used with personal computers are typically referred to as __________ and they are designed to be installed on a single computer.
7. There have been many different versions of ________ over the years; the next few sections chronicle the main developments of this operating system.
8. _________ is an operating system developed by Linus Torvalds in 1992 when he was a student at the University of Helsinki in Finland.
9. The mobile operating system designed for Apple mobile phone and mobile devices, such as the iPhone and the iPod Touch, is _______.
10. Creating a _________ means making a duplicate copy of important files so that when a problem occurs, you can restore those files using the backup copy to avoid data loss.
11. Linux is an operating system developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991 when he was a student at the University of Helsinki.
Answer Key for Review Questions
[edit | edit source]- operating system
- multitasking
- buffer
- spooling
- command line interface
- personal operating systems
- windows
- Linux
- iOS
- backup
- True
Review Reference
[edit | edit source]References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://us.norton.com/
- ↑ https://turbofuture.com/computers/The-Five-Types-of-System-Software
- ↑ http://ecomputernotes.com/fundamental/disk-operating-system/difference-between-application-software-and-system-software
- ↑ http://www.buzzle.com/articles/application-software-vs-system-software.html
- ↑ http://uwf.edu/clemley/cgs1570w/notes/concepts-3.htm
- ↑ http://www.computerhope.com/os.htm
- ↑ https://support.apple.com/en-us/HT204681
- ↑ http://www.ni.com/white-paper/6424/en/
- ↑ https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/multithreading
- ↑ http://www.cs.um.edu.mt/~jcor1/oldwebsite/OS4.pdf
- ↑ https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/memory-management
- ↑ http://www.cs.um.edu.mt/~jcor1/oldwebsite/OS4.pdf
- ↑ http://www.cs.um.edu.mt/~jcor1/oldwebsite/OS4.pdf
- ↑ Understanding Computer Today and Tomorrow 14th Edition Comprehensive
- ↑ http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/b/buffer.htm
- ↑ http://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/DOS
- ↑ http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/m/msdos.htm
- ↑ http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/m/msdos.htm
- ↑ https://www.webopedia.com/TERM/D/DOS.html
- ↑ http://windows-operating-system-reviews.toptenreviews.com/a-brief-history-of-the-windows-operating-system.html
- ↑ http://windows.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-8/everywhere?ocid=Everywhere_O_WOL_Hero_Home_WinEverywhere_Pos1_01
- ↑ https://www.apple.com/osx/preview/
- ↑ https://www.linux.com/learn/new-user-guides/376-linux-is-everywhere-an-overview-of-the-linux-operating-system
- ↑ http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2013/10/the-navys-newest-warship-is-powered-by-linux/
- ↑ https://www.engineersgarage.com/articles/what-is-android-introduction
- ↑ http://www.techradar.com/us/news/phone-and-communications/mobile-phones/android-v-blackberry-smartphones-for-business-1136674
- ↑ http://www.apple.com/ios/whats-new/
- ↑ https://www.theverge.com/2015/2/3/7974759/windows-rt-is-dead
- ↑ http://www.pcworld.com/article/2042071/the-end-of-symbian-nokia-ships-last-handset-with-the-mobile-os.html
- ↑ http://www.windowsphone.com/en-us/features?ocid=sem_s_pcrid_30043429957_se_Google_kwd_windows%20mobile%207%20games_pmt_b
- ↑ http://www.android.com/about/
- ↑ http://www.apple.com/iphone/
- ↑ http://smallbusiness.chron.com/functions-file-management-program-41476.html
- ↑ http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/five-apps/five-fast-windows-desktop-search-utilities/
- ↑ http://www.krollontrack.com/information-management/hard-drive-management/
- ↑ http://support.microsoft.com/kb/2438651
- ↑ http://download.cnet.com/windows/file-compression/?tag=rb_content;main
- ↑ "Man Page for gzip (freebsd Section 0)". unix.com. 2001-05-24. Retrieved 2015-02-21.
- ↑ http://www.cat-5-cable-company.com/faq-what-is-a-Firewall.html
- ↑ http://www.ehow.com/about_7547911_purpose-firewall-software.html
- ↑ http://www.microsoft.com/security/pc-security/spyware-whatis.aspx
Application Software
Application Software Basics
[edit | edit source]

Application Software is a single or group of programs that allow access for specific tasks to be performed. Users of a computer should familiarize themselves with the variety of applications that are available. The purpose of computer applications is that it can greatly simplify a task for a user. Ways applications can help are to create and modify word processing, spreadsheets, databases, presentations, along with graphics and multimedia. [1]
Installed vs. Web-based
[edit | edit source]
There are two different types of application software: installed software and web-based software. Installed software must first be installed to the computer before it can be used. When you purchase an installed software, the company can either send you a physical copy of the software, usually in the form of a CD, or you might also have the option of downloading the software from the companies webpage. Web-based software is software that remains on the internet which you can use at an on-demand basis. Web-based software is also referred to as Software as a Service or Cloudware. Some web-based softwares include Google Docs, Dropbox, Prezi, and many others.[2]
Advantages and Disadvantages
[edit | edit source]- Web-based Software (advantages)
- Global access
- Able to run regardless of what operating system the computer has
- Back-ups/Updates are managed
- Web-based (disadvantages)
- Higher chance of lost data
- Slower productivity
- More expensive overtime
- Installed Software (advantages)
- Data secured
- Internet not required
- More control
- Installed Software (disadvantages)
- Limited access
- Must be installed on each computer
- Possible large upfront costs
Creating Application Software
[edit | edit source]With the ease of access to data, internet, and software becoming more popular on devices such as iPads, tablets, smartphones, etc. applications are not only being utilized, but first, they must be created. In order to simplify the process of creating and establishing an application, one must learn computer coding.

The two most popular software marketplaces as of right now are that of Apple’s App Store and Google’s Play Store. In order to create apps for the App Store, one must have a Mac computer to run the programming tools. One must then pay Apple to sign us as a developer in order to download those tools. The programming language used in those apps is called Objective-C. To create apps for the Play Store, one must have either a Windows, Mac, or Linux computer. The software development kit is free to download and you will need to know the programming language called Java.[4]
Software Ownership
[edit | edit source]After an application software program is developed, the author has what is called ownership rights. These rights specify exactly how the program can and cannot be used. For example, ownership rights allow the author to decide on whether or not the program can be sold, shared, or distributed. The ownership rights vary depending on the type of software. Types of software include commercial, shareware, freeware, and public domain.[5] Commercial software is software that is created and then sold for profit. For example, Microsoft Office Suite is commercial software. Shareware is another type of software that can make profit, however, shareware is initially free and then requests payment after a certain amount of time. For example, a computer game might have a ten day free trial, but after the trial is over the developer will ask for a payment. This payment would allow the gamer to play the computer game on a regular basis. Freeware is a type of software that is available for no charge by the developer. An example of freeware would be Internet Explorer and most other web browsers. Public domain software is similar to freeware, but should not be confused. While freeware is copyrighted, public domain software isn’t. Because public domain software isn’t copyrighted, people are able to copy, modify, and distribute the software.[6]
Software Suites
[edit | edit source]
A 'software suite, also known as application suite or productivity suite, is a group of related programs that interact together and are purchased together. The most well-known example is Microsoft Office, which includes Excel (spreadsheets), Word (documents), PowerPoint (slideshow), and Outlook (email). There are two primary benefits of software suites:
Enhanced Productivity
- It makes it easier for the user to work on multiple related projects at once. Someone can, for example, make a spreadsheet in Excel and then bring it into Word, keeping all of the formatting intact much more easily than if they used an unrelated spreadsheet program and text editing program.
Saves Costs
- Purchasing the entire Office suite is much cheaper than purchasing Excel, Word, PowerPoint, and Outlook separately. However, a user may not need all of the programs in a given suite, so buying the entire suite when only one or two programs are needed is not an ideal purchase; If not all of the programs are needed, then it would be more prudent to individually purchase the programs which are needed.[7]
Word Processing
[edit | edit source]Constructing a Word Processing Script
[edit | edit source]When constructing a word document there are a few things to keep in mind; character formatting, paragraph formatting, and page formatting. These three basic functions lay the foundation for most of the customization that is needed to create many word documents.
- Character Formatting
Character formatting changes the appearance of individual characters and relates to the size, font, color, and overall style of the letters or numbers being used. Character formatting also involves underlining, italicizing, and making bold those characters being used. This is great for making a word stand out or for underlining book titles.
- Paragraph Formatting
Paragraph formatting adjusts the spacing, alignment, and indentation of the paragraphs being formed. Spacing refers to the amount of lines left blank in between the lines being processed. A good example of this is double-spacing which is commonly used in an educational setting where a student has to write a paper for a specific instructor. Commonly double-spacing is used so that the instructor can make corrections to the document without having to mark over the actual words on the paper. Alignment refers to the way the paragraph is positioned in regards to the left and right margins. A left alignment is most commonly used when creating a word document and this setting aligns the words being formed to be flush with the left margin. A center alignment is usually used for titling a paper.
- Page Formatting
Page formatting refers to the width of the margins, the size of the paper being used, and the orientation of the page. The standard margin is 1.25 inches on both the left and right but these can be customized to suit need and preference. The paper size options reflect what can be used in the printer, and the orientation indicates whether the document will use the traditional or landscape positioning on that paper. Traditional orientation is 8.5 inches wide by 11 inches tall whereas landscape is the exact opposite at 11 inches wide by 8.5 inches tall.[8]
-
AbiWord Word Processor
Word Processing Tools
[edit | edit source]-
Business ID Template
Some of the basic tools that are employed in word processing programs that help to make the application more user friendly are tables, graphics, and templates. These tools allow for minimal effort and excellent results when adding features like these to a word document.
- Tables
Tables are used for organizing information and are composed of rows and columns in which data is placed. This is great for comparing and contrasting information as it's condensed and presented in a straight forward fashion. Tables can also be used for laying out entire documents, such as a resume, where information is sectioned off from one another. In this example, the entire report is formulated to a table instead of a small section as mentioned earlier.
- Graphics
Graphics are pictures, drawings, clip art or other images that can be inserted into a document from other programs or stored data on the computer. This can better illustrate situations where a picture or image highlights a point better than text or a table. The graphics tools also allow the user to manipulate images that have been imported by changing their color, contrast, brightness, size, etc. The process of customizing these images in the word processor provides an easy and fast way to explain the topic at hand.
- Templates
Another useful tool are Templates. These are preprogrammed arrangements of ideas and/or illustrations that are known to serve a purpose and are already organized for the user to interact with. Most often this means "filling in the blanks" and some common templates that should be recognized are resumes, business cards, identification cards, fax cover sheets, memos, invoices, and newsletters to name a few.[9]

Along with templates, some documents are required to look differently depending on the use; as a result of this we change the format of our documents. Any change in format in a document is a change in the overall appearance. Examples of formatting documents can range from MLA to APA format, requiring different sized margins, fonts, etc. In order to do this, Word has tabs that make navigating around your document easy and efficient. Word includes a Help Center convenient for users to receive assistance whether it is live online help or offline. In this Help Center, tools such as where and how contents are organized are listed in a user-friendly manner. While Word processing is simply creating, editing, saving, and printing, the creation and edition are made easy by Word for a variety of end results in the overall appearance of documents. In the time of typewriters, the “carriage return” was used when a line of text needed to move to the next line to continue. With present day Word, this is done automatically and is a process called Word Wrapping.[10] Other tools that Word offers which were not available are the ability to contain various fonts, edit proportions, and spacing is also made more efficient.
Spreadsheets
[edit | edit source]What is a Spreadsheet
[edit | edit source]
A spreadsheet is a group of values and other data organized into rows and columns similar to the ruled paper worksheets traditionally used by bookkeepers and accountants. The spreadsheet software is mandatory to create computerized spreadsheets. Microsoft Excel is a form of a spreadsheet. Spreadsheets can support keeping track of data, support in quickly formulating subtotals, populating visual graphs and charts and essentially is a working tool that can easily be shared. A worksheet is the single spreadsheet document. A workbook allows multiple worksheets to be saved together in a single spreadsheet file. Worksheets are divided into rows and columns. The intersection of a row is called a cell. One must enter content into the active cell, or current cell; it has a border around it to make it be easily identified. Data is entered directly into worksheet cells by clicking a cell to make it the active cell. Labels, constant values, formulas, and functions are the data that is entered into a cell. Before one enters a formula or function into a cell, one must begin with some type of mathematical symbol, usually the equal sign (=).[11] Spreadsheets are used to organize and calculate data. There is a maximum number of rows and columns in a spreadsheet which varies depending on the version of software you have.[12] It is essential to know how to use spreadsheets for school, work, sports, or anything that requires data!
Tables, Graphics, and Templates
[edit | edit source]
Tables, graphics, and templates are all available to a user with application software, such as Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, and PowerPoint. Tables are ways a user can organize data and information at their convenience. According to Microsoft Word, there are now many different available options for users who are looking for various kinds of tables. These different options include the following: the Graphic Grid, Insert Table, Draw Table, insert a new or existing Excel Spreadsheet table, and Quick Tables. The concept of using tables for data input is relatively simple. In order for a user to insert a table, the user must first open Microsoft Word. Once they have done this, they must click the "table" button to customize the table to achieve their needs. The overall format for a table consists of a large (or small) grid that can be altered by the amount of information the user has, ex. four columns five rows. Next, the user must insert the table into the word document by selecting "insert table" from the dropdown menu. Microsoft Excel contains pivot tables that are tables that include data from a spreadsheet with columns and rows that can be specifically selected. [13] Graphics in Microsoft Word are pictures, or clip art that are able to be inserted into a Microsoft Word document, Excel Spreadsheet, PowerPoint slide, or any other Office application. the most common graphic used in Excel is graphs. You can create graphs based on data taken from your spreadsheet. Graphics are inserted into these Office Applications to enhance the information presented in a Word Document, Excel worksheet, or PowerPoint slide. A user can insert their own picture through their office documents; add clip art, shapes, SmartArt, screenshot, or Word Art.[14] Templates are pre-constructed document layouts whose primary use is to assist a user in creating a specific type of document in a convenient amount of time. The different options of templates vary, but a few of the following are common ones used every day: agendas, brochures, calendars, flyers, fax covers, and many more. Templates are used to save a user time, and confusion in creating their document. [15]
How to use a Spreadsheet
[edit | edit source]When using a spreadsheet application, the user can use various concepts to calculate the data entered into the cells. These different concepts are provided in the program. Some very common concepts are charts, functions, formulas, and cell references.
Charts
[edit | edit source]Charts can be created as their own objects or can be embedded in the worksheet itself.[16] This is helpful when users need to analyze data or represent changing data. Some of the forms of charts are: line charts, scatter charts, bar charts, Venn diagrams, and the list goes on and on.
-
A chart generated using Excel.
Functions
[edit | edit source]A function is a pre-programmed mathematical formula that allows the user to perform calculations based on the data entered. Functions under spreadsheets perform simple calculations by using certain values (called arguments). If users wish to create their own formulas, they can use Visual Basic to write the formulas, and input values into the newly written formulas, reporting the data into the worksheet. There are many different reasons for having functions in a spreadsheet. One is for arithmetic functions that work with numeric data. The second is to use the statistical functions of the analysis and averaging tools. This is useful for finding the average of the numbers in a row/column of a spreadsheet. The next function is date for handling and converting dates. This function can be used to put consecutive dates on a spreadsheet in order. The next function is the logical function, which is used to handle logical data. An example of logical data is the AND/OR function. If something needs to be marked as yes when it is above 5 and no when it is below 5, then this is a logical function. The last type of function is a financial function that deals with monetary data. They all must start with an equal sign, the name of the function, and the beginning and end of parentheses. A comma or semicolon is used as a separator in the function, depending on the setting in the spreadsheet, and depending on which one is used. An example is =SUM(A1:A4), a function that will find the sum of these cells. Some of the most common functions are SUM, AVERAGE, IF, COUNT, MAX, and MIN.
-
A function being edited using VB in Excel.
Formulas
[edit | edit source]A formula identifies the calculation needed to place the result in the cell it is contained within. This means a cell has two display components; the formula itself and the resulting value.[17] Typically, a formula consists of five expressions: value, references, arithmetic operations, relation operations, and functions. By using these expressions, formulas can help to make tables, solve math problems, calculate a mortgage, figure out accounting tasks, and many other business-related tasks that use to be done tediously on paper.[18]
A formula always starts with an equals sign (=), followed by a constant, a function or a reference, then followed by an operator, and then followed by another constant, function or reference. A constant is a value that never changes; this includes numbers, dates, titles and other text input. References represent a certain cell, such as “A2”. An operator is usually a math symbol, such as “+” or “*” which tells the computer how to compute (add or multiply, respectively) the given constants or functions given in the formula. It is good to be careful that one knows the difference between a constant and a reference. If the constant “30” is input into cell A3, and the formula says “=30+2”, then if A3’s value changes, the expression of the formula will not change unless the formula itself changes. If one wishes to have a formula that returns the value of a cell, then the formula should read “=A3+2”. Another thing to note is that the operators will follow the basic “rules” of calculation. For example, the formula “=3+2*4” will add 3 to product of 2 and 4, rather than add 3 and 2, then multiply the sum times 4. (Parenthesis can be used to change the order: (3+2)*4 would add first, then multiply.) Operators are not always arithmetic, they can also be comparison, text concatenation, and reference operators. Comparison includes greater than, lesser than, greater than or equal to, and lesser than or equal to. To connect two values into one value, a text concatenation (the “and” sign i.e. “&”) is used. The signs used as reference operators are the following: a colon is used to reference two cells and all the cells between them (i.e. B1:B10); a comma is used to combine multiple references into one reference (i.e. B1:B10,C1:C10); and a space is used as an intersection operator.[19]
-
Using a formula in Excel.
-
Spreadsheet Graphics
Cell Referencing
[edit | edit source]Cell referencing refers to the ability to utilize a cell or range of cells in a spreadsheet and is commonly used to create formulas to calculate data. Formulas can retrieve data from one cell in the worksheet, different areas of the worksheet, or different cells throughout an entire workbook. There are two ways of doing this: relative and absolute cell referencing. A relative cell reference will adjust as the formula is copied from another cell while an absolute will not adjust. An example of this would be "=D2+F2" which is row 2 to row 3 which will equal "D3+F3". It is also important to note that a user can reference both the same sheet and other sheets in a book using this concept.
Pivot Tables
[edit | edit source]One the most powerful features available in the Microsoft Office spreadsheet program Excel, is pivot tables. Pivot tables allow you to manipulate large amounts of raw data.[20] It makes it easy to analyze the data in different ways, with a simple click and drag. Vast quantities of data can be summarized in a variety of ways. Calculations can be performed by row or column. Data can be filtered or sorted automatically by any or all of the fields. Excel can even recommend a basic layout of a pivot table based on the type of data selected. A wizard is available to assist in the creation of the table. An important thing to remember when using pivot tables, is that any time the original data source is modified, the data must be refreshed in the pivot.
Once the pivot table has been created and the data has been analyzed in a meaningful way, it can then be represented graphically using pivot charts. All the basic chart types available in Excel are available in the pivot chart menu. Much like the pivot tables they are built on, they can also be manipulated with ease. They can be filtered to display only the relevant information from the main data source. They can also be added to and refreshed very easily.
Database
[edit | edit source]A database is an organized collection of facts and information such as text and numbers, and often can hold still images, sounds and videos or film clips.[21] It is organizing data in such a way that a computer program can quickly select desired pieces of information. A database can also be referred to as an electronic filing system. For example, libraries, rather than have a file cabinet, provide access to academic databases for use in scholarly projects. Regular PC databases are organized by fields, records, tables, and files. A field (column) is a single piece of information like last name, address, phone number, and such. A record (row) is a one complete set of fields. A table is a collection of records. Lastly, a file is a collection of related tables.[22] A database file is created first, then tables that can be created in either datasheet or design view.[23] There are different kinds of databases, such as active, cloud, deductive, distributed, graph, hypertext, etc. For example, in hypertext database, any object can be linked to another object; this is useful for organizing a lot of information. A DBMS is database management software that allows the definition, creation, querying, update, and administration of databases.[24] Common database management software is Microsoft Access. Since many databases store confidential and important information, they require passwords and other security features in order to access the information.[25]
Queries and Reports
[edit | edit source]
Queries and reports are used to retrieve information from databases.[26] A query is almost like a search tool for the user of the database to find specific information like an item, number, name, etc. Like other documents made, a query has to be made and saved as well, for users to be able to come back and search it again. A query contains criteria that must be met for a record or row to be shown in the ending results of the specific query. Queries can also be made to show multiple columns or rows at a single time, instead of just one row or column. For example, a customer insists on buying a set of glasses for under $20 at Crate and Barrel.[27] The employee can then inquire “glasses under $20” and be able to tell the customer which kind to specifically look at. A report is used when acquiring a formal output. This can be a company logo or graphic with a page column heading. These can be created with the “Report Wizard button” on the “Create tab” from the Ribbon. Reports are mostly used with database tables or queries. Databases can be used more efficiently for customers shopping via the Internet. Today, online shopping is the newest sensation. For example, a specific dress can be found on Lord and Taylor’s [28] website for women, prior to going to the store by typing in the search bar. Examples of popular databases used are Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access, Oracle, MySQL, and IBM DB2.[29]

Deciding Which Database to Use
[edit | edit source]How does one know which kind of database to use? To someone not familiar with this kind of thing, it could be a situation where one does not even know where to begin. Something one must first consider is what they will be using the database for. Database Managing Systems can be broken up into two categories; server databases or desktop databases. Desktop databases are typically geared toward a single user, whereas server databases must accommodate multi-users and large amounts of data. Some familiar types of Desktop DB are Microsoft Access, Fox Pro, File Manager, or Paradox. Desktop DB’s are fit for storing less complex data and are less expensive than server DB’s, typically around one hundred dollars. They are also very user friendly and have web functionality that allows the user to publish data on the web. Server databases on the other hand are equipped to store and manage much larger amounts of data and allow for many users to have access to that data at the same time. Some popular Server DB’s are Microsoft SQL, Oracle or IBM DB2. Due to their complex functionality, these data bases are much more expensive, ranging in the thousands and up. Server DB’s are equipped with Application Programmer Interfaces (API’s) that allow for custom programming and applications. They are extremely powerful, being able to accommodate cluster servers and multiple high speed processors. They are also able to adapt well to the constant addition of users and data. After evaluating these two types of databases, one should have a better idea of which one will best suit their needs.[30]
Database Protection
[edit | edit source]
The database is one of the most essential parts of a business process. The ability to access and to operate data is a necessary condition for the running company. Permanent data loss puts the business in serious danger. According to some researchers, about a half of the companies affected by disasters and major loss of corporate data, have not been able to continue their activities. There are few most common reasons for database destruction: equipment failures, physical impact on the hardware of the database, errors of authorized users, database or operating system bugs and errors in application programs, intentional acts unauthorized users or programs. The primary protection tools such the user’s identification, the granting of different rights of access to database objects e.g. reading, adding, deleting, and changing along with data and programs encryption can provide the acceptable security level. Note, that the security model, based on the basic mechanisms of authorization and authentication does not solve problems such as stolen user IDs and passwords or malicious actions of some users with the authority. [31] It is important to understand best practices when ensuring database security. The first thing to do is to develop a plan, enforce a regulation, and adopt a checklist to use as the backbone of security standards. One should always report suspicious behavior immediately, to help minimize risk of attack.
Presentation Graphics
[edit | edit source]Intro to Presentation Software
[edit | edit source]
Everyone has different styles of learning. Some people are more visual learners meaning they prefer to learn through graphs and charts, while others are auditory learners meaning they prefer to learn through spoken presentations and lectures. Yet, no matter your learning style, there is one type of software that has been repeatedly proven to be a great method of sharing key information in an organized and relatively entertaining fashion. The successful software in question is presentation software.[32] Presentation software allows the user to create slides which they can piece together into a slideshow. It is a great way to organize and refine large amounts of information into the most important aspects because each slide has limited space and there is often time restraint when giving a presentation. Whether you're presenting information to a classroom or to a boardroom, the method of organizing information in a fluid manner remains the same. To add entertainment value, there are many variables within each example of software that can be manipulated, from text size and color to slide transitions and transition noises. Expert presentation software users can add photos and music to their presentations. Two of the most widely used examples of presentation software today are Microsoft Powerpoint and Prezi.

Presentation graphics is a type of software that allows users to create stylized audio and visual aids (sound effects, animation, etc.) typically for slideshows, reports, and public informational speeches. Presentation graphics incorporates tools for inserting various types of drawings, text and background schemes in a wide variety of fonts, colors, and patterns. Most systems can also import specific data from a spreadsheet application to generate customized charts and graphs. Presentation programs can be divided into two categories -- business graphics software and general multimedia authoring tools. Though some products are blended, the layout of business presentation software emphasizes fast learning and ease of use, while multimedia software offers a more sophisticated presentation that will likely require a higher level of technological understanding. Popular presentation software, such as Microsoft's Powerpoint or Apple's Keynote, may be purchased independently or as part of an office suite. Universally compatible products include Adobe Persuasion, Corel Presentations, Harvard Graphics, and Lotus Freelance Graphics. Free products include Google Slides, Prezi, PowToon, and Academic Presenter. All presentation platforms function similarly and provide nearly identical capabilities just with different visual layouts. Upon completion, the file(s) are usually saved to a computer, external storage device, or the cloud. During a presentation, users are able to view miniature images of slides on a device’s screen, and edit or direct their layout as they are simultaneously projected onto a larger screen or LCD projection panel for others to view. [33] powerpoint

Powerpoint is a Microsoft Office software used to present information and work as a visual aide. Powerpoint makes it easy to organize and present information in a visually appealing way such as charts, pictures, tables, video clips, and sounds. The various designs and color themes that come are built in the software and are ready to use. The slides themselves come with several options of pre-loaded layouts, using features such as bullet points, pictures, captions, and titles. These are easy to drag and drop to make rearranging very easy.[34] The idea of a digital visual is to help a presenter engage their audience and display their ideas in a more simple form. This also helps the presenter engage their audience. One feature that comes in handy is the ability to print the slides so either the presenter or audience can be informed ahead of time of what to expect. Meaning, there is a preview feature that allows the user to already know what topic is coming next. Powerpoint also has a notes feature in which you can input notes you may need for your presentation. The notes feature also allows you to print out the notes page with the slide show on it which is known as notes view. You can also adjust the size of the slide on the notes view so that all of your notes fit on the page and looks presentable. If all of your notes do not fit on the notes page provided, it will spill over to the next page. If you know their is a lot of wording, you can make a duplicate slide and hide it in the presentation, so you will have more room for your notes! Teachers, employers, and computer users all over the world have now become accustomed to using Powerpoint as their “go-to” visual aide. The image on the right shows a presenter using a Powerpoint as a visual aide.

The PowerPoint presentation graphics program provides the user with several assortment tools and operations for creating and editing slides. With those tools, one is able to add new or delete old slides that are previewed in the slide thumbnail tab area, usually found on the left side of the screen. One is also able to switch to the slide outline tab, which contains only the title and the main text included in the slide. If desired, using the Insert tab, the user can perform additional operations like exporting images, along with adding formatted tables, shapes, symbols, charts, and much more to better express their message. Additionally, to customize the PowerPoint to make it even more dynamic and presentable, text can be animated, and a unique transition can be added to the slides. With animation, text can be set to appear in a specific way in the slide during a slide show. Tons of special effects are provided for the user, including animations to make the text to fly, dissolve, fly, float, or bounce in. Similarly, one is also able to apply special effects to specific slides to transition from one slide to another in a specific manner. Additionally, Microsoft PowerPoint allows recorded narration to be played back as the slideshow is being presented, along with speaker notes. Furthermore, most presentation graphics programs also allow the user to print those speaker notes for the targeted audience’s convenience. [35]
Inside Scoop on New Presentation Software
[edit | edit source]
There are hundreds of ways we present information on a daily basis. Whether it is through verbal speech, pamphlets, posters, commercials, flyers, power points, etc. we are constantly presenting information and being presented to. Technologically, there are still many ways to present information to an audience. The convenient part is that the user do not just have to use programs like PowerPoint and Microsoft Word. One does not even have to use products that cost money because there are several new and innovative free ways to present that will surely grab the attention of your audience.
Prezi is one of those free presentation methods. It is Internet based, and similar to PowerPoint. However, it is much more user friendly, as well as interactive. PowerPoint seems to have a set order you have to follow. It goes slide to slide in a single order. With Prezi, if you decide you want to go in a different order or go back to something 6 slides back you simply zoom out a little and click the slide you wanted to return to. Prezi slides are set in a "path" and as you present, the presentation will zoom in and out of each slide which are all present on one master screen. This is much different from PowerPoint's single slide screens. Prezi has the ability to integrate many different forms of information into your presentation. You can upload YouTube videos, PDFs, Excel spreadsheets, photos, music, and voice overs. You can also time your slides and have them move to the next one automatically like in PowerPoint. However, these things are input through a much simpler process. Instead of all the clicks you have to do in PowerPoint to insert things such as a YouTube video, Prezi has a button labeled "Insert YouTube video" and once you click it, it asks for the video URL. After you enter that, it automatically uploads it to your presentation. There you can resize it and place it wherever you would like. The ability to see where one idea came from and how it is physically moving to the next idea makes Prezi a much more innovative presentation method. It can be used for entertainment, educational work, teaching, and even in the business world. It comes with many templates as well at the ability to create your own presentation from scratch.
Prezi also offers many interesting things PowerPoint does not: it has the ability to share the presentation via email, collaborate on a presentation with multiple people, give several people access to the editing of a single presentation, and a free mobile app. The app is free and allows you to present, create, and edit presentations on the go with or without Internet. It is a very useful program and definitely something to check out! [36]
Graphics and Multimedia
[edit | edit source]
Graphic Software
[edit | edit source]
Graphic software has a variety of application programs and has a wide range of different uses. Graphics software uses photo editing programs that are used to manipulate pixels from images from pictures. A useful program would be Adobe Paint Shop, which can be used to edit, change, and alter pictures however you would like them to be. Another category for creating images would be vector images which are bit-mapped images created by a digital camera and is able to be altered and the images are able to re-scale to any size with no loss of detail. Also, each object in a given picture can be layered over another which allows an individual to take out one specific object if they do not like how it overlaps or covers another object in the picture. Graphs, tables, diagrams, charts, and images usually present the information on a drawing program. This makes drawing programs most appealing to small businesses trying to advertise their product in a larger variety by creating business cards, stylish logos, and more advertising methods. Also, marketing professionals use drawing programs to create intriguing web pages, corporate images, and other business-related necessities. Drawing programs are used by architects, shipbuilders, aerospace engineers, home-designers, prosthetic engineers, landscapers, and construction managers because of the scale-to-size and fixed-point accuracy of such programs. Other common features of a drawing software program are batch conversion, text-to-speech conversion, auto-indexing, layout retention, and the ability to print. Newer programs that are being created come with unique features like TWAIN, which can be used by a Macintosh to allow image hardware devices to communicate with image processing software. Popular drawing program software in use today is computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), Adobe Illustrator, CorelDRAW, MS Paint, and GNU image manipulation program (GIMP). All of these types of software can be used by the public or by businesses.[37] As well as the programs, the graphics side of them is able to create images in 3-D modeling, as well as create animations which can be made through Photoshop. In able to add video or audio there is programs with multimedia content which the software is able to play and editing audio and video along with any editing. Overall, graphic software is really useful for personal, business and education purposes, whether it’s for creating a college or providing information with addition affect for the audience.[38]
Audio Capture and Editing Software
[edit | edit source]Audio capture and audio editing software is used to create and edit audio files. There are many different programs associated with these two types of programs. Some programs are designed to extract audio from CDs (ripping software) while others capture sound through input devices like a microphone, a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal.[39] Some programs are able to record sound and also edit that sound, or it can open a certain type of sound file, which enables the user to edit any piece in various ways. The extent to which the user can edit the sound depends on the complexity of the software. One program can only allow very basic functions like cutting and pasting while another program can add effects and modify every bit of the wavelength. This is an example of the distinction found between free programs and others deemed professional; however, that is not to say that just because a program is free it must be of a lower quality. Audacity is a free program that includes both audio capturing and editing elements.[40]
One professional audio editing program that does cost money is Pro Tools, created by Avid Technology.[41] This software works similar to a multi-track recorded and mixer, but has a wide array of digital features. One such feature that is commonly used in the software is MIDI, which stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface.[42] A MIDI device can link up to sixteen channels of information that allows electronic instruments and computers to communicate with each other. Through MIDI input, digital sounds and samples can be inputted into Pro Tools and can then be mixed and edited to the desired output.
Video Editing and DVD Authoring Software
[edit | edit source]The widespread availability of digital cameras and now phones with built-in camera devices combined with the massive popularity of sites like YouTube has led many to use video editing programs. These programs enable the user to modify their clips extensively, and like audio capture and editing software there are both consumer and professional offerings. DVD authoring is a process that many video editing programs include. More specifically it oversees the layout of the DVD: what clips will be used and how they will be played along with customization of the menu. After authoring the DVD via the program the user must burn it to an actual DVD for playback. This can be done using utilities included by Windows or Mac or by dedicated software.
For large and expensive projects, editors need advanced software that has a multitude of features and can handle the scale of such projects. One professional video editing program is Final Cut Pro, created by Apple. This software has advanced tools and capabilities to edit and create videos and clips. The most recent version, Final Cut Pro X, has new features that make video editing easier and more efficient such as a new dynamic editing interface, new multichannel audio editing capabilities, more precise inline clipping tools, and a streamlined interface that helps to keep media organized. Professionals can use this software to create complex movies ready for the big screen.[43]

A standard film-editing program on Mac is iMovie. It is a standard free program, tailored toward light editing for simple movies. Apple markets it as an editing program for home movies [44]. It is a simple ti use system, in incorporates file from the Internet, iTunes, iPhoto, garage band, and other online and Mac programs. While it is not at advanced as Final Cut Pro, it does do a good job editing movies. Mac has also added and iOS compatible version of the program for use on its mobile devices. This version is compatible with both the iPads, and iPhone product lines. However, iMovie’s capabilities are limited, as mobile devices lack the memory and processing power for extend editing of projects. Another feature built into iMovie is the ability to share directly to Internet websites. These include Facebook, twitter, and YouTube. In addition, there is a quick feature for emailing movies. Once edited movies are formatted and finalized, Apple runs its own video player known as QuickTime. This is a standard program, similar to Windows Media Player, and is compatible with both Macs and PC’s. Film editors like QuickTime as it is more reliable and has fewer bugs that Media Player, and it is less likely to corrupt video files. [[File:QuickTime 7 Icon.png|thumb|QuickTime 7 Icon]
Media Players
[edit | edit source]Living in the technologically advanced country that we do now, it is relatively understandable to say that, at some point or in another life, we have all heard some form of music or audio played off of an electronic device. Today, for most of us, these devices are things such as CDs, radios, iPods, phones, DVDs, and many more. These are all things that would be considered media players. They were designed with the purpose of playing audio or videos in mind. Today, many of these players are free and are programs that most of us have probably used at some point or another (such as iTunes or Windows Media Player). One thing it is important to keep in mind when using these is that although illegally downloading things may be easy, it definitely does not make it right. It is essential that we all keep the copyright laws in mind when downloading any type of audio or video.[45]
Graphics, Multimedia, and the Web
[edit | edit source]Today, it is rare to find a company that does not use some form of multimedia or graphics on their businesses web page. This is just one example of how important multimedia and graphics have become to the World Wide Web. Open up your browser and instantaneously you’ll see some form of graphics spread across the front page. Whether it’s a banner, GIF, logo, demonstration, or picture, I can pretty much guarantee you that it’s there. These graphics are nice because they easily add color and animation to the page, and make being there just a little bit more interesting for the user.[46]
Other Types Of Application Software
[edit | edit source]There are many types of application softwares. Every type of application software is made to serve a function or to help, for example software for business' or education. Desktop publishing refers to using a personal computer to manipulate text and images to create attractive documents as if they were created by a professional printer. Similar to this, personal publishing softwares are used to create documents for personal use, such as invitations, flyers, or calendars. Very common types of application software include education and entertainment. Entertainment software includes games, simulations, and other programs that provide amusement. Educational software can be found on personal computers, but a popular trend is to combine the hardware and software into a single product. For example, Leapfrog is well-known for their child look-alike laptops used for teaching.[47] Software such as OneNote and Notebook are examples of note taking software. These softwares are generally used by students and business people to take notes during lectures or meetings. Because of this, note taking software normally supports typed and handwritten input. Engineers and architects make use of design software such as CAD (computer-aided design). CAD plays an important role in the design of finished products and other fields such as art, advertising, or law.
Review
[edit | edit source]Key Terms
[edit | edit source]- Application Software
- Software designed to carry out specific tasks [48]
- Shareware
- Copyrighted software that is distributed on the honor system; consumers should either pay for it or uninstall it after the trial period for ethicality [49]
- Freeware
- Copyrighted software that may be used free of charge [50]
- Public Domain Software
- Software that is not copyrighted and may be used without restriction [51]
- Open Source Software
- Software programs made up of source code which is made available to the public. i.e. Wikibook [52]
- Web-Based Software
- Software that is delivered on demand via the Web; also referred to as Software as Service (SaaS) or cloudware.
- Word Processing
- Using a computer and word processing software to create, edit, save, and print written documents, such as letters, contracts, and manuscripts [53]
- Spreadsheet
- A document containing a group of values and other data organized into rows and columns; also called a worksheet in a spreadsheet program [54]
- Database
- A collection of related data that is stored in a manner enabling information to be retrieved as needed; a collection of related tables [55]
- Presentation graphics
- An image, such as a graph or drawn object, designed to visually enhance a presentation
- Graphics Software
- Application software used to create or modify images
- Ribbon
- One of the features found in the recent Microsoft Office applications that uses tabs to organize groups of related commands [56]
Accessibility Software
[edit | edit source]

Visual Aid Software
[edit | edit source]There is software that enables a user to access software even if they have a disability of some type. The same software can simply allow a user to access programs on their computer without visual interferences. An example of this would be f.lux. F.lux is a program that removes the blue tint from a users screen in order to prevent headaches and the light interfering with circadian sleep rhythms [57]. These applications are particularly useful when reading or writing word documents in a dark room.
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]1. A _____ is a collection of worksheets saved in a single spreadsheet file.
2. A _____ is a collection of related data that is stored in a manner enabling information to be retrieved as needed.
3. With a(n) _____ program, the source code for the program is made available to the public and so can be modified by others.
4. True or False. Changing the font size in a document is an example of a formatting operation.
5. A _____ is a collection of related fields in a database. Also called a row.
6. Software that is not copyrighted and may be used without restriction is _____.
7. True or False. Software can be installed on both personal computers and servers.
8. The location at the intersection of a row and column on a worksheet into which data can be typed is a _____.
9. True or False. Microsoft Office is one example of a software suite.
10. Copyrighted software that is distributed on the honor system; consumer should either pay for it or uninstall it after the trial period is _____.
Answers
1. Workbook 2. Database 3. Open Source 4. True 5. Record 6. Public Domain Software 7. True 8. Cell 9. True 10. Shareware
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http.//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Application_software
- ↑ https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/The_Computer_Revolution/Software/Installed_vs.Web-Based_Software
- ↑ http://www.excellerate.com/products/check-in-system/checkin-features/web-based-vs-installed-software-pros-and-cons/
- ↑ http://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/18/business/what-it-takes-to-be-an-app-developer.html
- ↑ Understanding Computers 14th Edition by Deborah Morley
- ↑ http://www.smhllaw.com/articles/?p=319
- ↑ http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-software-suites.htm
- ↑ http://jan.ucc.nau.edu/~lrm22/technology/wpbasics/wpbasics.htm
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Template_(word_processing)
- ↑ http://www.aauwnc.org/04-05/convention/workshops/tech/typewriter.pdf
- ↑ http://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/index.html?nbId=7345&nbNodeId=1013914#!&parentId=1013929
- ↑ http://www.theiia.org/intAuditor/itaudit/archives/2006/january/the-role-of-spreadsheets-in-todays-corporate-climate/
- ↑ http://www.pcworld.com/article/2459947/how-to-create-and-customize-tables-in-microsoft-word.html
- ↑ http://www.quepublishing.com/articles/article.aspx?p=1649256
- ↑ http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/templates/
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spreadsheet#Functions
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spreadsheet#Functions
- ↑ http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/overview-of-formulas-HA102748997.aspx
- ↑ http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/overview-of-formulas-HA102748997.aspx
- ↑ https://support.office.com/en-MY/Article/Create-a-PivotTable-to-analyze-worksheet-data-a9a84538-bfe9-40a9-a8e9-f99134456576
- ↑ http://www2.uncp.edu/home/acurtis/Courses/ResourcesForCourses/Databases.html
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/D/database.html
- ↑ http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/access-help/create-tables-for-a-new-database-RZ101772997.aspx?section=3
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Database
- ↑ http://www.tech-faq.com/what-is-a-database.html
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Query
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Crate_%26_Barrel
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lord_%26_Taylor
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Database
- ↑ http://databases.about.com/od/administration/a/choosing_a_db.htm
- ↑ http://www.zdnet.com/article/the-top-ten-most-common-database-security-vulnerabilities/
- ↑ http://www.jiscdigitalmedia.ac.uk/guide/pedagogical-uses-of-presentation-software
- ↑ "What is presentation software? – Definition from TechTarget". WhatIs. Retrieved 2024-04-21.
- ↑ https://www.boundless.com/communications/preparing-and-using-visual-aids/using-powerpoint-and-alternatives-successfully/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-powerpoint/
- ↑ http://presentationsoft.about.com/od/powerpointtipsandfaqs/f/ppt_overview.htm
- ↑ https://prezi.zendesk.com/forums
- ↑ http://www.globalspec.com/learnmore/industrial_engineering_software/imaging_graphics_software/drawing_software
- ↑ http://www.explainingcomputers.com/software.html
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microphone
- ↑ http://audacity.sourceforge.net/
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pro_Tools
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIDI
- ↑ https://www.apple.com/final-cut-pro/what-is/
- ↑ http://www.apple.com/mac/imovie/
- ↑ http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/m/mediplay.htm
- ↑ http://www.billiondollargraphics.com/web.html
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Educational_software
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Application_software
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shareware
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Freeware
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_domain_software
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Open-source_software
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Word_processing
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spreadsheet
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Database
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ribbon_(computing)
- ↑ Exposure to Room Light before Bedtime Suppresses Melatonin Onset and Shortens Melatonin Duration in Humans
Computer Networks
Networking Applications
[edit | edit source]
There are many different types of network applications. First and foremost is the internet, the largest network of networks in the world. Second, there are our phones, the oldest of which is POTS (plain old telephone service), which one day could be replaced by the newer technology, mobile phones. Mobile phones have been around for a few years now, and are beginning to replace home phone lines. Mobile phones can be separated into two groups, cellular phones and satellite phones. Cell phones work by communicating with cell towers in order to function. There are some dual mode phones which allow you to make phone calls through a WIFI signal, and switch to cell signal when out of WIFI range. Satellite phones work by communicating with satellites in space, this is primarily used with the military, where cell tower coverage is nearly impossible in some locations. While satellite phones can be used in rural and mountainous areas, the drawback to them is when there is a storm or heavy clouds, you can lose your signal. Satellites are also used with a GPS(global positioning system). GPS functions by transferring data between your device and satellites in space. They work similarly to sonar waves. After the signal leaves the satellite, your exact location will be determined based on the time it takes to get to you.
In addition to tracking subjects, satellites and networks are beginning to play a larger part in the field of search and rescue (SAR). Most ocean going boats and all airplanes carry some kind of emergency beacon on board. Aircraft carry an emergency location transmitter (ELT) and boats carry an emergency position-indicating radio beacon (EPIRB). Before the mid 2000’s these devices transmitted on 121.5 mhz, the international emergency frequency, which was monitored by SAR satellites. However, in 2009 [1], SAR satellites stopped monitoring 121.5 beacons in favor of the newer 406 mhz beacons. These devices guide SAR team to the site of a crash, but the signal is also embedded with data. This data includes the name of the owner of the beacon, the aircraft or vessel identification, and a precise GPS location. These capabilities are also being used on personal locator beacons (PLB). These devices are small enough to carry in a pocket, but powerful enough to send an emergency signal to a satellite. Hikers can use these if they are going to a remote area. The use of a satellite network allows for very precise tracking of these devices, and can bring rescue team to the site within two hours.

Computer networks consist of two or more computers or hardware devices linked together to enable connections between shared hardware, software, and data. A combination of networks that consist of telephone networks and computer networks are also becoming more commonly used in this generation.[2] The data is able to be passed along to other networks due to networked computing devices along data connections. A datagram, segment, or block is a unit of communication over a digital network, commonly known as a packet. The data breaks down into smaller units of data when needed. Once the data travels along the data connections, the pieces of data are reassembled into the original data chunk. Data is structured differently, depending on the protocol enforcing the data. The structure of a packet consists of a header and a payload. The header consists of titles regarding transmission-related information. The payload, however, consists of the actual data the packet is carrying.[3] Computer networks range from small private networks, to large computer networks. The Internet, or the World Wide Web, is the largest computer network, consisting of a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet. Via hyperlinks, a user of the Internet can access images, text, videos, etc.
Monitoring Systems are another form of networking applications. These systems specialize in locating a specific person, vehicle or device rather than pulling up geographical information like a GPS does. However, most monitoring systems use GPS in locating their targets. Radio Frequency Identification (or RFID) for example, can be used to locate a person or animal with an RFID chip embedded inside of it. Most commonly recognized for its ability to track pets that have the chip implanted, RFID has also moved into the human medical field. In fact, some breast implants in the United Kingdom have been chipped so that a physician can read information about the implant years after the surgery has been completed.[4] While this is the social reasoning for this type of chipping, it seems that medical records housed on inexpensive servers would suit this purpose just fine. The fact remains that RFID chips, which are about the size of a grain of rice, operate using a small silicon chip and a copper antenna which emit personal information about its owner. This information is then picked up by electronic networks feeding back information about the product, the person carrying it, and its location to the network. It is currently being used to track cattle and Alzheimer's patients as well as merchandise produced by manufacturers.[5] Other monitoring systems include vehicle tracking software such as the famous OnStar. This type of networking application has been expanded so that employers can spy on employees using company vehicles. With a simple installation, the latest vehicle tracking applications can feed information about the geographic location of a company vehicle, the speed of the vehicle, and even "hard breaking" events. Mobile phones aren't omitted either. Since most of the current mobile phones have stand alone GPS systems a person can track the movements of the individuals under their plan as well as their own phone if it is stolen.[6]

Multimedia networking has exploded as well. This type of networking offers digital multimedia content such as movies, music, and recorded t.v. shows to be viewed over a phone, p.c., or television. While most devices already have the required capabilities built in, some devices need may need a receiver. Placeshifting is common with this type of network which will allow an individual to download content from one place and view it in another, i.e. from a t.v. to a mobile phone. Similarly, VideoConferencing allows people to interact remotely from separate locations. Instead of streaming a movie in real time, a person can stream a video feed from a relative or business part who might be across the globe. They can then interact and speak as they normally would while viewing the mannerisms of others in real time. Also, through the use of videoconferencing Telemedicine has been used to diagnose and treat patients who are unable to access a doctor in person because of their poverty level, geographical area, or physical condition. Physicians, with the assistance of a member on site with the patient, use videoconferencing to conduct tests such as simple ear and throat checkups to procedures as complex as actual surgery in some cases.[7]
One relatively new use of networking is telesurgery, or remote surgery. As the name implies, this is surgery that takes place over distances: that is, the surgeon is not actually in the same room as the patient. A surgeon controls robotic arms that in turn perform surgery on the patient. Some advantages of this kind of procedure are that it mitigates the potential effect of a surgeon's hands shaking, the surgeon's arms rest comfortably throughout the entire procedure, and the surgeon can specify a task that (s)he wishes to have performed and ensure it is safe before the robotic arms actually carry it out. Initially, there was just computer-assisted surgery, where the surgeon sat only a few meters away, but now longer-distance telesurgery has been developed: the first telesurgical procedure was known as Operation Lindbergh and involved a New York doctor performing on a French patient across the Atlantic. Telesurgery still isn't especially widespread, but in time, it may see such uses as performing on astronauts in long-term space travel, performing on soldiers on or near battlefields, or working alongside or training surgeons in remote, developing countries. Time will tell how useful these kinds of procedures turn out to be, but they are definitely an example of a networking technology that would have been unthinkable just a few decades ago.[8]
Network Characteristics
[edit | edit source]Networks can contain many different characteristics that define how they function as well as their capabilities. These characteristics include certain factors such as topology, scalability or size, architecture, and media.[9]
Network Topology
[edit | edit source]
Network topology is how different nodes in a network are connected to each other and how they communicate. The five most common topologies are mesh topology, star topology, bus topology, ring topology, and tree topology. In a mesh topology, devices are connected with many excessive interconnections between network mode. In a star topology, the devices are connected to a central computer, and the nodes communicate across the network by passing data through the hub, which is the central computer. In a bus topology, it connects all devices on a local-area network called LAN. Bus networks are not very pricey, and they are easy to install. In a ring topology, it consists of a local area network whose topology is a ring. The messages travel around the ring. In a tree topology, it is considered a "hybrid" topology that combines characteristics of the bus and star topologies.[10]
Network Architecture
[edit | edit source]
Network architecture is the layout of the network. The hardware, software, communication protocols, and mode of transmission in the network architecture.[11] Two main types of network architectures are server-based, or client-server networks, and peer-to-peer (P2P) networks. Server-based networks consist of clients and servers. Servers are powerful computers that are able to transfer data and information among personal computers within the local network or even to other computers across the Internet.[12] Some server-based networks can be designed for certain purposes such as to connect all computers within a given area to a printer (print server) or to even contain data such as documents or other types of files (file server). A peer-to-peer network is a network that doesn’t utilize a central server. Instead, each computer (or peer) within a peer-to-peer network allows itself to use some of its resources to share with the entire network. For example, computers can give some of their processing power or bandwidth and share it with the network participants.[13] The network architecture plays an essential role in today's society; therefore, one should be aware of the network architecture, and the different types of network topologies as well.
Network Size
[edit | edit source]Network sizes are defined by a few three-letter acronyms: PANs, LANs, MANs, and WANs. Personal Area Networks (PANs) are networks that connect an individual's devices, such as bluetooth headsets and speakers. Local Area Networks (LANs) are networks that are used within larger areas such as corporate buildings but can also be used in hospitals or even college campuses. Some people, however, prefer to title networks on a college campuses and hospitals as Campus Area Networks (CANs) if they contain more than one LANs interconnected. A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) is used to connect computers within cities. Lastly, a Wide Area Network (WAN) is a network that contains numerous LANs and is able to connect computers across continents. The largest Wide Area Network is the Internet. Some people use other terms such as Global Area Network (GAN) which is a single network with connection points across the globe, usually used to connect large corporation, or Solar System Area Network (SSAN), which is numerous GANs, combined to connect planets within a single solar system. This technology, however, is not yet available.[14]
Network Media
[edit | edit source]Network media is the actual path which the signals travel to and from different components. These paths can either be physical wires, wired media, or radio signals, wireless media.[15]
Wired Networking Media
[edit | edit source]The wire used for networking media is called cable. The most common types of wired media include twisted-pair, coaxial, and fiber-optic cable.[16]
Twisted-Pair Cable
[edit | edit source]Twisted-pair cable is exactly what it sounds like: two wires twisted together. This design works because it creates an electrical current that flows through the wire, which creates a circular magnetic field around the wire that increases performance. Having the wires twisted, as opposed to being adjacent, helps there to be no crosstalk (the noise/interference sometimes generated by the wires). There are two sub-types of twisted-pair cable: unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP). Twisted-pair cable is most used for LANs such as telephone communication.[17]

Coaxial Cable
[edit | edit source]Coaxial cable is made of three components: the inside wire, the insulation, and the outside shield. The inside wire is made of two conducting elements, mainly copper and covering this is the layer of flexible insulation. A second layer of woven (braided) copper or metallic foil that acts as a second wire and as a shield that reduces that amount of outside interference. Lastly, there is a cable jacket to cover the second wire.[18]
Fiber-optic Cable
[edit | edit source]Fiber-optic cable is made of hundreds of clear glass or plastic fiber strands that are the size of a human hair. Data is transferred by light pulses at speeds of billions of bits per second. This is the newest and fasted type of cable, and while it is the most expensive, it is starting to replace the other types because its high-speed advantages are considered to be worth it.[19] They provide higher bandwith and can transmit data over longer distances than wired cables. They are also less susceptible to interference and doesn't require special shielding to avoid it. Also, since fiber-optic cables use light to transmit information, they lessen the need for signal boosters; light can travel longer distances without losing strength.
Wireless Networking Media
[edit | edit source]
Along with wired networks, there are also wireless networks. Wireless networks are networks that use radio signals to transmit data through the air in order for two or more devices to communicate, rather than physical cables. This gives people the opportunity to use e-mail or browse the internet from almost any location, provided there is a wireless network available. Many devices today are able to use this technology such as PCs, laptops, mobile devices, servers and printers. Wireless networks can be found almost everywhere including the home and public locations such as libraries, restaurants, coffeehouses and airports. Many people needing Internet access on the go will commonly take advantage of wireless hotspots. A wireless hotspot is a small range area with a usable connection that allows access to the internet.
There are also different types of wireless networks. Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANS) are networks that give access to the Internet to a small local area such as a college or library. Wireless Personal Area Networks (WPANS) allow connectivity of devices in smaller ranges, typically around 30 feet. This includes Infra Red technology which may be in a television remote, or Bluetooth. A Wireless Metropolitan Area Network (WMANS) allows for the connection of many networks in a metropolitan area such as in high-rises or big buildings. Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWANS) are networks that spread over much larger areas such as cities or countries and are available through the use satellite systems or antenna sites.
Wired Vs. Wireless Networking Media
[edit | edit source]
While the world may be going towards a wireless route when it comes to networking, is it really the best direction when it comes to connectivity? Let’s break it down to the benefits and disadvantages of each type of network media.
The benefits of having wired connection are that it it’s secure, reliable, and fast. They are also very much cheaper than having wireless connections. Another perk, especially for businesses or enterprises, is that wired connections can be controlled. This has security and productivity benefits. Disadvantages of wired connection are the sacrifice of space and portability or mobility, as well as actual physical safety and maintenance.[20]

The benefit of having a wireless connection is the actual lack of cables. This gives the actual physical freedom to use personal and office devices and has the advantage of a tidier environment. However, there is also a downside in terms of security, speed and reliability.
The best combination might be a system that has some wired connections and some wireless connections. Having a hybrid environment can balance out the disadvantages and take advantage of the benefits of having two types of network media.[21]
Types of Cables
[edit | edit source]There are different types of cables. The cable that connects a computer or network to a server or router or modem is called an Ethernet cable. The evolution of Ethernet cables began with the apparent that coaxial cables could not keep up with the demands of a growing and evolving network. The cables are listed in categories or "Cat" for short. The Cat 1 cables were primarily used for telephone modems and had a data transfer rate of up to 1Mbps. Cat 2,3,and 4 can all support computer networks and telephone traffic, and have maximum capacities of 4Mbps, 10Mbps, and 16Mbps respectively. When these cables are taken out of their casing, they look very similar. The same wires are present in all types of Cat cables; however, the number of wraps per inch increase in each version of Cat cables, therefore decreasing the amount of electromagnetic interference in the signal being transfered. The introduction to Cat 5 revolutionized networking because Cat 5 became the standard and it was classed as "ethernet" which means that it has the capability for high speed and high capacity data transfers (of 10Mbps - 100Mbps), as well as the ability regulate the transfers in order to prevent simultaneous transfers which would cancel out. After Cat 5, Cat 5e was introduced. The "e" stands for "enhanced". The Cat 5e "gigabit" cable - in theory - had the capacity for 1000Mbps (1 gigabit) transfer rates. This was accomplished by wrapping the strands of wire tighter, therefore cutting down on "crosstalk" or interference that caused disruptions in the data transfer. Later, Cat 6 was introduced with the addition of a physical isolator between line segments in the cable, which reduces interference to a greater extent, with a transmission capacity of 1000 Mbps (1 Gigabit per second).[22] Since 2013, Cat 7,8, and 8.1 have been introduced, but are only practical in a small amount of industrial settings.

Network Architecture & Network Topologies
[edit | edit source]
Network architecture is the layout of the network. The hardware, software, communication protocols, and mode of transmission consists in the network architecture. The network architecture plays an essential role in today's society; therefore, one should be aware of the network architecture, and the different types of network topologies as well.[23] Network topology is how different nodes in a network are connected to each other and how they communicate. The five most common topologies are mesh topology, star topology, bus topology, ring topology, and tree topology. In a mesh topology, devices are connected with many excessive interconnections between network mode. In a star topology, the devices are connected to a central computer, and the nodes communicate across the network by passing data through the hub, which is the central computer. In a bus topology, it connects all devices on a local-are network called LAN. Bus networks are not very pricey, and they are easy to install. In a ring topology, it consists of a local area network whose topology is a ring. The messages travel around the ring. In a tree topology, it is considered a "hybrid" topology that combines characteristics of the bus and star topologies.[24]
Data Transmission Characteristics
[edit | edit source]Data Transmission
[edit | edit source]
Data transmission is the actual transfer of data over a channel. The types of channels are copper wire, optical fiber, wireless communication channels, storage media and computer buses. This data is transmitted via signals, which can be electrical, radio waves, microwave or infrared. Data can be transmitted analog by using both analog and digital signals. The modem can change and process the digital data it receives. The data transmitted can come from the keyboard, which is the data source. The data transmitted can also be analog, such as from a cell phone, and can be digitized using source code. The source code is the computer's instructions, which are read and interpreted by the computer.[25]
Bandwidth
[edit | edit source]
Bandwidth is the amount of data that can be transmitted in a given amount of time. Bandwidth is also referred to as throughput. The measure of bandwidth can be bits per second (bps), or thousands of bits per second (Kbps), or millions of bits per second (Mbps), or billions of bits per second (Gbps).[26] Bandwidth refers to the capacity of a connection. A network medium with a higher bandwidth will allow more data to pass through in a given amount of time. Therefore, the higher the capacity, the better the performance. This is not always true, however, because performance depends on other aspects as well. Text data requires the least amount of bandwidth, while video data requires the most.[27]
Analog vs. Digital Signals
[edit | edit source]
Analog and digital signals are used to transmit information, usually through electric signals. Analog signal is a continuous signal and has constant fluctuations where a digital signal is discrete time signals generated by digital modulation. Analog signals are denoted by sine waves that are smooth and continues whereas digital signals are square waves that are stepping and discrete.[28] Analog signals would be things like human voices in the air and analog electronic devices (AM and FM radio, old telephones). Digital signals have only two levels of voltage: high and low.[29] It is an electrical signal that is converted into a pattern of bits. It has a discrete value at each sampling point. Each sample is defined with a series of bits that are either 0s or 1s. Digital signals are for things like computers, CDs, DVDs, and other digital electronic devices. Analog signal processing can be done in real time and consumes less bandwidth whereas there is no guarantee that digital signal processing can be done in real time and consumes more bandwidth to carry out the same information. The advantages of digital signal are that the recording does not degrade over time and groups of numbers can often be compressed by finding patterns in them.[30]
Transmission Type and Timing
[edit | edit source]
For the transmission of data and network media, there are two ways to send information. Serial transmission is sending data in a single path, one bit at a time. An example of this would be a classroom with students lined up in a single line at the door and leaving one at a time. The advantage of serial transmission is that only one line is used, so the cost is lower, at least compared to parallel transmission using multiple lines. The disadvantage is the cost of the entire transmission. Serial transmission is also not as fast because the bits are transmitted sequentially.[31]
Parallel transmission sends data one byte (or 8-bit) at a time, but each bit takes a separate route. This is a more efficient way to send or receive data. For example, a parallel transmission can be identified as students walking through a large hallway in a school to reach their particular classroom. This approach involves more space to receive data more efficiently.
Synchronous, asynchronous and isochronous transmission are the three different ways of serial transmission. Synchronous transmission is the transfer of data in groups and blocks, one after the other. The advantage of synchronous transmission is that it is faster, but the disadvantage is that it requires buffering and ensures that the sender and receiver have the same clock frequency.[32] Asynchronous transmission is not as widely used as synchronous transmission because it is sent when it is ready. The advantages of asynchronous transmission is that this method is cheaper if the lines are short, due to the idle time being short. Each character being all independent will not be interupted in the process. The signals can halso ave different bit rates and the transmission can start as soon as possible. Finally, Asynchronous transmission can send data all at once. The disadvantage of asynchronous, however, is that it is less efficient and slower, because there are gaps between bits.
Data can also be transmitted in three main different ways. Simplex transmission is when data is transmitted in only one direction. Half-duplex transmission sends data in either direction, but data can only be sent in one direction at a time. Full-duplex transmission sends data back and forth in either direction and can be done simultaneously.
Delivery Method
[edit | edit source]Data is delivered by using circuit switching, which is a specific path between a sender and a receiver. A telephone system is an example of circuit switching because the path is dedicated to only those two people for the time being. Once they are off the phone, the path is free to use by whomever else. Sending data over the Internet is called packet switching. The messages sent are detached in “packets.” While traveling through the Internet, the packets contain all information going from the sender to the receiver. Once the transmission is complete, the packets are put back together to create the correct message.
Signature Characteristics
[edit | edit source]Characteristics include the physical transfer of data, or a digital bit stream or a digitized analog signal, through a point-to-point communication channels (copper wires, optical fibers, storage media and computer buses). Data is represented as an electromagnetic signal, such as an electrical voltage, radiowave, microwave, or infrared signal. Its messages are symbolized in one of two ways. The first, known as baseband transmission, is completed by a sequence of pulses using a line code. The second, passband transmission, utilizes a specified set of continuously varying waveforms, created using a digital modulation method. Regardless of which technique is used, the receiver must synchronize itself with the transmitter. There are two distinct types of transmission -- Asynchronous and synchronous. In asynchronous, the two devices are relatively close to each other in speed. This means that if only small bursts of data are sent at a time, its synchronization will be successful as long as the receiver is able to synchronize with the immediate beginning of the data burst. In synchronous transmission, a significantly larger amount of data is sent in each block, which either contains, is preceded, or accompanied by signaling, thus permitting co-synchronization of the devices. The majority of all network backbone traffic today is synchronous.[33]
Communications Protocols and Networking Standards
[edit | edit source]The definition and usage of TCP/IP
[edit | edit source]

Communications protocol and networking standards are necessary in order to determine how devices on a network communicate and what requirements are needed in order for hardware and software manufacturers to develop computing products that function with other products. Techopedia, an online source of computing devices, explains communication protocol as “formal descriptions of digital message formats and rules. They are required to exchange messages in or between computing systems and are required in telecommunications.”[34] Protocol deals with issues concerning packet size, transmission speed, packet sequence controls, routing, and address formatting. These are just some of the many things that protocol and standards deal with in computing devices. Some popular protocols include File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), and Post Office Protocol (POP3). There's little argument that the most popular communications protocol being used today is TCP/IP. The protocol that's used for transferring data over the Internet, TCP/IP is actually a combination of two protocols. The TCP part of the equation stands for Transmission Control Protocol and it is culpable for data delivery. IP stands for Internet Protocol and it provides routing information and addresses. There are several reasons for the continued popularity of TCP/IP. One of these reasons is the flexibility of the dual protocols, as the core has been able to remain largely the same over 25 years, even with the immense growth of internet popularity. Another reason is the routing design, as TCP/IP is designed specifically to facilitate the routing of information over a network of arbitrary complexity.[35] Pretty much all operating systems have built in support for the TCP/IP protocols so that is also a big factor in their popularity.
One potential controversy related to IP's in particular was the scare when the Internet had run out of Internet addresses. The original IP version, called IPv4, had used up all the potential number combinations so no new folks would have been able to connect to the internet... that is, until IPv6 came out. It uses 128 bit addresses, versus the mere 32 bits of IPv4, ensuring that it will be another long time to go until we risk running out of internet addresses again.[36]
Ethernet (802.3) is the most widely used standard for wired networks. It is typically used in local area networking (LAN) with twisted-pair, coaxial, or fiber-optic cabling. There are many standards of Ethernet and each of those standards reaches a maximum speed. Terabit Ethernet standard is the most current standard that is being developed and improved. It will be used to deliver video, digital X-rays, and other digital medical images. In order for a device to be connected to an Ethernet network, the device needs to have an Ethernet port built into the device or added with an expansion card. Power over Ethernet (PoE) allows for electrical power to be set along in the cables of an Ethernet network. This is what allows security cameras to get electrical power while also maintaining a network connection.
Wi-Fi Standards (801.11)
[edit | edit source]
Wi-Fi, which uses the IEEE standard 802.11, is a very popular wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to provide wireless Internet connection to devices. It is perhaps the biggest theme that today’s technological generation revolves around. With the continuous evolving technology, almost every single mobile device now requires an Internet access, or a wireless network standard like Wi-Fi. Due to this, Wi-Fi hardware is built into virtually all portable computers, mobile devices, and even other portable products like printers, digital cameras, gaming consoles, etc. Consequently, the popularity of a Wi-Fi network in houses, businesses, and public hotspots—airports, hotels, coffee shops—has grown steadily. Supporting “roaming,” devices connected to a Wi-Fi network are able to move from one access point to another, as long it is inside or around the actual building or area. The speed and strength of a Wi-Fi network depends on various factors like the Wi-Fi standard or the hardware being used. For example, the most widely used Wi-Fi standards today are 802.11g and 802.11n. The 801.11n, the newest Wi-Fi standard, is in fact currently the fastest standard today, which is able to transfer data five times as fast as the 802.11g standard.
However, even though Wi-Fi seems like the next best technological invention after computers and the Internet, it does have some minor disadvantages that limit the ultimate use of it. For example, Wi-Fi networks have a limited range; one will lose the connection to a network if they move out of the range of that network, usually 300 ft. away from the actual router. They would then have to connect to the next available Wi-Fi connection. Another limitation of Wi-Fi is that many businesses may be physically too large for a conventional Wi-Fi network to cover the entire area. However, there are special networking connections known as WiMAX or Fixed WiMAX, that provide Internet access for a longer radius, stretching from 2 to 6 miles. Using multiple WiMAX towers, similar to cell phone towers, it is even possible to provide coverage to an entire city or any geographical area! [37]
Cellular Standards
[edit | edit source]
It is no secret that the technology used for mobile phones has vastly evolved over the years. What started out as basically a mobile brick has quickly transformed into a compact, highly productive, and speedy cellular communication device. However, many people are unaware of the generational breakdown of these devices. When the first generation mobile phone was released decades ago in the 1980s, it was produced with only the purpose of voice communication in mind. It was not until the second generation came out years later, around the 1990s, that we started to see both data and voice combined into one device. This generation is best known for its access to both Global System for Mobile communications (GSM) and Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) which greatly work to enhance speed and communication up to 14.4 Kbps. When the third generation came along in the 2000s, we saw companies start to use packet switching and access speeds as fast as 2 Mbps. This brings us to where we are today. Cellular companies across the globe are starting to utilize 4g technology and offer outstanding speeds of up to 20 Mbps. Though 20 Mbps is a lot faster than 3G’s speeds, which can be as low as 3.8 Mbps, it is not at the specified 100 Mbps that fourth generation phones are supposed to require. Fourth generation phones are using the LTE, Long Term Evolution, technology or the WiMAX technology, both of which allows for more capacity and faster speeds across the mobile network.[38] These two technologies are incompatible to each other and it depends on which mobile phone provider that you are using. Currently, Sprint is using 4G WiMAX, while Verizon and AT&T are using 4G LTE.[39] This is a necessity in today’s world as more and more people buy mobile smart phones and demand a very high amount of data to be transferred to and from their phones. These technologies use OFDM, orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing, instead of TDMA, time division multiple access, or CDMA, code division multiple access. This change in technologies is what the mobile phone market accepts as a difference between the third generation and fourth generation of phones because OFDM is significantly faster and more efficient, even though it is not as fast as the original specification.[40] Another plus for the fourth generation phones is that they can still access broadband Internet content that many consumers vie for. Hopefully in the near future, technology companies can actually provide mobile phone consumers with a phone that will reach speeds up to 100 Mbps. With technology constantly evolving and expanding, where will it take us next? Into what technological wonders is fifth generation technology going to bring us? [41]
Wireless Printers
[edit | edit source]
Wi-Fi is one of the most popular networking standards that uses wireless LANs. Certain devices come Wi-Fi enabled and some can be hooked up within the wireless network. One of the most popular devices being used today is the wireless printer. Not any printer can be used, however. Special printers nowadays have the Wi-Fi transceivers built into them to locate the available networks. The major advantage is that multiple computers can print to a printer in any location that you want. Another great advantage is that you can avoid the painful cable clutter that comes with all of the devices you could hook up to the computer. It takes much less time for a computer to connect to the printer through Wi-Fi then it does to download the software and connect it manually with a USB cord. One thing to consider though is how windows and doors might affect the strength of the signal. Security is something to think about as well. Some printers contain a WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) encryption that allows only special computers to connect if they activate the similar feature.[42] Believe it or not, these types of printers are actually reasonably priced compared to some of the other types of electronics out there on the market.
Networking Hardware
[edit | edit source]
Network adapters or "Network Interface Cards," (NICs) are used to connect a computer to a high-speed network. Most recently manufactured motherboards have them already built in. Otherwise, a NIC may be installed onto an open PCI expansion slot on the motherboard.
Modems are able to convert your computer's digital data to analog data that can be sent over telephone service lines and converts incoming analog data to digital data that the computer can work with. The better quality modems are able to do the work directly on the card. They are known to be faster and more efficient than a cheaper modem, go figure![43]

The term modem is short for modulator/demodulator. Modems are used to connect with internet services providers. They transfer data between the internet service provider and the computer. There are a few different types of modems available. Analog modems can be used with dial-up connections. Digital subscriber line or DSL and cable modems are used with high speed broadband connections. Integrated services digital network, or ISDN modems are used for even higher speed connections. [44]
Wireless routers have changed drastically in recent years. Once just a simple tool to broadcast the internet into a home or an office, today many wireless routers have additional functions and capabilities. They can offer multiple frequencies to help avoid interference. They can be setup to allow guest access to the network. Some even allow for the advanced security setup with enhanced features like parental control to limit access to certain websites. Another convenient feature is the addition of storage to the device. Some routers allow connection of external storage devices, while others have storage built in. Many routers also have mobile apps designed to control them. In the age of tablets and smartphones, the ability to control your network settings via a mobile device is key.
Hardware for Connecting Devices and Networks
[edit | edit source]
There are different configurations used in connecting devices to a network as well as connecting networks to other networks. An example of a configuration for a home network is a star topology where there is one central device that provides a connection for other devices. This central device, or hub, is not as efficient regarding the availability of bandwidth between the devices, specifically computers, that are connected to the hub. More exactly, the hub can lead to unnecessary traffic build-up because it repeats everything it receives to other devices. This may or may not be an issue depending on the size of the network. A small network will not have much issue with using a hub for a central device, but for other, larger networks a different device may be more practical. A switch is more suitable for larger networks. Like hubs, switches allow devices to communicate with each other. However switches contain ports that are designated for individual devices, which allows for a more efficient allocation of bandwidth for the devices as a whole.[45]
Routers are used to connect different networks together. [46] Because they maintain configuration information in a storage known as a routing table, routers can filter incoming or outgoing traffic.[47] Wireless access points are devices that allow a device access to the network. This, along with a switch, can be found in wireless routers. These routers connect both wired and wireless devices to a network, which then connects that network to the Internet. Another device is a bridge, which simply joins two LAN segments. An example of this would be connecting a game console to a home network.
Repeaters, Range Extenders, and Antennas
[edit | edit source]
Network repeaters regenerate incoming electrical, wireless or optical signals. Today, most data transmissions rely on Ethernet or Wi-Fi, both of which can only span a limited distance before the quality of the signal degrades. The goal of the repeater is to help preserve a tolerable signal over long distance while examples like Ethernet or Wi-Fi have trouble to.[48] While repeaters are available for both wired and wireless networks, repeaters for wireless networks are referred to as range extenders. Range extenders are commonly found in homes in order to eliminate "dead zones", or areas where the normal network doesn't offer coverage. A range extender will typically wirelessly connect to the network, then repeat the wireless signal. One of the most reliable and popular ways of increasing the range of a network is through the use of an antenna. Antennas are highly effective because of their ability to convert radio-frequency into alternating current, or vice-versa. The most common type of antenna is the dish antenna, which is used for satellite communications. An example of antennas being used can be seen on an everyday home rooftop, where dish-like antennas are often used for television signal [49]
Review
[edit | edit source]Review Definitions
[edit | edit source]Analog signal: A type of signal where the data is represented by continuous waves.
Bluetooth: A networking standard for very short-range wireless connections; the devices are automatically connected once they get within the allowable range.
Bus Network: A network consisting of a central cable to which all network devices are attached.
Coaxial Cable: A networking cable consisting of a center wire inside a grounded, cylindrical shield, capable of sending data at high speeds.
Ethernet (802.3): A widely used wired LAN networking standard.
Extranet: An intranet that is at least partially accessible to authorized outsiders.
Fiber-Optic Cable: A networking cable that utilizes hundreds of thin transparent fibers over which lasers transmit data as light.
Intranet: A private network that is set up similar to the Internet and is accessed via a Web browser.
Local Area Network (LAN): A network that connects devices located in a small geographical area, such as within a building.
Mesh Network: A network in which there are multiple connections between the devices on the network so that messages can take any of several possible paths.
Modem: A device that enables a computer to communicate over analog networking media, such as connecting to the Internet via telephone lines.
Private Area Network (PAN): A computer network for interconnecting devices centered on an individual persons work space.
Parallel Transmission: A type of data transmission in which bytes of data are transmitted at one time, with the bits in each byte taking a separate path.
Router: A device that connects multiple networks together; routes packets to their next location in order to efficiently reach their destination.
Serial Transmission: A type of data transmission in which the bits in a byte travel down the same path one after the other.
Virtual Private Network (VPN): A private, secure path over the Internet that provides authorized users a secure means of accessing a private network via the Internet.
Wide Area Network: a computer network in which the computers connected may be far apart, generally having a radius of half a mile or more.
Wireless Network: A network in which computers and other devices are connected to the network without physical cables; data is typically sent via radio waves.
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]1.) Third generation computers became smaller and more reliable than earlier computer generations, incorporating multiple transistors and electronic circuits on a singles tiny silicon chip by utilizing ______________.
2.) A small business needs a computer that can act as a server for a number of PCs and handle a number of users running different applications. The class of computer best suited to its needs would be a(n) __________.
3.) Programs designed to perform specific tasks or applications, such as computing bank-account interest, preparing bills, or creating letters, are contained in ____________.
4.) An example of system software is __________________.
5.) PC-compatible and Mac are the two major personal computer ____________.
6.) The purpose of a computer network is to allow computers to _____________.
7.) Computers and the traditional devices that we use every day- such as the telephone, TV, and home entertainment system- have begun to merge into single units with multiple capabilities; this trend is referred to as ____________.
8.) Having a basic understanding of computers and their uses is called _______________.
9.) The four main computer operations are input, output, storage, and _________.
10.) A mobile device based on a mobile phone that can be used to access the Web and e-mail wirelessly, as well as other capabilities such as taking digital photos, is often referred to as a(n) ___________.
Review Answers
[edit | edit source]Answers 1.) Integrated Circuits 2.) Midrange Server 3.) Application Software 4.) Windows, Osx, and Linux 5.) Platforms 6.) Communicate with each other, share software, and share hardware 7.) Convergence 8.) Computer Literacy 9.) Processing 10.) Smartphone [50]
- ↑ http://www.aopa.org/News-and-Video/All-News/2009/January/22/Whats-up-with-121-5-MHz-ELTs
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/N/network.html
- ↑ http://voip.about.com/od/glossary/g/PacketDef.htm
- ↑ http://www.rfidjournal.com/articles/view?11093
- ↑ http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gadgets/high-tech-gadgets/rfid.htm
- ↑ http://www.caranddriver.com/features/vehicle-tracking-systems-and-data-recorders-tested-gearbox
- ↑ http://www.americantelemed.org/learn
- ↑ http://www.surgeryencyclopedia.com/St-Wr/Telesurgery.html
- ↑ http://computernetworkingnotes.com/network-security-access-lists-standards-and-extended/network.html
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/DidYouKnow/Hardware_Software/Networking/tree_topology.html
- ↑ http://en.kioskea.net/faq/2761-what-is-network-architecture
- ↑ http://compnetworking.about.com/od/basicnetworkingconcepts/g/network_servers.htm
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peer-to-peer
- ↑ http://therealping.wordpress.com/2008/01/30/network-sizes/
- ↑ Understand Computers Today and Tomorrow 14th Edition Comprehensive
- ↑ Understand Computers Today and Tomorrow 14th Edition Comprehensive
- ↑ http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=31276&seqNum=3
- ↑ http://www.ciscopress.com/articles/article.asp?p=31276&seqNum=3
- ↑ Understand Computers Today and Tomorrow 14th Edition Comprehensive
- ↑ http://smallbusiness.chron.com/disadvantages-wired-technology-17833.html
- ↑ http://www.computerweekly.com/feature/Wired-vs-wireless-in-the-enterprise
- ↑ http://www.firewall.cx/networking-topics/cabling-utp-fibre/112-network-cabling-utp.html
- ↑ http://en.kioskea.net/faq/2761-what-is-network-architecture
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/DidYouKnow/Hardware_Software/Networking/tree_topology.html
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_transmission
- ↑ http://searchenterprisewan.techtarget.com/definition/bandwidth
- ↑ http://compnetworking.about.com/od/speedtests/g/bldef_bandwidth.htm
- ↑ https://www.diffen.com/difference/Analog_vs_Digital
- ↑ http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Analog_and_Digital_Conversion/Analog_vs_Digital
- ↑ https://www.diffen.com/difference/Analog_vs_Digital
- ↑ http://ecomputernotes.com/computernetworkingnotes/communication-networks/data-transmission
- ↑ http://ecomputernotes.com/computernetworkingnotes/communication-networks/data-transmission
- ↑ https://umuc.equella.ecollege.com/file/d0edbbfc-0779-4cd5-8203-51719a5ffc2e/1/CMIS435-1109.zip/Modules/M5-Module_5/popups/Data.html
- ↑ http://www.techopedia.com/definition/25705/communication-protocol
- ↑ http://www.tcpipguide.com/free/t_TCPIPOverviewandHistory-3.htm
- ↑ http://mashable.com/2011/02/03/ipv4-ipv6-guide/
- ↑ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/1473553/Wi-Fi
- ↑ http://www.mmfai.org/public/docs/eng/MMF_LTE%20Brochure.pdf
- ↑ http://www.mobileburn.com/definition.jsp?term=4G
- ↑ http://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/4G
- ↑ http://bpastudio.csudh.edu/fac/lpress/471/hout/3G.htm
- ↑ http://www.hp.com/global/us/en/wireless/wireless-basics.html
- ↑ http://www.kitchentablecomputers.com/nic.php
- ↑ http://www.techradar.com/us/reviews/pc-mac/networking-and-wi-fi/modem-routers
- ↑ http://www.darron.net/network/secondpage.html
- ↑ http://whatismyipaddress.com/routers
- ↑ http://compnetworking.about.com/cs/routers/g/bldef_router.htm
- ↑ http://compnetworking.about.com/cs/internetworking/g/bldef_repeater.htm
- ↑ http://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/antenna
- ↑ http://coursemate.cengage.com/CPReader/View/9781133114598/default.aspx?eISBN=9781133114598#da32b353-ffd5-4a88-91a8-c28f124d2211
Internet
Evolution of the Internet
[edit | edit source]
The internet has changed dramatically since its first incarnation. In 1969 the U.S. department of defense created ARPANET.[1] The original concept of this project was to connect researchers located in different places to be able to communicate and collaborate from far distances. The fear of nuclear attack was very prevalent at this time, so the team also wanted to make a network that could still operate after a nuclear attack. Therefore creating many different fail safes, and alternative routes for packet sending was necessary. As this project grew, more and more people gained access to the internet and began shaping it to what we know today. As we have described before, everyone who uses the internet is called an internet user. For these users to obtain access to the internet, you must go through an ISP (internet service provider.) Side note, while the internet is not owned by any one company or government, it is most assuredly not free. It costs money to build, run, and maintain the servers that bring you the funny cat videos.

Internet 2 is an amalgamation of different leaders in the field of academia, technology, industry, and government that formed together in order to collaborate on pioneering and innovative ideas that help advance education and research. They test new network applications and technologies using high-performance networks. Contrary to popular opinion, Internet 2 is not a gathering of minds who intend to replace the current Internet but congregate to ensure that the future Internet will be capable of operating with today's engineering. Internet 2 is currently being upgraded to 8.8 terabytes! This will aide in the ability to offer advanced telemedicine and long distance learning opportunities across connected countries through its network.[2]

The World Wide Web
[edit | edit source]The World Wide Web is different from the Internet. The Internet started out being used more by private industry and people, such as scientists, schools, and the government. The public did not use it for the most part because it was complicated and you had to have a computer to access it, which not everyone could. In 1989, Tim Berners-Lee came up with the World Wide Web and thought it would be a great way to organize information and replace the Internet. Although the Internet still exists and still exists today, the World Wide Web was a great tool for researchers at the time. The World Wide Web is not owned by a business or individual, but the Web is owned by it. The Web consists of things like HTML, URLs, and HTTP. HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language and is used to format documents on the Web. URLs are Uniform Resource Locators, which most of us are familiar with when we type in a Web site address. Finally, HTTP is the Hypertext Transfer Protocol. This is what allows people to click on a hyperlink and be redirected to that particular location. The World Wide Web has changed the way how school teach, businesses operate, and the way ordinary people access organized information.[3] Images and documents are now more readily available, and research and entertainment sites can now be found in one place.[4]
Using the Internet
[edit | edit source]Getting Set Up To Use The Internet
[edit | edit source]
Almost every household has access to the internet; therefore, it is important to know how to have access to the world wide web. There are five basic steps to set up an internet connection which consist of the following:
- One must connect the hardware. Different hardware and software contain directions in setting up. Use the directions to set up these systems.
- The internet needs a wireless connection or an Ethernet cable before it can go online. Therefore, the computer owner must make this connection.
- The computer owner must connect to the default IP address. The IP address usually consists of eight numbers, and it is broken up occasionally by periods.
- It is the internet's server's responsibility to show the computer owner how to actually establish the connection. One must then set up a name and password for security purposes.
- Save the settings, and the internet light will turn green to indicate one is online.[5]
Different Internet Connections
[edit | edit source]There are many different kinds of internet connections. A few of these connections consist of wireless, broadband, and dial-up. Wireless is a router or a network that connects to a hot spot. A broadband is connected directly to a broadband modern, and one needs a user name and password to connect. A dial-up is used remotely via a telephone line.[6] Different types of internet connections come with their own pros and cons and it is important to choose one that will work well with your lifestyle and your wallet.
Dial-up
[edit | edit source]Dial-up connection requires a phone line to function. Because of this, people cannot be using the phone and the internet at the same time. When connecting to the internet via dial-up, the computer tries to connect through the phone line and causes dial-tones and many numerous sounds to emit from the modem. Dial-up is also the slowest form of internet connection and has a maximum speed of 56 kilobits per second. It is also the most archaic type of internet connection and only about 3% of Americans are still using it.[7][8]
Wi-fi Hotspots
[edit | edit source]`Wi-fi hotspots are another form of internet connection in which a wireless access point, such as a router, has a direct connection to the internet and allows people to connect wirelessly through the use of wi-fi. Although they aren’t used very much at home, wi-fi hotspots are often used at locations such as restaurants, hotels, and airports. Many restaurants such offer free wi-fi to entice customers, while others have a fee for using their internet.[9]
Broadband over Fiber
[edit | edit source]
A new technology called broadband over fiber (BoF) is a direct connection option for internet access. Internet service providers are starting to adopt this new technology and sell it for a fee.[10] For example, Verizon's version of broadband over fiber is called fiber-optic service (FiOS). FiOS, in particular, is able to provide services such as telephone, television, and internet. BoF is advertised on Verizon's FiOS webpage as a network that, "provides bandwidth to meet today's digital demands and the possibilities of tomorrow."[11] This statement is probably used because BoF's data transfer speeds are much faster than other services. In fact, with fiber-optic cabling, data transfer can travel at the speed of light. One drawback of BoF is that it is very expensive. In order to create a fiber-optic network, you must invest a lot of money in constructing an essential infrastructure. Another negative with broadband over fiber is that the cables are very sensitive. This means that cables can not be installed on telephone poles or underground. Cables must be installed above ground, usually in piping, so that the cables are protected from bending and shifting. BoF is practical and efficient for small networks due to less complex construction of infrastructure. This being said, the United States probably won’t have nation wide BoF networks.[12]
Selecting an ISP
[edit | edit source]There are many different Internet Service Providers, some of the most popular include Comcast, AT&T, Verizon, and Time Warner Cable.[13] When you choose an ISP, there are many factors to take into consideration. Some of those factors include price, type of internet connection you want, speed, customer support, types of devices you use, and cancelation policies.[14]

Some internet service providers, such as Verizon and Google, are now starting to offer fiber-optic internet connections. Fiber-optics allows unsurpassed connection speeds, both upload, and download. Fiber-optic internet connections employ Fiber-optic cables that transfer large amounts of data through hundreds of stands of glass or plastic based on entirely light based, optical technology. The technology has existed for many years, but many may have begun to hear that it has become more commonly available over the recent years. After implementing fiber-optics in commercial internet service packages, Internet Service Providers are now able to confidently boast connection speeds exceeding 100 gigabits per second, speeds that are much more desirable to many households as well as businesses.[15] Fiber optic networks are, to no surprise, very expensive.
Large-scale ISPs may not be ready to spend hundreds of millions, if not billions, on citywide fiber networks, so the technical transition to fiber-optic is a lengthy process. Google alone spent over 80 million dollars to reach 150,000 households with their fiber-optic connections. Only a small handful of cities currently have the luxury of a fiber-optic connection, and it may take some years before the technology is available to a majority of households.[16]
Searching the Internet
[edit | edit source]Search Engines
[edit | edit source]
Search sites are websites that are specifically created to help search the Internet. Examples include, “Google,” “Bing,” “Yahoo! Search,” and “Ask.com.” There are also many other not as well known search sites. Search sites generally use a search engine, which is a program for the retrieval of data from a database or network. A search engine includes a spider, which goes to every page on every Web site that wants to be searchable and reads it. Then there is a program that creates an index from the pages that have been read. Then a program that receives your search request and compares it to the index, then gives you results.[17] Most search sites today are designed for keyword searches, which is when you type in keywords describing what you are searching for. A directory search is the other kind of search that some sites allow and it uses lists of categories instead of a search box.[18] Many search sites will also contain tools that can be used to find information. Many sites try to present their results as clearly as possible. They will also tend to make suggestions about things that are similar to what you searched that may help you find what you are looking for.[19]

When it comes to search sites, there are a few that almost everyone is familiar with. The common phrase, “Google It,” is an indication that Google has become a household name when it comes to search engines. Google boasts an astounding 1,100,000,000 monthly visitors. With numbers like that, it is easy to see why Google has become the household name for search engines. However, few are as familiar with some of the other search sites that are available today that provide the same kind of service that Google does. One of these lesser known search sites is Duck Duck Go. One of this site's great features is that it does not share any of its clients' data with other search sites which makes for less advertisement pop ups and stronger privacy for the user. This has appealed to more and more users after information surfaced that the U.S. has direct access to the servers of major search engine companies allowing the U.S. government to gain knowledge of exactly what people are searching for. This information inspired the founder of Duck Duck Go, Gabriel Weinberg, to start this company in 2008, to ensure the rights and privacy of its users. Gabriel Weinberg was quoted as saying, “Search data is arguably the most personal data people are entering into anything. You’re typing in your problems, your desires. It’s not the same as things you post publicly on social networks.” Duck Duck Go has is a great alternative to larger search engines and for users who really value their privacy.[20]

Search Strategies
[edit | edit source]
Searching for particular information can be fun but also can be very frustrating. Here are few different search strategies which can help to find the information needed, such as simple, complex, phrase, natural language and default Boolean Logic searching. Simple searching is the easiest method of using a search tool.[21] The user can type one or more key words (spelling counts) in the search box then click on the search button. Complex searching is using Boolean Logic[22] to improve search efficiency. The words such as AND, OR, and NOT are entered between keywords to refine the search. In phrase searching, a user should enclose quotation marks when searching for specific phrase. Most search engines like Google, Bing, and such recognize this protocol. Natural Language searching is allowing a user to type a sentence or question just the way he/she might like and the search tool will try to determine key words and locate pages based on these words. Default Boolean Logic searching allows a user to type key words as in simple search. Search tool, depends on its default, will use OR or NOT. If a user is tired of typing, she/he can click on the microphone icon in the Google app or Chrome’s search box to search by voice.[23]
Beyond Browsing and Email
[edit | edit source]Instant Messaging and Text Messaging
[edit | edit source]Communication is quite possibly the most important tool that humans can hone. While e-mails are a fast and environmentally-friendly method of Internet-based communication, there are two types of messaging that are faster and easier. These two types of messaging are: instant messaging and text messaging. Instant messaging, also referred to as chat, allows you to type out a message on your keyboard and then press 'enter' to have it sent immediately to the other party. Unlike emails, where you have to wait for the other person to be around at their computer to read the message, and THAT is assuming your email didn't get lost because of a faulty spam filter, IM's create a connection that is almost as good as being in the same room with the friend. To instant message a friend, you typically both need the same IM client, of which there are many free varieties such as AIM, MSN, YIM, and Skype.
Text messaging, which is also called SMS (Short Message Service), used to be the most popular means of speedy communication though it has been on the decline.[24] Text messaging allows users to send fast and typically short notes with their cellular phones. While text messaging used to be quite expensive, majority of cellular plans sold today include unlimited texting.[25] Text messages, like emails, need to be waited for and can sometimes not make it to the right place without a glitch. Instant messengers, however, tend to have a better track record.
Online Shopping: Amazon and More
[edit | edit source]
Online shopping is so convenient for many who are on the go. There are no hours of operation to abide by, no lines to wait in, and consumers do not even have to leave the comfort of their own home to get what they want. There are some downsides of online shopping, such as not being able to try on clothes to see if it is the right size. The largest online retailer is Amazon.com. Shoppers seems to go-to website for all online shopping needs. The retailer started as an online book store, but now offers purses, electronics, movies, music, and even sports equipment, just to name a few. Sellers can create accounts fairly easy and try to sell their goods. Buyers need to be the cautious ones and look into the reviews to see who they are buying from. One advantage of shopping with Amazon is that they have an A-Z guarantee that helps the buyers resolve conflict with the sellers.[26] Amazon expanded their services to include areas such as Amazon Art, Amazon Instant Video, Amazon Prime, Amazon Local, Amazon Wireless, Amazon Fresh, and Amapedia. One controversy that comes up with Amazon.com, as well as online shopping, is that consumers are not paying their true county sales tax. Instead they are paying the sales tax that Amazon collects.To challenge Amazon, Google has decided to start to expand its e-commerce role. Google wants to compete with amazon and their ability to sell merchandise around the world. Google is allowing consumers to search for something and Google would tell them if there is somewhere nearby to purchase that item. It is a great retaliation against amazon. They would charge $95 a year or $10 a month, or pay $4.99 per order. Google is also offering overnight shipping.[27]
Online Banking
[edit | edit source]Online Banking has become increasingly popular in this tech-savvy generation. Most banks now allow transactions to be done online through their website or through phone apps. While some people question the security of making transactions online, the biggest advantage is that online banking is very convenient. People can set up accounts through a few simple steps, can make transactions between different accounts they have, transfer money, make payments on credit cards, and more. Some only-online banks have formed and are gaining popularity because they have less fees and thus are cheaper. Some banks try to offer deals with higher yield to make online banking more appealing. Lastly, it is handy to have 24/7 access to speedy transactions, which traditional banks cannot offer. Online banking did have a shaky start, but now it is growing quickly.[28] According the Bankrate website, 65% of consumers use online banking.
Pros and Cons
[edit | edit source]In the last few years, online banking has become increasingly mainstream. For some, it is the new norm, as having to make daily or weekly trips to the bank can be both unpleasant and inefficient. For the most part, online banking is advantageous -- and though the pros certainly outweigh the cons, no system is flawless.
First, an obvious pro is convenience. An ability to pay the majority of bills online, whether it is through a checking, savings, money market account, etc. is something that is necessary in our fast-paced, demanding world. Many creditors offer an automatic plans to ensure customers are not charged penalties if they forget to pay a bill. In addition, there is also mobile capability. Most banks feature mobile-friendly websites that allow customers to bank on-the-go. The applications banks offer are typically free, and are being implemented with new features all the time in an effort to expand availability to smartphone users. Lastly, the ease of navigation is comparable to that of any other website. To prevent or assist with issues, most banks have 24-hour live customer service or e-mail customer service.
The most significant con to online banking is security, with computer hacking and identity theft being such widespread problems. Despite the best security measures, there is always risk that someone, somewhere will be able to gain access to your bank account and/or sensitive information. Another concern is transaction issues. There are some aspects of banking that should be done behind a teller’s desk instead of a monitor or screen. Depositing cash, certain types of international deals, and similar difficulties may be challenging to address or solve via the internet. Another, less threatening issue for those who frequently make impulse purchases or budget poorly is a lack of money management, as instant access to a balance can precipitate irresponsibility. [29]
Social Media
[edit | edit source]

Besides texting, instant messaging, and online shopping, there are hundreds of other things you can use the Web for. One of the main things people use it for today is social media. Things from Facebook and Twitter to email and online newspapers are all forms of social media, or sites used to share information to groups of people over the Internet. The problem with the huge explosion that has been the beginning of the social media era is that it is becoming increasingly difficult to believe information posted online. The Internet has evolved so much that now we are able to even perform video and telephone functions through it. Sites like Skype are taking advantage of this technology. According to the FCC (Federal Communications Commission) the technology used by Skype, Vonage, and other similar Companies is called VoIP. They define this technology as one “that allows you to make voice calls using a broadband Internet connection instead of a regular (or analog) phone line”.[30] Essentially, performing telephone functions through the Internet is VoIP. Social Media has seemingly encompassed the younger generations of today; while it has been slower to catch on with the older generations, it is something that has been increasing over time. Skype had recently acquired a newer company called Qik and plans on dominating the new way for people to communicate using mobile video messaging. Skype Qik is supposed to be very simple, and it is exactly like texting but all video. A person can send a Qik video to anyone and they do not even have to have the app. These conversations are asynchronous and Skype Qik is a great idea for communication since things like Facetime have been a big trend. The thing with Facetime though is that someone has to answer the phone and both people need to use it at the same time; with Skype Qik people have the ability to have that type of video interaction but at no specific time. Skype Qik was developed by Microsoft, and is available on a PC or Mac, and for the iPhone, Android, or Windows phone.[31]
Another popular social media app is Snapchat. This app allows people to send pictures, videos, and texts, just like other apps, but the catch is that once the picture/video/text is opened, it disappears after the set amount of time and cannot be see again. Snapchat has many features which make Snapchat photos and videos more fun and interesting than on other apps. Such features include filters, different text fonts, and the ability to draw on the pictures/videos with different colors. In addition to these original features, Snapchat has added a feature called “My Story” where users can create a chain or video of multiple pictures and videos combined. This story is not sent to one specific person, rather any of the user’s friends can see it; the set time in this feature determines how long the picture shows in the “slide show” and the story is available for only twenty-four hours. The latest feature is “geolocation” which can give you the time, weather, miles per hour, or other site-specific filters based on your location.[32]
RSS and Podcasts
[edit | edit source]
First invented by Netscape, Really Simple Syndication (RSS) is an online tool designed to quickly distribute new articles and other content when it is changed or added to. The reason for its invention was because it was an easy way for Netscape to share headlines and stories from other sites, and automatically add it to their own. To help people keep updated on their favorite websites, RSS uses an XML code that constantly scans a website and then broadcasts those updates to all the subscribers through its RSS feed. Subscribing to an RSS feed—usually for free—is fairly simple, as all one has to do is sign up with a feed aggregator, which will store all of one’s RSS subscriptions, and then click the subscribe link on the associated Web page. Finally, its feed content will automatically be added to their browser feed list, similar to the Favorites Feed list in Internet Explorer. For better accessibility for today’s evolving generation, RSS feeds can also be delivered to mobile phones and maybe even directly to televisions sometime in the future. [33]
Another simple way to gather useful information from the Web is a Podcast, which is simply a recorded audio or video file that can be downloaded from the Web. Derived from the combination of the words “broadcasting” and “iPod,” podcasting is a form of audio broadcasting, which can be listened on one’s iPod. However, this is not a limitation since podcasts also be listened to on computers via the Windows Media Player or iTunes, or smartphones. The difference between podcasting and simply downloading and listening to music online is the fact that with podcasting, files come to you through syndication, instead of the other way around. Much like the blogs and websites mentioned previously, podcasts can be subscribed to in order to download new podcasts whenever they become available. [34]
Online Testing
[edit | edit source]Online testing is becoming a new alternative for taking tests in this technology-based world that we live in nowadays. Online tests can be used for both objective tests, like multiple choice or true/false, or performance-based tests, like a concussion test. The state of Washington started using online testing in the spring of 2010 to administer tests of math and science for grades 3-8.[35] This testing format creates more options for a teacher’s curriculum. Usually, one or two days are necessary to complete a test in class, but with an online test, no class days are taken up. This allows for the teacher to either go more in-depth on topics, allow for more Q&A during class room time to make sure his or her students understand the material, more time to prepare for an online test day, or it allows for more material to be covered. All of these options are great for the education system because students gain more knowledge from their tuition. One problem with online testing is security. How would a teacher know if the right student is taking the test, if the student is looking online or using another person to help them? To overcome this obstacle, technology companies are creating devices like the Securexam Remote Proctor system that takes a 360-degree image of the room and uploads it to a server where the teacher of the class can view it. All in all, online testing is the wave of the future for the education system with testing.
Blogs, Wikis, and Other Types of Online Writing
[edit | edit source]
A blog is a Web page that contains short, frequent updated entries in chronological order, typically as a means of expression or communication. Blogs can be written by anyone, including ordinary people, celebrities, or even experts of certain fields. As blogs become more and more popular, commercial advertising begins to be commonly seen on more of the popular blogs. Some of the most popular blogs are websites that offer information or helpful tips to their readers. For example, as of October 2014, the top three most popular blogs are: Huffington Post, TMZ, Business insider.[36] Another form of online writing, most often used for education purposes, is the wiki. Wikis are a way of creating and editing collaborative Web pages quickly and easily. Unlike a blog, wikis are meant to be edited by anyone, not just the owner of the typed information. One of the largest wikis is Wikipedia(Wikibooks is an example of a wiki too). While wikis are helpful and collaborative, erroneous information can be added intentionally. As a result, it is recommended to be careful when fully trusting a wiki page. Another type of online writing is an e-portfolio. An electronic portfolio is a collection of an individual's work accessible through a website. Today. e-portfolios are commonly linked to student-related information, such as resumes, papers, or projects.
Online Gaming
[edit | edit source]
Everywhere you look, young people are using smartphones, notebook computers, iPads, etc. Often, they are not just using these devices for school research, homework, or studying. Young people can be seen playing games on computing devices as young as 3 years old. Online gaming is a rapid habit that is starting from a very young age. Often, the habit carries into the young adult years for many individuals. Nowadays, there are whole web sites whose sole purpose is hosting games that can be played online. Online games can be played alone or with other individuals who are also online. The games that are designed to be played by multiple players are called online multiplayer games. Some examples of online multiplayer games are Doom, EverQuest, Final Fantasy, City of Heroes, and World of Warcraft. Also, gaming devices, such as, PlayStation 3, Xbox 360, and Wii, are deigned to be Internet-enabled so they can be connected to the Internet to play with other players. Online gaming has also been associated with Internet addiction. An article about online gaming addiction in The Kernel, states that often individuals are playing online games 12 hours a day. The article explains that individuals that develop online gaming addiction lose jobs and loved ones, have withdrawal symptoms, and develop migraines and back problems. The article states that it is a very real problem and will potentially continue to grow in the population as the Internet becomes more readily available to more and more people.[37]
Video Chatting
[edit | edit source]
Video calls have played a major part in science fiction for decades. They were a major part of the film 2001: A Space Odyssey, and many other films and TV shows of that genre. Now, video chatting capabilities are found as standard on most desktops, and mobile devices. On of the most well known programs, and the program that pioneered video chatting, is Microsoft’s Skype. In recent years, Skype has been joined by Apple’s Facetime, and a video chat program embedded in Google Hangouts. Skype is compatible with Microsoft, Mac, and Linux computers, and there is and app for mobile devices. Facetime however, is only available on Apple devices, although the company has promised to make it compatible with other devices at some point. Google Hangouts, being a part of Google online app suite, is available as long as the user is able to access the Internet. There are other free source programs, but these three are the most common and the most trusted by security programs. Some free source options that now have become very popular is Facebook's Messenger App and WhatsApp; these are both available for download on most smartphones. Video chatting was touted as a futuristic ideal, but in recent years, this has not held true. Video chatting use has decline in favor of texting and online testing apps. These may be the future as opposed to video chatting. [38]
Censorship and Privacy
[edit | edit source]Censorship
[edit | edit source]Censorship is the control of the information distributed within a society and has been a sense of dictatorships throughout time. It’s the suppression of offensive expressions that are used for when people want to provoke their personal political or values to another group. Typically now censorship is filtered by the government to control the information that is given to the public. Censorship by the government is typically unconstitutional because of the freedom of speech and is highly fought against in the First Amendment. However, other countries routinely censor information and have strict rules against their citizens posting information that the authorities do not like, for example, China and North Korea. On another note, when individuals in US are on strike or boycott an event they are protected by the First Amendment which can be dangerous but they are still known to be protected. Some private censorship campaigns are best countered by groups and individuals speaking out and organizing in defense of the threatened expression.[39][40]
Fighting Internet Censorship
[edit | edit source]
Internet users who live in countries where the government tries to block or inhibit Internet use can still sometimes access material that is supposed to be forbidden. One way to do this is via a proxy, where Internet connectivity is routed through another server. If, for example, Facebook is blocked, an Internet user can use connect to a proxy server that, in turn, connects to Facebook, giving the user access to Facebook without directly connecting to it.[41] A VPN (Virtual Private Network) can also be used to bypass such laws; however, different providers provide different layers of security (some do not log any information, some providers encrypt whatever is sent etc), and it is generally better to pay for one than try to use a free VPN. There is also a browser dedicated specifically to Internet activity known as TOR for "The Onion Router", which proves multiple layers of encryption, like layers of an onion, as the data people are submitting or accessing is routed through multiple different 'nodes' and encrypted in between each one. The idea is that this will provide total anonymity, so that people cannot be tied to their access of or posts on certain websites. While it is sometimes given a negative connotation as a tool only for criminals, TOR is actually incredibly useful for people in countries whose governments are trying to oppress their citizens' freedoms of speech and press.[42] In short, while it is not easy or necessarily safe for people in these nations to access everything they should be able to access on the Internet, it is possible, and there are some means of circumventing government censorship of the Internet, which is not always holeproof.
Web Browsing Privacy
[edit | edit source]
Privacy is of great importance to all users of the Internet. According to Wikipedia, internet privacy involves the right or mandate of personal privacy concerning the sorting, repurposing, provision to third-parties, and displaying of information pertaining to oneself via the Internet.[43] This has been a subject of concern for decades. For example, one article that addresses the potential implications of privacy and computer dates back to 1965.[44] While it is certain that privacy can be infringed, a simple awareness of how exactly certain processes, like using a search engine, interact with a user can be help deal with some of these concerns.
When one uses a search engine, such as Google, small files known as cookies are created to help identify preferences for the user. This enables a more accurate and quicker response when beginning a new session. To put this into context, cookies can help retrieve information like what was in a shopping cart for a previous session. However, third-party cookies can be more of an issue to some. Companies use these cookies to target advertisements towards users depending on their browsing patterns. Using the Internet Options in Internet Explorer (for Windows) can help one decide what types of cookies can be allowed as well as delete all cookies off the hard drive.
A more serious threat to internet privacy is spyware, which refers to any software that is installed without knowledge of the user that obtains information about that user through an Internet connection. The degree to which these programs can cause harm range from simple annoyances (e.g. setting a homepage to something else) to full-scale threats on system integrity (e.g. rewriting the Windows registry to restrict the user from changing the homepage back to its original state).
Adware, while related to spyware, is less harmful. Adware is usually installed alongside other software, and this leads to advertisements that appear on-screen. This can be installed without prior knowledge during the installation of another program by not reading the licensing agreements that came with the program. Therefore it is important to read carefully the agreement to ensure unwanted software is kept away from the computer.

In order to prevent personal information from being compromised and to keep your computer and internet running smoothly there are several precautions that should be taken to ensure that your web browsing experience is a safe and private one. Perhaps the easiest method to do this is by activating private browsing on your internet browser application. Once turned on the browser can not save any files or data to your local machine, including cookies, cache, and history. If you are using regular browsing, these files can still be deleted through your browser or another application. Disposing of these files ensures that online sites cannot track your activity on the web. You can also use programs to ensure that you are not being targeted for certain advertisements because of your browsing history, a common occurrence in the modern marketing age. To be very anonymous on the internet, a Tor network can be setup that encrypts the data you are sending so that your IP address is not compromised.[45] Another similar method is proxies, which are intermediates that receive and deliver information requested. This keeps your personal computer information private as the server is technically the one making the request, not you.[46]
E-mail Privacy
[edit | edit source]
It is extremely important to always make sure that any important or confidential information being shared over the Internet is being done in a private and confidential way. One of the unfortunate downfalls to everything being done electronically today is that we lose a sense of privacy. Things are much easier to attain on the Internet, and sadly there are hackers out there who spend their time trying to break into and gain access to this confidential information. If you are going to send important information electronically, it is necessary that you send it in an encrypted message. Encrypted messages make it so that others cannot hack into your e-mails and read what you are saying. One of the more recent controversies with privacy in e-mailing has to do with Google mail. Google has come out saying that they should be able to read the information sent by any of its Gmail users. People find issue with this because they are gaining personal and confidential information that individuals do not want out there. The purpose of sending a specific email to a specific individual is so that it can be done in privacy, with the hopes that only that recipient will receive it. However, today this is unfortunately not the case, and if you are going to send mail electronically, one needs to proceed with caution.[47]
Review
[edit | edit source]Review Definitions
[edit | edit source]Mobile Phone:A phone such as a cellular, or satellite phone that uses a wireless network.
Cell Phone:A mobile phone that communicates via a cellular network.
Satellite Phone:A mobile phone that communicates via satellite technology.
Dual-Mode Phone:A mobile phone that can be used with more than one communications network, such as with both a cellular and Wi-Fi network.
Global Position System (GPS:A system that uses satellites and a receiver to determine the exact geographic location of the receiver.
Videoconferencing:The use of computers, video cameras, microphones, and networking technologies to conduct face-to-face meetings over a network.
Telecommuting:The use of computers and networking technology to enable an individual to work from a remote location.
Telesurgery:A form of robot-assisted surgery in which the doctor's physical location is different from the patient's physical location and the doctor controls the robot remotely over the Internet or another network.
Telemedicine:The use of networking technology from the location of the doctor to provide medical information and services to the patient in a different location.
Wireless Network:A network in which computers and other devices are connected to the network without physical cables; data is typically sent via radio waves.
Star Network:A network that uses a host device connected directly to several other devices.
Bus Network:A network consistent of a central cable to which all network devices are attached.
Mesh Network:A network in which there are multiple connections between the devices on the network so that messages can take any of several possible paths.
Personal Area Networks (PANs):A network that connects an individuals's personal devices that are located close together.
Local Area Networks (LANs):A network that connects devices located in a small geographical area, such as within a building.
Wide Area Networks (WANs):A network that connects devices located in a large geographical area.

Intranet:A private network that is set up similar to the Internet and is accessed via a Web browser.
Extranet:An intranet that is at least partially accessible to authorized outsiders.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs):A private, secure path over the Internet that provides authorized users a secure means of accessing a private network via the Internet.
Analog Signal:A type of signal where the data is represented by continuous waves.
Digital Signal:A type of signal where the data is represented by 0s and 1s.
Serial Transmission:A type of data transmission in which the bits in a byte travel down the same path one after the other.
Parallel Transmission:A type of data transmission in which bytes of data are transmitted at one time, with the bits in each byte taking a separate path.
Twisted-Pair Cable:A networking cable consisting of wire strands twisted in sets of two and bound into a cable.
Coaxial Cable:A networking cable consisting of a center wire inside a grounded, cylindrical shield, capable of sending data at high speeds.
Fiber Optic:A networking cable that utilizes hundreds of thin transparent glass fibers over which lasers transmit data as light.
Cellular Radio:A form of broadcast radio designed for use with cellular telephones that broadcasts using antennas located inside honeycomb-shaped cells.
Microwave Station:An earth-based device that sends and receives high-frequency, high-speed radio signals.
Communications Satellite:An earth-orbiting device that relays communications signals over long distances
Infrared (IR) Transmissions:A wireless networking medium that sends data as infrared light waves.
TCP/IP:A networking protocol that uses packet switching to facilitate the transmission of messages; the protocol used with th Internet.
Ethernet:A widely used wired LAN networking standard.
Wi-Fi:A facility allowing computers, smartphones, or other devices to connect to the Internet or communicate with one another wirelessly within a particular area.
WiMax:An emerging wireless networking standard that is faster and has a greater range than Wi-Fi.
Wi-Fi Direct:A standard for connecting Wi-Fi devices directly, without using a router or an access point
Bluetooth:A networking standard for very short-ranged wireless connections; the devices are automatically connected once they get within the allowable range.
Ultra Wideband (UWB):A networking standard for very short-range wireless connections among multimedia devices.
WirelessHD:An emerging wireless networking specification designed for connecting home consumer devices.
Wireless USB:A wireless version of USB designed to connect peripheral devices.
TransferJet:A networking standard for very short=range wireless connections between devices; devices need to touch in order to communicate.
Network Adapter:A network interface, such as an expansion card or external network adapter.
Network Interface Card (NIC):An expansion card through which a computer can connect to a network.
Modem:A device that enables a computer to communicate over analog networking media, such as connecting to the Internet via telephone lines.
Switch:A device used to connect multiple devices on a single (typically wired) network; forwards packets to only the intended recipient.
Router:A device that connects multiple networks together; routes packets to their next location in order to efficiently reach their destination.
Wireless Access Point (WAP):A device on a wireless network that connects wireless devices to that network.
Wireless Router:A router with a built-in wireless access point; most often used to connect wireless devices to a network and an Internet connection and often contains a built-in switch.
Bridge:A device used to bridge or connect two LANs; most often used to connect wired devices wirelessly to a network.
Repeater:A device on a network that receives a signal and retransmits it.
Range Extenders:A repeater for a wireless network.
Antennas:A device used for receiving or sending radio signals; often used to increase the range of a network.
TOR: "The Onion Router" a browser dedicated specifically to Internet activity which proves multiple layers of encryption, like layers of an onion, as the data people are submitting or accessing is routed through multiple different 'nodes' and encrypted in between each one.
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]formatting files References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ wiki: ARPANET
- ↑ http://www.internet2.edu
- ↑ http://webfoundation.org/about/vision/history-of-the-web/
- ↑ http://www.nethistory.info/History%20of%20the%20Internet/web.html
- ↑ http://www.wikihow.com/Set-Up-an-Internet-Connection
- ↑ http://windows.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-vista/what-are-the-different-internet-connection-methods
- ↑ http://www.cnet.com/news/3-percent-of-american-adults-still-cling-to-dial-up-internet/
- ↑ http://www.packetworks.net/blog/internet-connection-types
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hotspot_(Wi-Fi)
- ↑ Understanding Computers 14th Ed. by Deborah Morley & Charles Parker
- ↑ http://www.verizon.com/home/fios/
- ↑ http://www.wisegeek.com/what-are-the-pros-and-cons-of-fiber-optic-broadband.htm
- ↑ http://www.practicalecommerce.com/articles/3225-20-Top-Internet-Service-Providers
- ↑ http://www.easyt1.net/blog/10-things-to-consider-when-choosing-an-internet-service-provider
- ↑ http://arstechnica.com/business/2014/04/one-big-reason-we-lack-internet-competition-starting-an-isp-is-really-hard/
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fiber-optic_communication
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/S/search_engine.html
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/K/keyword_search.html
- ↑ http://webaim.org/techniques/sitetools/
- ↑ http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2360059/DuckDuckGo-little-known-search-engine-refuses-store-data-users-doubles-web-traffic-amid-NSA-tapping-scandal.html
- ↑ https://www.bcps.org/offices/lis/models/tips/searchstrategies.html
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/B/Boolean_logic.html
- ↑ https://support.google.com/websearch/answer/134479?hl=en
- ↑ http://blog.brosix.com/why-instant-messaging-is-now-more-popular-than-sms/
- ↑ Cell Phone Plan Cost
- ↑ http://www.ioba.org/newsletter/archive/8%284%29/toolbox2.php
- ↑ http://www.dailyherald.com/article/20141014/business/141019213/
- ↑ http://www.bankrate.com/finance/checking/pros-cons-online-checking-accounts-1.aspx
- ↑ http://www.nasdaq.com/article/the-pros-and-cons-of-online-banking-cm386361
- ↑ http://transition.fcc.gov/voip/
- ↑ http://www.theverge.com/2014/10/14/6973625/skype-qik-video-messaging-features
- ↑ http://mashable.com/2014/08/13/snapchat-tips-and-tricks/
- ↑ http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-rss.htm
- ↑ http://www.entrepreneurs-journey.com/230/what-is-a-podcast/
- ↑ https://www.k12.wa.us/Assessment/StateTesting/OnlineTesting.aspx
- ↑ http://www.ebizmba.com/articles/blogs
- ↑ http://theweek.com/article/index/255964/the-psychology-of-video-game-addiction
- ↑ http://www.howtogeek.com/186267/the-3-easiest-ways-to-video-chat-online-or-on-the-go/#
- ↑ http://gilc.org/speech/osistudy/censorship/
- ↑ https://www.aclu.org/free-speech/censorship
- ↑ http://www.rfa.org/about/help/web_access.html
- ↑ https://www.torproject.org/
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_privacy
- ↑ http://www.multicians.org/fjcc6.html
- ↑ http://www.cnet.com/how-to/five-smart-ways-to-keep-your-browsing-private/
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proxy_server
- ↑ http://www.foxnews.com/tech/2013/09/05/google-seeks-to-dismiss-gmail-privacy-lawsuit-says-it-has-right-to-scan/
Security
Unauthorized Access and Control Systems
[edit | edit source]
A Firewall is a type of security system that creates a wall that checks all incoming and outgoing messages to ensure only authorized traffic goes through. There are many different forms of this application such as Norton[1] and Windows Security Essentials.[2] Another way to protect your information is through encryption. Encryption basically scrambles and makes any message sent unreadable to anyone who does not have a key. The key is then used to decrypt the scrambled message into the original format. Whenever you go to a website that has an 'S' after the HTTP that means it is a secure web page, meaning the entire web page is encrypted. Therefore, people hacking to your web browser cannot get you credit card number or SSN. One question that arises is, "Can't you just make every website a secure web page?". The simple answer is money, a site owner needs to pay someone to encrypt the site. Then to send the data takes up more bandwidth, and slows down traffic in general. Cheaper web hosts may provide secure security features and backup services but have limitations. Another form of protection is a VPN (Virtual Private Network). A VPN creates a link between the user and some other destination. In order to access the VPN you will need a username and password, in order to keep it more secure and to block out hackers.

Firewalls can work in a number of ways, but a couple types of firewalls are more widely used over others. The two most common firewalls are packet-filtering and proxy.
Packet-Filtering Firewall
- Advantages
- A packet-filter simply examines each packet to determine whether it is safe or not. After examining a packet, the filter will either allow in or block out the packet depending on if it’s safe or not.
- Packet-filters are common among routers, switches, wireless access points, etc.
- Disadvantages
- A disadvantage of using a packet-filter firewall is that some packets that are safe may be blocked by accident. This means that it is possible that parts of information could be missing due to a packet being blocked.[3]
Proxy Firewall
- Advantages
- Most Secure - direct connections are limited by packets being sent from one computer to the proxy, and then mirrored over to the computer on the receiving end.
- More secure decisions are able to be made in application settings through strong analysis.
- Disadvantages
- A disadvantage of a proxy firewall is that it can slow down the transfer speed of packets.
- While using a proxy firewall it is difficult for someone to figure out the location of where packets were sent from.[4]

The Internet was created as an open system for the free exchange of information. Due to the openness of an ideology, the Internet provides to “bad guys” the significantly greater opportunities for the penetration into information systems. Firewalls make it possible to filter incoming and outgoing traffic that flows through your system. The Firewall uses one or more sets of rules to check the network packets as they enter or exit through a network connection. Firewalls can be used to protect individual hosts or to protect an entire network; it may be built-in into the Operation System or installed separately. The network Firewalls are the more complicated systems, combined hardware and software. There is no universally accepted classification of firewalls. But according to the methods of deploying it is possible to identify three following types of them.
- A filtering router is a router or server running on a program that is configured to filter incoming and outgoing packets. The filtering of packets is done on the basis of the information contained in TCP and IP packet headers.
- Firewalls based on session layer gateways. This type of router is a repeater for TCP connections. The gateway receives specific service requests from authorized clients and establishes a connection to the destination after verifying the requested session.
- Firewalls based on application layer gateways. To protect against some of the vulnerabilities inherent in filtering routers, the firewall should be used by applications to filter connections to services, such as Telnet and FTP. Such applications are called proxy services. Such gateways eliminate direct interaction between the client and authorized external hosts. The gateway filters all incoming and outgoing packets at the application layer. Application layer gateways facilitate protection; because interaction with the outside world is achieved through a small number of authorized applications that have complete control over all incoming and outgoing traffic. Note that application layer gateways require separate applications for each network service. These categories can be thought of as the basic components of a true firewall. However, these components reflect the key features that distinguish a firewall.

Biometric Access Systems identify an individual based on their fingerprint, iris, or facial features or other unique physiological characteristic. Keystroke Dynamics recognize an individual's personal typing pattern to authenticate the user as he/she types a username or password. Fingerprint readers and retinal scanners isolate an unchangeable property in an individual in order to identify them and offer high security based on these measures. They are typically used to control access to high risk facilities such as government property, prisons, and corporate headquarters. Fingerprint scanners have also been equipped into laptops in order to offer a higher standard of protection in securing personal files. In the same way, a person can download face recognition software onto their laptop as well. Because biometrics are entirely unique to the user, they are extremely accurate. In the same way no two people will have the same fingerprint, a persons facial features and iris' are as equally unique. In fac the odds of two person with same features is about 1 in 10^78 power.[5]
See [Wikipedia:Firewall (Networking)]

Identification Systems are a type of Access Control System that reassures whoever wants to access your system has authorization. It is a great tool to ensure the safety and privacy of users and are useful for everyday computers and accounts, business accounts, and much more.[6]
Possessed Knowledge Access Systems use passwords based on information only the user should know. Downsides to this system would be the ability to forget this information or for it to be found out by someone who should not know.
Cognitive Authentication Systems require users to think of their answers to certain personal questions such as their first pet, where they were born, where they have been on vacation, etc. The disadvantages to this system are the same as Possessed Knowledge Access Systems; with a lapse of time a person is more likely to forget their answer to a security question, especially if it had multiple answers.
Possessed Object Access Systems are a way to identify you with a physical object such as a keycard or badge.
Access Control Systems link up to different types of readers that have the ability to hold data and retrieve it when needed. Some may even have function buttons that let them collect different data used for timing and attendance purposes.

Many WI-FI connections are unfortunately left unsecured. This allows for any individual with a WI-FI compatible device to potentially piggy back the network. Once an individual is connected to a network, most devices connected to that network become available for a skilled hacker to view. This leaves an opening for many possible risks, especially if that network has a high traffic of sensitive information or data.[7] Some war driving software exists which allows a user, usually with a portable device, to identify many unsecured networks in a short amount of time. This gives a hacker to identify a large number of potential targets. Cyber-Crime has become increasingly prevalent over the years. Hackers are notorious for the various crimes they commit. Using malicious software, a skilled hacker is capable of stealing credit card numbers, bank account numbers, and other personal information, some of which make it possible for them to even steal identities. Using a program such as a keylogger, a hacker can monitor keystrokes without the individual knowing, allowing them to acquire sensitive information such as a credit card number, social security number, bank account, or password. A skilled hacker with an understanding of web design can create a phishing website and acquire account information from unsuspecting website visitors.[8]
Public Hotspot Safety
[edit | edit source]
Public hotspots are public networks, usually found within buildings such as restaurants, airports, and hospitals that allow a free or fee-based wi-fi connection to nearby users. Because these hotspots are public, it is beneficial to take certain precautionary measures when using them. Some of these safety measure include, disabling your computer automatic wi-fi connection feature. Many modern computers will automatically connect to any available wi-fi networks and it is important to be aware of this. Also, using a firewall can protect connections from working in the opposite direction. Instead of your computer connecting to the wi-fi, there is a chance that other softwares or devices that are perhaps malicious will try to access your computer through the network. Also, you should avoid viewing or inputting personal information while using a public hotspot. Avoid online shopping which requires a credit card as well as using passwords which can link to sensitive accounts. If you are viewing and inputting personal information then try using a virtual private network through the public hotspot which will avoid others from accessing your data. Other precautions include turning off file sharing, using antivirus software, and watching to see if others are trying to look at your computer screen within the public area.[9]
Computer Sabotage
[edit | edit source]Malware
[edit | edit source]
Malware is a term for unwanted software that gets installed on a user’s computer and performs malicious tasks. It can be as simple as pop-up windows containing advertising, otherwise known as Adware, or it can cause significant damage in the form of a Virus. A Virus is a program that can replicate itself and spread to other computers by inserting its own code, wreaking havoc along the way. There are different types of computer viruses that can cause different kinds of damages to a computer. Another form of Malware is Spyware. Spyware can track a computer user’s web browsing habits, obtain private information, and transmit that information to advertisers without the user’s knowledge.
Unfortunately, without adequate protection, it is rather easy for a user to inadvertently allow malware installation. It can be as simple as clicking the wrong box in a pop-up window on a website. Protection from malware is available through various security software programs. When first purchasing a computer, it may have security programs already. Often times, if a computer is already infected, it can block anti-malware apps. One of the benefits of Malwarebytes is that it can be installed even a PC already has malicious programs on it.
Botnets and Computer Viruses
[edit | edit source]
A botnet is a large group of computers that are ran on multiple bots that have been taken over; botnets are a serious threat to computer users because of their devious ways of taking over computers. At the time, computer owners did not know their computers were being altered. Botnets are commonly used for DDoS attacks, click-fraud, phishing campaigns, key logging, and host malicious web sites. There are warning signs a computer user should be aware of if he or she's computer is apart of a botnet. For example, the computer will be extremely slow, one will receive emails accusing he or she of spam, and the computer user will have email messages in his or her's outbox that was never sent. botnets can be controlled by using command and control software.[10] Also, a malware is any type of deleterious software. A computer virus is a common type of malware that ruins computers. A virus can attach itself to programs so when the program runs, the virus will also run. There are many harmful effects that could come with a computer virus. For example, a virus could delete important data, send out fake emails, and could possibly delete the information that contains on the hard drive. If a computer does becomes infected, you are able to remove it with antivirus softwares. It is not impossible to remove viruses, but it is beneficial to have the software before the problem occurs.[11]


Although computer viruses in the past were sometimes designed to create confusion and mischief, more recent viruses have been designed to inflict much more serious damage. The perpetrators of creating such viruses are more often working for foreign governments or intelligence agencies. In recent years there have been several viruses that have become well known due to the large amount of damage they caused. One such virus was called Conficker Virus and affected Windows-based Pc’s in 2009. This worm crawled through millions of computers which created an immense botnet that was able to steal financial information and data. The virus is still affecting computers today. Another well known virus was called agent.btz and occurred in 2008. This virus spread through infected thumb drives and was found on Pentagon computers. It was believed to be the work of foreign spies, and lead to the creation of U.S. Cyber Command, an agency created to battle cyber war. PoisonIvy, another computer virus launched in 2005, allowed the attacker to control the infected user’s computer. This malware is known as remote access Trojan. It allows the hacker complete control of a computer. Once control is gained, the hacker could manipulate files and even get access to the computers speaker and webcam. PoisonIvy affected both defense and chemical industries in the West. Computer viruses are a serious threat. With the world relying on computers for everything from personal use to national defense, it is vital that computers be safeguarded against viruses. The next section goes on to describe security software.[12]
Data, Program or Website Alteration
[edit | edit source]
Alteration attacks could take many different forms and occur when someone makes unauthorized modifications to code or data, attacking its integrity.[13] Alteration attacks have a range of consequences such as altering, destroying, suppressing, or stealing output, usually to conceal unauthorized transactions.[14] For example, students are changing grades, employees are altering or deleting corporate data as well as hackers changing social networking accounts and posting statuses on victim’s behalf. Many politicians like French President Nicolas Sarkozy whose Facebook page was hacked in 2011[15] are under website alteration attack. Alteration attacks can happen to anyone even the Government. In 1996 U.S. Central Intelligent Agency’s website was altered by Swedish hacker and in 1998 ;) The New York Times’ website was hacked.[16] Although people may feel helpless against these attacks, victims of sabotage have the law on their side. A person who knowingly, willfully and without authorization creates, alters or deletes any data, information, image, program, signal or sound contained in any computer, system or network which, if done on a written or printed document or instrument is guilty of forgery.[17] In 2012, the IC3 (receives, develops, and refers criminal complaints of cybercrime) received and processed 289,874 complaints, averaging more than 24,000 complaints per month. Also, unverified losses reported to IC3 rose 8.3 percent over the previous year.[18]
Security Software
[edit | edit source]Security software (also called as antivirus) is a program that runs alongside other programs on a computer to try and prevent viruses from penetrating into the system. If security software does not prevent the virus with its defensive properties, then it can detect a virus and detect the user. Most viruses can be removed by security software, but if there is one that cannot be removed, the software will “corner” the virus so that it cannot ruin any other areas in the computer system. Viruses are a big problem for every computer that uses the internet, no matter what type of activity is done on the internet. Viruses can be used for theft, corruption of data, destruction of data, or system failure. Operating systems nowadays have built-in antivirus software such as Windows Antivirus. It is a great feature for those who don't want to spend money on protection, in fact, for most people the basic antivirus software that comes with the operating system is all they need.
Online Theft and Fraud
[edit | edit source]Identity Theft
[edit | edit source]

Identity theft is when someone steals others identity in order to gain access to their bank accounts and possibly rent apartments or take out loans in that persons name. They then use their credit cards to make purchases. It usually begins when someone gets the name, address, and social security of someone from thrown a discarded document, usually mail. They can also get people’s information form the Internet. Identity theft is typically grouped into two subcategories. One is true name identity theft and that is when the thief uses another person’s information to open new accounts. The other kind is account takeover, which is when the thief uses someone else’s personal information to gain access to their existing accounts.[19] There are different techniques such as skimming and social engineering.
- Skimming is when the thief uses a device that reads and stores credit and debit card numbers and stores them for later retrieval by the thief.
- Social engineering is when you pretend to work at a place (say at a telecommunication company or bank) and ask people for their information.[20]
- Thieves rummage through garbage, trash in business, public dumps to get what they are looking which is someone’s personal information.
Some good indicators that your account identity has been stolen are if there are withdrawals that you can’t explain, not getting bills in the mail, refused checks, IRS contacting you, bills received that you are not aware of, and if your health plan will not cover you. All of these are big indicators that your identity has been stolen. It is important to be aware of bank transactions to be cautious of these thieves. There are certain types of Identity theft as well. Tax related would be one of them. If a Social Security number is stolen that can be used to get a tax refund or job. If you get paid by someone you do not know or find more than one tax return those would be big indicators that someone stole from you. Contacting the right people immediately would be the first thing to do in any situation dealing with identity theft. The IRS can help if a Social Security number has been stolen and they can protect the account. Children can also have their Social Security number stolen so it is important to keep that information private and on file.[21]
Phishing
[edit | edit source]Scammers use email or text messages to trick you into giving them your personal information. They may try to steal your passwords, account numbers, or Social Security numbers. If they get that information, they could gain access to your email, bank, or other accounts. Scammers launch thousands of phishing attacks like these every day—and they’re often successful. The FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center reported that people lost $30 million to phishing schemes in one year. But there are several things you can do to protect yourself. Scammers often update their tactics, but there are some signs that will help you recognize a phishing email or text message. Phishing emails and text messages may look like they’re from a company you know or trust. They may look like they’re from a bank, a credit card company, a social networking site, an online payment website or app, or an online store. Phishing emails and text messages often tell a story to trick you into clicking on a link or opening an attachment. They may
• say they’ve noticed some suspicious activity or log-in attempts
• claim there’s a problem with your account or your payment information
• say you must confirm some personal information
• include a fake invoice
• want you to click on a link to make a payment
• say you’re eligible to register for a government refund
• offer a coupon for free stuff
If you get an email or a text message that asks you to click on a link or open an attachment, answer this question:
Do I have an account with the company or know the person that contacted me?
If the answer is “No,” it could be a phishing scam. If you see them, report the message and then delete it.
If the answer is “Yes,” contact the company using a phone number or website you know is real. Not the information in the email. Attachments and links can install harmful malware.
If you think a scammer has your information, like your Social Security, credit card, or bank account number, go to IdentityTheft.gov. There you’ll see the specific steps to take based on the information that you lost. If you think you clicked on a link or opened an attachment that downloaded harmful software, update your computer’s security software. Then run a scan.
If you got a phishing email or text message, report it. The information you give can help fight the scammers.
Step 1. If you got a phishing email, forward it to the FTC at spam@uce.gov and to the Anti-Phishing Working Group at reportphishing@apwg.org. If you got a phishing text message, forward it to SPAM (7726).
Step 2. Report the phishing attack to the FTC at ftc.gov/complaint.
Pharming, Drive-by Pharming, and Online Auction Fraud
[edit | edit source]Many people today are victims of identity theft. Another type of fraud or scam is called Pharming. Pharming is usually a fraudulent domain name intended to redirect a website’s traffic to another “trick” website. Pharming can be conducted either by changing the hosts file on a victim’s computer, or by the exploitation of a vulnerability in DNS server software.[23] Sometimes this happens via email. The hacker gets ahold of the user’s email address and sends the code or website to the specific user. Once the user receives and opens the email, the hacker can receive the user’s information. Pharming usually happens most often with DNS servers at a company with a common and well-known Web site. The hacker can change IP addresses intended for the company URL. Then the company URL is routed to the “poisoned” URL, which then takes over the Web server. This method of pharming is useful to the hacker because the “poisoned” Web site is usually made to look exactly like the company Web site. Once the user logs in, the hacker captures the username and password for the first time. The user receives a login message error and is then returned to the original company Web site.
Drive-by Pharming is a little more recent. This method is used by logging into the user’s personal routers by using a common password that a script within a website can run. When it is accessed, the information on the router can be modified to suite the hacker.[24]
Online auction fraud happens when a payment online goes to the seller, but the item is never delivered. For instance, if a buyer wants to make a bid online and buy tickets to a show or a concert, the buyer pays the seller for the tickets, and the seller never sends them. Many people are scammed each year and need to be careful with who they are trusting over the Internet.
Ransomware
[edit | edit source]Ransomware are programs that are designed to encrypt a user's PC and demand payment for the access of the files. Often these come into the user's PC through means described earlier in this article. The user will be forced to pay the ransom demanded by the program author (generally) though a virtual currency like Bitcoin which makes it hard for police to track the criminal.
Unfortunately, in this case, there is little hope of recovery; many ransomwares do not release free decryption programs. Bleeping Computer is the best place to go for help if you have been infected by one.
The problem is especially acute for corporates: many have paid over $50,000 to restore vital information affected by the ransomware.[25] The best way to protect against ransomwares is to take frequent backups; that way, if you do get infected, you can easily restore from your backups.
Protecting Against Online Theft and Fraud
[edit | edit source]Protecting Against Identity Theft
[edit | edit source]Just as the Internet is always evolving for good, there are also constantly scheming e-criminals hoping to take advantage of those who aren't careful with their online identities. Identity Theft is one of the scariest things that can happen to a person, especially if they don't have a strong friend or family base to help convince the proper authorities of their true identity. There is not one universal way to protect yourself from identity theft; instead, there are a number of steps you should take to keep yourself fully protected. The first thing you can do is be responsible with your bank accounts and credit cards. If you're checking your balance every day, you will be quick to see if there are any suspicious discrepancies occurring. It is essential to download your bank's mobile application, so you can get alerts on all of your transactions. [26] The next important step to protect against identity theft seems simple but can be easily overlooked: do not give out your personal information on the internet. This includes phone numbers, addresses, or anything else that hackers could potentially trace back to something you hold valuable. Some individuals can be targeted by thieves through fake emails and text messages who urge them to give up their information. You can protect yourself from identity theft is being wary of your mail. It is very easy for an e-criminal to send you a destructive link in an email that looks like it came from one of your friends, where one small click will lead you into a world of pain. Just follow these few rules and you will be doing fine online. One of the most easiest ways to protect yourself is to create a long, strong password. Creating a difficult password will prevent thieves from hacking into your personal information.
Avoiding Phishing E-mails
[edit | edit source]Due to the advantage taken of today’s improving technology, phishing has emerged as one of the most damaging forms of identity theft. Using very convincing and persistent language, e-criminals are able to trick millions of users into revealing confidential information over the Internet. As mentioned earlier, to lure people in to clicking an attached link, e-criminals tend to steal the identity of a legitimate and well-known company to write a very “important-sounding” e-mail, solely for the purpose of tricking the reader into thinking the contents of the e-mail really are significant. Nonetheless, however urgent the e-mail may seem, it is actually designed to steal your money! A typical phishing e-mail will usually consist of: spelling errors, links, threats to make the content seem urgent, and a popular company name to sound reliable. If examined carefully, some phishing expeditions may be fairly easy to spot, due to the poor spelling and grammar used, making it obvious that the message is not from a legitimate company. The link in the e-mail is used by the cybercriminals to install malicious software on your computer, ultimately enabling them to steal personal and sensitive information off of your computer. The e-mail could also even ask you to provide personal information, such as your bank account number, credit card number, or your Social Security Number; this should automatically be a red flag for the recipients because an authentic business would never request such information in any way other than in person. Therefore, if one is alert and careful about the content they receive in an e-mail, they can ultimately help protect their identity and their money, even if the e-mail seemed rather urgent.

The act of a phisher setting up a Web site that appears to look like the legitimate business is an act called Web site spoofing. Phishing emails can be sent to a wide group of people or can be personalized and sent to one person. This more targeted trend of phishing is called spear phishing because it targets a specific individual. A phisher may gather personal information from a networking site and send an email to a particular individual in order to convince the recipient that personal login information or account information is needed. Phishers may also do something that is called typosquatting, which is setting up spoofed Websites with addresses slightly different from legitimate sites in the hopes that a user would supply login information via the spoofed site when they arrive. Another form of online threats include pharming. Pharming is another type of scam that uses spoofing. With pharming, the criminal reroutes traffic intended for a commonly used Web site to a spoofed Web site set up by the pharmer. The pharmer makes changes to the DNS server. The DNS server is the computer that translates URLs in to the needed IP addresses to display the Web page corresponding to a URL. A pharmer will usually target company DNS servers. Lastly, online action fraud can also be a concern for Internet users. This threat occurs when an online auction buyer pays for merchandise that never is delivered.[27] [28]
Digital Certificates
[edit | edit source]
One way of protecting yourself from online thefts or frauds is by looking for a digital certificate when browsing the Web or looking through e-mails. A digital certificate is granted by Certificate Authorities, which prove to the person that the website they are accessing is secure. A digital certificate binds the owner of a website to a specific pair of electronic keys, one being public and the other private. This allows the owner of the certificate to encrypt their files and e-mails and provides the user with the knowledge that their actually is an owner to the website that they are on. A digital certificate tracks who sends an email and who receives an email. This can protect users from giving away their credit card numbers to unprotected websites that try to scam people of their money. A digital certificate can either be an SSL or EV (Extended Version) SSL. The SSL digital certificate is the ordinary certificate that still requires an application and verification process while the EV SSL requires a more in-depth verification process. For users, an EV SSL digital certificate indicates that it is more secure than just an SSL digital certificate, while both of them are considered to be safe. This can be represented by the fact that when you enter an EV SSL webpage, the address bar turns green and for an SSL webpage it doesn’t change color at all. A digital certificate, in general, is definitely a good security advisor for users on the Internet.[29]
The Safety of Using PayPal
[edit | edit source]
Internet users have to be very cautious of the information they put on the internet. PayPal seems to be a popular e-commerce business that many people use and willing give their private information to. Is this payment processor to be trusted? PayPal makes the lives of everyday internet consumers much easier. Its secure server stores your credit card information so payment over the internet is more efficient. Not much effort has to be put in by the individuals that use this payment processor. Other accounts require a vast amount of paper work to be signed beforehand.[30] One drawback to using PayPal is that there is a long list of rules the users must abide by, and if a user breaks any of these rules their money could be locked for up to six months while under investigation. An interesting feature that was added to PayPal in 2006 was an additional security option. Instead of only entering a login id and password, PayPal users can choose to type a six-digit number code in as well. This lowers the risk of malware bots trying to hack into the account. There is a fee associated with this added security measure. Users might be discouraged to protect their accounts because of this additional fee. They should still take caution when it comes to entering personal information into PayPal. Users should also be cautious when placing orders online using PayPal because they're at a greater risk for their credit card information to be stolen.
The Safety of Digitally Storing Cards
[edit | edit source]
New forms of paying have appeared or rather a new way of paying thanks to companies like Google and Apple. Apple Pay and Android Pay are ways of paying wherein the user puts their credit cards or debit cards into their phones and can then use their phones or smartwatches to use their credit cards instead of bringing the physical cards with them. You can also use in app purchases by using your fingerprint on the latest Apple phone. With the phone’s it uses biometrics to make sure the owner is using Apple Pay and with smartwatches they use passcodes. But the real question is this new way of paying secure? Apple claims that it is so. In fact, they claim that it is actually more secure and that they will never upload the details on your cards to their servers. In fact, if your smartphone or smartwatch was ever stolen, you have the ability to revoke the information on your smartphone or smartwatch. Also Apple creates a Unique Device Account Number in order to protect your purchases when making transactions. However, there are those who do believe that this may not be safe. The best way to not have to deal with the risk is to not use Apple Pay. There are also applications like Snapchat and Venmo in which you can send money using your credit card information. This is a fast way to receive money but can be risky. A thief can login to your account and steal your information. All in all, it is not safe to store any personal information [31]
Basic Home Network Security
[edit | edit source]
Many people have wireless networks in their homes, but they may not necessarily keep these networks as safe as they can or should. If somebody else accesses your network without your knowledge or consent, then they may do things on that network that you do not desire, they can use up your allotted data usage, and, most concerning, they may be able to get your personal information. Therefore, people with wireless home networks should take precautions to keep them secure. First, networks should always have some sort of a password to keep them safe; a network should never, ever be left unsecured, because then absolutely anybody within range can go on it. Typing any password at all is better than nothing, since it'll deter people from mooching, but—as is always the case—it is not wise to go with a predictable password such as the network name, 'password', 'Internet', etc. Something that is meaningless on the surface level but has a deeper meaning for you is a better way to go; for example, the first letters of words in an individual phrase that only you will remember. Also, to add yet another layer of security, you can make it so that your network is not available to other users by default but instead they must know the network name; this way, for a hacker to gain access, they would have to guess both the ID of the network and the password, which is highly unlikely. With these incredibly simple steps, one can make their network incredibly secure compared to one that has absolutely no measures preventing access from anybody within a certain physical proximity.[32]
Personal Safety
[edit | edit source]Cyber-bullying
[edit | edit source]This is a new way of bullying especially for the amount of social networks and how it has influenced our society today. Unfortunately, it happens 24 hours of the day and anything can be posted or distributed anonymously in which it could be difficult to track where the bullying is coming from. And as everyone is informed these days, once something is on the internet, there is no way to permanently delete the comment after it has been sent. It happens when individuals are bullied through electronic technology. For example, you can cyber bully over text message, emails, rumors send through any type of social networks. There’s no way to prevent an individual from making a comment that could be known as the start of cyber bullying, but simply ignoring or reporting the comment to either a parent, friend or any type of guidance person could benefit you most in not having the bullying continue. To elaborate, you can simply block the individual that had started the commenting and keep any type of evidence of the bullying for future documents in case it gets worse. A last important note is to recognize the signs of attitudes if a student were to be cyber bullied; some reactions are abusing drugs and alcohol, skip school, receive poor grades and have lower self-esteem.[33]
Activity: Delete Cyberbullying - Preventing Cyberbullying
Cyberstalking
[edit | edit source]
Cyberstalking is the use of the internet, email, or other electronic communications to stalk another person. This occurs when there is a continuous pattern of malicious or threatening activity from an individual. Cyberstalking is considered the most dangerous form of harassment over the internet and is punishable by law. Depending on the state, punishments can range from misdemeanors to felonies.[34] Victims of cyberstalking can be targeted by strangers online who find personal information somewhere on the web or by more personal colleagues or individuals who know the person they are targeting well. Unfortunately, cyberstalking can move beyond the computer and become a problem in the real world if the stalker discovers or knows how to find the individual personally. This is a very serious issue and should be brought to law enforcement agencies or even the FBI. It is important to not give away any personal information that can be used to stalk you and to ensure that you trust anyone or anywhere that you may be giving personal information to online. The best solution to stop cyberstalking is to not respond at all or to change the information on what ever resource the cyber stalker is using to harass you.[35]
Online Pornography
[edit | edit source]
Along with the lifespan and constant evolution of the Internet came the controversial issue of online pornography. Though pornography has unfortunately been around on paper for centuries, electronic access has made it much easier, quicker, and more convenient for any individual to get ahold of it at any given time. With this online access comes a much bigger and more controversial issue. It has introduced people, especially children, to new and substantial safety issues.
Though child pornography is banned and illegal, there is a considerable amount of it being circulated and passed throughout the Internet. With the link that has been made between this horrible content and child molestation, it is reasonable to be concerned about the spike that this will bring. Not only does it encourage sick people to do horrible things, but the computer also gives them an outlet to meet and dishonestly introduce themselves to children. It is unfortunate that today we have to be concerned about what could come from our children talking to people on the Internet; however, it is important that we voice these risks and make sure that parents take every precaution possible to keep their children from ever experiencing these horrific possibilities. [36]
Protecting Against Cyberbullying, Cyberstalking, and Other Personal Safety Concerns
[edit | edit source]Safety Tips for Adults
[edit | edit source]While it may seem unnecessary to state, the Internet is accessed by not only those with good intentions but also those who can pose a threat in a variety of ways. It is important to be aware of this fact because it is quite easy to forget how vast of an entity the Internet is and countless masses who use it daily. This makes for the task of safeguarding information from those who mean harm an important responsibility. Some of the ways one can prevent cyberbullying, cyberstalking and other issues are by using names that are gender-neutral. This hides the identity of the user, and this is important for female users because unfortunately they are more likely to be targets compared to male users.[37] Also, one should not give phone numbers, addresses and other personal information to strangers for obvious reasons. A way to prevent cyber bullying is to not be a cyber bully yourself. Bullying people online is not only unethical but it will increase the number of users targeting you.
Safety Tips for Children and Teens
[edit | edit source]Monitoring how children and teenagers use the Internet through the computer, smartphone, game console, etc. is the most important step in protecting them. It is recommended to place certain restrictions on how they use the Internet so that they do not access certain sites that might make them more susceptible to dangerous individuals or certain sites (e.g. adult sites). There are certain softwares parents can download to monitor what their children are doing online. There are also softwares to block inappropriate websites which is more common to find in children's schools. It is also important for older teens to understand the potential ramifications, including not only personal but also legal issues, that can arise from sending explicit messages or pictures via text messaging. Although teenagers may think that they have deleted text message or a picture, someone can still obtain the image.
Using Your Computer In A Safe Way
[edit | edit source]One of the best ways to stay safe online is to make sure you have your computers operating system and antivirus / anti-malware software update and set scanning schedules however the most important part of protection is user awareness. A recent blog post from Antivirus Talk details a list of good computer rules. Remember the majority of the time the user has allowed a virus onto the system. [38]
- Always run antivirus software (at least the built-in Windows Defender)
- Don’t go To Websites You don’t Know
- Don’t open Emails if you don’t know where they are from
- Use A different password for everything
- Keep your system up-to-date
- Don’t install unknown programs
- Don't send/give out your passwords
- Lock your computer when you are not by it in a public area
- Don't leave your computer in your car or lying around
By just following these rules you have the best chance of a safe journey online.
Network and Internet Security Legislation
[edit | edit source]
New legislation is frequently introduced to address new types of computer crimes. Unfortunately, it's difficult to keep pace with the rate at which the technology changes. Along with this, there are both domestic and international jurisdictional issues because many computer crimes affect people in geographical areas other than one in which the computer criminal is located. Regardless, computer crime legislation continues to be proposed and computer crimes are being prosecuted. Some of the most important and impactful laws follow: Computer Fraud and Abuse Act of 1984- Makes it a crime to break into computers owned by the federal government. Identity Theft and Assumption Deterrence Act of 1998- Makes it a federal crime to knowingly use someone else's means of identification, Social Security number, or credit card, to commit any unlawful activity. Homeland Security Act(2002)- Includes provisions to combat cyberterrorism. One of the most famous cases of a cyber crime happened quite recently, the criminals charged in 2013. Five cyber criminals were responsible for a hack that targeted companies more than $300 million. They did this by stealing usernames and passwords, personal identification information, credit card and debit card numbers through secure computer networks. The criminals were sentenced up to 20 years in prison, depending on the amount stolen and involvement with the hacking group.[39]
Review
[edit | edit source]Important Terms
[edit | edit source]- antivirus software:[40]Software used to detect and eliminate computer viruses and other types of malware.
- biometric access system: An access control system that uses one unique physical characteristic of an individual (such as a fingerprint, face, or voice) to authenticate that individual.
- bot: A program/service that does tasks which would be tedious to do do manually. However, it can also be used for criminal activities, like for DDoS purposes.
- botnet: A group of bots that are controlled by one individual.
- computer crime: Any illegal act involving a computer.
- computer sabotage: An act of malicious destruction to a computer or computer resource.
- computer virus: A software program installed without the user’s knowledge and designed to alter the way a computer operates or to cause harm to the computer system.
- computer worm: A malicious program designed to spread rapidly to a large number of computers by sending copies of itself to other computers.
- cyberbullying: Children or teenagers bullying other children or teenagers via the Internet.
- cyberstalking: Repeated threats or harassing behavior between adults carried out via e-mail or another Internet communications method.
- denial of service (DDoS) attack: An act of sabotage that attempts to flood a network server or a Web server with so much activity that it is unable to function.
- digital certificate: A group of electronic data that can be used to verify the identity of a person or organization; includes a key pair that can be used for encryption and digital signatures.
- digital signature: A unique digital code that can be attached to a file or an e-mail message to verify the identity of the sender and guarantee the file or message has not been changed since it was signed.
- dot con: A fraud or scam carried out through the Internet.
- encryption: A method of scrambling the contents of an e-mail message or a file to make it unreadable if an unauthorized user intercepts it.
- firewall: A collection of hardware and/or software intended to protect a computer or computer network from unauthorized access.
- hacking: Using a computer to break into another computer system. (I bet you need this for class.)
- identity theft: Using someone else’s identity to purchase goods or services, obtain new credit cards or bank loans, or otherwise illegally masquerade as that individual.
- malware: Any type of malicious software.
- online auction fraud: When an item purchased through an online auction is never delivered after payment, or the item is not as specified by the seller.
- password: A secret combination of characters used to gain access to a computer, computer network, or other resource.
- pharming: The use of spoofed domain names to obtain personal information in order to use that information in fraudulent activities.
- phishing: The use of spoofed e-mail messages to gain credit card numbers and other personal data to be used for fraudulent purposes.
- possessed knowledge access system: An access control system that uses information only the individual should know to identify that individual.
- possessed object access system: An access control system that uses a physical object an individual has in his or her possession to identify that individual.
- private key encryption:A type of encryption that uses a single key to encrypt and decrypt the file or message.
- public key encryption: A type of encryption that uses key pairs to encrypt and decrypt the file or message.
- secure Web page: A Web page that uses encryption to protect information transmitted via that Web page.
- security software: Software, typically a suite of programs, used to protect your computer against a variety of threats.
- spear phishing: A personalized phishing scheme targeted at an individual.
- Trojan horse: A malicious program that masquerades as something else.
- two-factor authentication: Using two different methods to authenticate a user.
- unauthorized access: Gaining access to a computer, network, file, or other resource without permission.
- unauthorized use": Using a computer resource for unapproved activities.
- virtual private network (VPN):A private, secure path over the Internet that provides authorized users a secure means of accessing a private network via the Internet.
- war driving:Driving around an area with a Wi-Fi-enabled computer or mobile device to find a Wi-Fi network to access and use without authorization.
- Wi-Fi piggybacking:Accessing an unsecured Wi-Fi network from your current location without authorization.
Questions
[edit | edit source]Choose the correct option
[edit | edit source]1. Which of the following is an example of something used to gain access to a possessed object access system? [41]
a. password
b. smartcard
c. username
d. pin
2. The most common type of possessed knowledge, comprising secret words or character combinations associated with an individual, are:
a. security keys
b. passcodes
c. usernames
d. passwords
Fill in the blanks
[edit | edit source]3. Driving around looking for a Wi-Fi network to access is referred to as ________.
4. _______ access control systems use some type of unique physical characteristic of a person to authenticate that individual.
5. A(n) ____________ can be used at a Wi-Fi hotspot to create a secure path over the Internet.
6. A(n)____________ can be added to a file or an e-mail message to verify the identity of the sender and guarantee the file or message has not been changed.
7. ______________ identifies an individual based on their fingerprint, iris, or facial features or other unique physiological characteristic.
8. This type of theft/fraud is often targeted to social media sites because it is easier to find personal information on people.
True or false?
[edit | edit source]9. A computer virus can only be transferred to another computer via a storage medium.
10. An access control system that uses passwords is a possessed knowledge access system.
11. Using a password that is two characters long is an example of two-factor authentication.
12. Secure web pages use encryption to securely transfer data sent via those pages.
13. A virtual private link can be used at a Wi-Fi hotspot to create a secure path over the Internet.
Answers[42]
[edit | edit source]- B
- D
- War Driving
- Biometric
- Virtual Private Network or VPN
- Digital Signature
- Biometric Access System
- Spear Phishing
- F
- T
- F
- T
- T
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://us.norton.com/
- ↑ http://windows.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security-essentials-download
- ↑ http://www.networkworld.com/article/2255950/lan-wan/chapter-1--types-of-firewalls.html
- ↑ http://www.bullguard.com/bullguard-security-center/pc-security/computer-security-resources/how-proxy-firewalls-work.aspx
- ↑ http://www.biometricupdate.com/201308/human-recognition-systems-integrates-biometric-access-control-with-cscs
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Access_control#Access_control_system_components
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wardriving
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keystroke_logging
- ↑ http://us.norton.com/travel-hotspot-security/article
- ↑ http://www.ucalgary.ca/it/help/articles/security/awareness/botnets
- ↑ http://www.ucalgary.ca/it/help/articles/security/awareness/botnets
- ↑ http://www.smithsonianmag.com/ist/?next=/science-nature/top-ten-most-destructive-computer-viruses-159542266/
- ↑ http://www.sans.edu/research/security-laboratory/article/alter-code
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer_crime
- ↑ http://www.nydailynews.com/news/facebook-hackers-french-president-nicolas-sarkozy-resign-article-1.150369
- ↑ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/130595/cybercrime/235711/Sabotage
- ↑ http://law.justia.com/codes/nevada/2013/chapter-205/statute-205.481
- ↑ http://www.fbi.gov/news/pressrel/press-releases/ic3-2012-internet-crime-report-released
- ↑ http://money.howstuffworks.com/identity-theft.htm
- ↑ http://legal-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/identity+theft
- ↑ http://www.consumer.ftc.gov/articles/0040-child-identity-theft
- ↑ https://www.consumer.ftc.gov/articles/how-recognize-and-avoid-phishing-scams
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pharming
- ↑ http://highsecurity.blogspot.com/2007/02/pharming-and-drive-by-pharming.html
- ↑ US hospital pays $55,000 to hackers after ransomware attack|ZDNet
- ↑ http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/how-to-tech/how-to-protect-against-identity-theft2.htm
- ↑ https://www.fdic.gov/consumers/consumer/alerts/phishing.html
- ↑ http://www.microsoft.com/security/online-privacy/phishing-symptoms.aspx
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20160313023806/http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd361898.aspx
- ↑ http://www.xsitepro.com/the-pros-and-cons-of-using-paypal-as-your-primary-payment-processor.html
- ↑ http://www.express.co.uk/life-style/science-technology/591309/Apple-Pay-UK-Launch-Safe-Safer-Contactless-Credit-Debit-Card
- ↑ http://www.pcworld.com/article/130330/article.html
- ↑ http://www.stopbullying.gov/cyberbullying/what-is-it/index.html
- ↑ http://www.ncsl.org/research/telecommunications-and-information-technology/cyberstalking-and-cyberharassment-laws.aspx
- ↑ http://www.cyberangels.org/security/stalking.php
- ↑ http://www.popcenter.org/problems/child_pornography/
- ↑ http://www.cyberbullying.us/research.php
- ↑ http://www.antivirustalk.com/
- ↑ http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2013-07-25/5-hackers-charged-in-largest-data-breach-scheme-in-u-s-.html
- ↑ http://coursemate.cengage.com/CPReader/View/9781133114598/default.aspx?eISBN=9781133114598#53c50e83-32b2-46bf-8d09-fe73e2cb62b2
- ↑ http://coursemate.cengage.com/CPReader/View/9781133114598/default.aspx?eISBN=9781133114598#4dc6772a-b649-4893-be5d-6acb8ff8bead
- ↑ http://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/index.html?nbId=7345&nbNodeId=1013914#!&parentId=1013935
Multimedia
Web-Based Multimedia
[edit | edit source]Overview

Whether you know it or not, you have seen multimedia and you should be semi familiar with it. Multimedia is exactly what is sounds like, It refers to the literal combination of multiple types of media. If you go to humble bundle.com[1] you will see an excellent assortment of multimedia. You have a countdown, which is your animation, you have images of the games you can get. When you click on an image you will get an expansion showing you a description and an embedded YouTube[2] video. Now that you understand the basics you can see all of the different uses of multimedia in your favorite websites. While this sounds great and having multimedia will make any site better, remember too much of anything is not good.
Web-based multimedia, however, is a term used to describe the multimedia (sound, video, or animation, text and images) found within web pages. Similar to others, web-based multimedia pages display information requested by the user through hyperlinks. Multimedia web sites are interactive, often containing elements with which the visitor directly works. Examples of this would be playing or pausing a video clip or game, and controlling a 3D object. At one point, web-based multimedia was strictly limited as both computers and internet services were too slow to support it. Over time, the significant increase in computer and broadband connection speeds have Web-based multimedia possible, and the success of Web-based multimedia is growing rapidly. The vast majority of sites today feature some form of multimedia. For example, it is often used for advertising, as regular website content (TV shows and photos posted by TV networks or podcasts), informative videos of available products offered by companies, or as "user-generated content", such as videos uploaded to YouTube or pictures uploaded to Flickr. [3]
Web Based Multimedia Applications come in a wide variety and can be found all over the Internet. A website that contains more than one type of media is considered to be multimedia. Sites that contain sound, video, animation, and/or images alongside text fall into this category. Typically, these sites use multiple applications such as these to convey certain information to the viewer of the web page. Manufacturers might use photos and PDF based user's manuals to transfer key points of interest about their products to the viewers. In other cases, multimedia can be used as a teaching tool where visitors learn through instructional videos or a news site might use podcasts and television footage to update their readers through their websites. Images and sound are also employed by many musicians when visiting their sites alongside the text-based dates of their tour. Entertainment also plays a large factor in web based multimedia applications. With the rise of Internet video streaming, people can now watch their favorite t.v. shows when they have the free time to do so, and from anywhere there is an Internet connection. Websites like Netflix and Hulu use sound, video, and often thumbnail photo icons alongside their descriptive text of the shows available. Some things to keep in mind concerning these multimedia applications are Internet connection speed and bandwidth. Most of these video streaming websites; whether news, sports, or t.v. shows, etc. require a minimum broadband connection speed of 500Kbs for standard definition viewing. The minimum speed requirement increases as the definition increases and vice versa. Bandwidth plays an important role as well since some service providers put a cap on the amount of information that can be processed. Most "smart" phone service providers set a cap of 1Gb or 2Gb a month and charge additional fees if this ceiling is ignored. Considering that a standard definition, one hour t.v. show can be close to 200Mb, it is wise to pay attention to the bandwidth being consumed as this can rapidly add up.[4]

There are many advantages that web-based multimedia can offer. One of the biggest benefits of web-based multimedia is that it can address many different types of learning styles. For example, when being taught how to make a paper airplane, someone may prefer written instructions, while someone else may prefer picture instructions. Multimedia can offer picture instructions with captions in order to meet both people’s learning styles. Another advantage of web-based multimedia is that it can make information more enjoyable and interesting to a user. Text-only information can get very boring, but multimedia could be implemented in order to spice up a web-page. For example, when learning where countries lay on a map, a simple picture might not portray the information in an enjoyable fashion. With multimedia, an interactive map could be created and used instead of a picture. An interactive map may be a more enjoyable way for a user to learn the material due to the fact that they must engage with the multimedia. Along with web-based multimedia’s advantages come disadvantages. One disadvantage of web-based multimedia is that it can be very costly and time consuming.[5] Websites that use multimedia generally take more time and skill to develop than a text-based website. Businesses often hire someone to create and arrange multimedia on their webpages.[6]

Augmented Virtual Reality
Augmented Virtual Reality is the augmenting or adding-on of certain computer-generated elements to the real world usually through a display. Augmented Virtual Reality can be applied to many different types of technologies and industries and is currently growing within e-commerce. Some companies, such as IKEA are using the technology of Augmented Virtual Reality to give consumers a better view of how furniture will look in their home. Other uses include the application of Augmented Reality within the automobile industry. Certain manufacturers are utilizing the technology within windshields. This is known as Head-Up-Display and is used to allow drivers to see their MPH, fuel gage, and many other information that you would need while driving, without forcing them to take their eyes off the road. Another use of Augmented Virtual Reality is with Google Glass. Google Glass allows users to have all the features of a phone within a display on their glasses and with the use of voice commands. Also, some developments are being made to incorporate Augmented Virtual Reality within the medical field. Although Augmented Virtual Reality is a recent development, it is being used more and more within many devices and will possibly be a social normality within a few years.[7]
Multimedia Elements
[edit | edit source]The Five Multimedia Elements
[edit | edit source]
Text, image, audio, video, and animation are the five multimedia elements. The first multimedia element is text. Text is the most common multimedia element. The text expresses the information the developer is trying to get across to their viewers. Even though pictures grab the viewers’ attention, text is a good idea to include, as well, just in case the picture does not load. The second multimedia element is an image. An image catches the viewers’ attention much more quickly than just plain, old text. Almost every multimedia application contains images. The most common images are JPEGS and PNGs. Also, Photoshop and Paint.NET create high tech visual effects which are common with images. The third multimedia element is audio. Most of the time, audio files are deployed using plug-in media players. A few audio formats include RealAudio, MIDI, Wave, WMA, and MP3. The developer will compress the format to shorten the time. Before the file is downloaded, one can stream the audio. The fourth multimedia element is video. The web is the most common place where videos are seen concerning multimedia elements. A few digital video formats are Flash, MPEG, AVI, WMV, and QuickTime. Streaming digital videos can increase the speed of the playback. Developers use videos to hold on to the viewers’ attention. The fifth multimedia website is animation. Animation draws in the younger crowd. adobe flash is the most common tool for creating these animations. Animations are the most creative and fun multimedia element! [8]
Serif vs. Sans-Serif Fonts & Font Choice
[edit | edit source]
All fonts, or typefaces, are either serif or sans-serif. "Serif" is Latin for "with feet," while "sans-serif" is Latin for "without feet", and that is the difference: serif fonts have small lines, or serifs, at the bottom of the letters, as if the letters have feet. Sans-serif fonts lack these "feet."[9] Times New Roman is the most common and easily recognizable serif font, while the most common and recognizable sans-serif fonts are Arial, Helvetica, and Comic Sans MS. There is some disagreement about whether serif fonts are easier to read than sans-serif ones, or vice versa, but in general, serif fonts are preferred for large bodies of text, especially on physical, printed , while sans-serif fonts are preferred for smaller things, such as headlines, and electronic messages.[10] Even past the question of whether to use a serif vs a sans-serif font, one should be careful about which specific font one is using. Different typefaces carry different connotations. A potentially more formal font, such as Times New Roman, would not be suited to something more informal like an invitation to a young child's birthday party; likewise, an informal font like Comic Sans would be very inappropriate for formal messages. When choosing a font, consider the purpose of the message and the audience.
Video
[edit | edit source]
Video provides a powerful impact in a multimedia program. It starts with continuous event and breaks it up to frames, whereas an animation starts with frames. Video formats are made up of container and codec(s). The container describes the structure of the file like where the various pieces are stored, how they are interleaved, and which codecs are used by which pieces. A codec is a way of compressing the file to decrease file size, while maintaining quality.[11] Some of the most common video file formats are Audio-Video Interleave (.avi), Flash Video Format (.flv), Moving Picture Experts Group 2 (.mp2), Moving Picture Experts Group 4 (.mp4), QuickTime (.mov), and Windows Media Video (.wmv).[12] In multimedia applications, the digital video is gaining popularity because the video clips can be edited easily, it can be stored like any other files in the computer and the quality of the video can still be maintained, and the video can be transferred within a computer network which allows non-linear editing in any part of the video.[13] Just like in audio, in streaming video the traveling information is a stream of data from a server. In 2006, people watched more than a million streaming videos a day on YouTube.[14]
JPEG, GIF, and PNG Formatting
[edit | edit source]
GIF and PNG are two different formats which images are available in. GIF simply means Graphics Interchange Format and is typically used for animations and sometimes single images as well. The images are compressed or made smaller; they are using what is called loss-less data compression. This compression makes it so that the image does not lose quality even if it is compressed due to its ability to have uniformed color with well-defined edges. A GIF is not the best quality format for images because of its limit of colors, which is one of the reasons that PNG was created. PNG are Portable Network Graphics. Their ability to compress is higher quality and allows for alpha transparency, which is basically creating the image with a background so that it looks transparent either partially or fully.[15] They can store more color depth but also take up more space than GIFs in some cases. In cases where this does not apply it is because their ability to have better compression in 8-bit data ends up being smaller than GIFs.[16] PNGs are unlike GIFs because they do not support animations, and are a single-image based format.[17] These formats are used in many Web pages today and are both arguably as important.

The Joint Photographic Experts Group committee created the file format that is otherwise known as JPEG. JPEG is a technique and file format used to compress color images, digital photos, and other digital graphics. Many users who store photographs on their computer will recognize the JPEG file extension recognized as “.jpeg”, or “jpg”. The file size of a selected image can be optimized for different uses, otherwise known as editing a photo to the desired sizes. The file format does so by using a type of compression of the image known as “lossy compression”. The definition of lossy compression is defined as the ability for the image to decrease in file size, taking away a slight decrease in image quality. JPEG files are widely used by consumers as a way to save photos on their computer to view at their desire. However, a user may have interest in sharing these images through e-mail, or a website. As considering using a JPEG file on a website or through email, a user must consider the file size in comparison to the amount of quality of the image. For instance, if a user is interested in posting a photograph on a website of theirs, they must consider file size and formatting. Also, with e-mail, a user must consider the quality of the image they will be sending. The higher the quality of the image being sent, the larger the file size must be. If a user is sending this file over their cellular phone, it may require the use of more data to send a larger file size.[18]
Audio
[edit | edit source]
There are many different types of audio files, and the each have their of distinct advantages. The most ubiquitous audio file is the MP3. MP3’s have become the standard audio files on most devices and on most websites. The advantage of MP3 file over different formats is their small size. MP3 files can be compressed, as they do not contain the inaudible sections of an audio track. While this results in good quality audio, while taking up a small amount of space, in certain situation, audio quality can suffer. The compression of MP3 file can distort vocal sounds, and can result in a ‘tinny’ sound. Because, some computers, primarily Windows-based PC’s use WAV files to store audio files. These files are uncompressed, so they take up a large amount of space, but they are of better quality than most MP3 files. As most desktop PC’s have room to spare, better audio quality is substitutes for more space used. Another file type common on windows computers is WMA. This format is optimized for use by Windows Media Player. Is primary advantage is that is copyright protected, but it can only be used on Windows Media Player. Another common audio file is DCT. This type of file is encrypted, and used for medical applications where patient confidentiality is needed.[19]
Multimedia Web Design
[edit | edit source]Basic Design Principles
[edit | edit source]The main thing about designing a website is that the whole point is to create a site that is interesting and will bring customers or people to look at it. Not only that, but you have to keep it interesting; people don't want to see the same things on a website at all times. It needs to be updated and changed as time passes. Another important thing to remember is that many people aren't that tech savvy. It is important to keep the website somewhat simplistic. Confusing websites draw people away. It is important to make sure your webpages load quickly, which can be done by choosing multimedia elements carefully and to modify them as necessary, like optimizing photos to make them run as efficient as possible. Nowadays another important thing to consider when creating a website is whether or not people are going to be able to view it from other devices such as their phones, their tablets, or whatever else. It may be beneficial to also create a mobile version of the site. Its important to look at what browser people can use for this website. Some sites have certain features that can only be accessed by certain browsers, it is important to make sure to use features that work well on all common browsers. It would also be beneficial to use features that don't require plug-ins. When people visit a site they are not going to want to have to install something just to go on the site or to access something on the site. It is also important to look at the size of the page content.[20] You want to be sure that your information can be seen on all computer screens.

Web site design can be extremely time consuming and costly. Successful businesses and agencies typically have both the time and the money to have intricate web sites designed. However, for a company just starting out, those things may not be available yet. Fortunately, there are many sites today that offer free website design. Some great sites that offer this are Wix.com, Weebly.com, Yola.com and Moonfruit.com. This could be a great way for a brand new company or organization to be able to get their name out on the web and begin getting some recognition. These free sites make it easy for one who may not know much about web design, as they typically offer easy to use templates and offer step by step instruction along the way to guide one through the design process. Although the web design site is free, users will first have to purchase a domain name. These are available at companies such as GoDaddy, Register.com, Domaine.com and Dyn.com. After purchasing a domain name, it is time for the user to begin filling his site with content. The user has a great deal of freedom in customizing his site to contain the elements desired. Many of the sites mentioned earlier also provide tutorials to help get the site up and running. After the design of the website is complete, the creator can now publish it and get ready for some recognition. It is important for the creator to update the website often and to market the site as much as possible. For any organization or company that may be just getting off its feet, deciding to use a free site to do its web design might be a good option, and with so many sites offering this service, it seems silly not to.[21]
Using Flow Charts, Page Layouts, and Storyboards
[edit | edit source]When talking about website design, a flowchart is used to show how different web pages relate to each other. A flowchart is basically a map of the website. There can be links between the lines of the flowchart to take you where you want to go. When designing a website, you can make it as simple or as complicated as you want. Oftentimes, the flowchart is designed in the early stages of the website because it provides a good building ground for the website.[22] Page layout is used in the designing of a website. Typically people create two page layouts; one for the home page and one for all the other pages. This is when you design where you want the different logos, like the home page button, and its when you decide how visually exciting you want your website. While it’s important to make it visually interesting, it is also important to keep it simple so that it does not get too confusing.[23] Storyboards are also something commonly used in website design. Storyboards are a series of pictures that depict what is going to happen on each screen. They are typically used when creating something animated.[24]
How to Start a Storyboard
[edit | edit source]There are a few steps to take to make a great storyboard for a web site design. It is important to bring your ideas even if you think they are not that good. Next you need to draw them out on paper; One paper is faster and you can always toss it away if it doesn't look the way you want. Additionally it is good to use paper because on paper anyone can add to the design and you do not have to have a lot of experience making web sites. After drawing it out next is to find a focus from those drawings to make sure that each part of the website is completed. Following, take notes to see if there is anything that needs to be added. After that take the drawings that are completed and put them in a mind map to see the website more visually. Then critique the storyboard and make adjustments to the design. It is also important that other people look at it as well so you can various opinions on the storyboard.[25] When the storyboard is all finished make sure that the navigation, site structure, and content are done well. For navigation it is important to have everything at least a click away, at the maximum it should be 3. For site structure check if it is too complex and that there are visuals, glossary, table of contents, and or an index. The content should be understandable, creative, and flow together. Google.com[26]
Navigational Design Considerations
[edit | edit source]
While creating a Web site, it is important not to overlook small details. The structure of the site is the most significant part for easy navigation. Headlines and main menus need to be organized in a way that is understandable for users. Many experts and Internet users agree that it should only take up to three mouse clicks to return to the main page and to search more easily. Different forms that are used in Web sites include search boxes, drop-down menus, site maps, text-based hyperlinks, navigation bars, and menu tabs. Images can also be another hyperlink to transfer to another page on the site. It is crucial that the Web site has the same links in the same location as the previous page. Things would get confusing if the user had to look over each navigation button every time they entered a new area on the site. Long Web pages should be separated into shorter, more concise pages to avoid loading and scrolling. On many Websites today users will see “Back to Top” to navigate back to the top of the page, mostly on long Web pages. Most importantly, a link to the Home Page should be listed on every Web page according to the Web site.[27]
Access Considerations
[edit | edit source]Device Compatibility and Assistive Technology should be taken into consideration while creating a multimedia Web site. As our society grows with more ways to reach the Internet than just the computer, Web site creators need to be aware of the fact that the public is using their Web sites on Smartphones, Tablets, iPads, and much more. The layout may be different on these smaller devices than would a desktop computer. Sites are now creating multiple ways to work with any form of technology. With stricter disability laws being put into place, we have started to think about different ways to inform the physically disabled via the Internet on Web sites. Braille display [28] and screen readers [29] are just some of the newly advanced technology that can be used. Alternative text [30] can be used, which is a text description for a web page image. These text descriptions of images are valuable for vision impaired users of the web site.

Refreshable Braille Displays are an electronic device, connected to a computer via a serial or USB cable, which uses small metal or plastic pins that move up and down to display braille characters so a blind person can read what is displayed visually on the computer.[31] The “refreshable” quality means that the braille display is constantly changing as the user scrolls the mouse around the web page or document. The user can move the mouse around by through either the command keys or cursor routing keys located on the device, or through Windows and screen reader commands.[32] Typically screen reading software, or just a screen reader, is used in conjunction with a digital braille display to give the ultimate experience for people with vision loss. A screen reader translates information on a web site into electronic text, which is sent to a speech synthesizer (so output is heard audibly) or to the refreshable braille display. The only thing that the screen reader cannot read is graphics; this is why it is important to include descriptions of pictures and “hover-over” captions when designing a web page to be sensitive to those with vision disabilities.[33] While some may only need the speech synthesizer, most prefer to have the refreshable braille display because it provides direct access to information and thus increases efficiency in completing tasks; allows the user to check spelling, grammar, and formatting of their own input and is quiet, so it can be used anywhere without it be being disturbing to others. Refreshable Braille Displays come in 40, 70, and 80 character displays and can range from $3,500 to $15,000 depending on the character display.[34]
Creating a Web Site using HTML, XML, XHTML, CSSs
[edit | edit source]HTML
HTML or Hypertext Markup Language is mostly used to create webpages. HTML is a code made up of small pieces called tags. Tags are small pieces of the HTML code that give commands to the computer on how to format whatever it is linked to. tags begin with a less than symbol (<), then the command is written, then closed with a greater than symbol (>). That is the beginning tag. Next the text it applies to is inserted. Then, the tag is ended with a less than symbol (<), followed by a common slash (/), then the same command code as it began with, then a greater than symbol (>). So, your basic code will look something like this: </(insert code)> Applied Text Here </(insert code)> .
There are so many different things you can do with HTML. You can highlight text (even in different colors), you can make text different colors, you can (Hover Mouse Here), as well as bold face or italicize text. These are just some of the basic modifications that can be created by using HTML formatting.There are even ways to insert images as well hyperlinks. Here I have inserted A Link to Our Wikibook Homepage and even the pictures you see to the right. The possibilities are almost endless when using HTML.
The biggest problem with HTML is that most people do not want to take the time to sit down and learn all of the little codes and specifications. It is very useful when trying to organize webpages once it is mastered. HTML allows users the ability to manage where images, videos, animations, and text formatting are all located. It is a very powerful and useful design tool and something that seems to be somewhat overlooked and taken for granted.

The newest version of HTML is HTML5, which is being created to replace both HTML and XHTML. HTML5 is designed to be simpler and many things have changed or added to the coding for HTML5. The DOCTYPE and character encoding declarations have both changed to be simpler to code. Along with new declarations have come new elements for semantics, controls, graphics, and multimedia because more and more websites are becoming more complex with more information being packed into a website. Some of the new semantic elements include <header> and <footer>, which make it easier for a web designer to indicate where a new page will begin and end. New controls for HTML5 markup language include the date, time, and a calendar to help users be more aware. The biggest addition for HTML5 is the <audio> and <video> multimedia elements, because a multitude of users love to be able to listen or watch something that is useful on the website. This is especially true for e-commerce websites because potential buyers would like to be able to see a product in use, which can be shown through a video. All in all, HTML5 is a newer markup language that simplifies the coding for web designers and also makes their websites more appealing to look at.[36]
A Brief History Of CSS
[edit | edit source]To make your website truly stand out, it needs a sense of style greater than what HTML and its ilk can provide. This is where CSSs come into play. CSSs stand for Cascading Style Sheets, and they offer a way to not only specifically style a Web page but even the entire Web site to which it belongs. Before CSSs there had been individuals who created style sheets for their own purposes but thought it unnecessary to publish their developed syntax, believing that each browser should decide how best to display pages to its users. When Web page writers issued complaints that they couldn't customize more deeply, they were generally ignored, forced to deal with browsers that offered consistently fewer options for the sake of streamlining. To address this, a Norwegian by the name of Hakon Wium Lie offered a first draft of Cascading HTML Style Sheets in 1994. He couldn't have imagined how popular his development would become.[37] CSSs offer plenty of room for style without being needlessly complicated like some of its rival setups, such as DSSSL. The easiest way to describe what makes CCS stand out as a language is how it works to separate the content of a page from its display.[38] CSS3 is the most popular variation of CSS right now, but number 4 is already growing in notoriety.
XML and XHTML
[edit | edit source]
Similar, yet very different than HTML, another type of markup language is called Extensible Markup Language, a universal format for structured documents and data on the Web. The biggest difference between the two markup languages is the fact that HTML describes presentation, whereas XML describes content. Simply, HTML describes the actual content such as text and graphic images, but only in terms of how it is to be displayed and interacted with. On the other hand, XML describes the content in terms of what data is being described. To do so, XML tags are then assigned to pieces of data. Once the data is tagged, it can be used with any XML document. XML is called “extensible” because the data contained in XML documents can be extracted and used whenever needed. [39]
Another version of HTML that is based on XML is known as the Extensible Hypertext Markup Language, or XHTML. It combines the flexibility of HTML with the extensibility of XML. This language is used to create Web pages while also supporting XML, unlike HTML. This way, XML controls the actual content displayed, while XHTML controls the appearance and format of the Web page. However, one major difference between XHTML tags and HTML tags is the fact that there are stricter rules about how the markup tags are written. For example, unlike HTML, while using XHTML, all tags must be written in lowercase letter, every tag must have an end tag, and quotation marks are required for values. [40]
AJAX
[edit | edit source]
Many modern websites use a technology called AJAX, for fast and effective interaction with the visitor. AJAX has become a very popular method to retrieve data from the server in the background and the Dynamic Update page. AJAX stands for "Asynchronous JavaScript And XML". Developing code to JavaScript for AJAX implementation from scratch is very time consuming and tedious process. However, many libraries JavaScript, including jQuery, have excellent high-level AJAX implementation as a set of methods and functions that make it easier and faster to build web sites. AJAX is a development technique for Web applications in which JavaScript code in the visitor's browser communicates with the web server asynchronously, i.e. in the background. When you click links or forms contained on Convectional Web page a request is being sent to a new URL on the web server. The server sends a completely new page of HTML, which a browser displays, replacing the original page. When using technology AJAX, JavaScript code makes a request to the URL on the server. The code may also send the data along with the request. JavaScript code then processes the response from the server, and acts accordingly. For example, the calculation can be made with the returned data is added or updated widget on the page, a message to the visitor to update the database on the server. Since AJAX request runs in the background, the code JavaScript (and a visitor) can continue to work with the page during query processing. The process is hidden from the visitor, who does not need to leave the page they are currently viewing time. This makes the page with AJAX is very pleasant to use. [41]
Multimedia Web Development (Scripting, Development Tools, Authoring Software, and Testing)
[edit | edit source]Creating the Multimedia Elements
[edit | edit source]
Multimedia presentation uses graphics, sound clip, video clips, and text to deliver a message to the audience. All you need is a multimedia authoring program and a computer in order to create a presentation. The reason in using multimedia will be able to not only get the message you want to convey to the audience out but it provides a creative way in making it for the viewer. These following are types of situations that would see yourself wanting to use multimedia presentations in order to provide a creative presentation. One is for projects in order to show your teacher or a classmate in a more formal setting, another would be a class exhibit for the library or computer lab, for a more personal use you could utilize it as a diary, and the last two ways would be in a slideshow format and or utilize it for a yearbook. The three C’s in making a good multimedia presentation would be keeping it Clean, being Consistent and bring Character to the presentations. Next you will need to design the presentations in which make it able to be presentable and attract the attention of the audience. To continue, you’ll have to plan your presentation. Make an outline and make sure you understand the major topics of the presentation. Next the presenter will have to choose their media; multimedia elements support the main points of the presentation. Certain data will benefit the presentation as well, like, charts, graphs, maps, images and videos. Afterwards, review revise and rearrange so you know that the information is accurate and ready to be presented.
Creating the web Site
[edit | edit source]
Web site developers use a number of tools to create web sites. These can be divided into three large groups: markup languages, scripting languages, and web site authoring software. Markup languages are the foundation; they are coding systems that create the overall structure/appearance of the web page by the use of tags. Tags are commands that allow the web page designer to arrange text and multimedia. HTML, or Hypertext Markup Language, is the dominant markup language used today. The current version is HTML5, and it is intended to replace both HTML and XHTML, another markup language.
Scripting languages allow the developer to create instructions, or scripts, that run in the code of the web page. One example of a very popular scripting language used today is Javascript. Scripting languages are found everywhere.[42] For example, Ajax technology is found in the widely-used services Google Maps and Gmail. When used in combination with markup languages, scripting languages can enable developers to implement a wide-range of features and content into their web pages.

Web site authoring software is used to make more complex web pages where developers can take advantage of commands that automatically generate tags and Cascading Style Sheets, which are used in the look and formatting of what was written by the markup language. This enables the developer to work in a more productive manner because animations, effects, backgrounds, etc. can be applied all at one time. For example, when menu options are selected, the appropriate JavaScript or other code used to add animation or interactivity is generated. Along with this, web site authoring programs almost always have the capability to include a variety of multimedia elements, like Shockwave and Flash animations, animated GIFs, video clips, and audio clips. Two of the most popular web site authoring programs are Adobe Dreamweaver and Microsoft Expression web. There are a few general features of web authoring applications a designer should know. This includes WYSIWYG, which stands for What You See Is What You Get, users can click and drag various website elements to a design canvas without having to code these widgets manually. Advantages of authoring software also include the ability to set up and use templates to ensure consistency between webpages and multi-media can be inserted into webpages. However, a disadvantage for using a web site authoring software is that it's not intuitive and easy to pick and use, some training or technical knowledge is needed. Web sites developed with these tools may not be coded efficiently, which leads to increased load times for users. Also, one needs a basic understanding of HTML. Furthermore, web site authoring software can be an expensive purchase.[43]

Website Builders are web-based tools that make it easy to create websites for small businesses or for personal purposes. One of the big advantages of using a website builder is that it no longer requires a very extensive knowledge of HTML. So it require minimal technical knowledge to create a website. Another advantage is that it is made to be user friendly. So making a website has been made to be an easier and less daunting task. Another big advantage, especially for businesses, is that they offer mobile web design. Now that smartphones have become the norm. Most websites have a mobile version to them. So some website builders give responsive design to websites wherein they change when viewed on a mobile device as opposed to a computer. There are also plenty of website builders. Some may be free others may not. But mostly those that require payment also end up being the ones with the most features. A disadvantage of website builders though is that they can be expensive and while they give you a domain and an address, once you want to move your website to another host, some may not be able to thanks to a custom code they use.[44] Most website builders will include "What You see is what you get" builders that let you create it by dragging and dropping website elements into the content area. However, sometimes it is hard to differentiate between quality website builders since some products are not up to their task (costing more money or time than anticipated) but still it is a great and easy way to set up one's “virtual storefront”. [45]
Other Content Development Tools

ActiveX is a component of the software in Microsoft’s Windows operating system. Many of Windows’ applications such as Internet Explorer, Microsoft Office, and Windows Media Player use ActiveX in order to embed their functions into other applications. Microsoft Internet Explorer replacement browser, Microsoft Edge, will not support ActiveX, marking the end of the technology.
Testing, Publishing, and Maintaining the Site
[edit | edit source]It is extremely important, before your webpage goes out, to make sure that it is up and running and functioning at one hundred percent capability. This means that there cannot be any bugs, glitches, or error pages displayed when a user is utilizing your web page. Though this may seem easy enough, there are many different steps that one should go through to make sure their page is up to speed. Every link, icon, animation, picture, and etc., needs to be tested. Many websites like to utilize the software that is out there that will manually do these needed checks for you, however it is still important to keep an eye out personally for anything that could be raising red flags. At this point, after vigorous testing, the site should be set and ready to be published. All though the page has been successfully published, the work does not stop there. Many people like to think that they are set for the future, but these pages require constant maintenance. The publisher needs to be constantly checking to make sure everything is still running smoothly, things are still up to date, and links and animation are still functioning. With out this much needed maintenance, a site becomes difficult and outdated, and users will go out of their way to make sure that they do not use it.[46] [47]
Bandwidth Considerations
[edit | edit source]In the age of the Internet, nearly everyone is online one way or another; however, not everyone has unlimited access. There are still people who only have mobile phones that are capable of accessing the World Wide Web, but with data limits. When creating a website it is important to consider this.[48] When a website is created, it has individual elements that have varying sizes. For example, recently the search engine "Google" has redesigned their logo and, in turn, reduced the size of the image from 6,380 bytes (6Kb) to 305 bytes.[49] This allows people with data limits to access the website more, because every time the page is loaded, it uses less data.
Demand for Multimedia web Site Development
[edit | edit source]
In this day and age everything is online, everyday individuals go online and they use the Internet for different purposes. There is a lot of money in the industry to make web sites. The demand for these sites is that they are intriguing, useful, and navigable to users. Companies hire web designers and web developers to create multimedia elements and create sites for the online presence of the company. As a web designer, you need to have knowledge in Photoshop, Illustrator, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. A good web developer needs to know all the things that a web designer needs to know plus advanced programming skills. Graphic design has truly emerged as a demanding field of the economy with new technological developments in multimedia and software. As mentioned above, HTML5 and CSS3 are new coding techniques that are available for developers. Students interested in these fields should continue to study HTML and CSS.[50]
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ https://www.humblebundle.com
- ↑ http://www.youtube.com
- ↑ http://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/index.html?nbId=7345&nbNodeId=1013914#!&parentId=1013939
- ↑ http://www.slideshare.net/kenshin1017/introduction-to-multimedia-4663053
- ↑ Understanding Computers 14 ed. by Deborah Morley & Charles Parker
- ↑ http://computingclass6hishamuddin.blogspot.com/2012/07/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-using.html
- ↑ http://www.vidhyalive.com/
- ↑ http://smallbusiness.chron.com/5-components-multimedia-28279.html
- ↑ http://graphicdesign.stackexchange.com/tags/serif/info
- ↑ http://www.fonts.com/content/learning/fontology/level-2/making-type-choices/serif-v-sans-for-text
- ↑ http://www.slideshare.net/shortcomp/4-multimedia-elements-video
- ↑ http://www.w3schools.com/html/html_media.asp
- ↑ http://www.slideshare.net/azmankadir/multimedia-element-presentation
- ↑ http://computer.howstuffworks.com/internet/basics/streaming-video-and-audio.htm
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_compositing
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graphics_Interchange_Format
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Portable_Network_Graphics
- ↑ http://graphicdesign.about.com/od/Definitions/g/Jpg-Files.htm
- ↑ http://www.nch.com.au/acm/formats.html
- ↑ http://desktoppub.about.com/od/designprinciples/
- ↑ http://www.wikihow.com/Create-a-Free-Website
- ↑ http://www.edrawsoft.com/flow-chart-design.php
- ↑ http://designshack.net/articles/layouts/10-rock-solid-website-layout-examples/
- ↑ http://www.fastcodesign.com/1672917/the-8-steps-to-creating-a-great-storyboard
- ↑ http://www.fastcodesign.com/1672917/the-8-steps-to-creating-a-great-storyboard
- ↑ http://public.wsu.edu/~ericsson/story_bd.html
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Web_navigation
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Refresh able_braille_display
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Screen_reader
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Alternative_text_for_images
- ↑ http://www.afb.org/info/living-with-vision-loss/for-job-seekers/careerconnect-virtual-worksites/retail-worksite-for-blind-users/refreshable-braille-display-3652/12345
- ↑ http://www.afb.org/ProdBrowseCatResults.asp?CatID=43
- ↑ http://www.afb.org/info/screen-reading-technology/5
- ↑ http://www.afb.org/ProdBrowseCatResults.asp?CatID=43
- ↑ http://www.compapp.dcu.ie/~humphrys/Notes/Internet/index.html
- ↑ http://www.w3schools.com/html/html5_intro.asp
- ↑ http://www.w3.org/Style/LieBos2e/history/
- ↑ http://mashable.com/2012/10/24/css-for-dummies/
- ↑ http://www.w3schools.com/XML/xml_whatis.asp
- ↑ http://personalweb.about.com/od/basichtml/a/409xhtml_2.htm
- ↑ http://www.w3schools.com/ajax/ajax_intro.asp
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scripting_language
- ↑ http://www.teach-ict.com/as_a2_ict_new/ocr/AS_G061/313_standard_applications/types_software/miniweb/pg6.htm
- ↑ http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2484510,00.asp
- ↑ http://1stwebdesigner.com/easiest-website-builder/
- ↑ http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/publisher-help/prepare-publish-and-maintain-your-publisher-web-site-HA010094760.aspx
- ↑ http://go.hrw.com/eolang/myomed/bringit.htm
- ↑ http://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/index.html?nbId=7345&nbNodeId=1013914#!&parentId=1013939
- ↑ http://gizmodo.com/how-could-googles-new-logo-be-only-305-bytes-while-its-1728793790
- ↑ http://www.orientinfosolutions.com/articles/multimedia-web-design.php
Review
[edit | edit source]In the world we live in today, we are constantly bombarded by multimedia through billboards, signs, logos, texts, ads, emails, and our day to day web browsing. Below is a list of vocab from the chapter and the words general definitions. Below the list is a set of fill in the blank questions. Use the vocab list to help you fill the blanks. Some words may not be used. Then check your answers at the bottom of the page.
1) Multimedia: Integration of a variety of media.
2) Web-based Multimedia: (aka rich media) refers to multimedia of any kind located on a Web page.
3) Virtual Reality (VR): used in E-commerce to show what a product or service will look like or do in the real world.
4) Text: used to supply basic content and is important in most Web sites.
5) Images/Graphics: digital representations of photographs, drawings, charts, and other visual objects.
6) GIF: (Graphics Interchange Format) used most commonly with non-photographic images and is the standard format for Web page images.
7) PNG: (Portable Network Graphics) the responding format created in 1996 because of issues with the GIF format.
8) JPEG: (Joint Photographic Experts Group) the standard format for photographs based on the Web.
9) Thumbnail Image: smaller images (similar to icons) that are linked to the full size images of larger files.
10) Java Applet: a small program in a Web page designed to perform a specific task from calculations to animations.
11) Animated GIF: a group of GIF images stored together in one animated file.
12) Flash or Silverlight: Animation developing tools.
13) Audio: All types of sound (music, voice, and effects, etc).
14) Video: a continuous stream of visual information that is broken into frames when the video is recorded.
15) Web Site Design: refers to the process of planning what your Web site will look like and how it will work.
16) Flowchart: describes how things relate to one another.
17) Page Layout: illustrate the layout and navigational structure of a Web site.
18) Storyboard: an ordered series of sketches depicting each page or screen in an animation sequence.
19) Alternative Text: captions of images to allow those who are unable to view the images the clarification of what they are missing.
20) Web Site Development: Creating a Web site after it has been designed.
21) Markup Language: a coding system used to define the structure, layout, and general appearance of the content of a Web page.
22) HTML (Hypertext Markup Language): The original Markup Language designed for creating Web pages.
23) XML (Extensible Markup Language): a set of rules for exchanging data over the Web.
24) XHTML (Extensible Hypertext Markup Language): a version of HTML that is based on XML.
25) Cascading Style Sheets (CSSs): specifies the styles used with a Web page or an entire Web site.
26) Wireless Markup Language (WML): language based on XML that is used to create Web pages to be displayed on WAP-enabled wireless devices (such as older mobile phones and those used in some developing countries).
27) JavaScript: developed to enable Web authors to implement interactive Web sites.
28) AJAX: A set of Web standards designed to better handle Web page interactivity by downloading only new data from the Web server, instead of redownloading the entire Web page.
29) Web Site Authoring Software: a type of application program used to create Web pages and entire Web sites.
Quick Quiz:
1. HTML, XML, and _______ are all forms of _______.
2. Multimedia (sound, video, animations, text, and images) located on Web Pages is known as __________ or rich media.
3. Many sites such as https://www.youtube.com integrate _______ and _______ into their site to provide entertainment to viewers and/or listeners.
4. The three main types of images include ¬¬¬¬¬¬______, _______, and ______.
5. Placing pages in a ¬¬¬_____ show how they are related, while using a _____ shows the order of specific animation sequences.
Answers: 1. XHTML (Also Acceptable: CSS or WML or XRML); Markup Languages 2. Web-based Multimedia 3. Audio; Video 4. GIF; PNG; JPEG 5. Flowchart; Storyboard
E-Commerce
What is E-Commerce?
[edit | edit source]E-commerce, short for electronic-commerce, is “a term for any type of business, or commercial transaction, that involves the transfer of information across the Internet”. [1] Currently, e-commerce is mostly used via the Internet, but before the Internet was available, a form of electronic transactions occurred over Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). Businesses and customers used EDI by setting up a data link specifically reserved for commerce between them. [2] In 1979, Michael Aldrich invented the concept of “teleshopping” which gave the base structure that evolved into the online shopping ability we know today. In the 1990’s, websites like Amazon and eBay were created. Because e-commerce is now done through the Internet, it has made a global market-place for businesses and consumers to make trades and transactions all across the world. [3] For example, businesses in Europe can ship items to customers in America, and vice versa. Just like any other technology, a user needs to know how e-commerce works and how to navigate through it. One of the basic concepts is knowing what a "shopping cart" is and how to use it. A "shopping cart" is a software that allows buyers to have a virtual chart, just like you would at a physical store, to collect multiple items and be able to buy all the items at once when you “check out”. [4] Other concepts that one should know are the advantages and disadvantages of shopping online.
Advantages of E-Commerce
[edit | edit source]For businesses, the most prominent advantages to using E-Commerce are the reduced costs associated with it, the broader customer base, the increased customer satisfaction, and the potentially higher sales it produces. Because E-Commerce transactions are done through a website and not a brick and mortar store, much of the overhead associated with running a retail store is reduced. The need to pay for heating, lighting, staffing, and restocking a store is practically eliminated. This results in fewer employees and smaller facilities which in turn allows for larger capital gains. Usually, only a company headquarters is needed along with a few warehouses that can cover larger areas than a single retail store normally would. Also, more individuals can be reached through a website rather than the small geographical area that a retail store would cover. Multiple retailers are required to cover larger geographical areas, but with E-Commerce anyone anywhere can access the website at anytime! This increases the possible number of customers dramatically. Websites also allow people to shop from the comfort of their own home without having to consume time and money (gas) to view a company's products in their retail store. Plenty of times have people gone to the store for a specific item only to be disappointed that it wasn't in stock. With E-Commerce this doesn't happen. The comfort provided, the time saved, and the money saved can easily increase the consumer's satisfaction. The potentially higher sales is another advantage. By using E-Commerce, a business can be open every hour of the year and accessible to everyone across the globe. They're no longer limited by a geographical area or a 40-hour work week.[5]
For consumers, the greatest advantages lie in its convenience, selection, customization, price comparison, and potential cost savings. As mentioned above, the convenience of shopping from home (in your underwear if you like) is very appealing to many consumers. Shopping can be done during anytime of the day or night through the use of a website and it is no longer a necessity to rush home from work to buy an item before its store closes. A person can also compare the prices, quality, and features of multiple items from multiple stores. Their selection is no longer limited to the facilities closest to them, but to their attention span. Before, consumers would drive from store to store comparing these characteristics before driving back to make their final purchase. The time, effort, and expense involved in this type of comparison is nullified through E-Commerce. Many individuals want to make their purchases unique to their preferences. With the option to communicate with a company directly through their site instead of buying a pre-manufactured item on a store shelf, the ability to customize the item they are looking for is greatly improved. The company can take the order and payment while putting it through to the warehouse so that the final product to be shipped is tweaked to the consumer's desire. Also, the ability to save on cost is increased for the consumer using E-Commerce. The person can compare prices to find the lowest and often the item can be shipped to their front door for less than it would normally have taken to find it in a motor vehicle. They say time is money, so if your spending less time looking for what you need then you can potentially spend more time working for what you want.[6]
Disadvantages of E-Commerce
[edit | edit source]
As mentioned above, there are a lot of advantages, but it is not perfect. One of these disadvantages is that those who are running the site must keep the site open 24/7 since at any point it is morning somewhere in the world. This takes money to run the servers and takes money to pay the programmers to make the site in the first place. Also a business that is running a site should make it interesting by having something change, like having a daily deal like Newegg[7] or return coupons like Kohls[8], otherwise people may not return to the site. Another disadvantage is that anyone can make a website, driving competition and prices. So, some sites may spend extra money on multimedia for some extra allure.

There are disadvantages for consumers as well. E-commerce doesn't have the same kind of physical, personal interaction that traditional commerce has, and for some consumers, the asocial experience of sitting behind a screen and clicking a virtual cart icon isn't as desirable as the experience of actually getting out and pushing a cart around, even if it can be easier. E-commerce is also slower: if you purchase a good from a physical store, you have it right there that same day, but if you have to wait for shipping, it'll typically take at least several days before it arrives. Also, very many goods can't be purchased online, so even to the extent that e-commerce is useful, it isn't useful in all areas or for all purchases. The fact that anyone anywhere can set up an e-commerce website is as risky for consumers as it is undesirable for businesses; some sites may be fraudulent and set up to steal info or get a consumer to waste money on faulty goods. Thus, when considering making an electronic purchase, a consumer should consider whether the convenience outweighs the artificiality, whether the goods they desire can wait and can actually be purchased online, and should take reasonable security measures to ensure that they're buying what they want.[9]
Safe Practices for E-Commerce
[edit | edit source]Using E-Commerce for anything from home shopping to online banking can be very convenient for both the consumer and business. However, when using E-Commerce, there are possible disadvantages. Fraud and hacking are something everyone should be informed about. One tip for a business to safeguard against these things is to use a secure platform. Shawn Hess, a software manager for VoIP Supply states, “Put your e-commerce site on a platform that uses sophisticated object-orientated programming language.” Another tip for businesses to use is to use a strong SSL (Secure Socket Layer) authentication. This provides both Web and data protection. This will authenticate the identity of a business and encrypt customer data in transit which protects the company and consumer from having their financial information stolen. Another way for businesses and consumers to protect themselves in E-Commerce is by using strong passwords. A business should require the consumer to make a password consisting of a minimum number of characters as well as symbols and numbers. Using more complex passwords makes it less likely for a criminal to access the site. A business would also be able to avoid threat by layering its security. They can use firewalls to stop a cyber attack before someone is able to get into the network and gain important information. Being aware of the possibility of fraudulent and criminal activity and knowing ways to protect oneself from it is extremely important for both businesses and consumers, especially since E-Commerce continues to expand globally.[10]
E-Commerce Business Models
[edit | edit source]Four E-Commerce Business Models
[edit | edit source]
There are four types of E-Commerce business models. The four types of E-Commerce business models are B2C which stands for Business-to-Consumer, B2B which stands for Business-to-Business model, C2C which stands for Consumer-to-Consumer, and B2G which stands for Business-to-Government. When working, selling, or buying with any of these models, it is important to be familiar with what each model contains. B2C represents most of E-Commerce websites. Businesses that sell to consumers are considered B2C. Online stores and shopping are all examples of B2C. B2B are businesses selling products to other businesses. B2B are usually larger companies that are supplying a service to other businesses. For example, office max is a business that sells office supplies to other businesses. Also, they are almost always doing business over the web. C2C is a website that consumers sell to other consumers. People are brought together to sell and buy products for this model. For example, EBay is a common place for consumers to sell and buy items. B2G consists of businesses working with the government. For example, the IRS is a way for businesses to pay their taxes through the web. These four E-Commerce business models are very common in this day-in-age. [11]
Business-to-Consumer
[edit | edit source]
Business-to- consumer (B2C) model is a business or transactions conducted directly between a company and consumers who are the end-users of its products or services. [12]The term became popular during the dot-com boom[13] of the late 1990s. While many online B2C websites shut down, the companies such as Amazon and Priceline survived and became the most successful companies in the world. This model is likely familiar to most people. If a person have purchased an item online for their own use, the person e-tailed. The concept was first developed in 1979 by Michael Aldrich, an English inventor, who connected a television set to a transaction processing computer with a telephone line and coined the term "teleshopping."[14]
Business-to-Government
[edit | edit source]A “B2G”, meaning business-to-government is a variation of the term B2B, or business-to-business approach to commerce, also called e-government. It refers to businesses and government agencies using the Internet to mutually exchange information and trade with each other more efficiently. This is prompted by government solicitations that are accepted by businesses offering something a government needs. A site specializing in B2G services may provide businesses with a single place to locate tax applications and other financial forms, the ability to send in payments, or request answers to specific questions. B2G may also include e-procurement services, whereby businesses understand the purchasing demands of agencies, who in turn request proposal responses. B2G generally supports the idea of a virtual workplace, or the collaboration of businesses and agencies working on a contracted project. This is done by sharing a common site to coordinate online meetings, review plans, and manage progress. This concept also incorporates the rental of online applications and databases designed specifically for government agencies. According to the Gartner Group, B2G revenue grew from approximately $1.5 billion in 2000 to $6.2 billion in 2005. The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 has spurned the use of B2G. [15]
Business-to-Business
[edit | edit source]
Business-to-business (B2B) is a type of commerce transaction that exists between businesses, such as those involving a manufacturer and wholesaler, or a wholesaler and a retailer. A typical supply chain involves multiple business to business transactions, as companies purchase components and other raw materials for use in its manufacturing processes.[16] An example that illustrates the business to business concept is automobile manufacturing such as buying tires, glass for windscreens, and rubber hoses for its vehicles.[17] B2B is also used in the context of communication where employees from different companies can connect and communicate with one another, such as through social media like Linkedin.com
A well-known business to business supplier is Grainger. Grainger is known for have a massive catalogue that contains almost any product a company needs, not matter if that company is clothing retain of tool manufacturing. Grainger’s system is unique in that their online order system and brick a mortar locations work together seamlessly. When you order from most online wholesale business, your order is processed and shipped from a central warehouse. This can result in high shipping costs, and order delays as the order is filled, and eventually shipped from the central warehouse. Grainger has a central warehouse where they ship from, but the also can ship from their individual brick an mortar stores, which function as satellite warehouses. Because of this system, shipping time is dramatically reduced, sometime measure in hours as opposed to days, since the order is coming from a few miles away as opposed to a few states away. Further, shipping is less expensive, and is some cases free because of the short distance. Also, if you want to see a product for yourself or get advised about a product, you have the option of going to a Grainger store and talking to a sales person there. Grainger’s system combines the efficiency and ease of online ordering with the familiarity of the physical store. [18]

Consumer-to-Consumer
[edit | edit source]
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) is a type of electronic commerce in which consumers buy, sell, or trade products and services from one another through a third party website. [19] The third party website can be either fee-based or free as long as transactions are between consumers. Some popular websites known for Consumer-to-Consumer transactions include Craigslist, eBay, and AutoTrader. There are many advantages of C2C e-commerce. Because business transactions are done between consumers and not businesses, buyers and sellers do not need to account for taxes. Also, the transactions are done on a personal level and there are no legal obligations like companies might have. This allows for prices to be negotiated and sometimes bartering can take place. Most transactions that take place on websites like Craigslist, however, are paid for with cash, so it is difficult to return items or purchase them with credit cards. There is also a lot of safety concerns with consumer-to-consumer transactions. Because many sales are completed from people’s houses, there is a lack of privacy. Also, because the buyers may be going to someone’s house to buy a product, there are in danger of being kidnapped. That is why many Craigslist users suggest meeting in a public area. The best part about C2C commerce is that there are many different websites that you can use to match both the product you are selling as well as the way you would like to sell it. If you don’t want to have someone coming to your house through Craigslist, then you can simply sell your item through eBay and ship it to another consumer. It is all about putting more power into the consumer’s hands. [20]
E-Commerce Web Sites
[edit | edit source]
Ecommerce began to gain traction in the early nineties and has grown rapidly ever since.[21] Ecommerce offers many advantages over traditional brick and mortar stores. Consumers can easily search for the products and services they are looking for. Online retailers, or e-tailers, are incredibly convenient, in that they are available 24 hours a day. Today, most brick and mortar retailers also have an ecommerce option. While an ecommerce consumer does not get the immediate gratification of having their purchase immediately in hand, they can place orders from the comfort of their own home without having to deal with the hustle and bustle of a shopping mall. Some stores offer a combination, allowing a customer to order their merchandise online, and pick it up almost immediately at their local store. E-tailer sites like Amazon paved the way for many others. Amazon is arguably one of the most successful e-tailer sites around. It began as an online bookstore with a primary focus on the customer experience. It was so successful that it did not take long before it expanded beyond the sale of books. Today, you can order almost anything from Amazon. They have also crossed over from strictly being an e-tailer to an e-tailer and subscription site with its Amazon Prime offering.
Manufacturer and E-Tailer Sites
[edit | edit source]
Manufacturer and E-tailer sites are basically just companies that can sell their product directly to their customers via a website. [22] They are just online stores. Most websites like this have an online catalog of their products for the consumer to look at and choose their desired product. Then if the product is shipped to the home there is a shipping fee, or some products like music or books can just be directly downloaded. This would include websites like Amazon, Charlotterusse, or Walmart.
Subscription Sites
[edit | edit source]
Subscription sites are an online product that a consumer purchases and pays periodically and then receives the product periodically via the Internet. An example would be Netflix, which is a monthly fee and then you can receive streaming of movies or TV shows through the Internet. Some sites are considered subscription sites even if they don’t require a monthly fee. They may just require you to subscribe to their site to receive all the information provided. [23]

One of the most popular types of subscription e-commerce is video-on-demand (VOD) and audio-video-on-demand (AVOD). These subscriptions allow a consumer to access video and audio whenever they want. Some popular examples of subscription e-commerce are Netflix, Hulu, Pandora, and Spotify. While Netflix and Hulu allow a user to access movies or TV shows, Pandora and Spotify allow users to access countless amounts of streamed audio. The biggest benefit a subscription offers to a consumer is that the consumer no longer needs to wait for specific broadcast times in order to watch or listen to a program. Sometimes airlines take advantage of subscriptions in order to please their customers during long flights. The airlines that support VOD will often have a small screen on the backsides of headrests. This in-flight entertainment system usually allows each individual passenger to select various cartoons, TV shows, and movies. Airlines that support AVOD will often have an embedded unit in armrests. This unit usually allows a passenger to listen to various music channels.[24] In the past few years the online subscription market has taken off. Companies like HBO and Amazon have created their own VOD services. HBO’s VOD service is called HBO Instant and has become popular in 2014. Amazon’s VOD service is called Amazon Prime and is believed to have inspired the Amazon Fire TV.[25]
Brokerage Sites
[edit | edit source]
A Brokerage Site is used to bring sellers and buyers together to simplify transactions between the two. The site earns revenue as a form of commission for every sale it incurs. Online auction sites are examples of brokerage sites, in that they enable consumers to buy and sell goods and services to one another. The site acts as a median between the two. One clear example of this is eBay. Business online auction sites are online auctions sites that are mostly for business transactions. An automatic bidding system is used by eBay so that consumers can easily keep up with the bidding process if he or she wishes to make a bid on a specific item. There are rules put in place so that every bidder is treated the same. A dynamic pricing site can be used instead of online auction sites. Priceline.com is an example of how this works: buyers are allowed to bid on items for sale, and the seller can then make the final decision of who shall receive the item. Financial brokerage sites are also used between buyers and sellers for stock, bonds, opinions, and more. These sites earn money by charging for each transaction. Real estate and travel are other types of brokerage sites. A market exchange site matches organizations with different goods or services to sell with buyers and to help the buyers look for specific items that the suppliers can provide. Commodity exchanges are sometimes used when dealing with natural resources and raw goods.
Implementing E-Commerce
[edit | edit source]Business Models and E-Commerce Applications
[edit | edit source]


If you're a business owner living in today's technological age, your eye is surely on expansion through e-commerce. Whether you are the owner in question who is tech-savvy enough to build your own site, or a third-party Web page developer, there are 5 rough steps to keep in mind to ensure the success of your e-commerce endeavors.
The first of these steps is to just figure out what your website hopes to accomplish. You can either pick one model (such as B2B, or Business to Business) or combine a few of them depending on your ambition and the needs of your business. Within this model, you also need to be making decisions such as whether your site will be taking a Storefront approach (basically being an online version of a physical store) a Subscription approach (where customers pay for premium content that is web-only), or even Affiliate Marketing (where your business would sell the products of another business for a commission).[26] As you browse the Web and study the models of your competitors you'll get a good idea about what is and is not the goal of the e-commerce site you are creating. A business to consumer model is just selling straight to the consumer. E-bay is a good example of a consumer to consumer business model. Consumer to consumer is really convenient since it always the buyer to pay the owner on the spot, not tax, no driving, etc. It is also nice for collector items that are hard to find. Anyone can go on this website to be able to sell and buy items. It is just an online auction and is also worldwide. E-bay is not free though, a user has to pay an invoice fee if they sold or listed anything. [27] The last business model is to have business to government. These businesses usually already have a previously drawn contract with the government because they have something that the government needs. An example of a business to government is actually being able to pay fees online. If a business has a fee to pay they can just go online and pay it off. It is also more convenient to have fees available to pay online because the use of mail is declining. Before the use of these government websites a person would have to send in the mail of have to go somewhere to pay it off.
The next important step is deciding on the applications of your e-commerce page. If you're a business owner creating a Web page, it's a given that one part of your site will be online selling, but there are ways you can establish the name of your company that go above and beyond so your customers will remember you in a positive light and keep coming back, hopefully with their friends and family in tow. These extra features are called e-commerce applications and they can range from merely providing in-depth product information to providing technical support, or even letting them track online purchases through the mail. For the adventurous and creative developers, you can program games, surveys, and even music, all for the sake of providing a more intriguing online shopping experience.[28]
After selecting the appropriate business model and type of Web site along with the desired e-commerce application, another valuable procedure to consider is the procedures for handling electronic financial transactions. The kind of payment type an e-commerce Web site uses depends on the type of site it is and the types of customers involved. The available payment options will usually be displayed on the checkout page of the Web site. Nowadays, credit card processing is the most used payment option. A business needs to open an e-commerce merchant account (a.k.a. an Internet merchant account) in order to accept credit cards. A bank is hired by the merchant to monitor the transactions with credit and debit cards and usually charges a monthly fee, a transaction fee, and a commission for this service. Customers are also able to use single-use virtual credit card numbers, which they request by logging onto their credit or debit card account. A virtual credit card number can be used to purchase an item online so that hackers cannot intercept the actual account number during the transition. Smart cards are also becoming increasing popular. A smart card is a credit or debit card that is embedded with a computer chip. The chip usually contains identifying data for authentication purposes. Other customers online may use PayPal, digital gift certificates, gift cards, and digital wallets. [29]

Navigation Through a Web-based E-Commerce
[edit | edit source]For customer satisfaction, the ability for them to find their way around to the products and information they need is very important. If something takes too many clicks to find then businesses start to lose customers due to their inability to change with the pace of technology. With the steps to implement Web-based E-Commerce covering different ways to successfully please consumers, storyboards, flowcharts, etc., can be used to improve navigation through E-Commerce Web-sites. Making “parent categories” that have more depth is an effective way to increase consumer satisfaction when browsing. Drop down menus that have many options make it so people do not have to guess where their product/service will be located, but instead have the actual category listed out for them along with many others. Along with this, sub categories should be put in appropriate places to separate the options as well. Another interesting navigation tool is the ability for users to see “what’s new” on the business’ web page. With this available, new products can increase their popularity and in turn make the businesses more money. When users see a picture, their instinct is to click it to find information such as price or availability of colors, sizes, etc. If the link on a picture goes elsewhere, consumers will often be irritated or give up on a search. [30] All of these small methods can build up to create a better experience for any user; and can boost a company’s sales.

Now that practically everyone has a smartphone, businesses should make sure that their websites have a mobile version. Otherwise, their website would not be as accessible to everyone who may want to do business with them on their phones. When they do make a mobile version of their website, they might as well take advantage of the fact that the consumer is using a smartphone by making use of its features such as using the phone's camera for scanning credit cards or using the touch screen interface for easier interaction. They should also make it easier for the consumer to ask for help if they did not know what they were doing or how to do something. Because no matter how much you try to make a website accessible or user friendly there will be someone who will not know how to use or do something. Of course, to minimize the need for help you might as well make the website simple and organized. Otherwise, the need for help would be very necessary and that is not very good for business. Another good tip is to add supplemental information to whatever is on your website to minimize confusion.[31]
Effective E-Commerce Websites
[edit | edit source]The fourth step to follow when implementing Web-based e-commerce is designing and developing an effective Web site. If not the most, Web site design and development are definitely a few of the main features that have to be straight on-point to gain or manage existing customer support. Whereas Web site design is the process of planning what a Web site will look like and how it will function, Web site development is the process of actually building the Web site, testing it out, and publishing it on the Internet for public use. Without obstructing the site’s usability, a Web site creator’s ultimate goal is for the Web site to be balanced equally between its attractiveness and user friendliness, while still providing 100% security. Therefore, in addition to perfect design and development, e-commerce sites also have to ensure that order forms and checkout pages are located on a secure Web server, to avoid any potential security threat. With that step comes another responsibility of continually evaluating the security of the Web site and any collected sensitive data to ensure that the customer, or the user’s, security and privacy are being taken care of diligently. Lastly, all of the previously mentioned e-commerce features can be created using two types of software: Storefront software and Shopping Cart software. The storefront software facilitates the creation of an online store; while on the other hand, the shopping cart software is designed to add only the ordering and checkout capabilities to an existing Web site. [32]
E-commerce is something we are bombarded with on a daily basis. Any time that we go to the internet we are almost guaranteed to see an ad or access some kind of site that is selling something to consumers. Whether or not we choose to click and access these sites is another story. Although, when we do, there are a few things that these sites can take advantage of to try to ensure user purchases are made. Firstly, these sites are going to want to look appealing to the group they are advertising to (e.g. a website selling kids toys would want to be colorful and full of pictures not just plain black and white text with limited images). Next, it is important that the website be user friendly. This involves: easy navigation, pages loading in a timely manner, and having some special perks like a search box or a dropdown of links to all the main pages on the site. While these are not necessary things to create a website, they are useful things for websites to contain in order to satisfy visitors. Other helpful, but not necessary, things to include are contact information, special promotions, and even social media links so customers can share about their experience with the site[33].
In the realm of E-commerce, there are two things that are very important: the shopping cart and security when processing transactions. Have you ever bought (or tried to buy) something from a site and had a hard time finding the shopping cart? Or have you had trouble editing the items in your shopping cart? These problems are big E-commerce no-no's and something most sites do try to avoid. However, they do still happen. The shopping cart is something that, ideally, would be accessible and easy to find from any page on a website, and once you are looking at the items in your cart, it should be simple to modify the items (add or delete products). Another thing that E-commerce sites should do is ensure that their checkout page is in fact secure. When purchases are made online, most people use their credit/debit cards to pay for their items. With the number of people in the world who know how to hack computer systems or decrypt code, it is important that websites ensure the security of such important personal information. Without this security there would be virtually no way to protect yourself from credit fraud or identity theft. While there are still ways for people to access the information, it is much harder to access it from a secured site. There are a few ways to check a sites security including the "http://" section of a URL being green in color, the URL beginning with "https" instead of just "http", as well as the security certificates that most secure sites will post on their pages to advertise their security to their customers.
E-Commerce Sales and Marketing Strategies
[edit | edit source]Click Fraud
[edit | edit source]
Click fraud is an illegal practice that occurs when individuals click on the Web site’s advertisements in order to increases the number of click through to the advertiser. The individuals who use click fraud use it in order to increase their own personal banner ad revenues and also by companies who use click fraud as a way to deplete a competitor's advertising budget. Click fraud was once known to be a very large problem within paid searches in which Google was first introduces with the invalid click to be known as a metric. A metric was intended to provide some insight into how much fraud was occurring and ease the minds of advertisers. Google identifies three areas they determine to be invalid clicks: Manual clicks intended to increase your advertising costs or to increase profits for website owners hosting your ads, Clicks by automated clicking tools, robots, or other deceptive software, Extraneous clicks that provide no value to the advertiser, such as the second click of a double-click. The difference between then and now and the source of the invalid clicks of today. Click fraud still occurs in paid search, and at some level always will. However, the engines at this point do a solid job at monitoring the problem. The issue for search marketers is to ensure the metrics don't go out of whack from a normal level of variance. Meanwhile the focus will be on emerging media types where fraud is ahead of the development curve.[34]
Procedures for Handling Electronic Financial Transactions
[edit | edit source]
There are different ways an e-commerce site can set up payment options, and it is important to understand what type of payment option is best for the nature of the site. Credit cards, debit cards, PayPal, Bill Me Later, and gift cards are the most common payment options used by e-commerce sites. Payment by credit/debit card is the dominant method. Businesses usually open an e-commerce merchant account to allow for these payments. For payment with credit, a buyer makes a transaction with the credit card where money is then transferred from the credit credit card company to the merchant account. For debit cards, money is simply taken from the checking account and transferred to the merchant account. Businesses pay fees to the banks for this service. A relatively new system is for consumers to use low-cost card-swipe devices that enable merchants to get by the higher rates when the card is not physically present. Airline and travel sites are some businesses currently taking advantage of this method.
Virtual account numbers, smart cards and prepaid credit cards are all used to better improve the security and safety of both the transaction process and the account information of the card holder. These cards can be secured with a PIN and/or a one-time password (OTP) to decrease the chances of a hacker obtaining account information.
Online payment services, like PayPal, and the use of gift cards, coupons and digital gift certificates are two other popular payment options. PayPal allows individuals to transfer money from their online payment account to another, and it is the prefered payment method for transactions on Ebay.[35] This type of service is prefered because it does not require consumers to reveal their credit card numbers to the merchants, and merchants pay lower fees than conventional credit and debit card purchases. Lastly, gift cards, coupons, and digital gift certificates allow gift recipients to select their own items at an online store. These can be purchased in physical or digital form where the codes are then entered in the checkout process. Also, coupons are becoming much more popular with the increasing use of mobile phones.

Virtual account numbers work the same as the number on the actual card. However, they are used with limits set by the user within a certain time frame. The primary use of this virtual account number is to enable users a safer way to use a single credit card for purchases by using a temporary account number. The code is a typical 16- digit code. Users claim that this option takes around 60 seconds to set up. The way a user can set up these virtual account numbers is very simple. First, a user must log-in to their credit card account, navigate through a few boxes, and set the expiration date. Although the concept of virtual account numbers is not new, they are becoming more popular today. Especially with the expansion of smart phones. The actual account number is not a physical card, and it is primarily used for online transitions. With security becoming an increasing primary factor for users to consider, virtual account numbers seem very handy. Many consumers choose to shop online. With the use of virtual account numbers, users can be assured security from the first payment they make. The set time limit makes it very convenient to fit the consumer's needs. Overall, with such effective security features, it is a surprise that virtual account numbers are not used as often. [36]
Bitcoins
[edit | edit source]Bitcoin is a new cryptocurrency, which was created by an unknown programmer (or a group of programmers) under the pseudonym Satoci Nakamoto. This happened in 2009. Nobody knows where this man is and what his name is in the real world. Cryptocurrency Bitcoin has the basic functions and properties of conventional money from different countries. It could exchange, stored and used to purchase. However, Bitcoin is cryptocurrency, which is a type of digital currency. Its emissions and accounting based on different cryptographic methods. A decentralized operation occurs, in a distributed computer network. Cryptocurrency - this is the real software, the growth rate of which depends on supply and demand, not by subsequent investors. Each member of the network can make instant transactions cryptocurrency without intermediaries. That is, the buyer sends the money directly to the seller. No need to go to the bank, you simply send Bitcoins to the person. Coins in the system are the cryptographic (mathematical) hash functions. Each of them is completely unique and cannot be used twice. Bitcoin can be used to purchase goods and services on the Internet anonymously. Moreover, it is easier and cheaper to make international payments because Bitcoin is not tied to a particular country. To store Bitcoins have a few options. Offline purse is being installed and is created on your PC. Usually, it is encrypted to prevent tampering. But, there are some cons, if you forget the password to log into a purse or on your computer hard drive died you lost your money. Online Bitcoin wallet has advantages over the offline version. You can access it using not only PCs but also tablet or phone. One of the main problems of these wallets is that all the data stored on the server. Many online stores or retail outlets that accept bitcoin currency side by side with local currency, debit cards or credit cards, opens the window of opportunity for users to compare the benefits of shopping via bitcoin payment. [37]
Driving Business through Meta Tags
[edit | edit source]
Keeping and maintain your company’s website is very important in working towards driving business. Many of us, when we search the Internet, are not just going directly to one specific page. We want to browse and find what pages pull up for the topic in which we are searching for. That is why most of us use search engines such as Google, Yahoo, etc. The problem is, you need to make sure that your getting business and traffic from these searches. Most of the time, people don’t make it past the second page of results to find what they are looking for, so what does a company need to do to make its page relevant? They use meta tags, which are essentially labels that search engines such as Google and Bing can use to find web sites related to search terms. For example, a hair salon’s website would likely include meta tags such as haircuts, hairstyles, and other related terms. Good website design includes many variations of meta tags, to increase search matches. This is crucial to making sure that the page is getting the traffic that it needs to drive business. [38]
Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act
[edit | edit source]
Domain names are unique and are registered through an official domain name registrar. This forces businesses to come up with a very unique website domain name that will only attract their customers. Some people try to register domain names in the hopes of stealing profit from a company or another person, but this is actually illegal. The Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act protects businesses trademarks in cyberspace, by making it illegal for others to create a confusingly similar domain name with the intent to profit off the trademark without regards to the goods or services of the original trademark owner. This can be related to the recent news of Johnny Manziel’s friend trying to trademark “Johnny Football” in the hopes of profiting off of Johnny Manziel’s legacy. The only difference is that the ACPA affects online domain names instead of the actual trademark. There are many factors that are considered when a domain name is registered. This includes if the domain name is the legal or nickname of the registrant, if the registrant has a trademark of the same name, if the intent of the website is to harm the trademark owner’s good will, if the registrant resells the domain name without having ever used it for the sell of goods or services, and multiple more factors. All of this has come into fruition to help protect trademark owners from being scammed out of their rightful profit and to stop people of ill will from buying a wrongful domain name. [39]
Search Engine Optimization
[edit | edit source]
Search site optimization is one way that a website can make themselves more easily found online when being searched for through search engine websites like Google. Typically, the most popular website with the most relevant information based on the searched keywords is displayed as the top result. To optimize a website, one can edit the content of the website itself and the HTML code so that when the search engine is crawling through its database that page is determined to be more relevant. Another way of optimizing a website is through increasing the amount of backlinks, or incoming weblinks that lead to that page. The more back links that a website has, the more popular the website is to the search engine. In the modern world, search engine optimization is a huge deal for any businesses that are trying to promote themselves on the internet. Regardless of the size and content of a website, proper search engine optimization can get any web page to the top of the search results, which would therefore increase the overall visits to that site. [40] Most users of search engines do not look much farther than the first few results or the first page, making it crucial for any company trying to break into the business and beat the competition to be amongst those results. [41]
Advertisement Strategies
[edit | edit source]Business' employ several online advertisement strategies in order to appeal to the consumer. A popular method of displaying a product or to promote a business is to place banner ads on popular websites. Banner ads are size-able pictures that display what the business would like it to, and when clicked on, the ad will link the user to the business' page. While banner ads used to be static ads, today it is much more popular to use dynamic banner ads such as videos or animations. To place banner ads, typically an online advertising firm is used and the company pays a fee to each Web site on which the ad is displayed, as well as a fee to the advertising company. Another advertisement strategy is the use of behavioral ads, which are ads that are targeted to individuals based on their preferences, buying habits, or interests. These preferences are usually determined by cookies places in participating Web sites by advertising networks. The data that behavioral advertising collect about the consumer is not tied to personal information, but rather online activity. Examples of what a behavioral ad tries to find out about the consumer includes the consumers age, gender, and purchase interests.[42]
Review
[edit | edit source]brick-and-mortar store A conventional store with a physical presence.
brokerage site A type of Web site that brings buyers and sellers together to facilitate transactions between them; the site earns revenue in the form of commissions on sales made via the site.
digital wallet A program or online service that holds a buyer’s information (such as electronic payment, billing, and shipping information) that can be used to speed up online purchase transactions.
dot-com An Internet-only store with no physical presence.
e-commerce The act of doing business transactions over the Internet or similar technology.
meta tag A special HTML or XHTML tag containing information about a Web page that is added by the person creating the Web page and is used primarily by search sites.
online auction site A Web site where potential buyers bid on an item and, at the end of a set time period, the highest bidder buys the item as long as all bidding criteria (such as minimum selling price) have been met.
online payment service A type of payment service accessed via the Internet and used to make electronic payments to others, such as via deposited funds, a bank account, or a credit card.
search site optimization (SSO) The process of evaluating a Web site and making changes to improve search site results.
shopping cart software E-commerce software designed to add ordering capabilities to an existing Web site.
storefront software E-commerce software that facilitates the creation of an online store.
subscription site A site that sells access to its online content.
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]1. What is the process of evaluating a web site to improve the search site results?
2. What is a program that holds a buyer’s information?
3. What is a type of Web site that brings buyers and sellers together to facilitate transactions between them?
4. What is a special HTML tag containing information about a Web page?
5. What is a web site where potential buyers bid on an item?
6. What is a type of payment service accessed via the Internet which are made to make electronic payments to others?
7. What is E-commerce software that facilitates the creation of an online store?
8. What is a site that sells access to its online content?
9. What is a type of Web site that brings buyers and sellers together to facilitate transactions between them?
10. What is a conventional store with a physical presence?
11. A brokerage site is a type of web site that brings buyers and sellers together to facilitate transactions between them?
12. An online payment service is a type of payment service accessed via the Internet which are made to make electronic payments to others?
Answers: 1. search site optimization 2. digital wallet 3. brokerage site 4. meta tag or online auction site 5. online auction site 6. online payment service 7. storefront software 8. subscription site 9. brokerage site 10. brick-and-mortar store 11. True 12. True
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://www.networksolutions.com/education/what-is-ecommerce/
- ↑ http://www.networksolutions.com/education/what-is-ecommerce/
- ↑ http://blog.templatemonster.com/2010/09/08/history-of-ecommerce-timeline-infographic/
- ↑ http://www.networksolutions.com/education/what-is-ecommerce/
- ↑ http://forbstudents.blogspot.com/2009/05/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-e.html
- ↑ http://tokokoo.com/2010/07/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-e-commerce/
- ↑ http://www.newegg.com
- ↑ http://www.kohls.com
- ↑ http://ecommerce.about.com/od/eCommerce-Basics/a/Disadvantages-Of-Ecommerce.htm
- ↑ http://www.pcworld.com/article/2042408/15-ways-to-protect-your-businesss-e-commerce-site-from-hacking-and-fraud.html
- ↑ http://www.ecommerce-web-hosting-guide.com/ecommerce-business-models.html
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/btoc.asp
- ↑ http://www.techopedia.com/definition/26175/dot-com-boom
- ↑ http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/5085-what-is-b2c.html
- ↑ http://searchcio.techtarget.com/definition/B2G
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/btob.asp
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Business-to-business
- ↑ http://www.grainger.com
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Consumer-to-consumer
- ↑ http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/consumer-to-consumer-c2c-e-commerce-definition-business-model-examples.html#lesson
- ↑ http://money.howstuffworks.com/history-e-commerce.htm
- ↑ http://www.thefreedictionary.com/e-tailer
- ↑ http://www.thefreedictionary.com/subscription
- ↑ https://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Video_on_demand.html
- ↑ http://variety.com/2014/digital/news/amazon-adds-hbo-series-to-prime-instant-video-including-boardwalk-empire-sopranos-1201187916/
- ↑ http://smallbusiness.chron.com/types-ecommerce-business-models-2447.html
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EBay
- ↑ http://www.getelastic.com/7-wicked-ecommerce-applications-of-shopping-apis/
- ↑ http://www.sba.gov/content/online-payment-services
- ↑ http://www.smashingmagazine.com/2013/11/11/guidelines-navigation-categories-ecommerce-study/
- ↑ http://mashable.com/2011/08/01/tips-better-website/#Ao_hWvZO0uqS
- ↑ http://www.smartwebby.com/web_site_design/webdesign_tips.asp
- ↑ http://www.hongkiat.com/blog/essential-things-ecommerce-site-should-have/
- ↑ http://searchenginewatch.com/article/2261638/Click-Fraud-is-a-Small-Problem-in-Search-These-Days
- ↑ http://pages.ebay.com/help/pay/paypal.html
- ↑ http://money.usnews.com/money/personal-finance/articles/2011/09/30/should-you-use-a-virtual-credit-card-number
- ↑ http://www.forbes.com/sites/johnrampton/2014/07/02/how-bitcoin-is-changing-online-ecommerce/
- ↑ http://searchenginewatch.com/article/2067564/How-To-Use-HTML-Meta-Tags
- ↑ http://cyber.law.harvard.edu/property00/domain/legislation.html
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/S/SEO.html
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Search_engine_optimization
- ↑ http://www.truste.com/consumer-privacy/about-oba/
Information Systems
What is an Information System?
[edit | edit source]
A system is a group of procedures and different elements that work together in order to complete a task. Now we can add on to this to get information systems. Information systems are much the same. There are elements and procedures to work to complete a task. The difference is information systems are used to generate information for the users on a need basis. Information systems manage and process data as soon as they're created. They can also be used for long term planning or just the day to day work. While systems are great and can ease your life, they are static, which means someone will need to change the systems when new needs arise. This is called system development. While it could be costly, there really is a need for system development since things change constantly, such as any time there are new laws or a new policy within the company.

Some information systems are meant to be used by all levels of employees while others are specifically designed to handle the needs of employees with certain responsibilities. As one goes higher up the company ladder, it can be seen how responsibilities may increase relative to position. It is for this reason that some information systems are designed to hone in on the needs of certain level employees. At the ground level, employees generally make job-related decisions that are based on "on-the-job" input without having to consider how those decisions will affect other departments or employees in other positions. These usually involve transaction systems such as point-of-sales or warehouse systems that record stock and inventory. Operational managers such as supervisors or foremen use separate information systems designed to meet short term goals and gains. They might use systems that show the productivity of employees or the cost-effectiveness of certain changes they've made in production. Middle managers are a step up from this and use information systems that house a broader range of information to make more tactical decisions. These decisions are usually aimed at a farther sighted goal than those of Operational managers and often need more intelligence pulled from data systems in order to reach these objectives. Middle managers might be more concerned with how to improve yearly gains and may use systems that will deliver more detailed information about specific locations of factories or retailers in certain states. Executive managers think in terms of the future and the direction of a company related to their peer corporations. They make very strategic decisions to ensure the survival of the entire company as a whole in relation to the economy and competition. The systems they use might include the stock market, which tracks the progress of a lot of businesses. Because the needs of each position increases, the decision support systems needed to make well judged verdicts must increase as well.
Types of Information Systems
[edit | edit source]The Four Essential Information Systems
[edit | edit source]

There are many different types of information systems. Even though there are many systems, the four that will be elaborated are the following: transaction processing systems, customer relationship management systems, business intelligence systems, and knowledge management systems. Transaction processing systems are used for processing and output functions for the core operations of a business, storage, and data collection. The purpose of this system is to collect input and then produce the output. An online air ticket booking system is an example of a TPS. Customer relationship management systems are usually used by business owners for sales and marketing efforts. This system helps businesses keep record of customer activities, purchasing trends, product defects, and customer inquiries. CRM systems also allow business partners to communicate with each other which contributes to a successful business. Business intelligence systems are essential for businesses to predict sale patterns for their company. BIS are essential in collecting data from different companies. Financial Institutions are an example of this type of system; it is used to create credit risk models that study the number and amount of lending given to the sectors. Knowledge management systems organize the knowledge within an organization and then share it. KMS brings innovation, top quality performance, integration, and knowledge to an organization. Small and large enterprises can benefit from this type of system. Business owners view this system as a valuable attribute to their company because it provides quick responses to their customers and partner questions.[1]
Office and User Productivity Support Systems
[edit | edit source]
There are systems implemented in many institutions (ex. Universities, hospitals, corporations) that help users in everyday tasks including the creation of documents and other content through applications as well as communication. These systems are one of the oldest and most simple types of systems that have been created when institutions started going towards paperless solutions.[2] Document Processing Systems are support systems that allow users to create documents with the use of software and/or hardware. Often these systems include software applications such as Microsoft Office or Apple iWork and hardware such as scanners. Document Management Systems are systems that both store and organize the documents. The goal of these types of systems is to make documents easier to find by placing them in one centralized repository. A Content Management System is essentially the same as a Document Management System except that it also manages multimedia documents such as pictures or videos. Although they may seem simple because we use them everyday, Document Processing and Document/Content Management Systems can be very complicated when taken to a larger scale because it includes not only the organization and creation of a database, but also ensuring the security of the documents within the system.[3] Another common type of Office and User Productivity Support Systems include communication systems. These can be any sort of software that allows users within an institution to communicate. Common communication software includes email, videoconferences, and messaging. Unified communication such as these not only support sharing pertinent information quickly but also better collaboration, remote work capabilities, centralized communication and assistance with navigating tasks.
Transaction Processing Systems
[edit | edit source]Any computer application that helps process business transactions is called a transaction processing system (TPS). Order entry systems, payroll systems, and accounting systems are three main types of TPSs. Order entry systems simply record order data. For example, when purchasing an item from Wal-Mart’s website, your order is recorded by an automated order entry system. The type of order entry system Walmart's website uses is an e-commerce system due to the fact the order was made over the internet. There are also order entry systems that work with physical transactions, called point-of-sale systems. For instance, if someone were to purchase a product at Wal-Mart (not online), the order would be processed at a register using a point-of-sale system. A payroll system is another type of a TPS that is used by almost every employer. Payroll systems basically organize, compute, and issue paychecks. These systems automatically take out the correct amount of taxes and other deductions from an employee’s pay. Accounting systems are a type of TPS that records financial transactions. Three types of widely used accounting systems are accounts payable systems, accounts receivable systems, and general ledger systems. Accounts payable systems keep track of how much a seller owes a buyer, while accounts receivable systems keep track of how much a buyer owes a consumer. General ledger systems are systems capable of putting together account data to form financial reports.[General default colors and sounds system active solving setting complete by 1][4]
Enterprise Systems
[edit | edit source]
An enterprise system is an integrated information system that is made to support business processes, information flows, reporting, and data analytics in complex organizations. Its main function is to coordinate all of the major processes of an organization and integrate those processes into the different departments of the organization. Some of these application processes may include sales and distribution, financial accounting, investment management, materials management, production planning, maintenance, and human resources. Because it is integrated, it allows data to be used for several purposes.[5] There is a central database that collects all the data from all of the applications, and then in return it feeds out the data as output to all of the processes of the organization. So, once data is given by one of the processes, then all the processes have access to that data. An example would be a university or college that uses an enterprise system to manage all student records, enrollment applications and acceptance, finances, human resources, etc.[6] Many companies are starting to implement enterprise systems because it is an easy way to combine the core functions of the company with technological advancements. It is an easy way because the enterprise system is a single software architecture that fuses all the core processes of a business to function as one unit. The synchronized functioning of the processes makes it easier and more efficient to for multiple departments to work together and it is also helpful for managers as they can better oversee multiple tasks and project at one time.[7]

Enterprise systems were created to eliminate the problem of the shattering of important information in large businesses. Most companies have so much information stored in so many different areas that when information needs to be retrieved, it becomes a hassle. If a company’s information is shattered and cannot be retrieved when needed if retrieved at all, it will eventually reflect into their sales. An enterprise system is a single database which gets information from all of a company’s activities. Whenever someone changes information in any area, the system will then update it throughout and make the information up to date. The amount of productivity and speed can really increase when a company begins using this system. This also gives them the ability to be organized and function on a larger level. Inside of an enterprise system there are modules. Some modules are used universally by all companies and other (such as human resources) are specific to each company. Configuration tables are also part of what makes an enterprise system. These are how a company can make their system unique to their business. They can change certain parts of the system such as not only having an inventory, but instead having inventory accounting. Enterprise systems help with logic and organization in companies and provide a better “flow” in how things are run.[8]
Data Mining
[edit | edit source]"Data mining" sounds like a kind of unnerving term or a violation of privacy, but it isn't really. It just refers to any "process of analyzing data from different perspectives and summarizing it into useful information"—in other words, taking a lot of data about anything, including public information, and analyzing it with software to a useful end that can't easily be reached by a human alone. It's using computers to sift through a large amount of data that a human being can't analyze. For example, supermarkets regularly have computers analyze massive amounts of data on which items are more or less frequently purchased in which locations so that they can stock stores with items that will be purchased by more individuals in that store's location. They also might change the prices of items slightly on certain days when those items are more commonly purchased, and they stock items close to one another that are often purchased together. There are many other uses of data mining besides just these (which are examples that have actually occurred, not just hypothetical ones), but in general, data mining is most frequently used via corporations to cut costs or increase revenues.[9]
Data Mining Techniques
[edit | edit source]Because prediction is the main goal, predictive data mining is the most common type of data mining, with popular and practical business application. The process consists of three stages: (1) Exploration, (2) Model Building and Validation/Verification, and (3) Deployment
Stage 1: Exploration. Begins with data preparation which may involve the cleaning and transformation of data, selecting subsets of records, or performing preliminary feature selection operations (to bring the number of variables or fields to a manageable range). It also may involve simple, straightforward predictors for a regression model, in order to identify the most relevant factors and determine the complexity, and/or a general nature of models.
Stage 2: Model building and validation. Involves considering various models and choosing the best one based on their predictive performance (offering stable results across samples). Many techniques (Bagging, Boosting, Stacking, and Meta-Learning) developed to achieve this are based on so-called "competitive evaluation of models," which uses different models on the same data, analyzing their performance, and choosing the best.
Stage 3: Deployment. Using the model selected as best in the previous stage and applying it to new data in order to generate predictions or estimates of the expected outcome.[10]
Computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing
[edit | edit source]
Computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) are computer systems that are used to design and manufacture products.[11] CAD is used to assist in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. It is used to increase the productivity, improve the quality, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. It is used in many applications such as automotive, shipbuilding, and aerospace industries, industrial and architectural design, prosthetics, and many more. Also, CAD is used to produce computer animation for special effects in movies, advertising and technical manuals.[12] CAM is used to control machine tools and related machinery in the manufacturing of work pieces.CAM can also assist in all operations of a manufacturing plant, including planning, management, transportation and storage. The primary purpose of CAM is to create a faster production process and components.[13] Compared to manual machines, there are several advantages to using CAM such as speed (CAM is faster because machining speeds are higher), greater accuracy, greater consistency (every finished product is the same), efficiency (production can run 24 hours a day, 7 days a week) and sophistication (CAM is able to machine difficult shapes, eg tracks on a circuit boards).[14] After the model is generated in CAD, it can be input into CAM software which then controls the machine tool.
Decision Support Systems
[edit | edit source]A specific type of support system often used by businesses is known as a decision support system. Decision support systems were originally being researched as early as the 1960’s, but began interacting with users in the middle and late 1980’s. A decision support system enables a user to make decisions on demand, and interactively. These systems use both internal and external data to provide a user the tools to organize the decision-making information. The concept of decision-making is to primarily allow the user needed information to make particular decisions. The system is not necessarily making the decision for a user; it is simply retrieving relevant information that will assist them in their decision. With that being said, DSS systems are primarily used to uncover unstructured information regarding issues middle and executive managers may face. Once the data is retrieved from either internal or external sources, the system allows human-friendly access to retrieve the data. Examples of prospective data gathered would be: inventories of information, comparative sales figures, and projective revenue. This system is indeed relatively simple to use through its interaction with the user of the system. DSS systems also allow great flexibility for the program, appealing to various ranges of information. The system can also adapt to the user’s environment as well.[15]

You may not realize it, but whenever you fly on an airline, a massive amount of data has to go through a series of programs and locations and be approved before your flight can occur. These decisions are made at an airline’s dispatch center. At a center, flight data information such as weather, weight, passenger information, and gate availability are all put together and interpreted to make a safe flight. United Airlines is a good example of this. They consolidated their dispatching center to one location, the 27th floor of the Sears Tower in Chicago. Their facility takes up an entire floor of the building and brings everything for a flight together. A standard computer program is used to interpret all the data needed for a flight. After the dispatcher prepares a flight, the information can be transmitted directly to an airplane flight deck, or a United airport facility. The flight can then go as planned. At the same time, a dispatcher can decide to cancel a flight if the information calls for it, or if there is some kind of crisis to deal with. Because of special programs and new technology, your flight can be completed safety, and without long delays.[16]
Artificial Intelligence
[edit | edit source]Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems are systems that allow computers to perform actions that are characteristic of human intelligence. These can include systems such as expert systems, which provide the user with the kind of advice one would expect to receive from a human expert. This can help businesses and individuals make important decisions and predictions that will increase performance and further enchantments. There are also neural networks, which are systems in which the human brain recognition process is mimicked by a computer. This can be used in processes such as medical reading or biometric identification. Another advancing technology is robotics, or the study of robots. A robot is a device that can respond to sensory input, and is controlled and programmed by human intelligence. With constant advancement in technology pertaining to artificial intelligence, one would be well advised to seek out the possible effects of these “life like” computers. Ray Kurzwell, author, inventor and futurist, proposes the idea that artificial intelligence, genetics, nanotechnology and robotics will soon result in a human-machine civilization. He believes that in the not so near future, due to advancements in genetics that will allow for scientists to reprogram genes to eliminate disease and curb the aging process, man and machine will merge, “allowing one to transcend biological mortality.” Mr. Kurzwell may be a bit ahead of his time with his ideas and theories, but at the rate technology progresses in this age, it is hard to predict the heights it will reach[17].
Some predictions have been made for 2017 in the field of artificial intelligence. Two of these predictions are reinforcement learning and generative adversarial networks. Reinforcement learning is a process in which a computer works to answer a question or solve a problem and then associates the positive outcome of solving the problem with the actions it took to solve it. In this way, the computer learns without explicit instructions or examples. Reinforcement learning is expected to be useful in real-world situations such as automated driving and industrial robotics. Generative adversarial networks are systems consisting of one network that generates new data after learning from a training set, and another network that tries to discriminate between real and fake data producing realistic synthetic data. Real-world uses for this could be to make video game scenery, to de-blur pixelated video footage, or to apply stylistic changes to computer-generated designs[18].
IBM Watson and Cognitive Computing
[edit | edit source]
IBM Watson, developed by a research team led by David Ferrucci, is a question answering computer system capable of answering questions posed in natural language. [19] IBM Watson was given its name after Thomas J. Watson, IBM's first CEO. IBM Watson combines artificial intelligence and sophisticated analytical software in order to perform its question answering capabilities. [20] In order to understand how IBM Watson functions or what its capabilities truly are, one must first understand the concept of cognitive computing. Cognitive computing, with still no official definition, refers to hardware/software that mimics the functioning of the human brain and helps to improve human decision-making. Some features that cognitive computers display are adaptability, interactiveness, contextualism, and iteration. [21] In order to display IBM Watson's abilities, in 2011 Watson challenged and beat the top-two ranked Jeopardy! contestants, Ken Jennings and Brad Rutter. The Watson system was placed between the two contestants and, just like the other two competitors, had no internet access. [22] IBM Watson uses IBM's DeepQA software and the Apache Unstructured Information Management Architecture framework and runs on the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 operating system. [23] As a result of the components that make up IBM Watson, the applications for its use are nearly endless. Currently IBM Watson's focus areas are commerce, education, financial services, health, internet of things, marketing, supply chain, and human resources. [24] There are currently four IBM Watson products that are available for public purchase including Watson Discovery, Watson Conversation, Watson Virtual Agent, and Watson Knowledge Studio. [25]
System Development
[edit | edit source]The Information Systems Department
[edit | edit source]The information systems department is also referred to as the information technology department. It is responsible for running, maintaining, and developing the computers and information systems in an organization. They also ensure the programs run smoothly. It includes all the computer and network personnel of that organization. The IT person that is most involved in system development is the system analyst. The system analyst manages the things related to designing and implementing modified systems. This person should be the first level support in the case of system-related issues. A person who is very important to system development is the business analyst. It is one of the biggest growing jobs because of the large increase in the use of technology. It is all about finding the most effective use of electronic communication.[26]
Systems Development Jobs
[edit | edit source]
Some other IT jobs are business analysts, application programmers, operations personnel, and security specialists. A business analyst will analyze the organization and its documents in order to assess and process that information. They help understand the policies and actions that a business has and then helps to achieve their business goals. Business analysts make a strategic plan, look at the business model analysis, process design the organization's work, and then interpret for technical systems. An application programmer will take the technical and functional parts of a business and review the tech system. They look for ways to increase efficiency, manage things better, and enhance the work system to perform at its best. An application manager will usually create new applications that combine programs together for efficiency.[27] Operations personnel look at things more from a day to day basis and look at ways to improve upon things. This job is useful because they get to see the progression of things in the business from one day to the next. Security specialists will create a secure system to protect the company’s data and information. They will make sure that not everyone will have access to everything in the company’s database. Additionally, they monitor and respond to security incidents.[28]
Becoming a Systems Developer
[edit | edit source]
In order to be a systems developer one must have basic coding skills. One must know at least one programming language. One must know how to fix problems on the fly if ever a system failure occurs. One must learn to keep maintenance of such systems so that the chances of system failure is minimized. The field itself is highly technical in nature involving plenty of computer science and mathematics in an environment which is always and rapidly evolving with technology. One must also learn how to work in a group for in an organization you will most likely have a defined role in a group of programmers and system developers. So not only must you have the technical skills but also the soft skills such as communication and teamwork. Possibly even leadership if you were to take in a position wherein you are the leader of the group. You can also work as an adviser to those who are using the systems in business settings. The most important role of the systems developer is to be the support system in the organization in order for everything to be able to run as smoothly as possible.[29]
Outsourcing
[edit | edit source]
In the industry today, many businesses have been outsourcing their work. Outsourcing occurs when businesses hire others outside of their company to perform different tasks, like creating new software or databases for the company. Some examples of outsourcing today include customer service, technical support, payroll accounting, and credit card processing. This is becoming more prevalent through the years because outsourcing has many advantages to the business itself. Offshore outsourcing is another term used, but the work is done in another country. India, for example, is one country that generates much revenue from offshore outsourcing alone. Although many speculate that American jobs are at risk, outsourcing to other countries benefits the business as a whole. The company saves a lot more money than if they were to keep technical support, customer service, etc. in the primary country of that company. Another advantage of having offshore outsourcing is that there can always be someone working on a project, gathering information, and helping a client because of the different time zones. A lengthy project can be completed faster than would a normal project worked on in just the United States because 24 hours a day, somebody is always working on the project. One downfall of outsourcing is cultural differences. Language barriers can be detrimental to a company at times. Homesourcing is a new trend that many companies are taking advantage of and adopting. This is the transfer of service industry employment from offices to home-based employees with appropriate telephone and Internet facilities. Another aspect that companies have to look into is security with newly outsourced employees when they are first hired.
SDLC - System Development Life Cycle
[edit | edit source]The System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is composed of six steps. These steps are as follows: preliminary investigation, system analysis, system design, system acquisition, system implementation, and system maintenance. Each step is important and builds up on the step(s) that happened previously. While these are generally the steps always used, they do not always occur in the same order. The effects are still the same.[30] Below is an explanation of each of the six steps.
Step 1: Preliminary Investigation
[edit | edit source]
As the first step in the SDLC, preliminary investigation plays a large role in determining whether or not a system or system modification would be worth making. The main point of doing a preliminary investigation is to determine what problems need to be fixed and what is the best way to go about solving those problems, if solutions do in fact exist. An initial support group should also be identified. A feasibility report is the product of the preliminary investigation in most cases. The feasibility report is essentially a compatibility test between the current business/system and the new system/modifications. The report will tell companies if they can afford the change, if it will work with the other systems and technology already in their company, and if it will be beneficial to the company to make the changes. If all these things come back positively from the systems analyst, then the system will receive the "all clear" to head to the next step of the SDLC.
Step 2: System Analysis
[edit | edit source]This second step, system analysis, is used to investigate the problem on a larger scale and fine tune all the information a company has on the issue. Data collection and analysis are the two main points of interest inside system analysis. Gathering information about the current system and users allows analysts to develop an idea of what seems to be the real problem and how they should go about fixing it through data analysis. The main outcome from this step is a grouping of organized data about the current system and the new/modified systems improvements to come.

To illustrate systems that are based on the concept of objects, tools like use case diagrams and class diagrams are used. Use case diagrams are used to describe the behavior of the target system from an external point of view, while also illustrating the users who interact with the system. On the other hand, class diagrams provide an overview of the target system by describing the objects and classes, and their relationships, inside the system.

As mentioned above, system analysis is the phase of system development where the problem area is fully studied in depth and the needs of system users are assessed. The tools that will help accomplish this phase of collecting data and data analysis are entity-relationship diagrams (ERDs), data flow diagrams (DFDs), decision tables and decision trees, business process modeling notation (BPMN), and class diagrams and use case diagrams. To describe the use of these tools in depth you will need to understand that any tools or processes used during this phase will aid in understanding the problems or issues of the current systems and how to improve them. So you will see several visual aids, charts, tables, diagrams, models, etc. All this is to help clarify and make sense to all personnel involved how the current system may be improved. Essentially, the new system requirements are defined and; in particular, the deficiencies in the existing system must be addressed with specific proposals for improvement. Entity-relationship diagrams and data flow diagrams are used to model the entities in a system and the flow of data between the entities. So, these kinds of diagrams will create a visual for the logical interaction between the individual entities that use the system. Business process modeling notation is a graphical, standardized notation used to model a business process. This type of modeling is similar to a flowchart and is meant to be understood by all users of the system.[31]
Step 3: System Design
[edit | edit source]
After all of the data has been analyzed, it is time to design a blueprint for the system that specifies what it will look like and how it will work. First you have to develop the design by using a few key tools. One important tool is the creation of a data dictionary, which describes the characteristics of all data that is used in a system. Other important creations that the systems analyst will use include different diagrams which help to better describe the proposed system. It has been argued by some that the ever-increasing rate of developing technology has made it impossible for the every day systems analyst to do their job thoroughly. The economics of industry are pushing in a way that doesn't favor design, only production.[32] Whether this is truly the case, system design leaves little room for error, as time is money.
In addition to a data dictionary, the systems analyst also has to create input designs to help illustrate the input screens and other user interfaces that will be used to input data into the new system. To ensure that the data is input accurately and secured against data loss, it is essential for the system design to contain some form of a security feature. Also, an output design helps identify the specific outputs required to meet the information requirements, select methods required for presenting that information, and design reports, or other documents that carry the information. Lastly, once the new system has finally been designed, a cost-benefit analysis is performed to determine whether the expected benefits (tangible or intangible benefits) of the new system are worth the expected cost. This analysis will then help determine if the design for the new system is worth implementing. [33]
Step 4: System Acquisition
[edit | edit source]
Once the design blueprint has been approved, it's off to the proverbial grocery store. The organization needing a system will have a set budget and a list of components needed to make their system work properly. With this budget comes a few courses of action. The first thing to think about is whether the company should create their own software for their system or buy the software from others. It is typically cheaper and less time consuming to buy preexisting software but the customization options are limited. If the preexisting software doesn't offer the options required of the system blueprint, then the company will likely have to make custom software to meet their needs.

Assuming that it okay for the company to buy preexisting software, the next step is to choose where to buy from. To help them choose, they can prepare an RFP, or request for proposal, which asks vendors what software the company might need to consider buying. If they already know what software they need and just want potential prices, the company can file an RFQ, or request for quotation.[34] After filing for the RFQ, the company must evaluate all of the bids from the vendors offering different software. The company, in order to make the most profit, should evaluate each bid and figure out which one has charged the lowest price while also reaching the necessary criteria for the company’s system. The Purchasing Department of a company usually decides which vendor deserves to receive the quote.[35] The decision is usually helped by the use of a benchmark test. A benchmark test is a systematic process that evaluates both the hardware and software of a system. Some determinants used for the test include examining for the amount of workload that a system is capable of processing, the capability of solving complex scientific problems using a range of computations, offering legitimate data for the system to process and viewing the performance and scalability of the software, and many more. These benchmark tests can be offered through third-party organizations where there sole purpose is to test the offered systems. These tests allow for the company to immediately discard incapable systems offered by vendors. Sometimes benchmarks are not capable of being performed due to a company’s location or accessibility, but for the most part they are a great way to assist in evaluating which bid is the best.[36] After all of the required software has been purchased it is time for the next step.
Step 5: Implementation
[edit | edit source]
The implementation phase of the System Development Life Cycle is an important one.[37] In this phase, the new system is installed and made functional in the production environment, after thorough testing. End user testing is imperative to assure a smooth transition. Any required documentation, including instructions and manuals should be developed during the process. Training, for both the system administrators and end users, should also occur during this phase. During some implementations, it is convenient, and sometimes even necessary to run the old system and the new system in parallel. Once implementation is complete and all users are fully operating in the new system, the old system can be removed completely. One of the advantages of a parallel adoption relates to risk. Should the new system fail for any reason, the old system is still in place. Productivity can continue with limited effort in restoration of the old system. There are certain situations where parallel implementation is ill-advised. A significant negative consequences of parallel implementation relates to efficiency. In order for both systems to function effectively, data must be entered into both systems to keep them current. This requires duplication of work and redundancy in effort to maintain consistency.
In this step, users get the old data ready to be moved, called data migration. Once that is complete, they can begin installing new hardware and software. There are four ways of converting data to new a system: direct conversion- the old system is deactivated and the new one is implemented right away; parallel conversion- both systems are operated at the same time until it is known that the new one is working, then the old one gets deactivated; pilot conversion- only one new system is installed within an organization and once it is known that it works then the rest are implemented; and phased conversion- the new system is implemented by modules by using direct or parallel conversion. There are some advantages and disadvantages of using each method. For example, the easiest and fastest method is direct conversion. [38] The final action in this step is training the users with manuals, for example.
Step 6: System Maintenance
[edit | edit source]Often the system maintenance is the ongoing process throughout the life of the system. Maintenance can include updating software or updating what is already installed. Many of you play an active role in this step already. For example, how many of you keep up with the newest updates for your Apple applications? You are taking part in system maintenance.
Once a software has been fully implemented, it goes through a post-implementation review to evaluate how the new system is running and whether or not it is completing its intended tasks. System maintenance includes modifying existing software or adding completely new features to the existing software, as well as fixing any glitches or bugs and checking security. System updates are usually scheduled for off-peak hours, such as late at night to keep the system running smoothly for users.[39] Updates can be manually downloaded by the user or automatically downloaded through the server. Automatic updates ensure that the user is constantly using the most up-to-date version of the software. For many organizations, system maintenance costs more than the production of the actual system itself. If the system is well designed it should be able to be easily updated and maintained. Poor design makes it difficult to implement new features, which could end the software’s life cycle early. Once a major change is determined to be the best option for a software, an organization must go through the system development life cycle again to replace the old system from scratch. This next version may be completely different than the old version with completely new features, or just an updated version of the old features.
System Development Approaches
[edit | edit source]
Most system development projects include the six basic SDLC phases. However, the exact sequence and tasks performed during each phase, and the names and number of the phases, may vary depending on the organization and the type of system being developed. For example, smaller systems in smaller companies may skip or condense some activities, while other development projects may go back and repeat a previous step to refine the process before moving on. In efforts to improve the system analysis and design process, different methods have been developed. Some of these methods include the waterfall method, the iterative approach, and the end-user method. Each of these methods have different advantages and disadvantages in a way that they could be used to fit and optimize different kind of projects.[40] These methods can be compared to our methods of vacation planning. People don't design their entire vacation plan as the first step and then execute it, without modification, as the second step. Instead, when the first day of vacation is over, they might use that day's experience as a basis for modifying the plan for the second day. In this way, system designs are similar.
Traditional Approach
[edit | edit source]
A traditional approach for the system development has five phases which have to be completed in chronological order. First phase is the preliminary investigation. In this process, the team of development investigates the need for possible software automation in the given system. At the end the team creates a document of specific recommendations for the candidate system. It includes the personnel assignments, costs, project schedule, target dates, identifies problems and constraint. The second phase is systems analysis which is the study of a problem, prior to taking some action. It refers to the study of the business area or application, usually leading to the specification of the new system. The third phase is systems design which is defined as those tasks that focus on the specification of a detailed computer-based solution. The analyst focuses on three basic elements: the output that must be provided by the system, the source data, or input that the user will provide to the system, the processing needed to produce the output, given the input. The fourth phase is system acquisition financial institutions should ensure that systems are developed, acquired, and maintained with appropriate security controls. This leads us to the last step which is system implementation, in this phase, the production system is installed, initial user training is completed, user documentation is delivered, and the post implementation review meeting is held. When this phase is completed, the application is in steady-state production. Installation the biggest aspect is that the entire system is planned and built and built before anyone gets to use it or test it, so every aspect to every phase is essential to the traditional approach for system development.[41][42]
Iterative Approach
[edit | edit source]
Unlike the traditional approach, the iterative (repetitive) approach allows for system testing during development.[43] The emphasis here is on incremental changes through a process known as prototyping. Prototyping is the creation of software application prototypes. Prototypes, generally speaking, are early models of some product that is created for testing purposes. With software prototyping, developers are able to receive crucial feedback from testers early in the beginning stages of development. For this reason the iterative approach accounts for potential risks that developers face (e.g. accounting for user needs, verifying accuracy of initial project estimates). With that, the iterative approach acts as a response to the traditional development cycle, which is more likely to have “higher software costs and poor estimates of time and cost” due to the expense of changing a finished product. As the product moves closer to release, the cost of implementing changes increases exponentially.[44] It is a difficult task because the whole system has to be modified to incorporate sudden changes, and this can have undesirable results. Prototyping resolves this by knowing what the user really wants, which leads to increased user involvement. Interaction between users and developers is vital because it ensures what tasks need to be accomplished on the end of the developer. Overall the iterative approach addresses some of the problems that might not be possible for the traditional approach to address.
The End-User Development Approach
[edit | edit source]
As opposed to the iterative or traditional approach, which both focus on professional users, the end-user development approach is focused solely on configuring the development of the system and is often done using tools or programs. Instead of having to be highly educated and a professional in the area of software or programming, someone trying to develop a simplistic and easy system can use these programming tools and develop something of their own. A good example of this is sending out an email that someone wanted to be addressed to many people. This is usually used in small businesses, tasks, or daily projects, and is not something that an intricate business would ever use to run their day-to-day software programs. However, it is a nice alternative from having to start all over from the beginning and developing brand new software for simple tasks. The end user development approach is also convenient for a user who wants to make something their own and customize the way the software runs to fit their personal needs. This approach is extremely useful for individuals who don’t have the knowledge, time, or money to put into building new software from the ground up. The software is easy to use, personal, and a great alternative to the other two options.[45]
Review
[edit | edit source]Vocabulary Words
[edit | edit source]business intelligence: The process of gathering, storing, accessing, and analyzing data about a company in order to make better business decisions.
computer-aided design: A general term applied to the use of computer technology to automate design functions.
data mart: A collection of data related to a particular subject or department in a company.
decision support system: A type of information system typically used by upper management that provides people with the tools and capabilities to organize and analyze their decision making information.
enterprise architecture: A comprehensive framework used to describe and manage an organization’s business functions and systems.
enterprise system: A system that is used throughout an entire enterprise (business, organization, government agency, and so on).
geographic information system: An information system that combines geographic information with other types of data (such as information about customers, sales, and so forth) in order to provide a better understanding of the relationships among the data.
intelligent agent: A program that performs specific tasks to help make a user’s work environment more efficient or entertaining and that typically modifies its behavior based on the user’s actions.
management information system: A type of information system that provides decision makers with preselected information that can be used to make middle-management decisions.
product lifecycle management (PLM) system: A system designed to manage a product as it moves through the various stages of its life cycle, from design to retirement.
robot: A device, controlled by a human operator or a computer, that can move and react to sensory input.
robotics: The study of robot technology.
system acquisition: The phase of the system development life cycle in which hardware, software, and other necessary system components are acquired.
system design: The phase of the system development life cycle in which a model of the new system and how it will work is formally established.
system implementation: The phase of the system development life cycle that encompasses activities related to making the system operational.
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]- What is a collection of elements and procedures that interact to accomplish a goal?
- An __________ is a collection of elements (people, hardware, software, and data) and procedures that interact to generate information needed by the users in an organization.
- What is a conceptual blueprint that defines the structure and operations of an enterprise (a business, organization, government agency, or other entity.)
- __________ include the hardware and software needed to create electronic documents, as well as to convert printed documents into electronic form so they can be processed or archived electronically.
- What are programs that perform specific tasks to help make a user's work environment more efficient or entertaining?
- What are software programs that can make decisions and draw conclusions, similar to a human expert?
- The IT person most involved with system development is the _________
- When an organization hires an outside firm to perform specific tasks, it is referred to as _______
- What is the phase of system development in which the problem area is studied in depth and the needs of system users are assessed?
- What focuses on specifying what the new system will look like and how it will work?
Answers:
- System
- Information system
- Enterprise architecture
- Document processing systems
- Intelligent agents
- Expert Systems
- Systems analyst
- Outsourcing
- System analysis
- System design
- "Impact Of Computers." 123HelpMe.com, Sep 2014. Web. 8 Sep 2014.
- Lee, Ellen, "5 Ways Technology Is Transforming Health Care." Forbes, Jan. 2013. Web. 8 Sept. 2014.
- McBride, Michael. "Ranking Top 10 Hospital EMR Vendors by Number of Installed Systems." Dark Daily, March 2011. Web. 08 Sept. 2014.
- "Using Computers To Advance Health Care." Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Jan. 1996. Web. 07 Sept. 2014.
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://smallbusiness.chron.com/types-information-systems-organization-43097.html
- ↑ http://www.contentmanager.eu.com/dms.htm
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Document_management_system
- ↑ http://www.slideshare.net/sonnaco/transaction-processing-system
- ↑ http://rashedchowdhury.com/2012/11/12/what-is-an-enterprise-system-how-does-enterprise-software-work/
- ↑ http://it.emerson.edu/department/erp/
- ↑ http://www.ehow.com/facts_7584818_benefits-challenges-enterprise-systems.html
- ↑ http://www.im.ethz.ch/education/HS08/davenport_hbr_98.pdf
- ↑ http://www.anderson.ucla.edu/faculty/jason.frand/teacher/technologies/palace/datamining.htm
- ↑ http://documents.software.dell.com/Statistics/Textbook/Data-Mining-Techniques
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/C/CAD_CAM.html
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer-aided_design
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer-aided_manufacturing
- ↑ http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/design/electronics/manufacturing_processesrev2.shtml
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Decision_support_system
- ↑ http://www.arnnet.com.au/article/544575/inside_united_airlines_nerve_center/
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transcendent_Man
- ↑ https://www.technologyreview.com/s/603216/5-big-predictions-for-artificial-intelligence-in-2017/
- ↑ Wikipedia: Watson (computer)
- ↑ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/IBM-Watson-supercomputer
- ↑ Wikipedia: Cognitive computing
- ↑ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/IBM-Watson-supercomputer
- ↑ Wikipedia: Watson (computer)
- ↑ http://www.ibm.com/watson
- ↑ http://www.ibm.com/watson/products.html
- ↑ http://www.wisegeek.org/what-is-an-it-department.htm
- ↑ http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-an-application-programmer.htm
- ↑ http://work.chron.com/computer-security-specialist-do-13655.html
- ↑ http://www.prospects.ac.uk/systems_developer_job_description.htm
- ↑ http://www.veracode.com/security/software-development-lifecycle
- ↑ http://searchsoftwarequality.techtarget.com/definition/systems-development-life-cycle
- ↑ http://scholar.harvard.edu/files/waldo/files/ps-2006-6.pdf
- ↑ http://worldinfo4u.com/what-input-design-output-design-system-design/
- ↑ http://www.buyingexcellence.com/should-we-use-an-rfp-or-an-rfq/
- ↑ http://www.cvtc.edu/about/quotes-bids-proposals/pages/default.aspx
- ↑ http://www.nersc.gov/assets/Trinity--NERSC-8-RFP/Documents/N8BmkInstructAug6Final.pdf
- ↑ https://airbrake.io/blog/insight/what-is-system-development-life-cycle
- ↑ http://web.archive.org/web/20080727015416/http://web1.arthurphil-h.schools.nsw.edu.au/~computin/Year12/SDD/02_AppSWAapproaches/assets/MethodsOfImplementation_AdvDisAdv.pdf
- ↑ http://www.wisegeek.org/what-is-system-maintenance.htm
- ↑ http://www.umsl.edu/~sauterv/analysis/termpapers/f11/jia.html
- ↑ http://vcampus.uom.ac.mu/cse1010e/chapter_8/c8_Sections3.htm
- ↑ http://business-finance.blurtit.com/105917/what-is-the-traditional-development-approach
- ↑ http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/library/may05/bittner-spence/
- ↑ http://www.silvercrestconsulting.com/gui/pdf/1237375021.pdf
- ↑ http://www.interaction-design.org/encyclopedia/end-user_development.html
Program Development
Program Design and Development
[edit | edit source]



Procedural programming is more or less self-explanatory, it’s procedural so it will go step by step in order to solve a problem. This was a much older type of programming language that has since been outdated by object-oriented programming. However, this type of programming is very important and should be well understood if you want to understand the concepts of programming and what all goes into it. This process is also called imperative programming in some contexts, meaning top-down languages; this is how the programming functions, from a top to bottom procedural order. This is what makes this process self-explanatory in a way, because in order for something to work and pass along a message we assume it to go in this order. Along with going step by step in order to solve a problem, the list of instructions must be sent to the computer in order for it to know what to do with this information. It relies on routines, or procedures, that have multiple steps that need to be carried out. Procedural programming has been somewhat of a stepping stone for other types of programming because of its simplicity. It is an older type of programming and is now outdated by another popular form which is object oriented programming.[1] Object oriented programming is more focused on objects to make a program instead specific steps. An object, such as a person, should have a name, or be able to walk, which can be seen as a method in object oriented programming. Having a method in this programming is like having a procedure in procedural programming.[2] One of the most popular object oriented programming languages is Java,[3] which is used virtually everywhere. Objects within an object oriented program consists of attributes. If you have ever played D&D[4] you know that your character has different attributes that would define them. If you have an object you can change its attributes like size, shape, and color.
Aspect Oriented Programming is a form of programming that compliments Object Oriented Programming (or OOP) by allowing the developer to modify OOP in a way where the system can grow to meet new requirements. It keeps the original model, which was developed in OOP, but allows for new syntax without having to change the compiler being used or reconfigure the editor either. In essence, it is complimentary to the previously developed OOP style and allows the application to adopt new characteristics over its lifetime without having to be completely remodeled or redeveloped. This ability for an application to be adapted to the current trend in technology prolongs the usefulness and life span of the application, which then benefit the users of that application as well.[5]

Adaptive software development consists of cyclical speculation, collaboration, and learning rather than the more traditional approach of linear planning, building, and implementation. First, the term "speculate" is used because outcomes can never be fully predicted to the point of planning as it would be a waste of time to wander around aimlessly without any organized approach. A mission is still defined; it is acknowledged that the mission can never be inclusive of all possible outcomes and may need to be changed. Second, the term "collaborate" shows that management, per this model, does not focus exclusively on "managing the doing" —i.e. delegating instructions and seeing fit that they are followed but also focuses on fostering and maintaining a collaborative environment that is needed for real growth to take place. It can be difficult because, per this model, the environment is often at the edge of chaos, so to speak, given that a project can't be fully structured because then nothing new can emerge. However, things can't teeter over the edge into anarchy. Finally, there is a focus on learning from mistakes on the part of both the developers and the consumers. These three-phase cycles are short so that small mistakes, not large ones, are the ones from which lessons are learned.[6]
Program Development Life Cycle - Analysis, Design, Coding
[edit | edit source]
The following are six steps in the Program Development Life Cycle:
1. Analyze the problem. The computer user must figure out the problem,
then decide how to resolve the problem - choose a program.
2. Design the program. A flow chart is important to use during this
step of the PDLC. This is a visual diagram of the flow containing the
program. This step will help you break down the problem.
3. Code the program. This is using the language of programming to
write the lines of code. The code is called the listing or the source
code. The computer user will run an object code for this step.
4. Debug the program. The computer user must debug. This is the
process of finding the "bugs" on the computer. The bugs are important
to find because this is known as errors in a program.
5. Formalize the solution. One must run the program to make sure there
are no syntax and logic errors. Syntax are grammatical errors and
logic errors are incorrect results.
6. Document and maintain the program. This step is the final step of
gathering everything together. Internal documentation is involved in
this step because it explains the reason one might have made a change
in the program or how to write a program.[7]
Writing Code
[edit | edit source]
Computer code is a series of statements that have been assigned a function by a higher level language (typically referred to as source code). This language is similar to English and has been converted to machine language using a type of program known as a compiler. Because code is used to instruct computers to perform a wide array of tasks, there are many different kinds of languages and programs available. One of the most important aspects of coding is deciding which jobs (creating a web page, writing a game, etc.) a computer will do. Regardless of what is chosen, the majority of codes utilize plain-text because of its compatibility. Though the actual content is written this way, documents are each given a unique file extension that is indicative of their type. One can write a simple code with a basic word processor or text editor. However, using a software application (specifically designed for coding in a particular language) is significantly more effective and efficient. As with a document written in English, where word processing software is used to aid in detection of spelling errors and non-standard grammar, a coding editor provides comparable tools to ensure accuracy. A code editor is also known as an integrated development environment (IDE), which is a software application for formatting. Using a code editor decreases the chances of errors in codes and time spent reading a code. A large downfall of working with IDEs is a lack of flexibility. While some IDEs work with multiple programming languages, a sizable amount are very specific for only one language. [8]
Flowcharts and Pseudocode
[edit | edit source]
During the design process of the Program Development Life Cycle, it is important that programmers (and non-programmers) are able to visualize the way in which the program will work. Certain tools such as flowcharts and pseudocode are used to simplify the design process and allow the developers to see the program before any actual coding is used. A common type of design tool is the flowchart. A flowchart can be either handwritten or created with software such as Visual Logic or Flowgorithm. Using software helps you save your work digitally which can be more reliable.[9] Many of these software programs have similar symbols to represent certain actions such as input, output, assignments, and various types of loops. For example, a rhombus represents inputs and outputs and a rectangle represents a process. Flowcharts are also useful for education tools because they focus more on the concept of programming rather than focusing on the syntax of languages. Another type of design tool is pseudocode. Pseudocode is very similar to a programming language except that it uses non-syntactical words to summarize the processes of a program. Pseudocode cannot be compiled or executed but it does serve as a good starting point for programmers.[10] Here is an example of pseudocode:
- If user’s age is greater than or equal to 18:
- Print “You can vote”
- Else Print”You cannot vote”
Compiler
[edit | edit source]
A compiler is a special program that processes statements written in a particular programming language and turns them into machine language or "code" that a computer's processor uses. When executing (running), the compiler first parses (or analyzes) all of the language statements syntactically one after the other and then, in one or more successive stages or "passes", builds the output code, making sure that statements that refer to other statements are referred to correctly in the final code. A compiler works with what are sometimes called 3GLs (FORTRAN, BASIC, COBOL, C, etc.) and higher-level languages.[11] There are one-pass and multi-pass compilers as well as just-in-time compiler, stage compiler, and source-to-source. The compiler front end analyzes the source code to build an internal representation of the program, called the intermediate representation. The compiler backend includes three main phases, such as analysis, optimization, and code generation.[12] Because compilers translate source code into object code, which is unique for each type of computer, many compilers are available for the same language. For example, there is a FORTRAN compiler for PCs and another for Apple Macintosh computers. In addition, the compiler industry is quite competitive, so there are actually many compilers for each language on each type of computer. More than a dozen companies develop and sell compilers for the PC.[13] There is also something called a decompiler - which translates from a low level language to a high level language. [14]
Program Development Life Cycle - Debugging and Testing, Implementation and Maintenance
[edit | edit source]Control Structures
[edit | edit source]
A control structure is a diagram used to show how functions, statements, and instructions are performed in a program or module. The diagram shows exactly when an instruction is performed, and how it’s performed. Most importantly, a control structure shows the order of the instructions.[15] There are three basic types of control structures: sequence, selection, and repetition. Choosing a specific control structure depends on what you want the program or module to accomplish. A sequence control structure is the simplest and least complex control structure. Sequence control structures are instructions that are executed one after another.[16] The structure could be compared to following a recipe. A more complex control structure might be a selection control structure, a structure that involves conditions or decisions. This means that the structure can allow different sets of instructions to be executed depending on whether a condition is true or false.[17] The last basic control structure is a repetition control structure, which is sometimes called an iteration control structure. This control structure is used when repeating a group of code is necessary. The code will be repeated until a condition is reached. Repetition control structures are used when looping is needed to reach a specific outcome.[18]
Testing Program Design
[edit | edit source]
Good program design needs to be specific. The program design is very important, especially because it involves the overall step-by-step directions regarding the program. A programmer must test the program design to ensure that it runs correctly and that there are no mistakes. The operation a programmer must do to complete this task is called desk checking. Desk checking allows the programmer to run through the program design step-by-step. Essentially, the programmer runs through lines of code to identify potential errors and to check the logic. The programmer uses tracing tables to keep track of any loop counters. The goal of checking the program design is to avoid running into mistakes further on in the program development cycle. The sooner the mistake is caught in the development cycle the better. If the error is not found until later in the developmental cycle, it may delay a project. Therefore, a programmer must make sure they pay strict attention while desk checking. Advantages to desk checking include the convenience of hands-on "proof-reading" of the programmer’s own code. The programmers wrote the code themselves, so it is an advantage that they can work immediately with familiar code. A disadvantage to the desk checking system includes potential human error. Since a computer is not checking the design code, it is prone to human error.[19]
Debugging
[edit | edit source]Debugging is basically making sure that a program does not have any bugs (errors) so that it can run properly without any problems. Debugging is a large part of what a programmer does. The first step to debugging is done before you can actually debug the program; the program needs to be changed into machine language so that the computer can read it. It is converted using a language translator. The first goal of debugging is to get rid of syntax errors and any errors that prevent the program from running. Errors that prevent the program from running are compiler errors. These need to be removed right away because otherwise you cannot test any of the other parts of the program.[20] Syntax errors occur when the programmer has not followed the correct rules of the programming language. Another kind of error is a runtime error, which occurs while the program is running and it is not noticed until after all syntax errors are corrected. Many run time errors are because of logic errors, which are errors in the logic of the program. It could occur when a formula is written incorrectly or when a wrong variable name is used.[21]

There are different types of debugging techniques that can be used. One technique called print debugging, or also known as the printf method, finds errors by watching the print (or trace) statement live or recorded to see the execution flow of the process. This method originated in the early versions of the BASIC programming language. Remote debugging is the method of finding errors using a remote system or network, and using that different system to run the program and collect information to find the error in the code. If the program has already crashed, then post-mortem debugging can be used through various tracing techniques and by analyzing the memory dump of the program. Another technique is one created by Edward Gauss called wolf-fence debugging. Basically, this method find the error by zeroing in on the problem by continuous divisions or sectioning until the bug is found. Similar to this is the saff squeeze technique which uses progressive inlining of a failure test to isolate the problem.[22]
Debugging a program can be done by using the tools provided in the debugging software. Typically, and especially with high-level programming languages, specific debugging tools are already included in the. Having language-specific debugging tools make it easier to detect the errors in a code, because they can look for known errors as opposed to tediously “walking through” the code manually. It also good to note that fixing one bug manually may lead to there being another bug; this is also why language-specific debugging tools are helpful. There are also debugging software for embedded system as well.[23]
Testing/Implementation and Maintenance
[edit | edit source]
Relating to getting a program up and running, many things need to happen before it can be used. One step is to test the program. After the debugging process occurs, another programmer needs to test the program for any additional errors that could be involved in the background of the program. This person needs to perform all of the tasks that an actual user of the program would use and follow. To ensure privacy rights, test data is used in the testing process. However, this still has the same structure and feel to the actual data. The tester needs to check for possible input errors as well, as this would create many problems and issues in the future had it not been checked. Companies usually implement different types of tests. An Alpha test [24] is first conducted, which is on-site at the company, and Beta tests are sent out to different states or countries to ensure the program is 100% ready for use. The Alpha test occurs before the Beta test. Once the debugging and testing are finished, the program is now in the system and the program implementation and maintenance phase are completed. Program maintenance still needs to be kept up, in case of future errors. This is the most costly to organizations because the programmers need to keep improving and fixing issues within the program.

As stated earlier, a program goes through extensive testing before it is released to the public for use. The two types of testing are called Alpha and Beta testing. First, it is important to know what each test does. Alpha testing is done “in house” so to speak. It is done within a company prior to sending it to Beta testing and its intention in this early stage is to improve the product as much as possible to get it Beta ready. Beta testing is done “out of house” and gives real customers a chance to try the program with the set intention of catching any bugs or errors prior to it being fully released. Alpha testing is the phase that takes the longest and can sometimes last three to five times longer than Beta. However, Beta testing can be completed in just a few weeks to a month, assuming no major bugs are detected. Alpha testing is typically performed by engineers or other employees of the company while Beta testing occurs in the “real world”, temporarily being released to the public to get the widest range of feedback possible. During Alpha testing, it is common for there to be a good amount of bugs detected as well as missing features. During Beta testing, there should be a big decrease in the number of these problems. When testing in the Alpha phase is over, companies have a good sense of how the product performs. After Beta testing is complete, the company has a good idea of what the customer thinks and what they experienced while testing. If all goes well in both phases, the product is ready to be released and enjoyed by the public. The length of time and effort that is put forth in order for the world to enjoy and utilize the many programs on computers today is often overlooked. Information such as this gives the user a new appreciation for computers and computer programs.[25]
Program Development Tools
[edit | edit source]Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) Tools
[edit | edit source]
ALM, Application Lifecycle Management, are tools that manage an application throughout its entire life cycle. They are very helpful for programmers who are under increasing amounts of stress to develop new programs quickly. The helpfulness comes from wide range of features that the ALM tools can offer. One example is how many ALM programs come with built-in program design tools, along with the ability to generate the program code from the finished design to create the application. This code generating ability saves companies time and money that they don't have to put towards outsourcing, especially if they have a small number of programming staff. In addition to code generators, another important tool that can be included in ALM programs is 'requirements management'. Essentially, requirements management is defined in exactly that way, referring to keeping track of and managing program requirements as they are defined and then modified throughout the process of developing the program. The larger the company, the nicer ALM toolset they can purchase; there are many ALM toolsets on the market to choose from.[26]
Application Generators
[edit | edit source]
Application generators are extremely useful devices. They can be used by amateurs/people with less experience or by professionals. The point of an application generator is to make a task simpler than it is. Even if it is just changing a few basic formatting characteristics, these generators can make it so that the user only has to type in a specific key or command in order for all the actions to happen at once with much less effort. One of these useful generators is called a Macro. A macro is an application generator that simply makes it possible to perform repeated actions instantaneously on a single command. The idea is that it will make reformatting or calculating things much easier, thus saving the operator time.[27] Most Microsoft programs contain a macro recorder which allows users to easily record all inputs and commands they use and associate them with a keyboard shortcut for future repetition. Other application generators create reports and forms which make things such as memberships, records (such as medical treatments, history, and vaccinations), and even insurance claims more organized and easier to access.
RIA Tools
[edit | edit source]
Other types of tools include device software development tools, software development kits (SDKs), application program interfaces (APIs), and rich internet application tools (RIAs). A rich internet application offers many of the same features associated with desktop applications. They are more interacting and engaging than other web-based applications. Some big names in this area are Microsoft, Adobe, and JavaScript. Microsoft actually has a very put together developer’s website that goes into some detail about how to create such applications. It includes information such as things to consider before starting an RIA, such as the audience. [28]A few key features about RIAs include direct interaction, partial-page updating, better feedback, consistency of look and feel, offline use, and performance impact. [29] Direct interaction allows for a wider range of controls, such as editing or drag-and-drop tools. Partial-page updating allows for real-time streaming and cuts down on load time waiting for a response from a server. RIAs can provide users with quicker feedback because of the partial-page updates. Also, it is sometimes possible to use RIAs offline when there is no connectivity. One downside to RIAs is that smaller devices, such as mobile phones, often times do not have the means necessary to run such applications. In order to stay secure, most RIAs process their applications in an isolated range of the desktop, called a sandbox. The sandbox constricts access and visibility to the operating system and to the application server.
AngularJS
[edit | edit source]AngularJS (commonly referred to as "Angular.js" or "AngularJS 1.X") is a JavaScript-based open-source front-end web application framework mainly maintained by Google and by a community of individuals and corporations to address many of the challenges encountered in developing single-page applications. The JavaScript components complement Apache Cordova, the framework used for developing cross-platform mobile apps.[30] According to JavaScript analytics service Libscore, AngularJS is used on the websites of Wolfram Alpha, NBC, Walgreens, Intel, Sprint, ABC News, and approximately 12,000 other sites out of 1 million tested in October 2016. AngularJS is the 10th most starred project of all time on GitHub.[31] AngularJS is is built on the belief that declarative programming should be used to create user interfaces and connect software components, while imperative programming is better suited to defining an application's business logic. The framework adapts and extends traditional HTML to present dynamic content through two-way data-binding that allows for the automatic synchronization of models and views. As a result, AngularJS de-emphasizes explicit DOM manipulation with the goal of improving testability and performance.[32] AngularJS two-way data binding is its most notable feature, largely relieving the server backend of templating responsibilities. Instead, templates are rendered in plain HTML according to data contained in a scope defined in the model. The $scope service in Angular detects changes to the model section and modifies HTML expressions in the view via a controller. Likewise, any alterations to the view are reflected in the model. This circumvents the need to actively manipulate the DOM and encourages bootstrapping and rapid prototyping of web applications. AngularJS detects changes in models by comparing the current values with values stored earlier in a process of dirty-checking, unlike Ember.js and Backbone.js that trigger listeners when the model values are changed.[33]
Node.js
[edit | edit source]
Node.js is an open source, cross-platform JavaScript run-time environment for executing JavaScript code serve-side.[34]Node.js enables JavaScript to be used for server-side scripting and runs scripts to produce dynamic web page content before the page is sent to the user’s web browser. Server-side scripting is a method of designing websites so that the process or user request is run on the originating server.[35]Node.js is used to send messages, packages, and files quickly and efficiently. JavaScript is known for not having a concept of thread – which means that JavaScript’s thread has a different component of process. This process is JavaScript without a browser.[36]Companies are turning to Node.js to create applications because it is:
- Easy to Learn
- Allows freedom in building apps
- Ability to create front-end and back-end language
- Active Community
[37] Node.js provides a flexible and fast development process that is simple to utilize!
Programming Languages
[edit | edit source]What is a Programming Language?
[edit | edit source]
A programming language is designed to communicate instructions to a computer and so the computer can interpret the instructions and make sense of them. They are used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine and algorithms. There are multiple languages created into this program which are created from different styles or forms. The description of a programming language is known to be split into the two components of syntax (form) and semantics (meaning). The syntax is the form in which the language is presented in and the actual sense or meaning of the instructions is the semantics. A program is written so that it can be understood by computer so that the instructions can be interpreted, translated into so the computer can eventually make sense of it. So the moment you turn on your computer after it starts to run programs, it interprets these instructions, tests the ram and resets all attached devices and loads the operating system from hard disk. Every operation that the computer holds has instructions that someone had to translate into a programming language. With every language, they have to be created, compiled and tested which tends to be a long and complex task.[38]
Categories of Programming Languages
[edit | edit source]Two categories that programming languages can fall under are procedural (programs that use the procedural approach) and object (for those programs that use the object-oriented approach). However, probably the most common way of categorizing programming languages is by their designation into a tier structure. Programming languages can fall under low-level languages, high-level languages, and very high-level languages. Low-level languages, which are made up of the first generation language, machine language, and second generation language, assembly language, are written at a very low level: programming consists of 0s and 1s for machine language and assembly language includes names and symbols for some of the 0s and 1s. These languages allow computer hardware to read commands quickly, but this happens at the cost of a much steeper learning curve as opposed to higher level languages.[39] High-level languages, on the other hand, are easier to use because they are closer to natural language. They are also machine independent: programs written on one computer can be transferred to another computer without modification. This is in contrast to the machine dependent-nature of low-level programs where modification is necessary. Lastly, very high-level languages, also known as fourth-generation programming languages, are more difficult to distinguish from high-level languages. Fourth-generation languages (4GLs) are known to be declarative, which does not specify exactly how a computer should go about processing a command. This results in programmers using very little code. Although, those languages deemed very-high level languages in the past (e.g. Visual Basic, Python, Perl) have now been called simply high-level languages [40]
There are some high-level programming languages that are visual programming languages or graphical programming languages. They are referred to by these names because they have a graphical interface. In these programs, instead of typing program code, a user can drag and drop objects to generate the needed code. There are even programs that incorporate visual elements that help with coding but also still require actual coding. These kinds of programs are called visual programming environments (VPEs) One of the first programming languages to use a visual programming environment was Visual Basic. The convenience of visual programming environments is that you can drag and place objects but also with a code is typed, the program assists in creating the code by listing options. These helps users learn appropriate codes. An online definition of visual programming environments describes it as software which allows the use of visual expressions (such as graphics, drawings, and animations or icons) in the process of programming. These visuals items are then used as graphical interfaces for textual programming languages. These kinds of visual programming languages software are also used for educational purposes and in the future may be the most common programming language. Scratch is one example of an educational visual programming environment for children. As mentioned above, Visual Basic was one of the first programming languages to use visual programming environment, but since then C++, Pascal, and Java have also begun to create visual programming environments.[41]
Common Programming Languages
[edit | edit source]
There are many programming languages out there that are still, to this day, used immensely on a day-to-day basis. Fortran, which is one of the older options, is used mainly in the scientific field for scientists, mathematicians, and formulating numerical formulas. Cobol is another programming language commonly used today, and typically can be seen utilized in business environments for everyday transactions. This language is seen as extremely time consuming, and more and more businesses today are starting to move away from it, towards quicker processes. Pascal is yet another language that is used commonly in math and science programs. The Pascal programming language obtained its name from the famous mathematician, Blaise Pascal. It was created by Niklaus Wirth, a member of the International Federation of Information Processing Working Group. He created the Pascal programming language because he wanted to include new features that past programming languages did not provide. It was originally created as a teaching tool and uses control structures in its software. The use of control structures helped the programming language become more structured and organized compared to other languages, which is why it was used as a teaching tool. Pascal was published in 1971 and revised in 1973, which allowed for it to stay prominent in colleges from the 1970’s and into the late 1980’s. One of the new features of Pascal was the new data types, like Integer, Real, Character, and Boolean. These new types are what allowed Pascal to become a programming language used strongly in mathematic programs. Another new feature was a strong data typing element, which allowed the compilers for Pascal to see and correct an incompatible assignment in one type in accordance to a variable in a different type. This further helped keep the organized structure of Pascal and enabled it to be used more in college level classes. Pascal was a great creation for the programming language world.[42]

Another common programming language is Basic. It is one of the most used languages because it can be considered user friendly. It was designed to be an uncomplicated and stressful language that is used typically for interactive programs. It is extremely easy to get to know, and many people enjoy its simplistic and understandable functioning. One aspect of basic is Visual Basic, which again uses their understandable language, but is focused on visual aid. These are just a few examples of the immense and intricate amount of languages that are out there. Though many of these are still used today, it is obvious that some of the older and more time-consuming software is on its way out.[43]

On the other hand, there are also some programming languages that are no longer widely used today. Among these programming languages are LISP and Prolog. Specified in 1958, LISP (LISt Processing) is the second-oldest high-level programming language, running right behind Fortran. It allows a code to be expressed in the same form as the data structures in the language, which is very beneficial when performing genetic algorithms or symbolic manipulation. On the other hand, in the early 1970s, Prolog was designed for natural language processing, and logical reasoning. This language allowed using similar grammars to translate logical representation back into language.[44] Being a dialect of LISP comes another language used to teach children how to program: The Logo Programming language. To act as a tool for learning, its features included modularity, extensibility, interactivity, and flexibility. Another third generation programming language not used today is PL/I, “Programming Language 1.” This language was developed as an alternative to Cobol (large-scale business applications) and Fortran (scientific and algorithmic applications). Lastly, and most importantly, comes one of the first object-oriented programming languages: SmallTalk. As there is no such language called SmallTalk any more, other different languages like SmallTalk-xx (the xx being the year that the language was finalized,) have gradually taken its place. Therefore, although new languages such as C, Java, or PHP have now taken over, old programming languages still play a significant role behind the shift to the new and better technology. [45]

C++ is a general-purpose programming language. It has imperative, object-oriented and generic programming features, while also providing facilities for low-level memory manipulation. It was designed with a bias toward system programming and embedded, resource-constrained and large systems, with performance, efficiency and flexibility of use as its design highlights. C++ has also been found useful in many other contexts, with key strengths being software infrastructure and resource-constrained applications, including desktop applications, servers (e.g. e-commerce, web search or SQL servers), and performance-critical applications (e.g. telephone switches or space probes). C++ is a compiled language, with implementations of it available on many platforms. Many vendors provide C++ compilers, including the Free Software Foundation, Microsoft, Intel, and IBM. Many other programming languages have been influenced by C++, including C#, D, Java, and newer versions of C.[46]

Python is an open source, dynamic object-oriented programming language. Python can be used to develop a variety of applications, including gaming, database, and Web applications. It's a freely available programming language and can run on almost any computer without needing to change the program. Python's compatibility is the reason it's used daily in the Google search engine, Youtube, NASA, and the New York Stock Exchange. Also, due to its readability, ease of acquisition, and extensibility, Python was recently chosen by MIT for students learning to program.[47] Another open source object-oriented programming language, often compared to Python, is Ruby. Ruby can be used to create both Web applications and general-purpose programming for Linux, Mac OS X, and Microsoft Windows computers. Similar to Python, Ruby uses a syntax that is relatively easy to read and write. A difference, however, is that Ruby tends to presume upon the programmer's intentions, while Python's information is typically plain in syntax. Ruby on Rails (RoR) is a framework for developing dynamic Web applications that are written in the Ruby programming language. RoR applications run on a variety of types of Web servers and with a variety of databases, consequently growing rapidly in use and popularity.
Java
[edit | edit source]
Java is another very common programming language. Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language that is designed to let developers write once, run anywhere. This means that the coding does not have to be recompiled for various platforms and can run the same on any system. The language was developed by Sun Microsystems in 1995 and was released to the public as open source software in 2007.[48] Sun Microsystems was later bought by Oracle. Java bases most of its syntax off the other programming languages such as C and C++. Java programs are compiled into the bytecode format, which can be run on any computer that runs Java virtual machine no matter how simple or complex the computer’s architecture may be. Java is used extensively in apps, both on computers and mobile devices. It is liked by app developers as it is easy to use, and compatible with most devices as most devices are able to read Java. One popular application for the Java language is Java applets, which are small programs that can be inserted into a web page of a java-enabled web browser. These applets can be used to run games, banner ads, scrolling text, or various other types of programs from inside the browser. These applets are inserted into the HTML statements of the web page just as an image would be added. The applet is downloaded from the host server of the webpage when being displayed, allowing for the program to run on the viewer’s computer.[49] Mobile devices are making use of Java in many of their systems, as it is compact, and can be used for many operations in the device. Android uses Java as a major part of their mobile operating system. While not the foundation of the operating system, Java is used for most of the non-basic functions. In regards to the mobile phone market, Java’s biggest competitor is Google, as they are marketing their own operating system for use on mobile devices. Java is found in most developed apps, but programmed to create simple programs from scratch. The major downside of Java, as with any programming language, is that it may expose weak areas that can be hacked. Java is currently on its 8th edition, with a 9th edition being beta tested.[50]
MS-DOS and Batch Files
[edit | edit source]Batch processing has been in use since the 1950's in mainframe computers. [51] This started on punch cards, however it developed into a fully digital language. MS-DOS is an acronym that stands for "Microsoft Disk Operating System". MS-DOS has an interface that is just a black screen with white text on it. Since the early days of computing, DOS has been used to read and write programs for a myriad of jobs. The MS-DOS Batch language is simply a text file that allows a user to create a sequence of commands that are executed as if they were typed in to the command line, with some enhancements for conditionals (making decisions based on whether programs fail or succeed). Over the years, various batch versions of varying capabilities have appeared on many computing platforms. The command prompt (as it is now called) still appears on modern Windows and Linux machines, and many IT professionals swear by it, and by the power and control it gives them. This ability to automate common tasks is often a budding programmer's first exposure to programming languages.
Key Terms Review
[edit | edit source]Procedural programming: An approach to program design in which a program is separated into small modules that are called by the main program or another module when needed.
Variable: A named memory location defined in a computer program that is used to store the current value of a data item used in that program.
Object-oriented programming (OOP): An approach to program design in which a program consists of objects that contain data (attributes) and processes (methods) to be used with those objects.
Aspect-oriented programming (AOP): An approach to program design in which different functions are clearly separated so program components can be developed and modified independently from one another, and the components can be easily reused with separate, nonrelated objects.
Program development: The process of creating application programs.
Program development life cycle (PDLC) The process containing the five phases of program development: analyzing, designing, coding, debugging and testing, and implementing and maintaining application software.
Problem analysis: The phase of the program development life cycle in which the problem is carefully considered and the program specifications are developed.
Programmer: A person whose job it is to write, test, and maintain computer programs.
Program design: The phase of the program development life cycle in which the program specifications are expanded into a complete design of the new program.
Flowchart: A program design tool that graphically shows step-by-step the actions a computer program will take.
Pseudocode: A program design tool that uses English-like statements to outline the logic of a program.
Unified Modeling Language (UML): A set of standard notations for creating business models; widely used for modeling object-oriented programs.
Control structure: A pattern for controlling the flow of logic in a computer program, module, or method.
Sequence control structure: A series of statements that follow one another.
Selection control structure: A series of statements in which the results of a decision determine the direction the program takes.
Repetition control structure: A series of statements in a loop that are repeated until a particular condition is met.
Program coding: The phase of the program development life cycle in which the program code is written using a programming language.
Coding: The process of writing the programming language statements to create a computer program.
Source code: A computer program before it is compiled.
Program debugging and testing: The phase of the program development life cycle that ensures a program is correct and works as intended.
Alpha and Beta Testing: Two types of testing that increase the success and lifespan of a product in the market. https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/what-is-alpha-testing-beta-testing. An Alpha test is first conducted, which is on-site at the company, and Beta tests are sent out to different states or countries to ensure the program is 100% ready for use.
Debugging: The process of ensuring a program is free of errors.
Object code: The machine language version of a computer program generated when the program's source code is compiled.
Language translator: A software program that converts source code to object code.
Compiler: A language translator that converts an entire program into machine language before executing it.
Interpreter: A language translator that converts program statements line-by-line into machine language, immediately executing each one.
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]1.) What is a computer program called before it is compiled?
2.) A program design tool that graphically shows step-by-step the actions a computer program will take is called a _______?
3.) What phase of the PDLC has the program code written using a programming language?
4.) If your job is to write, test, and maintain computer programs, you are a _______.
5.) What language translator converts an entire program into machine language before executing it?
6.) What process ensures a program is free of errors?
7.) What is the process of creating application programs?
8.) How many phases are there in the program development life cycle?
9.) List the phases of the PDLC in order.
10.) What is a software program that converts source code to object code?
Review Answers
[edit | edit source]1.) Source code
2.) Flowchart
3.) Program coding
4.) Programmer
5.) Compiler
6.) Debugging
7.) Program development
8.) Five
9.) Analyzing, designing, coding, debugging and testing, implementing and maintaining application software
10.) Compiler
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/object-oriented-programming-vs-procedural-programming.html#lesson
- ↑ http://education-portal.com/academy/lesson/object-oriented-programming-vs-procedural-programming.html#lesson
- ↑ http://www.java.com/en/
- ↑ http://www.wizards.com/dnd/
- ↑ http://www.onjava.com/pub/a/onjava/2004/01/14/aop.html
- ↑ http://www.adaptivesd.com/articles/messy.htm
- ↑ http://blog.teachbook.com.au/index.php/computer-science/software-development/program-development-lifecycle/
- ↑ http://study.com/academy/lesson/how-to-write-a-program-coding-testing-debugging.html
- ↑ Wikipedia: Flowgorithm
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/P/pseudocode.html
- ↑ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/compiler
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Compiler
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/C/compiler.html
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Compiler
- ↑ Understanding Computers 14th ed. by Deborah Morley & Charles Parker
- ↑ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/1086517/sequence
- ↑ http://www.thevbprogrammer.com/Ch05/05-03-SelectionStructure.htm
- ↑ http://www.cs.fsu.edu/~myers/c++/notes/control1.html
- ↑ http://www.ehow.com/facts_5941523_desk-checking_.html
- ↑ http://searchsoftwarequality.techtarget.com/definition/debugging
- ↑ http://www.techopedia.com/definition/16373/debugging
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Debugging
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Debugging
- ↑ http://www.thefreedictionary.com/alpha+test
- ↑ http://www.centercode.com/blog/2011/01/alpha-vs-beta-testing/
- ↑ http://www.infoq.com/research/alm-survey
- ↑ http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/help/macros-demystified-what-they-are-and-why-to-use-them-HA010007210.aspx
- ↑ http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee658083.aspx
- ↑ http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/335519/Rich_Internet_Applications?taxonomyId=16&pageNumber=2
- ↑ Wikipedia: AngularJS
- ↑ Wikipedia: AngularJS
- ↑ Wikipedia: AngularJS
- ↑ Wikipedia: AngularJS
- ↑ Wikipedia: NodeJS
- ↑ [[1]]
- ↑ [[2]]
- ↑ [[3]]
- ↑ http://cplus.about.com/od/introductiontoprogramming/p/programming.htm
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/M/machine_language.html
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Very_high-level_programming_language
- ↑ http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/visual+programming+environment
- ↑ http://groups.engin.umd.umich.edu/CIS/course.des/cis400/pascal/pascal.html
- ↑ http://www.freerepublic.com/focus/chat/2880277/posts
- ↑ http://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Lisp_(programming_language).html
- ↑ http://el.media.mit.edu/logo-foundation/logo/
- ↑ Wikipedia: C++
- ↑ http://python.about.com/od/gettingstarted/ss/whatispython_7.htm
- ↑ https://www.java.com/en/download/faq/whatis_java.xml
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Java_(programming_language)
- ↑ https://www.oracle.com/java/index.html
- ↑ https://www.microsoft.com/resources/documentation/windows/xp/all/proddocs/en-us/batch.mspx?mfr=true
Database
Database Definition and Examples
[edit | edit source]
A database is a collection of data that is saved and organized to allow easy retrieval when needed. It is the collection of schemas, tables, queries, reports, views, and other objects. In order to maintain and access the database you will need a DBMS (database management system). This kind of system manages and protects data so that the database is safe and secure. Databases are not limited to only computers; in fact, a phone book is an example of a database.[1] All of the names alphabetized and each column has its own category. There is a column for your name, phone number, and possibly a street address. With a relational database, all of the data within the row can be pulled up when you are looking for the specific attribute.

There are a few advantages to using a database management system. On the plus side, it has the ability to control redundancy, the integrity of the information being stored can be maintained, it can restrict access, it can share data, and can backup/recover information. A database management system can counteract redundancy by compiling the information in one spot. The same way that you can't have two audio files with the same name and extension in a single folder, you can't have the same file in a single database. This controls and can increase storage space. The integrity of the information being stored can also be increased based on the specifications of the database developer. This means that the constraints on the information put into the database (which is determined by the developer) will keep the data stored accurate. If a database is only able to store pictures, for example, then a music file will be rejected ensuring that a picture will always be retrieved from the database with 100% accuracy. This is a very simple example to get the idea across as the constraints imposed by the developer can determine different things. Databases can also share data as well allowing a developer to build multiple applications off of one source of information rather than having to create new stored files. Databases can also backup and recover data. If a computer system fails during a long, complex update then the database can restore the files to the place in the update when it is becomes operational again.[2]

Primarily, databases are used for collecting data and organizing, one may wonder what instances this may be used for. Some examples of databases are Microsoft Excel or Access. For an example of what these databases could be used for we can go with a situation: you are having a wedding and need to make an invitation list. For a process like this, users can utilize Microsoft Excel because their database will not have many types of transactions and should not become too uncontrollable. However, if this were to happen, Access would be more compatible with the material needed. Access is basically just a more advanced version of Excel that is only needed for uncontrollable databases or ones that need to be directly linked to others in order to access information in a systematized way. Either database can help you make informed decisions and can also help you make sense of the data in different ways. The storage in Access is not repetitive so it can essentially save space and improve accuracy.[3] Access also has different templates to choose from so that you do not have to create a new database from scratch. There is also a relationship you can establish between the tables so that you can navigate easier. For creating a wedding invitation list: you can decide who to invite and who not to invite to the reception and put those people in separate tables.[4]

Databases are also important in businesses. Especially when it comes to keeping inventory. Databases can be used for controlling inventory as well as reducing the time, cost, and effort of inventory management. Controlling your inventory is essential in order to have good and efficient business. A database can provide an up-to-date picture of stock levels and products. It helps in maintaining that the stocks keep up with the demand of the consumers. It can be used to provide forecasts and trends of demand in order to adjust adapt to the change of the market and maximize profit. It also provides automation which improves productivity. It can update stock levels automatically as well as control stock to ensure products are always available for consumers. This automation frees up employees to do more productive things such as help out customers. Speaking of customers, they always order things and want them delivered on time and right away. Well a database can help in increasing and maintaining the efficiency of orders and deliveries. They help make it easier to place orders and find products. While these are also important in business they can be applied to any organization that may have inventory. An example of such would be libraries. With the millions of books that a library can potentially carry, a database is not only important but necessary.[5]
Who Uses Databases?
[edit | edit source]
There are a number of individuals who create, use, manage, and secure database management systems. A database designer is responsible for designing a database. They work with people involved in the system development life cycle, such as systems analysts, to find out what kinds of data are needed and what relationships among the data should be studied, and they design the database based off of these. A database designer may also be referred to as a database architect, database engineer, or database analyst. Database developers create the database based on the work of the database designer, setting up its structure and user interface, typically with the use of the database management system. This may be the same as the database designer, and they work alongside the database programmer, who creates the programs necessary for the database to be developed. Database administrators, or DBAs, manage databases within an organization, maintaining them, monitoring user access to them, monitoring their performance, and performing backup. The users are the ones who actually "use" the database: they enter data into the database, update data within the database, and retrieve data from the database.[6]
Data Characteristics
[edit | edit source]
Data is a collection of facts. It can be values, measurements, numbers, words, measurements, and observations. Many businesses would not be as successful without data.[7] A data has a hierarchy; this hierarchy is a systematic organization of data. Fields, records, and files are a part of the data organization. Product names or quantities are the lowest level of the hierarchy, and the database is the highest level of the hierarchy.[8] Also, the data definition consists of the following: name, data type, description, and properties. This describes the properties that go into a database. If a computer user wants to look up all of the data definitions for a database, he or she would look up the data dictionary. A few key terms a computer user should be aware of, concerning data characteristics, consist of data field, record, file, and database. A data field contains a single fact of an entity. A record is a collection of related fields. A file is an organization of related business records. The database is the place where files are integrated. The data characteristic key terms are essential to be aware of for businesses who use a database.
Data Organization
[edit | edit source]
In order for a database to be efficient, its data must be organized in a fashion to make it easily and quickly accessible. This is called data organization. Data organization typically uses a primary key to identify where data is being stored. This allows for a specific record to be located efficiently. There are a few different methods that databases use in order to store and retrieve data efficiently. The two most common are Indexed Method and Direct Method. Indexed Method is the method in which a database uses an index to keep track of where data is stored within it. An index is a table that has the primary key as well as the location information for that key. Index organization allows for records to be looked up quickly and retrieve information from the database. Direct organization is faster than index organization. This is due to it using the key field and a mathematical formula called hashing algorithm to find where specific records are physically stored in the database. These systems are much harder to develop. They pave the way for an incident called collision, which happens when two or more records are assigned the same storage address. Some systems use both methods. The key field will first indicate where the record is located in the table, and then the hashing algorithm is used to find where the data is physically stored on the storage medium.[9]
The Data Dictionary
[edit | edit source]A data dictionary is a read-only set of tables that contain all data definitions in a database. The table structures are non-editable without a password. A password is needed to view or edit a table. The definitions included in the database include all of the following: tables, views, indexes, clusters, synonyms, sequences, procedures, functions, packages, triggers, and more. Keep in mind; the data dictionary does not contain any of the information located in the data tables, only the data about the tables. This specific data about the tables is otherwise known as metadata. The database dictionary includes information regarding how much space has been taken up by the schema objects and the amount of space that is left. [10] The information that is included in the database must be organized before put into the data dictionary. Data modeling, or putting a descriptive name to each data object, must be done for each independent object. Once that is done, the relationship of the data is described, along with the description of type of data. Type of data can include defining the object as text or an image. Once that is completed, the programmer must include a brief textual description regarding the data. [11]
Data Security and Privacy
[edit | edit source]
Data security is a must-have, and is required by most industry, business and legal mandates. Data security is what protects data from being breached (eg seen by people who should not see it), so that the information it contains cannot be disclosed or leaked. Data security also ensures the integrity of the data, meaning that no unauthorized changes can be made to data, data structures, configuration files, or logs. Data security programs can keep track of the files and monitor the transferring of data to prevent unauthorized access and stop any possible intrusions from occurring.[12]
Because technology has developed so much over the years, more and more actions are taking place online through the internet, apps, or other networks. This has raised the issue of privacy, as personal and sensitive information is often held in the databases of many organizations (hospitals, insurance companies, jobs, health care companies, etc.). To help solve this, privacy laws have been made to determine how companies and individuals can have the ability to choose what information can be given to third parties and what cannot be given out. In the United States, different privacy laws have been passed for specific industries or situations. Some of these laws include the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPPA), the Electronic Communications Privacy Act (ECPA), and the Video Privacy Protection Act.[13]
Classification of Databases
[edit | edit source]Single-User vs. Multiuser Database Systems
[edit | edit source]
Single-user database systems are located on one computer and they are designed for one user; often times, they are used for personal use and small businesses. Only one person can use the database at a time, so if one user is using the database the other users must wait until that user is done. While a multiuser database system is used for bigger businesses because it is a database that is accessed through a network. It is so more than one person can access and change the data in a system. Most use some kind of lock on the database so that there are no conflicts between people making changes. They can be on one computer or multiple computers.[14]
Client-Server and N-Tier Database Systems
[edit | edit source]
Most multiuser database systems are client-server database systems. Basically client-server database systems are servers that contain resources for other computers. It is when the client part, makes a service request from the server, which completes the request. For example a secretary using her PC (the client part) looks up the cost of a product on their system (ie on a server, not stored on her PC). The client is referred to as the front end and the database server is referred to as the back end.[15] Some of the client-server database systems have more than just the front end and the back end but also a middle part called a tier, which are referred to as n-tier database systems. In n-tier databases, the client and the database never communicate directly, all data is passed through the middle layer. The advantages of this database system is that the middle tier provides a layer of abstraction, that way you can change parts of the back end without having to modify parts of the front end. It is also a good way to separate responsibilities; they can also be more efficient.[16]
The Client Server Internet combinations gives IT another dimension to its organization. They first act like clients and servers of course, and they can access the internet as well to get into databases in distant locations. The final stage is to be able to create, view, use, modify, and delete applications as well as data. Software modules and hardware components are used to be able to actually perform functions. The client server connection are able to communicate with messages and these messages can be sent whether the server is online or off. The messages are sent through a network that may include both the intranet and internet. A network is a group of connected objects or people; the network is able to relay those messages to one another.
The main use for a client server is to produce a useful application for the business’s needs. Client servers use middleware which is an important part that allows for applications on the client end to be able to reach the actual network and talk to the server. It is the part that is in between the network and the application software. E-mails are a type of middleware since they are in between the network and the application.[17]
Centralized vs. Distributed Database Systems and Disk-Based vs. In-Memory Database Systems
[edit | edit source]
Centralized database systems are all located on one computer. This can either be a server or mainframe computer. Distributed database systems share a network and the data is divided between several computers connected to that network.
An advantage of a centralized database system is that all information is in one place. The disadvantage may be that a bottleneck might occur. Having all information on one computer can make it easier to some users, but difficult for others who want to access the files. One advantage of distributed database systems is that the database can be accessed using any computer on the network even if all the information is not on one computer. This is the preferred type of system to use for databases, because information can be easily found. It also ensures that all data will not be lost, if using the distributed database system over the centralized system. Because of the recent advances in technology, using the “cloud” is another way to store database information over the Internet. This concept goes hand in hand with disk-based and in-memory database systems.
Most databases are stored on conventional hard drives in computers today, but recently many are switching to in-memory databases. This can hold all data on the main memory of the computer. This creates faster performances than it would if using the disk-based system.
In-Memory Database
[edit | edit source]
An in-memory database (IMDB) is a database whose data is stored in main memory to facilitate faster response times.[18] In-memory databases are also sometimes referred to as main memory database systems, or MMDBs, and have become more popular in recent years for handing High-Performance Computing (HPC) and Big Data applications. Applications, such as those running telecommunications network equipment and mobile advertising networks, often use main-memory databases.
Three developments in recent years have made in-memory analytics increasingly feasible: 64-bit computing, multi-core servers and lower RAM prices.[19] The source is loaded into the system memory in a compressed, non-relational format. In-memory databases streamline the work involved in processing queries which provides faster and more predictable performance than from a disk (as access times and database requests are typically considerably faster when system memory is used as opposed to disk storage, particularly hard drive storage). Main memory databases are faster than disk-optimized databases since the internal optimization algorithms are simpler and execute fewer CPU instructions. Another advantage of in-memory databases comes into play when transactional data and analysis data is stored in the same database. It’s easier to carry out ad-hoc analysis as all of the data needed to analyze a business case is written to a single database.[20]
Database Models
[edit | edit source]Relational Database Model
[edit | edit source]Relational database management systems are important because they take several related tables and combine them in the least complex way that is possible. Essentially the RDBMS takes these smaller, less compact, tables and finds ways to relate them to one another based on singular variables to avoid repetition as much as possible. When creating such a database there are four main questions to ask: what is the point of this database? what information needs to be included in this database? which variables should be placed in which table to make the end result the least tangled/complicated? and how should this table be formatted? Once all those things are completed, one could use a program such as Microsoft Office's Access[21] to create a query by choosing specific related fields to display and organize. After this, one could use the query to generate a report which is essentially used to import the selected information into a singular database that would be easier to read through and find information from.

Relational database comes into play when an asset tracking database is needed, and spreadsheets are too large to use for the particular data. After the design of your new database, including the fields, data types, primary keys, and foreign keys, is finished, the next step is to actually go ahead and create the corresponding table for the database. The very first step to create a relational database is to create and name a new database file, which will contain all tables and objects included in the database. Next, using the table structure formed in the “design” phase of the process, each table in the database is created. And finally, once that table structure is complete, the last step is to enter the data into the tables, and relate different tables to each other as needed. In Microsoft Access, a table can be created under the Design View by entering each field name and specifying the data type and other properties as needed. However, if you wish to use your old or existing data in the new database, a process called data migration takes place by transferring the data from the old files to the new. Additionally, Design View also lets you make various sorts of edits in the form if you wish to have a specific layout or design—such as changing the form color, font size, the placement of the fields, or adding a heading, etc. [22]
Star Schema Model
[edit | edit source]
Star schema is one of the simplest database models and is commonly used as a model for relational data warehouses and multidimensional databases. It consists entirely of fact tables and dimension tables. Fact tables are an event or entity such as a sale and a dimension table consists of details about that event such as date, place, speed of delivery, etc. For example, a geography dimension table can be used to describe location data, such as country, state, or city. In a star schema, a fact table is surrounded by numerous dimensions that branch out, creating an image similar to a star. One of the advantages of a star schema model is that it is compatible with Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) which allows for data mining of specific information from different points of view. For example, a user can view the sales from a specific item at any specific time in the past.[23] One of the disadvantages of the star schema model is that it is a simplistic model so it is not capable of creating complex relational analytics. Star schemas are also denormalized so it is possible for redundancies to occur within the database.[24]
Types of Relationships
[edit | edit source]
There are three basic types of relationships among entities. These three types include: one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many. In a one to one relationship every row in one table is linked to one specific row in another table. This means that there must be exactly as many rows in the first table as in the second table. This type of relationship isn’t very common due to the fact that there isn’t always a benefit to the design of a database. There is no benefit to the design because if the data is directly related it would make sense to have all the data in one table. One way that one-to-one relationships could be beneficial is if some of the data is needed, but isn’t used often. The data that isn’t used often could be stored separately, and away from the more important data.[25] One-to-many relationships allow each row in a table to be related to many rows in another table. This type of relationship is beneficial to a database due to the fact that you can reference frequently used data in many different tables by only entering it into one master table. Usually, the number of rows in the first table would be less than the number of rows in a second, third, forth, and so on, table. One-to-many relationships are often used in libraries. For example, names of authors in one table could correspond with the books each author has written in different tables.[26]
Hierarchical and Network Database Models
[edit | edit source]
The hierarchical model is the oldest database models. It organizes data in a tree-like structure, using parent and child data segments. For example, it begins at the top of the tree with a single root. That stems into a lower level segment, which connects to other subordinate segments after. This is used to model one-to-many relationships. A disadvantage of using this model is that it requires data to be stored repetitively in multiple levels. This causes the database to function very slowly because it can be searching for information in lower levels as well. The network model uses a set structure. A set is comprised of an owner record type, a set name, and a member record type. This type of model shows many-to-many relationships. Parents can have multiple children, and children can have multiple parents. Both of these model types are outdated and no longer used for building new database applications. They are often less flexible than other model types. [27]
Also, all paths for accessing the data must be planned ahead of time and cannot easily be changed. Some places you might still see the hierarchical model might be in large systems that use high-volume transaction processing, like banks or insurance companies.
Object-Oriented Database Models
[edit | edit source]
Whereas other database models can only store conventional data (such as dates, numbers, and text), the object-oriented database management system (OODBMS) is far more abstract. In an OODBMS, you can store pretty much any kind of data you desire, along with the methods to be used with that data. To retrieve this more complex and varied data, the user sends queries written in object query language(OQL) which is an object-oriented version of SQL. OODBMSs are becoming increasingly prevalent because of the higher demands of computer users today. However, as is the case with any new technology, there is some resistance because of the downsides of OODBMSs.

One downside is how editing an OODBMS based application is more time consuming because changes have to be made to the other classes in the application that interact with instances of the parent class, versus an RDBMS system where edits can typically be independent of the parent application.[28] This is very time consuming and that means a lot of money has to be spent on making changes to the object-oriented database management system. Many companies in the business world have certain budgets set aside for the information department, which includes the database system used for the company, and the OODBMS is very costly. Another disadvantage for the OODBMS is the lack of support for security and views. The user of an OOBDMS cannot grant individuals’ access to certain objects or classes within the system, which either means the individual wouldn’t be allowed to see the system at all or that they would get access to everything within the system, something businesses might not like. Also, the OOBDMSs do not contain a view mechanism, which is a disadvantage for employees who like to see their work and also to make sure everything they put in is correct. Two more disadvantages of OOBDMSs that go hand in hand is the lack of standards for the system and the fact that there is no universal data model. Without standards for the system, the cleanliness of the system can be dragged down and it could be hard to use. Many people like when something is universal because then they know what is right and wrong, something that cannot see with the OODBMS.[29] Even with the extra difficulties, many important clients continue to operate using a OODBMS, one big example being Chicago Stock Exchange, which uses the system to manage stock trades.

After looking at the types of database models, there are 4 steps involved with designing a relational database. The first step in designing a relational database is to identify the purpose of the database and the activities that it will be used for. These activities can range from keeping track of rental properties, students grades, customer orders, or inventory. Databases are used in a wide variety of ways and knowing what you will use your database for will help you create your database and optimize its use. In knowing what purpose your database will serve, you will be able to determine the data (fields) that needs to be included in the database, then the fields can be organized into tables. It is good to group fields that logically belong together. Next look at the table structure and ensure that all fields are represented and in the proper table. Look to see if there is any redundancy in the data, that way you can restructure fields in order to minimize that redundancy. Lastly, finalize the structure of each table, listing each field’s name, type, size and so on and selecting a primary key (data definition). This procedure will assist you in create a database that will suit your needs and provide the information you request.[30]
Databases on the Web
[edit | edit source]Web Databases in Use
[edit | edit source]
There are many ways Web databases can be used. The most obvious way is the retrieval of information. Web databases provide a means for users to access the massive amount of information the Web has to offer, and this is made possible, in one way, by the use of search sites where databases provide links for the user. Other personal uses for databases include the storage of email addresses, telephone numbers, and other information for one who might create a site for friends and family.[31] On the business end, Web databases allow businesses to create “website polls, feedback forms, and client/customer inventory lists.”[32] This is a vital function that both large and small businesses can take advantage of to suite their needs. One, specific example relating to business-use of Web databases is the management of e-commerce-related activities. Here databases are used to provide information like pictures and pricing for products as well as order information and other necessary functions to enable efficient and reliable business transactions. Another feature of Web databases is their ability to display dynamic Web pages. These pages display information that changes depending on the input of the user, like a B2C site showing pages related to the interests of the consumer based on his or her past activities. From personal to business applications, Web databases are a vital part of addressing the tasks associated with Web-related activity.

Not only are websites becoming more and more personalized for the viewer, but the advertisements on the web page are as well. Companies including major search engine Google deliver targeted ads towards certain content and audiences. One method is contextual targeting, which analyzes keywords, word frequency, and link structures to determine what ads would match the content of the page. Placement targeting uses specific ads chosen by advertisers on certain web pages that are supposed to match what the viewer’s other interests may be and what other kinds of products they have to offer. Similar to this is interest-based advertising, which places advertisements relevant to certain interests on web pages that are commonly viewed by people with that similar interest. Google offers a program that people can use in order to set their interests so that ads are tailored towards their selections. Lastly, language targeting determines the primary language of the page and ensures that the advertisements shown will be in the same language. Advertisements would not work very well if the viewer could not even read what the product was that they were advertising! All of this information is placed into Google's ad search database which processes the information and ensures that the advertisement on your screen is going to be relevant to you.[33]
Middleware
[edit | edit source]
This is a computer software that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It is software that connects two otherwise separate applications, which can resemble "software glue.” For example, there are a number of middleware products that link a database system to a Web server. This provides the user to be able to receive data from the data base by using forms that are displayed on a Web browser, and it enables the Web server to return dynamic Web pages based on the user's requests and profile. As stated previously, the term middleware is used to describe separate products that serve as the glue between two applications. It is, therefore, distinct from import and export features that may be built into one of the applications. It is sometimes called plumbing because it connects two sides of an application and passes data between them. Distributed computing system middleware can loosely be divided into two categories. These categories are those who provide human-time services and those that perform in machine-time. This latter middleware is somewhat standardized through the Service Availability Forum and is commonly used in complex, embedded systems within telecom, defense and aerospace industries. [34]
How Web Databases Work
[edit | edit source]
In our technological world, we use web-based database requests on a daily basis. We are constantly visiting web pages, clicking on links and using the menu to navigate us through our activity on that page. Using middleware, the web server passes a request on to a database query and the information is stored and passed along to the database server. The database server then uses this information to direct the page to where it was intended to go. CGI Script is another way information is passed along. They use instructions via a programming language and accept and return the websites data to the user. Active server pages are yet another example of scripts used commonly on websites. They are very similar to CGI Scripts, yet they are exclusive because they almost always use VBS script or Java script. PHP Hypertext processor is a language that is becoming more and more popular everyday. This script is extremely similar to CGI scripts and active server pages yet are more highly compatible with other programs. The script functions using PHP tags and html codes to get their job done. These scripts are just some examples of what is used today and how information in transmitted on a web server.[35]
CGI Scripts
[edit | edit source]A CGI (common gateway interface) script is a set of instructions written in a programming language (such as C, Perl, Java, or Visual Basic) and designed to accept data from and return data to a Web page visitor. On very busy sites, CGI can slow down server response time significantly because it processes each request individually. The usual placement of a CGI script is in the remote web servers cgi-bin directory, but the exact location of this directory is determined by the web administrator for that machine.[36]
Active Server Pages
[edit | edit source]Active Server Pages (ASPs), Microsoft's first server-side script engine for dynamically generated Web pages, have the extension .asp. ASPs work similarly to Web pages utilizing CGI scripts, but the code to tie the database to the Web site is typically written in JavaScript or VBScript. With simple HTML pages, the client requests a web page from a server. The server just sends the file to the client, and the page is shown on the client's browser. With Active Server Pages, the server gets a chance to alter the file before sending it to the user. To use Active Server pages you must be running a Microsoft web-server. If you are running a Microsoft Web server, to run an ASP file, all you need to do is create a file on the web-server with a .ASP extension. When the browser requests the file, the web-server is smart enough to preprocess the file before sending it off to the client.
PHP Scripts
[edit | edit source]
PHP (PHP Hypertext Preprocessor) is a scripting language that is increasingly being used to create dynamic Web pages. Free to download and use,[37] It uses code similar to Perl or C++ that is inserted into the HTML code of a Web page using special PHP tags. Although PHP scripts perform tasks similar to CGI and ASPs, they have the advantage of high compatibility with many types of databases.
Review
[edit | edit source]Terms and definitions [38]
attribute A characteristic of an entity.
centralized database system A database system in which all of the data used by the system is located on a single computer.
client-server database system A database system where the database is located on a server and accessed by client devices.
collision an incident that happens when 2 or more records are assigned the same storage address.
column In a database, a field.
data definition The process of describing the properties of data that is to be included in a database table.
data dictionary The repository of all data definitions in a database.
data integrity The accuracy of data.
data privacy' Protecting the privacy of the data located in a database.
data security Protecting the data located in a database against destruction and misuse.
data validation The process of ensuring that data entered into a database is valid (matches the data definition).
database A collection of related data that is stored in a manner enabling information to be retrieved as needed; in a relational database, a collection of related tables.
database management system (DBMS) A type of software program used to create, maintain, and access databases.
direct organization A method of arranging data on a storage medium that uses hashing to specify the exact storage location.
distributed database system A database system in which the data used by the system is located on multiple computers that are connected via a network.
end-user database consist of data developed by individual end-users. Examples of these are collections of documents, spreadsheets, presentations, multimedia, and other files.
entity Something (such as a person, object, or event) that is important to a business or organization; typically becomes a database table in a database system for that business or organization.
field A single category of data to be stored in a database, such as customer names or employee telephone numbers. Also called a column.
form A formatted way of viewing and editing a table in a database. hashing algorithm a mathematical formula that finds where specific records are stored in the database.
hybrid XML/relational database A type of database system that can store and retrieve both XML data and relational data.
in-memory database (IMDB) A database that stores all data in memory instead of on a hard drive.
index A small table containing a primary key and the location of the record belonging to that key; used to locate records in a database.
indexed organization A method for organizing data on a storage medium or in a database that uses an index to specify the exact storage location.
metadata Data about data, such as the data contained in a data dictionary.
middleware Software used to connect two otherwise separate applications, such as a Web server and a database management system.
multidimensional database (MDDB) A type of database designed to be used with data warehousing.
multiuser database system A database designed to be accessed by multiple users.
normalization The process of evaluating and correcting the structure of a database table to minimize data redundancy.
object-oriented database management system (OODBMS)' A type of database system in which multiple types of data are stored as objects along with their related code.
primary key A specific field in a database table that uniquely identifies the records in that table.
query A request to see information from a database that matches specific criteria.
record A collection of related fields in a database. Also called a row.
relational database management system (RDBMS) A type of database system in which data is stored in tables related by common fields; the most widely used database model today.
report A formatted way of looking at information retrieved from a database table or the results of a query.
row In a database, a record.
single-user database system A database located on a single computer and designed to be accessed by a single user.
structured query language (SQL) A popular query language standard for information retrieval in relational databases.
table In a relational database, a collection of related records or rows.
Questions
Match each term with its example:
1.
A. When the database does not allow a user to enter a letter in a phone number field.
B. Requiring users to log on to a database system via a fingerprint reader.
C. Assigning a field the property of “required.”
i. Data definition
ii. Data integrity
iii. Data security
Fill in the blank
2. In a student information database, Name would be considered a(n) _______________, while all of Jennifer Mitchell's information would be a(n)___________.
3. Data _______ refers to accuracy of data.
4. When _____ organization is used, a hashing procedure determines where data is stored.
5. The term front end and back end refer to ______ database systems
True or False
6. Normalization is used to minimize data redundancy.
7. In a relational database, more than one table can be included in a database.
8. Using usernames and passwords is a data validation technique.
9. The network database model is the most widely used model today.
10. Dynamic Web pages commonly use databases.
Answers [39]
1. A. ii, B. iii., C. i.
2. field or column; row or record
3. integrity
4. direct
5. client-server
6. True
7. True
8. False
9. False
10. True
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://www.usg.edu/galileo/skills/unit04/primer04_01.phtml
- ↑ http://ecomputernotes.com/fundamental/what-is-a-database/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-dbms
- ↑ http://products.office.com/en-us/excel
- ↑ https://support.office.com/en-us/article/Training-courses-for-Access-2013-a4bd10ea-d5f4-40c5-8b37-d254561f8bce?ui=en-US&rs=en-US&ad=US
- ↑ http://smallbusiness.chron.com/importance-inventory-databases-retail-40269.html
- ↑ Understanding Computers: Today and Tomorrow - 14th Edition Comprehensive
- ↑ http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/data.html
- ↑ https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/master-data-services/hierarchies-master-data-services
- ↑ http://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/index.html?nbId=7345&nbNodeId=1013914#!&parentId=1013946
- ↑ https://docs.oracle.com/html/A96524_01/c05dicti.htm
- ↑ http://searchsoa.techtarget.com/definition/data-dictionary
- ↑ http://www-01.ibm.com/software/data/security-privacy/
- ↑ http://searchcio.techtarget.com/definition/data-privacy-information-privacy
- ↑ http://www.slideshare.net/raminder90/single-user-vs-multi-user-databases
- ↑ http://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/client-server
- ↑ http://databases.about.com/od/specificproducts/a/architectures.htm
- ↑ http://www.networkcomputing.com/netdesign/1005part1a.html
- ↑ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/in-memory-database
- ↑ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/in-memory-database
- ↑ http://www.gft.com/etc/medialib/2009/downloads/techreports/2012.Par.0003.File.tmp/gft_techreport_inmemorydatabases.pdf
- ↑ http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/access-help/create-a-query-based-on-multiple-tables-HA010096275.aspx
- ↑ http://office.microsoft.com/en-us/access-help/create-tables-RZ101772997.aspx?section=2
- ↑ http://searchdatamanagement.techtarget.com/definition/OLAP
- ↑ http://searchdatamanagement.techtarget.com/definition/star-schema
- ↑ http://www.databaseprimer.com/pages/relationship_1to1/
- ↑ http://www.databaseprimer.com/pages/relationship_1tox/
- ↑ http://wps.prenhall.com/wps/media/objects/14071/14409392/Learning_Tracks/Ess10_CH05_LT3_Hierarchical_and_Network_Data_Models.pdf
- ↑ http://slashdot.org/story/01/05/03/1434242/why-arent-you-using-an-oodms
- ↑ http://www.scribd.com/doc/6142698/oodbms
- ↑ http://code.tutsplus.com/tutorials/relational-databases-for-dummies--net-30244
- ↑ http://www.htmlgoodies.com/primers/database/article.php/3478121/To-Use-or-Not-to-Use-a-Database-That-is-the-Question.htm
- ↑ http://www.ehow.com/info_8219542_database.html
- ↑ https://support.google.com/adsense/answer/9713?hl=en
- ↑ https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.3/topics/http/middleware/
- ↑ http://guide.netfronts.com/Database-PHP-ASP/adding_dynamic_web_content.html
- ↑ http://snowwhite.it.brighton.ac.uk/staff/mas/mas/courses/html/html3.html
- ↑ http://www.w3schools.com/php/php_intro.asp
- ↑ http://coursemate.cengage.com/CPReader/View/9781133114598/default.aspx?eISBN=9781133114598#66897dee-5c5a-4b7d-8a74-0eac7f4de56c
- ↑ http://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/index.html?nbId=7345&nbNodeId=1013914#!&parentId=1013946
Computer Security
Hardware Loss or Damage
[edit | edit source]
Hardware loss is inevitable. With so many people wanting the latest and greatest, you could imagine that others might get jealous, or desperate. Hardware theft is prominent and a large issue in the world. For whatever reason, peoples personal possessions are stolen. They could be stolen for valuable information, or just to pawn off the items for some quick money. With 1.6 million phones being stolen, this is an issue that needs to be dealt with.[1] Hardware loss is not the only way someone could lose their laptop or Android.[2] Hardware damage can render any of the latest and greatest useless. Whether is was a clogged fan, spilled water, or dropping it on the floor. When that moment arises, you know that it could all be gone within a matter of seconds.
System Failure is the complete malfunction of a computer system. This may be due to hardware failure, severe issues with certain software on the computer, or even a computer virus. Frequently, system failure will cause the computer to freeze, reboot, or stop functioning altogether and the repercussions of such an event can be devastating for a business. The result is often either the loss of important data, delays in the transfer of important information, and in some cases even the inability to function properly. An easy example of a system failure can be seen in the lawsuit California issued against SAP Public Services Inc.[3] California's payroll was affected by SAP's software solutions which cost the people of the state of California $250 million as well as delaying the paychecks of numerous employees of the California government. In this case, there was no loss of data but rather delays in the transfer of information as well as the corruption of it. Some checks were overpaid, others were underpaid. In some instances the incorrect spouses were paid for child support which could have culminated in the court intervening for an unpaid mother or father. Insurance benefits were also denied to others because of the system's inability to transmit data regarding medical deductions. It can be easily seen how a system failure can affect multiple people on many levels with a case like this, and how quickly the ability to function properly can be the result. The corruption of data and the inability to transfer it swiftly produced one of the largest debacles in government at the state level in recent times.

Along with hardware loss there are also ways to prevent and deal with unfortunate situations along these lines. Knowing about computer security can prevent many incidents from occurring that could result in the loss of personal information as well as the money you have put into your computer. The first tool for containing computer security can simply be just making sure what you have on your computer is information that could not damage your life if it was lost. But we do not live in a perfect world, and sometimes things slip and a credit card statement or a password to important information can be released. In this case, you should take all steps to prepare yourself to deal with that situation before it is too late. Software programs are available and free, however, such as “Adeona” which can be installed very easily onto your desktop. This program tracks the location of laptops, and can even take pictures of the perpetrator if you have a Mac. There is a recovery tool which can send you a text file of the information contained about the theft of a laptop, which can then be taken to the police to hopefully resolve the issue and bring liberty to the situation. There are other programs like this are available, as well as alarms that can be put on your laptop if someone unplugs it or puts in a wrong password. Steps like this can be taken to prevent loss of your computer and help keep your information safe.[4]

As discussed before, hardware loss is a very unfortunate situation that can result in the loss of important data. The loss of data can be influenced by many things, including power shortages. A way an individual can protect their data is by using different devices that are available to purchase and use with their device. Surge suppressors provide an individual with the assurance that their hardware will be protected from damage in case there are electrical fluctuations. Surge suppressors work in a very simple way with few steps. The device protects an individual's hardware by channeling the extra voltage into the outlet's grounding wire, preventing the extra voltage from going to the device. However, the device still enables the normal amount of voltage to pass through to the device. An individual can also protect their hardware by investing in a uninterruptable power supplier, otherwise known as a UPS. These devices provide continuous power to the device if the power were to go out for a period of time. Another way that enables individuals to protect their data is by backing up their data. It is important for both businesses, as well as individuals to backup their data. There are multiple ways individuals can do so. One option that is available is to consider remote locations to store data, in case there is system failure at a main location. Another option is to store data through an internet "cloud" system. Overall, it is very important to backup data, regardless if an individual is convinced their data will not get stolen or destroyed. [5]
Locks
[edit | edit source]
One form of physical security that is available on most electronics is the "Kensington Lock" or "Kensington Security Slot" (a.k.a. the "K-slot"). It's ubiquity amongst electronics has allowed it to become an industry standard on everything from PC cases, to laptops, to monitors. This type of anti-theft protection was patented in 1999 by the company Kryptonite. [6] This security measure is most often used in the scenario of a coffee shop, as if someone was going to run off with a laptop, it would add another level of complexity, making the laptop cumbersome and also raise suspicion in the eyes of observers of a theft. There has not been any physical locking mechanism as common as this to date.
Mobile Device Management
[edit | edit source]
The management of mobile devices is very common within institutions such as schools or companies that have mobile devices for their students or employees. The management of mobile devices can apply to many different situations. For example, it can apply to the management of devices owned by the institution. It may also apply to the management of devices that are connected to the wireless network of the institution. Usually, the IT department of the institution utilizes a third-party software that allows certain restrictions to be placed on particular mobile devices whether it be phones, tablets, or laptops.[7] Some popular softwares include AirWatch which is distributed by VMWare [8] and maas360 which is distributed by IBM.[9] Apple also has their own device management software that is integrated into iOS devices.[10] Some restrictions that may be implemented by mobile device management include the restriction of certain websites or applications. IT may also completely block the ability to download applications or surf the Internet on the devices. Although restriction to apps can be implemented, the management of mobile devices also includes the installing of apps onto devices. For example, if an entire company shares information and files through an application such as DropBox, then the IT department may simply install the application onto every device. This also allows for IT to update the app when needed instead of relying on the individual users to download the update. Another use of mobile device management is the restriction of features on the phone. For example, IT may restrict access to the camera to avoid pictures being taken within the workplace.[11]
Ruggedized Devices
[edit | edit source]
Ruggedized devices are devices designed to withstand large amounts of physical abuse. There are two different classifications of ruggedized devices. Semi-rugged devices are able to withstand things like rain and dust, while ultra-rugged devices are able to withstand drops onto hard surfaces. These designs can also protect against accidental beverage spills and small burns. Ruggedized devices are often used by people who work outdoors. For example, construction workers, police officers, firefighters, and military personnel will often use ruggedized devices. Construction workers often use weatherproof stereos near worksites that prevent dust from getting in. Police officers will often have rugged laptops in their vehicles due to the possibility of extreme weather during investigations. Firefighters need their heart rate monitors and communication devices protected from high temperatures and the possibility of stray flames. Military personnel use rugged radios and video cameras during combat. Laptops and phones are among the most popular types of rugged devices.[12] Panasonic, an electronics company, produces a bestselling rugged laptop called a Toughbook. A Toughbook is usually very bulky and has a longer battery life compared to regular laptops.[13] Samsung produces a popular rugged cell phone called the Galaxy S5 Active. The Galaxy S5 Active was engineered for active lifestyles. It is water-resistant and shock-resistant.[14]
Mobile Devices
[edit | edit source]As mobile devices become more common place, new cases and mean of protecting them are becoming more and more common. This is especially prevalent for smart phones. Smart phone are a substantial investment, and as they are used quite often, there are many opportunities for the device to be dropped, soaked, or crushed. As people want to protect their device, cases are found on most phones. They can be quite simple, just a piece of formed plastic, or quite advanced, with some completely sealing off the phone from scratches, dust, and full water immersion. Phones are not alone regarding protective cases. As tablets are used more and more, special cases are being made for their protection as well. Some cases protect the device, and provide a mounting point to use on steering wheels, dashboard, or vehicle windows. Many of the mounts are removable so the device can go from a navigation aid back to a phone in seconds.[15] Cases usually have some kind of screen protector to protect against scratches and sun glare. These protectors are thin pieces of plastic, which stick to the screen of the device. The thin plastic allows for the continued use of the touch screen, and provides protection. As the plastic gets scratched, it can be replaced.

Encryption
[edit | edit source]
As discussed previously in this Wikibook, it is very important to encrypt one's data and prevent it from being accessed by outside individuals. Two specific encryption measures are full-disk encryption (FDE) and self-encrypting hard drives. Full-disk encryption consists of encrypting all of the data on a storage medium, not just the individual files. Self-encrypting hard drives are ones that automatically encrypt stored data without the user having to manually do anything to encrypt it. The encryption occurs completely automatically and invisibly to the user from the moment the hard drive is manufactured, and they provide full-disk encryption. The encryption cannot be turned off and does not interrupt the work flow of the user. These devices protect data even when employees violate company policy by turning off network security features. SEDs are still rather expensive, so they are not as commonplace now as they might be in the future if costs decrease. They only started shipping in 2009, so it is likely that in the future, they will become cheaper and more common, increasing security standards and helping to keep the data of individual users, companies and corporations, and governmental agencies inaccessible to and safe from outside forces and hackers.[16]
Software Piracy
[edit | edit source]Software piracy, a common name for file sharing, is the illegal copying and distribution of software. It is unauthorized by the copyright holder of the software, and it is a widespread recurrence in the computer era of today. If one purchases a software, he or she is not the owner of that particular software, but he or she is only licensed to the software. This means he or she can make copies, but for their own use only, or as stated in the End User License Agreement. In the United States and other countries, it is illegal to make copies of software, movies, CDs, etc., and then redistribute these copies to someone. In countries such as Sweden, copyright law restricts people to non-commercial sharing. A few common types of software piracy are the following: counterfeit software, OEM unbundling, soft lifting, hard disk loading, corporate software piracy, and Internet software piracy.[17] Software piracy is debated currently, with one side stating that it has a negative effect on the economy because it reduces the funding for ongoing developmental efforts, and it prevents users from getting high quality technical support and product updates, while the pro-sharing argument states that people should be allowed to share as they wish, and the financial benefit of corporations granted by Intellectual Property Law is unjust. However, BSA is a common software who is a global organization that forms to advance free, and open world transfer for legitimate software by advocating strong intellectual property protection. The BSA works with many software and commercial companies to stop file sharing.

What some people may not realize is that after purchasing software, they do not own the software, but have instead purchased a license to use the software. Upon purchasing software, the purchaser has agreed to certain limitations concerning the software, such as only using the software on one computer. The purchaser also agrees to not make any illegal copies or install it on a computer other than their own. Any illegal act concerning misuse or duplication of software is known as software piracy. There are many ways to prevent and protect against software piracy. One tip is to better educate consumers and businesses of the threat of piracy. Some consumers may be purchasing pirated material without even having knowledge of it. It is important for people to use credible sources when purchasing software. Also, it may help to make people more aware of the damage that using pirated material can cause. According to the BSA, (Business Software Alliance) revenue loss in software companies in 2008 reached fifty billion dollars. According to the BSA Global Software Piracy study, fifty seven percent of the Worlds computer users admitted to using pirated software. Whether it is the unauthorized installation of a program onto a computer, or the illegal distribution of software, it is considered software piracy and is punishable by the law. Perhaps educating people on the large deficits software companies experience due to piracy would make the act less prevalent.[18]
Electronic Profiling, Privacy Policy and Spam
[edit | edit source]Marketing Databases
[edit | edit source]
The most types of direct marketing require a database with customer information. With this information the seller can design communication taking into account the individual characteristics of prospective customers, both private individuals and companies. The database is being formed for a considerable time, or being purchased from specialized companies, supplying various specialized databases. Marketing databases - is the process of creation, maintenance and using of customer information for the purpose of contacting the latter and do the business. Along with information about the actual customer, has used the services of the company, they should be collected information about potential consumers. Databases should be constantly improved based on the accumulation of information about the value of the consumer - the frequency and the value of purchases made by him. This method of maintaining the database using the ranking values consumer received the name of the method RFM (Recency, Frequency, and Monetary) Value of Purchases. Other information required to replenish the database may include the payment method of purchase, Buyer, the character they buy goods or services. Marketing Database will be most effective if it is focused on building relationships. Direct marketing does not have to be like a "single shot", which are intended to entice buyers to a rapid response before they become distrustful. Building relationships with customers should be based on their life values (method CLV). Only in this case they will be long-term and will bring tangible benefits. However, before you start to build a relationship, you need to carefully select the most prospective buyers who can make the biggest contribution to the volume of sales made. To select these buyers, marketers often develop consumer profiles. Building relationships with customers by CLV is impossible without a comprehensive study of the characteristics and properties of consumer goods, as well as determine the degree of customer satisfaction and the availability of personalized information. However, with the information is too personal should be very careful, as their use in communication can lead to a negative reaction from consumers.[19]
Electronic Profiling
[edit | edit source]
Electronic profiling is when marketing companies collect information about an individual. They can get the information from purchases that a person makes on the Internet, as well as public information like births, marriages, vehicle registrations, etc. An electronic profile usually consists of a person’s name, age, telephone number, marital status, number and age of children, spending habits, and previous purchases. This is how online websites like Amazon can make suggestions of what someone might want to buy.[20] That information can then be sold to companies who may ask for it for marketing purposes. Most businesses that collect personal information have a privacy policy, which will tell you how your personal information is going to be used and as long as the business follows what they say in their privacy policy it is legal for them to sell your personal information. The problem with this is that sometimes privacy policies can be unclear in their intentions and they can be hard to decipher. Companies may also change their privacy policy often and people don’t take the time to read through it. Electronic profiling also leads to behavioral advertising, where someone might see advertisements about things in their area or about people that are around the same age and gender as them. It is kind of crazy that the computer knows that about someone and then can apply it to the things that person looks at.[21]

The Direct Marketing Association (DMA) is the main advocator of electronic profiling. Electronic profiling has become an entire industry, thus the DMA voices against privacy policies that would keep consumer’s information from being used for marketing and advertising. Profiling data has been sold long before the internet, however, online tracking has made it develop even more. While most of this information is sold for marketing or spam purposes, it can also be used for individual use. Websites such as whitepages.com and switchboard.com allow anyone to search for a person’s name and city, and results show up giving personal information including their house address, phone number, email address, and relatives. There are ways to avoid having your information out in the open. First of all, there are some common sense rules such as limiting how many organizations or stores information is given to, not giving out an email address when it is optional, and not giving out your social security number. According to the Electronic Privacy Information Center (EPIC), other ways to self-defend your privacy include the following: reading privacy policies, no matter how tedious or long it may be; being aware of when companies change their privacy policies, as many companies change them often; opting-out from pre-approved credit companies and from information sharing; making sure that when you opt-out from these things, that the permanent box is selected or else many times you can be re-added after a period of time; requesting a “temporary” change of address when filling out a Postal Service Change of Address Card so that the information does end up in any database and thus cannot end up in a profiling database; and lastly, be careful of catalogue merchants and be sure to ask that they do not sell your information; never buy anything from a telemarketer call or an infomercial, as they almost always are putting your information on an automatic “responder list”. It is always good to be cautious when giving information out, no matter what organization or personal is receiving it.[22]
Privacy Policy
[edit | edit source]
A privacy policy is a document that explains how an organization handles any customer, client or employee information gathered in its operations.[23] It usually declares what specific information is collected and whether it is kept confidential or shared with or sold to other firms, researchers or sellers.[24] The policy should also explain if data may be left on a user’s computer, such as cookies. According to best practices, the policy should disclose if data may be shared with or sold to third parties and if so, what the purpose is.[25] Personal information can be anything that can be used to identify an individual, not limited to but including name, address, date of birth, marital status, contact information, ID issue and expiry date, financial records, credit information, medical history, where one travels, and intentions to acquire goods and services. Most websites make their privacy policies available to site visitors.[26] For example, Facebook has updated its privacy policy to make it easier for users to understand, cutting around 70 percent of the previous privacy policy.[27] Critics also question if consumers even read privacy policies or can understand what they read. . A 2001 study by the Privacy Leadership Initiative claimed only 3% of consumers read privacy policies carefully, and 64% briefly glanced at, or never read, privacy policies.[28]
Spam
[edit | edit source]
Spam, officially known as Unsolicited Commercial Email (UCE) or Unsolicited Bulk Email (UBE), is the use of electronic messaging systems to send unsolicited bulk messages.[29] Spam can be sent to personal email addresses as well as to cell phones sent as a text message. Some frequently seen spam examples include advertising for specifically health-related products, pornography, and business opportunities, such as buying and selling stock. With a world full of technology and information around us, individuals can easily receive any email address from a number of ways. Companies receive email addresses either directly from the individual, or through 3rd parties that have a partnership with the other. Personal information can be entered into a database and then spam can be sent out to those individuals. Spam can also be sent over social media sites like Facebook, Twitter, or Google+. Many email clients now have a separate folder marked “spam.” This is helpful to individuals because they will now be able to see what is considered “spam” before they open the email or attachment. With text messages, most people ignore or delete those messages. Marketing databases are easy ways to get on a spam distribution list.[30] Surprisingly, most spam is considered illegal, however there are certain guidelines that hackers can follow to be able to send spam emails or messages. It is difficult to stop the spamming, but in recent years, many have been convicted of spamming materials being sent to customers and individuals.
Protecting Against Spam
[edit | edit source]
One way of safeguarding against spam is to protect the privacy of personal information. Individuals should protect your e-mail address and other personal information. Individuals can also surf the Web anonymously, opt out of some marketing activities, and use filters to limit your exposure to spam e-mails. One suggestion to avoid spam is to have two e-mail addresses. You should have one e-mail for personal address for family, friends, colleagues, and other trusted resources. The second e-mail should be a disposable or throw-away e-mail address which can be used for online shopping and signing up for free offers. One valuable piece of information is that less-legitimate sources of spam have unsubscribe links that do not work or that are present only to verify that your e-mail address is genuine! One online article suggests using the blacklist option in your e-mail. Blacklists permanently block emails form selected senders or servers. Once you blacklist a domain, server, or sender, those senders simply cannot contact you. The article also suggests to report spam to your e-mail provider, this will help over all to address the spam problem because the more you report spam the more your e-mail provider can work behind the scene to filter and block the sender, domain, or server from sending e-mails to you and other legitimate, personal e-mail addresses. Also, always be cautious of revealing personal information online. Lastly, make sure to use filters and opt out, which refers to following a predesigned procedure to remove yourself from marketing lists, or otherwise preventing your personal information from being obtained by or shared with others. When you opt out, you are instructing companies you do business with not to share your information with third parties.[31]
Properly Dispose of Hardware Containing Data
[edit | edit source]
A perfect way to unintentionally, yet practically hand your sensitive information to computer thieves would be carelessly throwing away your hardware containing that information, thinking it is no longer worth anything. When discarding an old computer, hard disk, or any other device which contains data storage media (eg, a hard drive or a flash drive), it is crucial to make certain there is absolutely nothing left on that storage medium.
The most basic problem is that, in most cases, deletion (eg, into a trash can icon) does not do what most people think. Instead, for reasons of efficiency (it's faster!), this sort of deletion merely marks the file space on the storage medium (eg, out on the hard drive) as no longer containing anything that must be saved, but is now free to use. The information in the "deleted" file is still present, and with special software, can be entirely recovered.
It is sensible to shred important discarded documents, DVDs, CEDs, and such so that the information they contain is effectively impossible to recover ("cross cut" shredding is far preferable, as it is much harder to recover). The data on hard drives or other storage media must be similarly rendered unrecoverable. Currently, the most commonly recommended technique is to overwrite the space used by the to be deleted file several times. The US Government has specified a series of such overwrites (all 0's, then all 1's, then random data, etc) if the storage media is to be reused. It is somewhat time consuming and users are often reluctant (or forgetful) to do so. Note that merely reformatting the storage space on a disk (which is often thought to be an effective way of "wiping" data from a hard drive), is not at all equivalent. Most such formatting does not overwrite the entire storage space on a disk, but rather only reestablishes block boundaries and pointers the file system requires to use the disk. The existing data is not removed, and with sufficient effort and skill can be mostly recovered.
Another way of disposing of discarded data is degaussing. Old data can be degaussed by exposing magnetic media to a very strong magnetic field. This is difficult in the case of a hard drive in which the magnetic surfaces are within a metal container, and most likely shielded by the other platters from the erasing field. Organizations with extremely high security requirements have been known to melt hard drives in a furnace, or to disassemble them and sand all the platter surfaces until the magnetic film layer is destroyed. Destruction of discarded data is so important in modern times that a great many businesses have developed and implemented a mandatory media sanitization or data destruction policy. [32]
Electronic Surveillance
[edit | edit source]Computer Monitoring Software
[edit | edit source]
One popular tool of electronic surveillance is computer monitoring software. This software is used specifically for the purpose of recording keystrokes, logging the programs or Web sites accessed, or otherwise monitoring someone's computer activity. Some of the highest rated computer monitoring software includes SpyAgent and WebWatcher.[33] It is legal to use this software, either on your own computer or the computers of your employees. However, installing it on another computer without the owner's knowledge is typically illegal. Considering that this software is created to pretty much make sure your kids, spouse, or employees aren't doing anything on the computer that you don't want them to be doing, there are some ethical issues to consider. On the one hand, sometimes kids need help building self-control and avoiding predators so having their internet time monitored can be helpful for parents to use as a teaching tool. On the other hand, if you are supposedly in a loving and trusting romantic relationship, one could argue that you shouldn't be spying on them to be sure that they aren't cheating. As humans, we enjoy being trusted to do the right thing... and we get less credit for doing what we're supposed to do if put into an environment where there is no opportunity to get away with something dishonest. Still, computer monitoring software continues to be popular, and that isn't likely to end in a global culture that grows increasingly paranoid.
Employee Monitoring
[edit | edit source]
Employee monitoring refers to companies recording or observing the actions of employees while on the job. Common employee monitoring activities include screening telephone calls, reviewing e-mail, and tracking computer and internet usage. Usually, the primary motive is to monitor internet usage for legal liability, but monitoring employee productivity can be for many reasons. Employee monitoring may sound unethical to the point of it being illegal; however, legally, employees have little recourse, and the few cases brought up to court tend to go against the employee.[34] An increasingly popular way of tracking employees comes in the form of smart of RFID-enabled ID cards. These cards are often used for access control (entering a building; automatically locking a computer when a certain distance is reached), but tracking an employee using GPS is also possible. Comprehensive employee monitoring systems can be expensive, so alternatives such as employee training and education are also often explored. Regardless of the techniques used, most believe that from an ethical perspective businesses should inform employees about their monitoring practices, even though they are generally not required to do so by law. However, legislation is starting to address employee monitoring. For example, several U.S. states are considering laws to prevent employers from implanting employees with RFID chips without the employee's consent. At least in the United States there are no strict laws surrounding employee monitoring, as the benefits of security, productivity measurement, and legal compliance outweigh the potential negatives. This is the case in most nations.

Employees need to be very aware of their actions while working on the clock, as companies can monitor exactly what employees are doing or saying and how productive and efficient they are being while on the clock. Phone calls can be screened, emails can all be archived, website browsing can be tracked, and their every movement can be watched through cameras. Some practices are more common in different workplaces. For example, retail stores generally keep their employees under close surveillance to make sure they are not allowing theft, or engaging in it themselves. Other office positions can remotely access the computer desktop of employees and see exactly what is open on their screen. What some might view as a more extreme case includes GPS based systems installed in company cars to make sure vehicles remain within designated areas. Some individuals see monitoring as a breach of their privacy, but employers are more concerned with the productivity, safety, and liability of their employees. An alternative to continuous monitoring would be frequent training and education. But undoubtedly surveillance and monitoring of employees will persist as employers worry about new avenues for individuals to misbehave at work due to advances in technology.[35]
Video Surveillance
[edit | edit source]

Essentially, the idea of video surveillance is exactly what it sounds like: the use of video cameras to survey an area of monitor what is going on. We see examples of this every day: traffic cameras, police car cameras, ATMs, most retail stores, and even many mobile phones. The world of technology expanding so much that it is becoming increasingly difficult to find places that are not under some sort of surveillance. Many offices and schools implement these systems to keep track of students/employees and ensure they have a visual record of an incident if anything were to happen. Police use this in their cars to obtain a record of their activities on the job. Retail stores and ATMs use them to reduce crime/theft. Most of us have, at one point or another, waved at those small black and white television screens that show us "on TV" in stores, when the truth is we were waving at the video camera recording our every action for someone to review later on. And, more shockingly, the photos and videos people take today just using their phones can be used to link persons to crimes, events, locations, and so much more. while the expansion of video surveillance does create some privacy concerns, it has been useful (especially combined with other technology like facial recognition) in solving crimes like discovering the people responsible for the Boston bombing, as well as many other crimes.[36] There are multiple problems with video surveillance other than privacy concerns. First off, politicians are trying to push for more video surveillance cameras to curb violent activities like terrorist attacks or murders. The only problem is that video surveillance will not stop these actions, even though it might help find the culprit. The person committing the action is not deterred by the fact of them being on camera, and in some cases the individual actually wants to be filmed to become infamous on news coverage of their actions. Another issue is the abuse of the video surveillance cameras. Reviewers of video cameras, mostly government officials, can blackmail people they are observing. An instance of this was when an official reviewed tape near a gay club and searched license plates to find the backgrounds of the men in the club to see if they were married in order to extort money. Other situations where this can happen are to prevent activists from meeting for racial, ethnic, or religious causes. A third issue is the fact that there aren’t many limits or controls on surveillance systems, and soon enough our every move will be watched by our government. This does lead to a privacy concern, but it should be noted. Many people like their privacy and video surveillance cameras are slowly chipping away at this right of the people. In total, there are many advantages and disadvantages to video surveillance.[37]

As technology evolved so did the advancements in video surveillance. One of these many advances is All-Weather Radio Frequency Surveillance. This security system makes use of radio frequency detection to detect things even under heavy weather conditions such as fog. This is used by the military in detecting intruders. Another innovation is something called SafeZone, which is a technology that can spot the presence of weapons by detecting the shape of firearms. The technology also triggers things such as calling law enforcement or locking doors. Maybe one of the most useful innovations is that of High Definition Video. Thanks to high definition video it has become easier for video surveillance to detect threats and compare faces to the criminal database. One innovation that is helpful for retailers is that of surveillance feeds on smartphones. By being able to put the surveillance feeds of cameras on smartphones it makes it easier for retailers to check their stores even while on the go. There's also the fact that surveillance is now offered as a service. This makes having video surveillance more accessible even for those who don't know how to use video surveillance. Even though video surveillance is something that some people don't accept, hopefully technology can still further improve video surveillance in order to at least try and make the world a little safer.[38]
Presence Technology
[edit | edit source]
Presence technology is the ability of one device connected to a network to recognize and identify another device on the same network. This gives the ability for one device to tell the other device’s status, such as if it is being used or available for communication. There are many different ways to implement this technology, including software, GPS, or RFID. A good example of this technology can be seen in Instant Messaging programs. A user is able to see whether or not other people are online and active on the messenger. Presence technology is an important part of the 3G wireless network.[39] Mobile phones use this technology all the time, such as being able to share your location with someone through GPS or seeing if the other person is typing on iMessage. Not only is this technology good for personal use but also for corporate use. Presence management can be used in many methods, for example to see if a certain employee is available to help a customer at the moment. Most of the time the user can change settings in order to allow certain features of presence technology to be activated or not in order to protect their privacy.
Software Piracy and Digital Counterfeiting
[edit | edit source]Digital Counterfeiting
[edit | edit source]
Digital counterfeiting is using computers and other digital equipment to make illegal copies of currency, checks, collectibles, and others. It is important to be able to prevent digital counterfeiting that way the value of the currency (if that is what is being counterfeited) will not lose its value. The prevention of counterfeiting is a concern of everyone and should not be taken lightly. The Treasury Department makes a new design of the currency every 7 to 10 years in order to not have the money all stay the same. New features on the currency help to make it harder or even impossible to remake. Watermarks and security threads are a few ways that the Treasury uses to help make the digital counterfeiting not possible. Watermarks are recognizable images on papers that can be viewed through transmitting light. On the 5 dollar bill, a 5 was added to the right of the portrait, while previously it was a watermark of Abraham Lincoln. Another watermark was added on the 5 dollar bill, it was a column of three smaller 5s and they are to the left of the portrait.[40] These small changes really do overall help with being able to prevent counterfeiting since they are harder to remake.
Software Piracy
[edit | edit source]
The unauthorized (and therefore illegal) copying of a computer program is known as Software Piracy. It is a widespread problem that often proves difficult to harness because computers are quickly and easily able to create exact copies of a single program. It is estimated that 42% of all software installed on personal computers globally (about 20% of all software in the U.S. and at least 90% in five countries) is installed illegally, leading to an annual monetary loss of $59 billion worldwide to software vendors. The act of pirating software includes, but is not limited to -- making illegal copies of programs and distributing them to others, businesses extending software to more devices than permitted in the end-user license agreement, retailers installing unlicensed copies of software on purchased computers, and illegally duplicating software and its packaging which are then passed off as legitimate. Pirated software, CDs, and DVDs may be downloaded from Web sites and peer-to-peer file sharing services, sold at online auctions, or disseminated other ways (regardless of profit), all of which are illegal. The SOPA has aimed to stop the illegality of pirating online materials, but it still remains illegal in the United States and most other countries. [41]
Computer Security and Privacy Legislation
[edit | edit source]Computer Security
[edit | edit source]
Computer security is the protection of computing systems and data that can be stored or accessed. Being educated about the computers security will benefit the user by enabling people to carry out their jobs, education, and research supporting critical business process, as well as, protecting personal and sensitive information. Good security standards found that 10% of the security safeguards are technical and the other 90% security safeguards rely on the computer user to adhere to good computing practices. When using a computer, it benefits the user by understanding how to keep their computer and data secure. Some key steps are to use secured passwords, making sure it’s personal that no one will discover and that you always will remember it, in addition to, making sure the computer is protected, not clicking on unknown links, and not downloading unknown files or programs onto the computer. To help reduce the risk, look out for padlocks that appear in the URL bar before entering any personal information. This leads to the risks of the security of personal information, loss of business information or loss of employee and public trust. Other risks can be known for expensive reporting requirements in case of securing personal, financial or health information.[42]
The U.S. Safe Web Act of 2006
[edit | edit source]The U.S. Safe Web Act was brought about in December 2006; the purpose of which was claimed to protect consumers from Internet fraud. With the growing popularity and growth of the Internet, this has become an increasingly dangerous threat. The Internet is consumed with fraudulent users, spyware, and telemarketing, and this law sought to put an end to some of this fraud. It gave the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) a decent deal more authority than they had previously had before it was passed, in hopes of protecting the consumers that use the Internet on a daily basis. There are a few things that the law changed that had not previously been allowed. First, it allowed the FTC to share information with foreign law enforcements and also aid them in investigations. In addition, it allows them to gain information from public law enforcement officials that they would not have previously been allowed to receive lawfully. This act also gave them more power and tools in consumer investigations. Finally, the act seems to strengthen the United States powers with other foreign countries, and allows them to share and work together in ways that previously would not have been allowed. In conclusion, it seems as though the whole purpose of the bill was to give the government more power, and to allow them to lawfully impose in more ways than before.[43]
Other Legislation Related to Privacy
[edit | edit source]
Related to the issues of computer privacy and personal privacy in general are the Do-Not-Call Implementation Act of 2003 and the CAN-SPAM Act of 2003. Both laws were created with the hopes of ensuring protection of privacy, yet whether or not these laws have accomplished this remains in question. The Do-Not-Call Implementation Act was designed to work in unison with the National Do Not Call Registry, which began in 2003 as well. This was developed to give individuals more control over the telemarketing calls that reach their households. The Do-Not-Call Implementation Act relates to the National Do Not Call Registry specifically in that it allowed for the enforcement of the registry by allowing for the Federal Trade Commission to collect fees for its maintenance.[44] U.S. Consumers can register by phone or online, and phone numbers now remain on the registry permanently because of the Do-Not-Call Improvement Act of 2007.
The CAN-SPAM Act of 2003 was designed to address the issue of unsolicited email messages (e.g. spam). According to the Bureau of Consumer Protection, the law covers all commercial messages, and it applies to not just business-to-customer messages but business-to-business messages as well.[45] The maximum penalty is $16,000 per violation, yet the effectiveness of this act remains in question because it remains largely unenforced. Critics assert that the law creates problems for state laws that would have “provided victims with practical means of redress.”[46]
Review
[edit | edit source]Key Terms
[edit | edit source]- Hardware theft
- The theft of computer hardware [47]
- System failure
- The complete malfunction of a computer system
- Freeware
- Copyrighted software that may be used free of charge [48]
- Full disk encryption (FDE)
- A technology that encrypts everything stored on a storage medium automatically, without any user interaction.[49]
- Self-encrypting hard drive
- A hard drive that uses full disk encryption (FDE) [50]
- Ruggedized device
- A device (such as a portable computer or mobile phone) that is designed to withstand much more physical abuse than its conventional counterpart [51]
- Surge suppressor
- A device that protects a computer system from damage due to electrical fluctuations [52]
- Uninterruptible power supply (UPS)
- A device containing a built-in battery that provides continuous power to a computer and other connected components when the electricity goes out [53]
- Disaster recovery plan
- A written plan that describes the steps a company will take following the occurrence of a disaster [54]
- Software piracy
- The unauthorized copying of a computer program
- Digital counterfeiting
- The use of computers or other types of digital equipment to make illegal copies of currency, checks, collectibles, and other items.[55]
- Marketing database
- A collection of data about people that is stored in a large database and used for marketing purposes
- Opt out
- To request that you be removed from marketing activities or that your information not be shared with other companies [56]
- Presence technology
- Technology that enables one computing device (such as a computer or mobile phone) to locate and identify the current status of another device on the same network [57]
Review Questions
[edit | edit source]1. Observing or reviewing employees’ actions while they are on the job is _____.
2. _____ _____ Software can be used to record an individual’s computer usage, such as capturing images of the screen, recording the actual keystrokes used, or creating a summary of Web sites and programs accessed.
3. ______ _____ is the use of video cameras to monitor activities of individuals, such as employees or individuals in public locations, for work-related or crime-prevention purposes.
4. True or False. Electronic profiling is the act of using electronic means to collect a variety of in-depth information about an individual, such as name, address, income, and buying habits.
5. Unsolicited, bulk e-mail sent over the Internet is ____.
6. A device that protects a computer system from damage due to electrical fluctuations is ____.
7. True or False. Encryption can be used for privacy purposes, in addition to security purposes.
8. Color copying money is an example of ____.
9. True or False. Very few major U.S. companies monitor the online activities of their employees.
10. The rights of individuals and companies to control how information about them is collected and used is called __________.
Answers
1. Employee Monitoring 2. Computer Monitoring 3. Video Surveillance 4. True 5. spam 6. Surge suppressor 7. True 8. Filter 9. False 10. Information privacy
- ↑ http://www.consumerreports.org/cro/news/2013/06/with-1-6-million-smart-phones-stolen-last-year-efforts-under-way-to-stem-the-losses/index.htm
- ↑ http://www.android.com/
- ↑ http://www.allgov.com/usa/ca/news/top-stories/state-sues-sap-over-failed-payroll-system-in-yet-another-tech-failure-131122?news=851725
- ↑ http://adeona.cs.washington.edu/
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/S/surge_protector.html
- ↑ Security anchor/tether assemblage for portable articles: U.S. Patent 6,081,9746,317,936 and 6,360,405 (Cornelius McDaid, John Ristuccia, Kryptonite Corporation - priority date: 1999-06-21)
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/M/mobile_device_management.html
- ↑ http://www.air-watch.com/solutions/mobile-device-management
- ↑ http://www.maas360.com/products/mobile-device-management/
- ↑ https://www.apple.com/ipad/business/it/management.html
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_device_management
- ↑ Understanding Computers 14th Ed. by Deborah Morley & Charles Parker
- ↑ http://www.panasonic.com/business/toughbook/fully-rugged-laptop-toughbook-31.asp
- ↑ http://www.att.com/cellphones/samsung/galaxy-s-5-active.html#fbid=pGXpDqukON3
- ↑ http://www.pivotcase.com
- ↑ http://www.computerweekly.com/feature/Self-encrypting-drives-SED-the-best-kept-secret-in-hard-drive-encryption-security
- ↑ http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/S/software_piracy.html
- ↑ http://www.safenet-inc.com/software-monetization/software-protection/
- ↑ http://www.marketing-schools.org/types-of-marketing/database-marketing.html
- ↑ http://www.geek.com/mobile/automated-electronic-profiling-the-art-and-science-550246/
- ↑ http://www.ecommercetimes.com/story/73966.html
- ↑ https://epic.org/privacy/profiling/
- ↑ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/privacy-policy
- ↑ http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/privacy-policy.html
- ↑ http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/privacy-policy
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Privacy_policy
- ↑ http://www.techtimes.com/articles/20324/20141117/facebook-updates-privacy-policy-releases-basics-help-protect.htm
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Privacy_policy
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spam_(electronic)
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Database_marketing
- ↑ https://www.americanexpress.com/us/small-business/openforum/articles/7-ways-to-get-rid-of-spam-forever/
- ↑ http://www.infosec.gov.hk/english/computer/disposal.html
- ↑ http://monitoring-software-review.toptenreviews.com/
- ↑ http://www.scu.edu/ethics/publications/iie/v9n2/brother.html
- ↑ http://www.huizenga.nova.edu/Jame/articles/employee-monitoring.cfm
- ↑ http://www.cnn.com/2013/04/26/tech/innovation/security-cameras-boston-bombings/
- ↑ https://www.aclu.org/technology-and-liberty/whats-wrong-public-video-surveillance
- ↑ http://www.cio.com/article/2375438/physical-security/5-innovations-that-make-video-surveillance-more-effective.html
- ↑ http://searchunifiedcommunications.techtarget.com/definition/presence-technology
- ↑ http://www.newmoney.gov/currency/5.htm
- ↑ http://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/index.html?nbId=7345&nbNodeId=1013914#!&parentId=1013950
- ↑ http://it.ucmerced.edu/security/information-security-awareness-training/what-computer-security
- ↑ http://www.ftc.gov/reports/us-safe-web-act-first-three-years-federal-trade-commission-report-congress
- ↑ https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/108/hr395
- ↑ http://www.business.ftc.gov/documents/bus61-can-spam-act-compliance-guide-business
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAN-SPAM_Act_of_2003
- ↑ http://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_is_hardware_theft_and_vandalism
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Freeware
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disk_encryption
- ↑ http://www.computerweekly.com/feature/Self-encrypting-drives-Whats-holding-back-SED-hard-drive-encryption-security
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rugged_computer
- ↑ http://www.thefreedictionary.com/surge+suppressor
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uninterruptible_power_supply
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disaster_recovery_plan
- ↑ http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/The_Computer_Revolution/Digital_Counterfeiting
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Opt-out
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telepresence
Ethics
Intellectual Property Rights
[edit | edit source]
Intellectual Property Rights are the legal rights which creators are entitled to. Creators are the people who produced intellectual property which are creative works that they have originally made. With these rights, creators can choose what can legally be done to the work and other rules that need to be followed. There are a variety of original works that can have property rights. Some of these include written work, drawings, graphics, and many more. Having these rights are very important because it allows someone to claim their intellectual ideas as their own. There is a company called WIPO which are a self-funding agency that has copyrights, patents, trademarks, industrial designs, and also geographical indications used in e-commerce. This system is around because they recognize that creative works need to be protected by law and that they are around to support a creative environment. This company even has a magazine which displays the work that they have protected and boosts the work of creators worldwide. They also run workshops and have different forms of training to help innovators improve their skills and become familiar with new developments. The ability to have an agency support you and your work is a great step in the world of creativity, and keeping those intellectual property rights is what will continue to help creators flourish.[1]

Copyrights are there to protect individuals' work, such as literature, art and music. Enacted in 1976, Copyrights give the original creator rights over what they created. In the case where the creator dies, they still retain rights 70 years after their death. So let's say someone buys a C.D. of a certain artist. Even though it is now their property, the artist still holds rights over the songs. Often times with trying to prevent piracy, many things will have digital watermarks, a slight change to content that most cannot see but identifies the copyright holder. All of this is necessary due to complaints of infringement. These measures must be put in place to protect original work.

Trademarks are words, phrases, symbols, designs, or a combination of these that are used as an identifier in order to help consumers identify and distinguish one product/service from another one which might be similar. This is also referred to as their "logo". Trademarks are usually registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPO) and use the letter R enveloped in a circle next to the logo to signify this. Trademarks which are claimed but unregistered are allowed to use the print tm alongside their logo to represent that a claim has been made so as to deter others from using it. The purpose of a trademark is to protect the logo from being used by competitors who may want to "knock off" a more reputable company, though trademarks also protect domain names as well. Many companies want to set up a website using a domain name which matches their product so a consumer can instinctively find their web address, and a trademark will often safeguard against another company using it.[2]
Patents are similar to Copyrights and Trademarks but protect a person's invention rather than their literary accomplishments or company logos. Patents are usually granted for a 20 year period and legally authorize the sole rights of an individual to manufacture or produce that which s/he invented. Often it is a unique product but it can also be a unique process such as the Born-Haber Cycle. Having your item patented, you are given the right to ban others from selling, making, using or importing your item for this certain number of years.
Ethics
[edit | edit source]
The general definition of the word "ethics" defines the elements important to humans' morals. Ethics could be referred to as specific values, standards, rules, and agreements. For example, not being involved in software piracy is a matter of ethics. Computer ethics is a set of morals that regulate the use of computers. It is important for computer users to be aware of the ethical use of copyrighted material, the ethical use of resources and information, and the ethical use of school, company, and employee information. There are a set of rules called the "Ten Commandments of Computer Ethics" - which are rules that speak for themselves. These commandments are:
- Thou shalt not use a computer to harm other people.
- Thou shalt not interfere with other people's computer work.
- Thou shalt not snoop around in other people's computer files.
- Thou shalt not use a computer to steal.
- Thou shalt not use a computer to bear false witness.
- Thou shalt not copy or use proprietary software for which you have not paid (without permission).
- Thou shalt not use other people's computer resources without authorization or proper compensation.
- Thou shalt not appropriate other people's intellectual output.
- Thou shalt think about the social consequences of the program you are writing or the system you are designing.
- Thou shalt always use a computer in ways that ensure consideration and respect for your fellow humans [3]
The 10 ethical computer commandments are simple rules to abide by when using a computer.
[4] Common issues of computer ethics are the following: privacy concerns, how computers affect society, and intellectual property rights. It is a very common and easy practice to burn a CD or movie for a friend. However, a better option would be to tell the friend to buy the CD or movie as an ethical alternative. The privacy of another person is also an ethical issue of today. People's information is easily accessible through the computer; the ethical solution would be to not access another person's private information unless given permission. Ethics certainly guide our behavior, and it is the source of the acts we will and will not partake in.[5]

One ethical issue introduced by the increased prevalence of new technology is the rise in cheating among students using technology. As students have more technology, they naturally have more ways to cheat—ways that adult teachers who don't use all the new technology might not be aware of. 35% of students in one study admitted to cheating by using a phone. This can be done by storing notes on a phone and looking at it in class, texting someone outside of the class for an answer, and so on. A shockingly large number of teenagers seem to not even 'realize' that this is cheating; around or over 20% didn't think that it was. They're so used to having their cell phones attached to themselves as a part of their body that they don't realize that it actually isn't something they're supposed to be using at all times, and they saw no difference between screaming an answer across a class room and covertly texting it to a friend.[6] Young people need to be aware that cheating is still present in technology so they don't get in trouble for academic dishonesty. Faculty need to be aware of how students might be cheating using their phones, iPads, etc. to prevent it in the classroom.
History of Computer Ethics
[edit | edit source]
Computer ethics is a concept that is growing larger every day with new advanced technology. Computer ethics first came about in the 1970's as computers were becoming integrated into homes. Computers today are used at home, in schools, and in almost every company. This field has taken ethics to a whole new level, especially due to privacy issues found throughout various businesses. This form of ethics is also now offered as a course to study at many universities around the world. Computer ethics includes the various philosophical aspects of ethics, as well as psychological and sociological interpretations. When the field was first discovered in the 1970's, applied ethics was used to describe the new concept. Applied ethics consisted of a combination of utilitarianism, as well as Kant ethics. At the time there was much controversy to what computers would bring to society. Some thought that computers would create more ethical issues, whereas others thought it put a so-called "twist" on old ethics. In the 1980's the computer was thought to be the closest object to a universal tool available to individuals. In essence, the integration of the computer into every day society was not easy. The generation of the computer was new, as well as exciting. But nobody had used it before, including businesses and individuals. There would have to be some form of ethical guidelines to using these new products that nobody had much experience with. Nowadays, computer ethics covers a wide variety of topics such as computers in the workplace, computer crime, professional responsibility, and privacy and anonymity[7].
Ethical Use of Music
[edit | edit source]The sharing of music over the internet has continuously been a problem over the past few years and it is still a major problem today. The music controversy began with Napster, a peer-to-peer file sharing web application that was created to allow users to share music files via the internet. Napster originally started as a small web application for a few friends to share music on, but as the application grew in users, it began to strike the attention of the music industry. Some artists, specifically Metallica and Dr. Dre who filed a law suit against Napster, were outraged at the web application and in 2001, Napster finally closed due to the losing of a lawsuit against the Recording Industry Association of America. Napster and other peer-to-peer sharing websites that still exist today, such as The Pirate Bay, Mediafire, and Megaupload, are a large controversy because the copying of songs for non-commercial use is legal under the fair use concept,[8] however, downloading files from a peer-to-peer website without compensating the artist is a violation of copyright law under Digital Millennium Copyright Act.
There are several websites that can be used to convert YouTube videos to a MP3 format you can download to your computer. The most well known of these programs is called ClipConverter, but there are other programs. ClipConverter is a free online-based service that converts any online video to a MP4 or MP3, and then these files can be downloaded to your computer. There have been similar programs in the past, but these have been deactivated due to pressure from Google, the owner of YouTube[9]. ClipConverter converter continues to operate because of the guidelines and rules placed on users. Users are allowed to download the videos for fair use meaning personal, non-commercial use. Personal use of a video is legal, but if a user sells the video for profit, or passes it off as his/her own, that is a copyright violation, and illegal. As a condition of using the ClipConverter service, the user agrees to use the video only for personal use, and agrees to not involve ClipConverter in any type of copyright lawsuit brought against the user. It is this policy and other strict user rules and policies that allow ClipConverter to operate in a legal way.

To combat the infringement of copyright law due to illegal file sharing, the music industry began placing Digital Rights Management (DRM) control on downloaded files so that they couldn’t be shared. However, this also stopped users from being able to transfer the files to other personal devices. Today, many music downloading services, such as Apple’s iTunes, have switched to MP3 or MP4 formats to allow users to view files on multiple personal devices.
Film Piracy
[edit | edit source]
The illegal copying and distribution of movies and TV shows is called film piracy. The rate at which people commit film piracy has been growing exponentially since 2004. This is most likely due to the fact that online peer-to-peer file sharing has become a lot easier.[10] According to the Motion Picture Association of America (MPAA), film piracy causes an estimated loss of $18 billion dollars per year worldwide. This statistic is estimated because the MPAA has to determine how many people would have actually watched the film if it weren’t for free, or at a discounted price. Ever since 2004, authorities have been pushing to reduce film piracy. In 2005 the Family Entertainment and Copyright Act was put into place. This act makes recording a movie in a theatre illegal in the United States. Besides laws, there have also been things like visual FBI Anti-Piracy Warning Seal’s added to DVD’s. This seal is shown when the DVD is played, and before the actual movie starts. However, this doesn’t always effectively stop a pirate from stealing the movie.[11] There are many software programs used by authorities and private companies to prevent the illegal trade of pirated movies. This software is able to monitor websites that host peer-to-peer file trading. If a company’s film is being misused over the internet, the software is capable of sending infringement notices and collecting important data. All of this information could be used to build a court case against the violator.[12]
Computer Hoaxes and Digital Manipulation
[edit | edit source]
A computer hoax, or virus hoax, is an inaccurate statement or story spread through computers, typically through an email. Usually the email warns the user about a virus or worm and instructs the user to forward the message (which spreads the virus) or recommends that the receivers download an infected file attachment. These virus hoaxes can often be distinguished by their lofty and enticing wording or by claims that sound formal and authorized. These types of emails use people’s fear of the internet to manipulate their actions and thus spread a virus or computer hoax; many consider these fake emails to be worms in and of themselves because of this.[13]
Digital Manipulation is editing or altering any type of digital content. The most commonly thought of is photo-shop, which is editing an image so that it has little to no resemblance of the original image. This can be anything from adjusting the “exposure” on a photo or using an airbrush tool, to combing two photos to make one or adding portions that were not in the original (such as a large moon covering half the sky behind the Chicago skyline).[14] But digital manipulation also includes altering text, music, movies, or voice interviews. The main issue when it comes to ethics in digital manipulation is ensuring that copyrights are not violated and the original digital information is not misused or misinterpreted. Also, intentions and purpose are key in deciding “how far is too far” when it comes to photo-shop or other editing methods.[15]
Computers and Your Health
[edit | edit source]Physical Health
[edit | edit source]There are some physical problems that can be caused by computer use such as eyestrain, blurred vision, fatigue, headaches, backaches, and wrist and finger pain. One kind of health problem that occurs is repetitive stress injuries, which is when doing the same thing over and over causes hand, wrist, shoulder, or neck pain. Using the keyboard and the mouse can cause repetitive stress injuries. One repetitive stress injury that is related to repetitive finger movement is carpal tunnel syndrome, which is a painful condition of the hands and wrists.[16] Another repetitive stress injury is related with typing on the smaller keyboards of mobile devices and this is called DeQuervain’s tendonitis. There can also be many eye problems caused by looking at a computer screen for too long. Another concern is hearing loss because many portable media devices can be turned up too loud and cause hearing problems. There is also a concern with radiation that can be emitted from wireless devices. Dr. Josh Axe, DNM, DC, CNS is a certified doctor of natural medicine and of chiropractic manipulation and is a clinical nutritionist, who believes electromagnetic radiation (RMR) from cell phones is harmful to our bodies and our brains, resulting in cancers, tumors and dementia. He also believes we need further testing to discover just how dangerous cell phones (and other EMR-emitting devices) really are[17]. There are ways to avoid the physical health problems caused by computers. One way is to make sure that you are comfortable while at the computer and that you use a good chair that will be supportive for your back and neck. It is also important to just be aware of these possible physical health risks caused by computers because it is something that is often overlooked.[18] Of course, to avoid EMR you'll have to avoid using cell phones, which is highly unlikely to happen.

As mentioned before, most people today interact with some type of computer daily. We have learned that there are many risk factors associated with the extended use of computers. Some of those risk factors include eye strain, fatigue and upper and lower body discomfort. Luckily, there is a solution to these problems. It is called ergonomics. Ergonomics is a technology which focuses on making the work space as functional, safe and comfortable as possible. One thing computer users should consider when using the computer is wrist strain. It is important for the user to keep his wrists as straight as possible. Some causes for a bent wrist can be the keyboard being too low or high, or it being tilted upward. A solution to this can be to adjust the keyboard to the appropriate height or adjust the height of the chair. Another solution could be to use a split keyboard or what is known as an ergonomic keyboard. Another risk people face with extended use of the computer is back discomfort or even back disorder. This can be caused by an inadequate chair that lacks support for the back. It can also be caused by a lack of foot support or from slouching due to fatigue. Some solutions to these problems would be to use a lumbar cushion or to utilize a foot rest. It is also important for a user to take frequent breaks and change positions often. Many people today are exposed to extended computer use whether it is for a job or for entertainment. It is important for computer users to know the risks associated with over-usage and to be familiar with ergonomics in order to create the safest and most comfortable environment for themselves.[19]
Computers in Medicine
[edit | edit source]
In the same way that computers can be hazardous to one's long term health, they can also be used to monitor and, in-fact, encourage healthy habits. Sitting at a computer sedentary for hours on end day-in and day-out can lead to eyestrain, headaches, etc. as was previously discussed. However, in recent years, health and medicine have capitalized on the use of computers to further their industry. In hospitals and labs, CAT scans, X-rays, EEGs, EKGs, heart monitors, blood pressure and blood sugar scanners, and much more have been used to assess and monitor an individual's health. Certainly these additions to the medical field have made medicine a much more precise science and helped countless individuals who were suffering. However, computers have not only been used in reactive situations. They now can also help an individual be proactive about their health with the introduction of embedded computers, monitors, and biometrics. One example of this is the three-dimensional accelerometer (better known by the brand name "Fitbit"). These technologies allow the mechanism to gather data about the human body, interpret the data into usable information, and also store it in case a medical professional needs access to real-time health records. They can give an individual information about heartbeat/heart rate, sleep patterns, amount of physical activity, etc. and, in some cases, can even recommend that a person change certain behavior to combat unhealthy habits. [20]
Stress of Ever-Changing Technology
[edit | edit source]
Today we see many kinds of changes that are causing a great deal of stress and anxiety. Most of these changes are directly related to the digital revolution and have only become problems in the last 10 to 20 years.[21] Modern technology has infiltrated the workplaces, people’s cars and their homes. According to the Angus Reid, 14% of Canadian workers identified new technology in the workplace as a significant source of stress. Never before have individuals been asked to adapt as rapidly. Instant communication and exponentially growing technology lead us to one of the few absolute truths – technology change is constant. Technology has reconfigured the nature of work and our social relationships on the job.[22] People feel overwhelmed by the volume of emails and calls that they receive. Though people cannot stop this technology roller coaster, they can use a variety of practical strategies to develop resilience and renew and replenish themselves. Some of the simplest skills that the people can learn to be more resilient to stress are deep relaxation and self-care. It can convert fatigue into energy and restlessness into calmness.[23]
Emotional Health
[edit | edit source]
Because of our fast growth and use of technology there are many positive advantages of using computers; however, in recent years emotional health has become an important factor when using computers and technology. The use of computers in general can cause much stress and anxiety for workers in different fields today. When computers were first introduced to the working field, secretaries had to learn how to change from a typewriter to a keyboard. Many people now widely understand the use of computers, but the downfall is keeping up with the changing technology. Every few years a new system, computer design, etc. is updated and sent out to the market. This makes operating a company more difficult when programs and systems need to be updated. Because the Internet can be accessed 24/7 the stress of being “on-call” is worrisome to many workers. They worry they do not have enough down time for themselves once they come home from work that day. In the U.S. information is right at citizens’ fingertips, which can sometimes create an information overload. There is always news to be caught up on, as well as catching up with email, text messages, and social media. Many can become exhausted from being on the computer (or cell phone) too much. This is called burnout which is long-term exhaustion and diminished interest in work. A more common type of “emotional health” deals with teenagers who have a technology addiction. Social media plays a huge role in this today.
Internet Addiction
[edit | edit source]
The virtual world is similar to reality. People can play their chosen online roles, similar to the masks people put on everyday. At the same time the virtual world seems to have advantages over the real world. You can achieve success through creativity while concealing defects. Virtual reality (VR) gives individuals the opportunity to take on any role without having to take any of the responsibility and without fear of the consequences of rejection or condemnation. The person feels protected and inaccessible and can easily express their opinions, even if they are not able to do so in real life. The virtual world gives the illusion of protection from loneliness. At the same time it provides an opportunity to get away from communicating with real people, whose opinion would have to be considered. VR allows you to simulate reality by creating a state of endless possibilities. Surfing the Net gives the feeling of being in the "flow" and a disconnection from reality with a sense of being in another world, another time, another dimension. [24]
Many people today are addicted to the internet but do not know that they are. There are many signs of internet addiction. A good example is if they are always thinking about the internet. If a person is using the internet more and more in order to receive satisfaction, this could be a sign of addiction. If they feel restless or depressed because they're not on the internet, this too could be a tell-tale sign of internet addiction. Some tips on breaking this internet addiction are to understand that they have a problem with the internet. Next is to build coping skills. Many people become addicted to the internet because it is their outlet for stress and anger. Being able to change the way a person copes with their problems would be extremely beneficial. There is also therapy, counseling and support groups to take advantage of and help with this addiction.[25] It is important to be able to overcome an internet addiction to be able to fully appreciate life.
Cyberbullying
[edit | edit source]
According to stopcyberbullying.org, cyberbullying occurs when a minor is tormented, threatened, harassed, humiliated, embarrassed or otherwise targeted by another minor using the Internet. These acts can be committed through interactive and digital technologies, or mobile phones. To be considered a true cyberbullying incident, minors must be involved on both sides, or at least instigated by one in an attempt to harm, another. If and when adults become involved, it then becomes cyber-harassment or cyberstalking, and is wholly different from cyberbullying. For most, it is usually not a one time event, unless it is a legitimate threat of serious harm. Children are typically aware of the extent of danger or hurtful ideas, while parents may be more concerned about offensive language used. Ultimately, cyberbullying could lead to a misdemeanor charge, though if the child is young enough, juvenile delinquency is an option. Often, it does not go that far, yet many parents try to pursue criminal charges. If hacking, password breach, or identity theft is involved, it can be a crime of state and federal law. [26]
Technology Access
[edit | edit source]The U.S. Digital Divide
[edit | edit source]
Though the exact percentage is argued over by the experts, we can be happy to know that in the United States the Digital Divide continues to shrink. About 80% of the population of the United States uses the Internet. They use the Internet at school, work, home, and everywhere else. It's rare to find a McDonalds, one of the lowest common denominator eating establishments, that doesn't have a Wi-Fi connection. Computers and Internet access are always getting cheaper, which is great news because staying connected to the world is such an important quality. We stay alive and thrive through building relationships of all different kinds and the Internet is a powerful means of obtaining these relationships. Not only that, but most jobs today require the use of the Internet in one way or another. Due to the importance of the Internet, however, the percentage of Americans using the Internet should be closer to 99%. According to Forbes, there are several reasons why some people have never used the Internet or don't use it very often. The biggest percentage of them said they don't want or need to go online, because they're either too busy or because they think the Internet is a waste of time. A slightly smaller number of them said it is difficult or frustrating to go online, either because they don't understand or are physically unable.[27] Ultimately, the importance of the Internet is understood the world over, meaning that the digital divide in the U.S. will continue to shrink so our country can stay competitive with Europe and Asia especially.
Global Digital Divide
[edit | edit source]
The Global Digital Divide is an issue that our world seems to be facing more and more as time goes on. Like the US Digital divide, it is a comparison of groups of people with access to technology but on a global scale instead of a country scale. The problem arrises when one country's people has more access to technology and /or communications than another country. Most developed countries have a majority of their population with some access to technology, however it seems that many developing countries lack the technological accessibility that the others have. The largest problem caused by this is the lack of education. The internet today is such a source of information that one could potentially gain their entire college degree while hardly ever stepping foot in a classroom. Many people around the world lack the opportunity to gain an education because of their lack of access to the internet and other technology that would help them to learn things at a faster, easier, or more efficient rate. The internet has so many uses: school courses, communication, language tutoring, translations, calculations, and so many more.[28]
More on the Digital Divide
[edit | edit source]
The concept that is called the Digital Divide is the reality that technology, specifically computers and the Internet, is not available to all individuals. The digital divide is thought to be based on physical access to computers, Internet, and related technology. Some people consider the people that have access to computers and the Internet but do not understand how to use it are also part of the category of people that do not have true access to digital technology. One article explains that there are multiple dimensions to the digital divide. It claims the difference in not necessarily determined by the access to the Internet, but by access to ICT (Information and Communications Technologies) and to Media that the different segments of society can use. Other factors that should be considered are the quality of connection to the Internet and the cost of access to the Internet. Researchers also report that disadvantages can take such forms as lower-performance computers, lower-quality or high price connections, difficulty of obtaining technical assistance, and lower access to subscription-based contents.[29] The reason that the digital gap is a concern for society is that information and communication technologies are vital to quality civic life. One article explains that access to new technology splits clearly along socio-economic class lines. According to U.S. census data, more than 30 million homes have no broadband access, most of them concentrate in some of the poorest parts of the country. According to another survey 84% of the teachers surveyed felt that today’s digital gap is leading to greater disparities between affluent and disadvantaged schools.[30] Technology can inform people by creating mutual understanding about different cultures and societies; technology also plays a part in education and governmental reform. By lessening the digital gap economic equality, social mobility, and economic growth will be more readily available.
Assistive Technology
[edit | edit source]
The Americans with Disabilities Act requires companies with more than 15 employees to make reasonable accommodations for anyone that has known limitations. Nowadays, there is hardware and software specifically designed to aid individuals with physical disabilities. The most common technology that has been introduced is used to help those who are visually impaired or hard of hearing. There are various input devices available today to assist users communicate, usually on the computer.
- Braille or large-print keyboards
- One-handed keyboards
- Switches, eye tracking systems
- Pointing Devices
- Voice Input devices
In addition to the various input devices, there are output systems as well. The most common one is a screen reader that can read text information for the blind. There are also printers that can print in Braille instead of the conventional ink. Assistive technology is not always the best option, however. Often times it can be too expensive for the individual and not match their exact needs. [31] Devices should be researched and tried out before purchasing. Training for these devices also needs to be taken into consideration. For example, what if this technology stops working for the user?

So how do some of these assistive devices such as Braille keyboards, one-handed keyboards, eye tracking systems, pointing devices, and voice input devices work? First off, made up of raised dots that signify a “language,” and thus can be read by touch, Braille keyboards allow the visually impaired population to type and enter any text for the computer in Braille. Secondly, to assist people with limited movement of only one hand, each of the one-handed keyboard’s key contains two letters (accommodating both the left and right side keys on a conventional keyboard), making it easier for all keys to be reached with just one hand. They also provide with the ability to input data to the computer hands-free through speech recognition systems. To act as mouse alternatives, many other pointing devices like foot-controlled mice (controlled solely by the feet), head pointing systems (directed using simple head movements), and eye tracking systems (tracking the movement of the eye) are commonly used. To add on to all these types of outstanding assistive technology, there is also another alternative input system known as “sip-and-puff” system, which is activated by one’s inhaling or exhaling! [32]
Next, once the data has been input into the computer using any of these assistive input devices, assistive output devices come into play. These devices include screen readers, which read aloud all the text information on the screen; Braille displays act similar to Braille keyboards as they continuously convert screen output into Braille form. Lastly, there are also Braille printers—sometimes known as Braille embossers—which transfer and print computer generated text into embossed Braille output. Therefore, instead of the traditional ink, the embosser creates raised dots on a page for the visually impaired to read.[33]
Assistive Technology in the Classroom
[edit | edit source]
Assistive technology can be especially helpful in the education setting. Thanks in large part to the mainstreaming and inclusion efforts in schools today, students of every ability are integrated into traditional classrooms. This integration can be greatly aided by the use of assistive technology. [34] Assistive Technology allows students with disabilities to learn and complete lessons more independently. Educators can use a variety of tools to help all types of students. Screen readers can be used to read text to visually impaired students. There are many programs available (some are even free) that can be used to read documents aloud to students. This can be helpful for both visually impaired students, as well as students that are cognitively impaired and unable to read. Close captioning and subtitling help students that are hearing impaired. Eye tracking systems as well as sip and puff systems are especially helpful for students with mobility impairments. Voice recognition software can also provide a way for students to write more efficiently without the use of a keyboard. Adding these technological advancements to the classroom allows students to participate in lessons and activities that would not otherwise be available to them.
Environmental Issues
[edit | edit source]
Green Computing
[edit | edit source]Green computing is the study of designing, engineering, and manufacturing using and disposing of computing devices in a way that reduces their environmental impact. [35]This refers to the use of computers in an environmentally friendly manner, but computing is not currently as environmental friendly. According to the guide to greener electronics only 2 out of 18 of the PC are considered on the green rating. The reason is because companies are subjected to make energy and hence cost saving in the face of rising electricity prices. One of the activates that could help environmental savings is existing hardware which can be in place of it there are software’s called LittleGreenGenie. This software permit certain individuals to measure reduce and carbon offset from computer use. Its stats that it takes about 1.8 tons of chemicals, fossil fuels and water to produce a typical desktop computer and there’s about one billion PCs sold. Although putting a computer on standby or sleep mode will save a lot of power, people are unaware that shutting down a computer doesn't completely turn it off because the computer power supply will remain physically switched on. This leads the motherboard still partially on waiting for a signal to boot up again. The following are certain tasks that can be beneficial in reducing energy consumption which are lower power hard drive, visualization, cloud computing, energy effecting coding, improved repair, re-use recycling and disposable and less pollutant manufacture.[36][37] The only true, current, disadvantage to green computing are underpowered devices and costs.
Solar Power
[edit | edit source]
Instead of reducing energy consumption and electricity costs, another option is to use solar power. Solar power is the conversion of sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic cells. These cells can be packaged into a frame, and a frame into an array, based on how much solar power is needed for the building or area. The process has slowly become cheaper due to our increase in technology and knowledge of solar power. As of right now, we are considered to be in our third generation of solar power because of our use of new materials like nanotubes, silicon wires, and solar inks. This is a step up from the first generation, which used solely silicon as a material, and then the second generation, which used thin-film solar panels. As the capability of solar power becomes cheaper, more products are incorporating solar power as a power source. Examples of this are the solar powered phone charger and solar powered calculator. Solar powered calculators have been around for a while because calculators do not require much energy, so the solar panel is very small and therefore cheap. The solar powered charger has come out more recently because the newer flexible technology made it feasible to produce. Solar power has been a greener way to consume energy.[38]
Recycling of Computers and Other Electronics
[edit | edit source]Given the reliance of the commercial world on computer technology it is easy to overlook the inherent unsustainability of computer production. Computers have become embedded in contemporary culture and play a crucial role in the global economy, but as the industrialized world continues to degrade the environment one must become aware of the negative impacts of computer use and consequently work with possible ways to reduce them. The Chicago Recycling Coalition states that, on average, 240 kg of fossil fuels are consumed in the process of producing a desktop PC.[39] In a time when fossil fuel supplies are decreasing at an alarming rate it is important now more than ever to be conscious of consumer decisions. The issue of fossil fuels aside, computers contain arsenic and mercury while computer monitors can contain several pounds of lead. This is one reason why simply disposing computers into landfills is problematic. Instead, the Chicago Recycling Coalition advises consumers to donate computers to various organizations and charities, give older computers to family and friends who need them, and find locations that offer recycling services. The EPA provides a utility that helps consumers and manufacturers know where they can donate or recycle their electronics.[40] Mobile devices, PCs and TVs make up the “Electronic Devices” category, and after selecting a device one can choose a company to see what services are offered.

Before recycling your computers you may want to do a few things. In order to protect your information and privacy, you should wipe out your hard drive. However, just deleting files is not enough. Cyber criminals are very capable people and they will find a way to find information on your hard drive that you “deleted” the information. There are programs on the internet that you can use to “sanitize” your hard drive. An even easier way is to just remove the hard drive altogether. Other ways to recycle your devices is to donate them. You could even help your community out by having a fundraiser to collect everyone’s technological garbage and then you can donate them. This not only helps the community but also the environment. Now if you’re not looking to get rid of your entire computer you do have a printer. You will always come to the problem of running out of ink. Instead of throwing out these old cartridges, you could just have them refilled. Not only is this good for the environment, but it can also help you save money because refilling ink cartridges is worth a fraction of the cost of buying new ones.[41]
E-Waste
[edit | edit source]
E-trash, or e-waste, is a growing problem in modern society. The issue of dealing with the huge amounts of electronics that are being outdated and thrown away asks the question; what do we do with all this junk? Although e-waste only makes up about 2% of America’s trash in landfills, it comprises 70% of the country’s toxic waste. A lot of this toxicity is because of the huge amounts of lead that can be found in electronics. Between 20 and 50 million metric tons of e-waste is disposed of every year, but only about 12.5% of e-waste is actually recycled properly. It is important to recycle e-waste not just to protect the environment but also to harvest the high amounts of precious metals within the electronics. Just in cell phones alone, over $60 million in gold and silver is dumped ever year.[42] Electronics can be taken to recyclers for support. There are many non-profit groups that offer recycling of old devices. There are also drop-off locations throughout the US that allow you to dispose of devices and batteries. A lot of “e-waste” is actually not waste at all, and can be recycled and reused if dealt with properly. E-waste is unfortunately shipped to developing countries illegally, which is not a responsible or ethical way of managing the waste.[43] In order to ensure that your e-waste is properly recycled you should find a recycling center near you. You can use this website http://search.earth911.com to find a local center and learn how to properly dispose of your electronic waste! [44]
Family Entertainment and Copyright Act of 2005
[edit | edit source]There’s no question that copyright laws are pushed to the side when it comes to copying illegal things such as movies, music, and videos. People act as if there is nothing to risk, and it does not matter if you break the law. However, the Family Entertainment and Copyright Act, which was passed in 2005, made these offenses just a little bit more serious. The law worked to make three offenses more defined and punishable than they were before. First, it made sure that no one was allowed to bring a camcorder into a movie and record it. This works to stop people from selling movies that they do not have legal copyrights to. Second, it worked to make sure that there was no illegal prerelease of movies that had not yet been released to the public. The act actually states that this offense is punishable by a large fine or even time in jail. Finally, it allowed certain technology to be installed into DVD players that permits the user to automatically skip or mute entire portions of a DVD, allowing them to get passed crude, violent, or inappropriate parts that they would not have wanted to watch. Basically, the law just worked to reinforce previous copyright laws that seemed to be pushed aside without users giving them any consideration.[45]
Other Related Legislation
[edit | edit source]
The Family Entertainment and Copyright Act of 2005 is just one example of the several laws surrounding intellectual property rights. The U.S. Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act of 1999 makes domain name cybersquatting illegal. This law was targeted at "cybersquatters" who register internet domain names containing trademarks with no intention of creating a legitimate website, but instead plan to sell the domain name to the trademark owner or a third party. For example, if a new trademarked company by the name of Shmauffle wanted to create a website called www.shmauffle.com, a person who bought the domain name, and is doing nothing with it, has to give it up to Schmauffle. Another major law is the Digital Millennium Copyright Act(DMCA), which makes it illegal to circumvent antipiracy measures built into digital media and devices. Other laws, such as ones to increase penalties for illegally sharing music via internet, are proposed on a regular basis. Legislation regarding ethics has proven to be much more difficult to pass. For example, laws surrounding the distribution of indecent or offensive material online can be declared unconstitutional based the right to free speech. As a result, very few ethically oriented laws have been passed in recent years.
Review
[edit | edit source]Terms and Definitions [46]
assistive technology Hardware and software specifically designed for use by individuals with physical disabilities.
burnout A state of fatigue or frustration usually brought on by overwork.
business ethics Standards of moral conduct that guide a business’s policies, decisions, and actions.
carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) A painful and crippling condition affecting the hands and wrist that can be caused by computer use.
code of conduct A policy, often for a school or business, that specifies allowable use of resources, such as computers and other equipment.
code of ethics A policy, often for an organization or industry, that specifies overall moral guidelines adopted by that organization or industry.
computer ethics Standards of moral conduct as they relate to computer use.
computer hoax An inaccurate statement or story spread through the use of computers.
copyright The legal right to sell, publish, or distribute an original artistic or literary work; it is held by the creator of a work as soon as it exists in physical form.
cybersquatting The act of registering a domain name with the intent to profit from the goodwill of a trademark belonging to someone else.
DeQuervain’s tendonitis A condition in which the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist are swollen and irritated.
digital divide The gap between those who have access to technology and those who do not.
digital manipulation The alteration of digital content, usually text or photographs.
digital rights management (DRM) software Software used to protect and manage the rights of creators of digital content, such as art, music, photographs, and movies.
digital watermark A subtle alteration of digital content that is not noticeable when the work is viewed or played but that identifies the copyright holder.
docking station A device designed to easily connect a portable computer to conventional hardware, such as a keyboard, mouse, monitor, and printer.
eco-label A certification, usually by a government agency, that identifies a device as meeting minimal environmental performance specifications.
ENERGY STAR A program developed by the U.S. Department of Energy and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to encourage the development of energy-saving devices.
ergonomic hardware Hardware, typically an input or output device, that is designed to be more ergonomically correct than its nonergonomic counterpart.
ergonomics The science of fitting a work environment to the people who work there.
ethics Overall standards of moral conduct.
etrash Electronic trash or waste, such as discarded computer components.
green computing The use of computers in an environmentally friendly manner.
intellectual property rights The legal rights to which creators of original creative works (such as artistic or literary works, inventions, corporate logos, and more) are entitled.
Internet addiction The problem of overusing, or being unable to stop using, the Internet.
notebook stand A device that elevates the display of a notebook or tablet computer to a better viewing height; can contain USB ports to connect additional hardware.
patent A form of protection for an invention that can be granted by the government; gives exclusive rights of an invention to its inventor for 20 years.
plagiarism' Presenting someone else’s work as your own.
repetitive stress injury (RSI) A type of injury, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, that is caused by performing the same physical movements over and over again.
trademark A word, phrase, symbol, or design that identifies goods or services.
Questions
True or False
1. All unethical acts are illegal.
2. Changing the background behind a television newscaster to make it appear that he or she is reporting on location instead of from inside the television studio would be an example of digital manipulation.
3. Carpal tunnel syndrome can be caused by using a computer keyboard.
4. As computer use has become more common, the potential for stress related to computer use has decreased.
5. Assistive technology is hardware and software designed to help all beginning computer users learn how to use a computer.
6. A software program would be protected by _____, while a corporate logo would be protected by _____ law.
7. Turning in a copy of a poem you found on a Web site as your original composition for a poetry class assignment is an example of _____.
8. Registering the domain name microsft.com to profit from it would be an act of _____.
9. The _____ can be used to describe discrepancies in access to technology by individuals within a country, as well as to compare access from country to country.
10. Match each term to its description or example, and write the corresponding number in the blank to the left of each description or example.
A. What the symbol © stands for.
B. Can vary from another's depending on his or her values, culture, and so forth.
C. A warning about a nonexistent virus spread via e-mail.
D. A subtle alteration of digital content that identifies the copyright holder.
i. Computer hoax
ii. Copyright
iii. Digital watermark
iv. Ethics
11. Hardware and software specifically designed for use by individuals with physical disabilities is called _____.
Answers [47]
1. False
2. True
3. True
4. False
5. False
6. copyright; trademark
7. plagiarism
8. cybersquatting
9. digital divide
10. A. ii. B. iv. C. i. D. iii.
11. Assistive Technology
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ http://www.wipo.int/about-ip/en
- ↑ http://www.wipo.int/trademarks/en/trademarks.html
- ↑ http://www.computerethicsinstitute.org/images/TheTenCommandmentsOfComputerEthics.pdf
- ↑ http://www.ethicalsociety.org/article/19/about-wes/ethical-culture-our-religious-heritage/faqs-about-ethical-culture/what-does-ethics-mean
- ↑ http://www.techterms.com/definition/computerethics
- ↑ http://www.ikeepsafe.org/cheating-technology/
- ↑ http://stanford.library.usyd.edu.au/archives/spr2006/entries/ethics-computer/
- ↑ http://www.dartmouth.edu/copyright/peer2peer/
- ↑ http://www.real.com/resources/youtube-to-mp3-converter/
- ↑ http://www.storyofmovies.org/common/11041/pdfs/film_piracy_teachers_guide.pdf
- ↑ http://www.forbes.com/sites/karstenstrauss/2013/03/06/tv-and-film-piracy-threatening-an-industry/
- ↑ Understanding Computers 14th Ed. by Deborah Morley & Charles Parker
- ↑ http://www.techopedia.com/definition/1678/virus-hoax
- ↑ http://www.astropix.com/HTML/J_DIGIT/ETHICS.HTM
- ↑ http://www.lightstalking.com/what-are-the-ethics-of-digital-manipulation-in-photography/
- ↑ http://sitemaker.umich.edu/state436/files/Physical_Issues.htm
- ↑ https://draxe.com/electromagnetic-radiation/
- ↑ http://www.safety.uwa.edu.au/health-wellbeing/physical/ergonomics/workstation#chairs
- ↑ http://www.apple.com/about/ergonomics/
- ↑ Jhonsa, Eric (May 7, 2015). "Fitbit files for IPO, reports strong growth/profits". Retrieved May 10, 2015.
- ↑ http://www.ucg.org/entertainment/how-can-we-cope-world-rapid-change/
- ↑ http://worksmartlivesmart.com/future-shock-stress-strategies-technology/
- ↑ https://georgeinstitute.wordpress.com/2013/09/27/dealing-with-stress-in-our-fast-paced-ever-changing-world/
- ↑ http://www.apa.org/monitor/apr00/addiction.aspx
- ↑ http://www.helpguide.org/articles/addiction/internet-and-computer-addiction.htm
- ↑ //http://stopcyberbullying.org/what_is_cyberbullying_exactly.html
- ↑ http://www.forbes.com/sites/kenrapoza/2013/10/14/why-15-of-americans-dont-use-the-internet/
- ↑ http://iml.jou.ufl.edu/projects/STUDENTS/Lui/index3.htm
- ↑ http://www.internetworldstats.com/links10.htm
- ↑ http://hechingerreport.org/content/technology-skills-scratch-surface-digital-divide_18096/
- ↑ http://www.pluk.org/Pubs/PLUK_ATguide_269K.pdf
- ↑ http://www.microsoft.com/enable/at/types.aspx
- ↑ http://www.humanware.com/en-usa/products/blindness/braille_embossers_and_writers
- ↑ http://www.readingrockets.org/article/assistive-technology-kids-learning-disabilities-overview
- ↑ https://www.techopedia.com/definition/14753/green-computing
- ↑ http://www.explainingcomputers.com/green.html
- ↑ http://www.greenpeace.org/international/en/publications/reports/Guide-to-Greener-Electronics-15th-edition/
- ↑ http://www.solar-facts-and-advice.com/solar-cells.html
- ↑ http://www.chicagorecycling.org/computers.htm
- ↑ http://www.epa.gov/osw/conserve/materials/ecycling/donate.htm
- ↑ http://www.carnegiecyberacademy.com/facultyPages/environment/issues.html
- ↑ https://www.dosomething.org/facts/11-facts-about-e-waste
- ↑ http://www.greenpeace.org/international/en/campaigns/toxics/electronics/the-e-waste-problem/where-does-e-waste-end-up/
- ↑ http://search.earth911.com
- ↑ https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2005/04/family-entertainment-and-copyright-act-passes
- ↑ http://coursemate.cengage.com/CPReader/View/9781133114598/default.aspx?eISBN=9781133114598#3ebb2c54-e38b-4716-ad74-68b62c24cc60
- ↑ http://ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/index.html?nbId=7345&nbNodeId=1013914#!&parentId=1013951