Mathematics for Chemistry/Print version
| This is the print version of Mathematics for Chemistry You won't see this message or any elements not part of the book's content when you print or preview this page. |
Table of contents
[edit | edit source]- Introduction
- Number theory
- Functions
- Units and dimensions
- Statistics
- Plotting graphs
- Complex numbers
- Trigonometry
- Vectors
- Matrices and determinants
- Differentiation
- Integration
- Some useful aspects of calculus
- Enzyme kinetics
- Some mathematical examples applied to chemistry
- Tests and exams
- Further reading
Introduction
[edit | edit source]- This book was initially derived from a set of notes used in a university chemistry course. It is hoped it will evolve into something useful and develop a set of open access problems as well as pedagogical material.
For many universities the days when admission to a Chemistry, Chemical Engineering, Materials Science or even Physics course could require the equivalent of A-levels in Chemistry, Physics and Mathematics are probably over for ever. The broadening out of school curricula has had several effects, including student entry with a more diverse educational background and has also resulted in the subject areas Chemistry, Physics and Mathematics becoming disjoint so that there is no co-requisite material between them. This means that, for instance, physics cannot have any advanced, or even any very significant mathematics in it. This is to allow the subject to be studied without any of the maths which might be first studied by the A-level maths group at the ages of 17 and 18. Thus physics at school has become considerably more descriptive and visual than it was 20 years ago. The same applies to a lesser extent to chemistry.
This means there must be an essentially remedial component of university chemistry to teach just the Mathematics and Physics which is needed and not too much, if any more, as it is time consuming and perhaps not what the student of Chemistry is most focused on. There is therefore also a need for a book Physics for Chemistry.
Quantitative methods in chemistry
[edit | edit source]There are several reasons why numerical (quantitative) methods are useful in chemistry:
- Chemists need numerical information concerning reactions, such as how much of a substance is consumed, how long does this take, how likely is the reaction to take place.
- Chemists work with a variety of different units, with wildly different ranges, which one must be able to use and convert with ease.
- Measurements taken during experiments are not perfect, so evaluation and combination of errors is required.
- Predictions are often desired, and relationships represented as equations are manipulated and evaluated in order to obtain information.
Numbers
[edit | edit source]- ==Numbers==
Real numbers come in several varieties and forms;
- Natural numbers are integers that are greater than or equal to zero.
- Integers are whole numbers used for counting indivisible objects, together with negative equivalents and zero, e.g. 42, -7, 0
- Rational numbers can always be expressed as fractions, e.g. 4.673 = 4673/1000.
- Irrational numbers, unlike rational numbers, cannot be expressed as a fraction or as a definite decimal, e.g. and
It is also worth noting that the imaginary unit and therefore complex numbers are used in chemistry, especially when dealing with equations concerning waves.
Surds
[edit | edit source]The origin of surds goes back to the Greek philosophers. It is relatively simple to prove that the square root of 2 cannot be a ratio of two integers, no matter how large the integers may become. In a rather Pythonesque incident the inventor of this proof was put to death for heresy by the other philosophers because they could not believe such a pure number as the root of 2 could have this impure property.
(The original use of quadratic equations is very old, Babylon many centuries BC.) This was to allocate land to farmers in the same quantity as traditionally held after the great floods on the Tigris and Euphrates had reshaped the fields. The mathematical technology became used for the same purpose in the Nile delta.
When you do trigonometry later you will see that surds are in the trigonometric functions of the important symmetrical angles, e.g. and so they appear frequently in mathematical expressions regarding 3 dimensional space.
Notation
[edit | edit source]The notation used for recording numbers in chemistry is the same as for other scientific disciplines, and appropriately called scientific notation, or standard form. It is a way of writing both very large and very small numbers in a shortened form compared to decimal notation. An example of a number written in scientific notation is
with being a coefficient termed the significand or the mantissa, and being an integer exponent. When written in decimal notation, the number becomes
.
Numbers written in scientific notation are usually normalised, such that only one digit precedes the decimal point. This is to make order of magnitude comparisons easier, by simply comparing the exponents of two numbers written in scientific notation, but also to minimise transcription errors, as the decimal point has an assumed position after the first digit. In computing and on calculators, it is common for the ("times ten to the power of") to be replaced with "E" (capital e). It is important not to confuse this "E" with the mathematical constant e.
Engineering notation is a special restriction of scientific notation where the exponent must be divisible by three. Therefore, engineering notation is not normalised, but can easily use SI prefixes for magnitude.
Remember that in SI, numbers do not have commas between the thousands, instead there are spaces, e.g. , (an integer) or . Commas are used as decimal points in many countries.
Exponents
[edit | edit source]| This section is a stub. You can help Wikibooks by expanding it. |
Consider a number , where is the base and is the exponent. This is generally read as “ to the ” or “ to the power of ”. If then it is common to say “ squared”, and if then “ cubed”. Comparing powers (exponentiation) to multiplication for positive integer values of n , it can be demonstrated that
, i.e. four lots of added together
, i.e. multiplied by itself four times.
For , the result is simply . For the result is .
can be reduced to multiplication like this if is an integer:
Order of operations
[edit | edit source]When an expression contains different operations, they must be evaluated in a certain order. Exponents are evaluated first. Then, multiplication and division are evaluated from left to right. Last, addition and subtraction are evaluated left to right. Parentheses or brackets take precedence over all operations. Anything within parentheses must be calculated first. A common acronym used to remember the order of operations is PEMDAS, for "Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, Subtraction". Another way to remember this acronym is "Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally".
Keep in mind that negation is usually considered multiplication. So in the case of , the exponent would be evaluated first, then negated, resulting in a negative number.
Take note of this example:
If evaluated incorrectly (left-to-right, with no order of operations), the result would be 16. Three plus five gives eight, times two is 16. The correct answer should be 13. Five times two gives ten, plus three gives 13. This is because multiplication is solved before addition.
Partial fractions
[edit | edit source]Partial fractions are used in a few derivations in thermodynamics and they are good for practicing algebra and factorisation.
It is possible to express quotients in more than one way. Of practical use is that they can be collected into one term or generated as several terms by the method of partial fractions. Integration of a complex single term quotient is often difficult, whereas by splitting it up into a sum, a sum of standard integrals is obtained. This is the principal chemical application of partial fractions.
An example is
In the above must equal since the denominators are equal. So we set first to +1 giving . Therefore B = -1/2. If we set instead , therefore . So
We can reverse this process by use of a common denominator.
The numerator is , so it becomes
which is what we started from.
So we can generate a single term by multiplying by the denominators to create a common denominator and then add up the numerator to simplify. A typical application might be to convert a term to partial fractions, do some calculus on the terms, and then regather into one quotient for display purposes. In a factorised single quotient it will be easier to see where numerators go to zero, giving solutions to , and where denominators go to zero giving infinities.
A typical example of a meaningful infinity in chemistry might be an expression such as
The variable is the energy E, so this function is small everywhere, except near . Near a resonance occurs and the expression becomes infinite when the two energies are precisely the same. A molecule which can be electronically excited by light has several of these resonances.
Here is another example. If we had to integrate the following expression we would first convert to partial fractions:
so
let then
let then
therefore the expression becomes
Later you will learn that these expressions integrate to give simple expressions in terms of the natural logarithm.
Problems
[edit | edit source]
Answers
[edit | edit source]
Polynomial division
[edit | edit source]This is related to partial fractions in that its principal use is to facilitate integration.
Divide out
like this
3x - 7
-----------------
x + 1 ) 3x2 -4x -6
3x2 +3x
---------
0 -7x -6
-7x -7
--------
1
So our equation becomes
This can be easily differentiated, and integrated. If this is differentiated with the quotient formula it is considerably harder to reduce to the same form. The same procedure can be applied to partial fractions.
Substitutions and expansions
[edit | edit source]You can see the value of changing the variable by simplifying
to
where
This is an example of simplification. It would actually be possible to differentiate this with respect to either or using only the techniques you have been shown. The algebraic manipulation involves differentiation of a quotient and the chain rule.
Evaluating gives
Expanding this out to the s and s would look ridiculous.
Substitutions like this are continually made for the purpose of having new, simpler expressions, to which the rules of calculus or identities are applied.
Functions
[edit | edit source]
A reader has identified this chapter as an undeveloped draft or outline.
You can help to develop the work, or you can ask for assistance in the project room.Functions as tools in chemistry
[edit | edit source]The quadratic formula
[edit | edit source]In order to find the solutions to the general form of a quadratic equation,
there is a formula
(Notice the line over the square root has the same priority as a bracket. Of course we all know by now that is not equal to but errors of priority are among the most common algebra errors in practice).
There is a formula for a cubic equation but it is rather complicated and unlikely to be required for undergraduate-level study of chemistry. Cubic and higher equations occur often in chemistry, but if they do not factorise they are usually solved by computer.
Solve:
Notice the scope or range of the bracket.
Notice here that the variable is a concentration, not the ubiquitous .
Units and dimensions
[edit | edit source]- ==Units, multipliers and prefixes==
It is usually necessary in chemistry to be familiar with at least three systems of units, Le Système International d'Unités (SI), atomic units as used in theoretical calculations and the unit system used by the experimentalists. Thus if we are dealing with the ionization energy, the units involved will be the Joule (J), the Hartree (Eh, the atomic unit of energy), and the electron volt (eV).
These units all have their own advantages;
- The SI unit should be understood by all scientists regardless of their field.
- The atomic unit system is the natural unit for theory as most of the fundamental constants are unity and equations can be cast in dimensionless forms.
- The electron volt comes from the operation of the ionization apparatus where individual electrons are accelerated between plates which have a potential difference in Volts.
An advantage of the SI system is that the dimensionality of each term is made clear as the fundamental constants have structure. This is a complicated way of saying that if you know the dimensionality of all the things you are working with you know an awful lot about the mathematics and properties such as scaling with size of your system. Also, the same system of units can describe both the output of a large power station (gigaJoules), or the interaction of two inert gas atoms, (a few kJ per mole or a very small number of Joules per molecule when it has been divided by Avogadro's number).
In SI the symbols for units are lower case unless derived from a person's name, e.g. ampere is A and kelvin is K.
SI base units Name Symbol Quantity metre m length kilogram kg mass second s time ampere A electric current kelvin K thermodynamic temperature candela cd luminous intensity mole mol amount of substance Derived units used in chemistry Quantity Unit Name Symbol Area m2 Volume m3 Velocity m s-1 Acceleration m s-2 Density kg m-3 Entropy J mol-1 K-1 Force kg m s-2 newton N Energy N m joule J Pressure N m-2 pascal Pa Frequency s-1 hertz Hz Approved prefixes for SI units Prefix Factor Symbol atto 10-18 a femto 10-15 f pico 10-12 p nano 10-9 n micro 10-6 μ milli 10-3 m centi 10-2 c deci 10-1 d kilo 103 k mega 106 M giga 109 G tera 1012 T peta 1015 P exa 1018 E Note the use of capitals and lower case and the increment on the exponent being factors of 3. Notice also centi and deci are supposed to disappear with time leaving only the powers of 1000.
Conversion factors
[edit | edit source]The , (sometimes call caret or hat), sign is another notation for to the power of. E means times 10 to the power of, and is used a great deal in computer program output.
Energy
[edit | edit source]An approximation of how much of a chemical bond each energy corresponds to is placed next to each one. This indicates that light of energy 4 eV can break chemical bonds and possibly be dangerous to life, whereas infrared radiation of a few cm-1 is harmless.
- 1 eV = 96.48530891 kJ mol-1 (Near infrared), approximately 0.26 chemical bonds
- 1 kcal mol-1 = 4.184000000 kJ mol-1 (Near infrared), approximately 0.01 chemical bonds
- 1 MHz = 0.399031E-06 kJ mol-1 (Radio waves), approximately 0.00 chemical bonds
- 1 cm-1 = 0.01196265819 kJ mol-1 (Far infrared), approximately 0.00 chemical bonds
Wavelength, generally measure in nanometres and used in UV spectroscopy is defined as an inverse and so has a reciprocal relationship.
Length
[edit | edit source]There is the metre, the Angstrom (10-10 m), the micron (10-6 m), the astronomical unit (AU)and many old units such as feet, inches and light years.
Angles
[edit | edit source]The radian to degree conversion is 57.2957795130824, (i.e. a little bit less than 60, remember your equilateral triangle and radian sector).
Dipole moment
[edit | edit source]1 Debye = 3.335640035 Cm x 10-30 (coulomb metre)
Magnetic Susceptibility
[edit | edit source]1 cm3 mol-1 = 16.60540984 JT-2 x 1030 (joule tesla2)
Old units
[edit | edit source]Occasionally, knowledge of older units may be required. Imperial units, or convert energies from BTUs in a thermodynamics project, etc.
In university laboratory classes you would probably be given material on the Quantity Calculus notation and methodology which is to be highly recommended for scientific work.
A good reference for units, quantity calculus and SI is: I. Mills, T. Cuitas, K. Homann, N. Kallay, K. Kuchitsu, Quantities, units and symbols in physical chemistry, 2nd edition, (Oxford:Blackwell Scientific Publications,1993).
Greek alphabet
[edit | edit source]
This section is a stub.
You can help Wikibooks by expanding it.Unit labels
[edit | edit source]The labelling of tables and axes of graphs should be done so that the numbers are dimensionless, e.g. temperature is ,
and energy mol / kJ etc.
This can look a little strange at first. Examine good text books like Atkins Physical Chemistry which follow SI carefully to see this in action.
The hardest thing with conversion factors is to get them the right way round. A common error is to divide when you should be multiplying, also another common error is to fail to raise a conversion factor to a power.
1 eV = 96.48530891 kJ mol-1
1 cm-1 = 0.01196265819 kJ mol-1
To convert eV to cm-1, first convert to kJ per mole by multiplying by 96.48530891 / 1. Then convert to cm-1 by multiplying by 1 / 0.01196265819 giving 8065.540901. If we tried to go directly to the conversion factor in 1 step it is easy to get it upside down. However, common sense tell us that there are a lot of cm-1s in an eV so it should be obviously wrong.
1 inch = 2.54 centimetres. If there is a surface of nickel electrode of 2 * 1.5 square inches it must be 2 * 1.5 * 2.542 square centimetres.
To convert to square metres, the SI unit we must divide this by 100 * 100 not just 100.
Dimensional analysis
[edit | edit source]
This section is a stub.
You can help Wikibooks by expanding it.The technique of adding unit labels to numbers is especially useful, in that analysis of the units in an equation can be used to double-check the answer.
An aside on scaling
[edit | edit source]One of the reasons powers of variables are so important is because they relate to the way quantities scale. Physicists in particular are interested in the way variables scale in the limit of very large values. Take cooking the turkey for Christmas dinner. The amount of turkey you can afford is linear, (power 1), in your income. The size of an individual serving is quadratic, (power 2), in the radius of the plates being used. The cooking time will be something like cubic in the diameter of the turkey as it can be presumed to be linear in the mass.
(In the limit of a very large turkey, say one the diameter of the earth being heated up by a nearby star, the internal conductivity of the turkey would limit the cooking time and the time taken would be exponential. No power can go faster / steeper than exponential in the limit. The series expansion of goes on forever even though gets very small.)
Another example of this is why dinosaurs had fatter legs than modern lizards. If dinosaurs had legs in proportion to small lizards the mass to be supported rises as length to the power 3 but the strength of the legs only rises as the area of the cross section, power 2. Therefore the bigger the animal the more enormous the legs must become, which is why a rhino is a very chunky looking version of a pig.
There is a very good article on this in Cooper, Necia Grant; West, Geoffrey B., Particle Physics: A Los Alamos Primer, ISBN 0521347807
Making tables
[edit | edit source]Statistics
[edit | edit source]
A reader has identified this chapter as an undeveloped draft or outline.
You can help to develop the work, or you can ask for assistance in the project room.Definition of errors
[edit | edit source]For a quantity the error is defined as . Consider a burette which can be read to ±0.05 cm3 where the volume is measured at 50 cm3.
- The absolute error is
- The fractional error is ,
- The percentage error is %
Combination of uncertainties
[edit | edit source]In an experimental situation, values with errors are often combined to give a resultant value. Therefore, it is necessary to understand how to combine the errors at each stage of the calculation.
Addition or subtraction
[edit | edit source]Assuming that and are the errors in measuring and , and that the two variables are combined by addition or subtraction, the uncertainty (absolute error) may be obtained by calculating
which can the be expressed as a relative or percentage error if necessary.
Multiplication or division
[edit | edit source]Assuming that and are the errors in measuring and , and that the two variables are combined by multiplication or division, the fractional error may be obtained by calculating
Plotting graphs
[edit | edit source]
A reader has identified this chapter as an undeveloped draft or outline.
You can help to develop the work, or you can ask for assistance in the project room.The properties of graphs
[edit | edit source]The most basic relationship between two variables and is a straight line, a linear relationship.
The variable is the gradient and is a constant which gives the intercept. The equations can be more complex than this including higher powers of , such as
This is called a quadratic equation and it follows a shape called a parabola. High powers of can occur giving cubic, quartic and quintic equations. In general, as the power is increased, the line mapping the variables wiggles more, often cutting the -axis several times.
Practice
[edit | edit source]Plot between -3 and +2 in units of 1.
Plot between -4 and +1 in units of 1.
Plot between -5 and +4 in units of 1.
Complex numbers
[edit | edit source]- ==Introduction to complex numbers==
The equation:
Does not factorise
without complex numbers does not exist. However the number behaves exactly like any other number in algebra without any anomalies, allowing us to solve this problem.
The solutions are .
is an imaginary number. is a complex number.
Two complex numbers are added by .
Subtraction is obvious: .
Division can be worked out as an exercise. It requires as a common denominator. This is , (difference of two squares), and is .
This means
In practice complex numbers allow one to simplify the mathematics of magnetism and angular momentum as well as completing the number system.
There is an apparent one to one correspondence between the Cartesian plane and the complex numbers, . This is called an Argand diagram. The correspondence is illusory however, because say for example you raise the square root of to a series of ascending powers. Rather than getting larger it goes round and round in circles around the origin. This is not a property of ordinary numbers and is one of the fundamental features of behaviour in the complex plane.
Plot on the same Argand diagram
Solve
(Answers -2 plus or minus 5i, 3/2 plus or minus 2i, i(-1 plus or minus root 2)
2 important equations to be familiar with, Euler's equation:
and de Moivre's theorem:
Euler's equation is obvious from looking at the Maclaurin expansion of .
To find the square root of we use de Moivre's theorem.
so de Moivre's theorem gives
Check this by squaring up to give .
The other root comes from:
de Moivre's theorem can be used to find the three cube roots of unity by
where can be .
Put , and
This is the difference of two squares so
Similarly any collection of th roots of 1 can be obtained this way.
Another example is to get the expressions for and without expanding .
Remember Pascal's Triangle
1 1 2 1 1 3 3 1 1 4 6 4 1 1 5 10 10 5 1 1 6 15 20 15 6 1
Separating the real and imaginary parts gives the two expressions. This is a lot easier than
Use the same procedure to get
and .
Trigonometry
[edit | edit source]- == Trigonometry - the sin and cosine rules ==
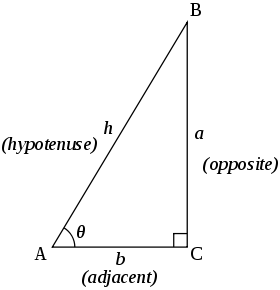
Trigonometric triangle In the following trigonometric identities, , and are the lengths of sides in a triangle, opposite the corresponding angles , and .
- The sin rule
- The cosine rule
- The ratio identity
Trigonometric identities
[edit | edit source]Remember this is a consequence of Pythagoras' theorem where the length of the hypotenuse is 1.
The difference of two angles can easily be generated by putting and remembering and . Similarly, the double angle formulae are generated by induction. is a little more complicated but can be generated if you can handle the fractions! The proofs are in many textbooks but as a chemist it is not necessary to know them, only the results.
Identities and equations
[edit | edit source]Identities and equations look very similar, two things connected by an equals sign. An identity however is a memory aid of a mathematical equivalence and can be proved. An equation represents new information about a situation and can be solved.
For instance,
is an identity. It cannot be solved for ; it is valid for all . However,
is an equation where .
If you try and solve an identity as an equation you will go round and round in circles getting nowhere, but it would be possible to dress up into a very complicated expression which you could mistake for an equation.
Some observations on triangles
[edit | edit source]Check you are familiar with your elementary geometry. Remember from your GCSE maths the properties of equilateral and iscoceles triangles. If you have an iscoceles triangle you can always dispense with the sin and cosine rules, drop a perpendicular down to the base and use trig directly. Remember that the bisector of a side or an angle to a vertex cuts the triangle in two by area, angle and length. This can be demonstrated by drawing an obtuse triangle and seeing that the areas are .
The interior angles of a polygon
[edit | edit source]Remember that the interior angles of a -sided polygon are (in degrees) or () (in radians)
For benzene there are six equilateral triangles if the centre of the ring is used as a vertex, each of which having an interior angle of 120 degrees. Work out the angles in azulene, (a hydrocarbon with a five and a seven membered ring), assuming all the C-C bond lengths are equal, (this is only approximately true).
Vectors
[edit | edit source]- ==Free Web Based Material from HEFCE==
There is a DVD on vectors at Math Tutor.
Vectors
[edit | edit source]Imagine you make a rail journey from Doncaster to Bristol, from where you travel up the West of the country to Manchester. Here you stay a day, travelling the next morning to Glasgow, then across to Edinburgh. At the end of a day's work you return to Doncaster. Mathematically this journey could be represented by vectors, (in 2 dimensions because we are flat earthers on this scale). At the end of the 2nd journey (D-B) + (B-M) you are only a short distance from Doncaster, 50 miles at 9.15 on the clockface. Adding two more vectors, (journeys) takes you to Edinburgh, (about 250 miles at 12.00). Completing the journey leaves you at a zero vector away from Doncaster, i.e. all the vectors in this closed path add to zero.
Mathematically we usually use 3 dimensional vectors over the 3 Cartesian axes , and .
It is best always to use the conventional right handed axes even though the other way round is equally valid if used consistently. The wrong handed coordinates can occasionally be found erroneously in published research papers and text books. The memory trick is to think of a sheet of graph paper, is across as usual and up the paper. Positive then comes out of the paper.
A unit vector is a vector normalised, i.e. multiplied by a constant so that its value is 1. We have the unit vectors in the 3 dimensions:
so that
The hat on the i, j, k signifies that it is a unit vector. This is usually omitted.
Our geographical analogy allows us to see the meaning of vector addition and subtraction. Vector products are less obvious and there are two definitions the scalar product and the vector product. These are different kinds of mathematical animal and have very different applications. A scalar product is an area and is therefore an ordinary number, a scalar. This has many useful trigonometrical features.
The vector product seems at first to be defined rather strangely but this definition maps onto nature as a very elegant way of describing angular momentum. The structure of Maxwell's Equations is such that this definition simplifies all kinds of mathematical descriptions of atomic / molecular structure and electricity and magnetism.
A summary of vectors
[edit | edit source]The unit vectors in the 3 Cartesian dimensions:
a vector is:
The hat on the i, j, k signifies that it is a unit vector.
Vector magnitude
[edit | edit source]A constant times a vector
[edit | edit source]Vector addition
[edit | edit source]Notice
Vector subtraction
[edit | edit source]Notice
Scalar Product
[edit | edit source]Notice
Notice that if this reduces to a square.
If A and B have no common non-zero components in , and the value is zero corresponding to orthogonality, i.e. they are at right angles. (This can also occur by sign combinations making zero. corresponding to non axis-hugging right angles.)
Vector product
[edit | edit source]Notice
The minus sign on the middle term comes from the definition of the determinant, explained in the lecture. Determinants are defined that way so they correspond to right handed rotation. (If you remember our picture of going round the circle, as one coordinate goes up, i.e. more positive, another must go down. Therefore rotation formulae must have both negative and positive terms.) Determinants are related to rotations and the solution of simultaneous equations. The solution of simultaneous equations can be recast in graphical form as a rotation to a unit vector in -dimensional space so therefore the same mathematical structures apply to both space and simultaneous equations.
Matrices and determinants
[edit | edit source]- ==Simultaneous linear equations==
If we have 2 equations of the form we may have a set of simultaneous equations. Suppose two rounds of drinks are bought in a cafe, one round is 4 halves of orange juice and 4 packets of crisps. This comes to 4 pounds 20. The thirstier drinkers at another table buy 4 pints of orange juice and only 1 packet of crisps and this comes to 6 pounds 30. So we have:
and
i.e.
If you plot these equations they will be simultaneously true at and .
Notice that if the two rounds of drinks are 2 pints and 2 packets of crisps and 3 pints and 3 packets of crisps we cannot solve for the prices! This corresponds to two parallel straight lines which never intersect.
If we have the equations:
If these are simultaneously true we can find a unique solution for both and .
By subtracting the 2 equations a new equation is created where has disappeared and the system is solved.
Substituting back gives us .
This was especially easy because had the same coefficient in both equations. We can always multiply one equation throughout by a constant to make the coefficients the same.
If the equations were:
and
things would go horribly wrong when you tried to solve them because they are two copies of the same equation and therefore not simultaneous. We will come to this later, but in the meantime notice that 3 times 8 = 4 times 6. If our equations were:
we can still solve them but would require a lot of algebra to reduce it to three (2x2) problems which we know we can solve. This leads on to the subject of matrices and determinants.
Simultaneous equations have applications throughout the physical sciences and range in size from (2x2)s to sets of equations over 1 million by 1 million.
Practice simultaneous equations
[edit | edit source]Solve:
and
Notice that you can solve:
because it breaks down into a (2x2) and is not truly a (3x3). (In the case of the benzene molecular orbitals, which are (6x6), this same scheme applies. It becomes two direct solutions and two (2x2) problems which can be solved as above.)
Matrices
[edit | edit source]The multiplication of matrices has been explained in the lecture.
but cannot exist. To be multiplied two matrices must have the 1st matrix with the same number of elements in a row as the 2nd matrix has elements in its columns.
where the s are the elements of .
Look at our picture of and as represented by a unit vector in a circle. The rotation of the unit vector about the -axis can be represented by the following mathematical construct.
In two dimensions we will rotate the vector at 45 degrees between and :
This is if we rotate by +45 degrees. For and . So the rotation flips over to give . The minus sign is necessary for the correct mathematics of rotation and is in the lower left element to give a right handed sense to the rotational sign convention.
As discussed earlier the solving of simultaneous equations is equivalent in some deeper sense to rotation in -dimensions.
Matrix multiply practice
[edit | edit source]i) Multiply the following (2x2) matrices.
=
ii) Multiply the following (3x3) matrices.
You will notice that this gives a unit matrix as its product.
The first matrix is the inverse of the 2nd. Computers use the inverse of a matrix to solve simultaneous equations.
If we have
In matrix form this is....In terms of work this is equivalent to the elimination method you have already employed for small equations but can be performed by computers for simultaneous equations.
(Examples of large systems of equations are the fitting of reference data to 200 references molecules, dimension 200, or the calculation of the quantum mechanical gradient of the energy where there is an equation for every way of exciting 1 electron from an occupied orbital to an excited, (called virtual, orbital, (typically equations.)
Finding the inverse
[edit | edit source]How do you find the inverse... You use Maple or Matlab on your PC but if the matrix is small you can use the formula...
Here Adj A is the adjoint matrix, the transposed matrix of cofactors. These strange objects are best described by example.....
This determinant is equal to: 1 ( 1 x 1 - 1 x (-1)) - (-1) ( 2 x 1 - 1 x 3) + 2 ( 2 x (-1) - ( 1 x 3) each of these terms is called a cofactor.
This thing gives the sign alternation in a form mathematicians like even though it is incomprehensible.
Use the determinant
to solve the simultaneous equations on page 47 by the matrix inverse method. The matrix corresponding to the equations on p47.2 is:
1 -1 2 6 2 1 1 = 3 3 -1 1 6 The cofactors are 2 1 -5 -1 -5 -2 -3 3 3 You may find these 9 copies of the matrix useful for striking out rows and columns to form this inverse.... 1 -1 2 1 -1 2 1 -1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 3 -1 1 3 -1 1 3 -1 1 1 -1 2 1 -1 2 1 -1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 3 -1 1 3 -1 1 3 -1 1 1 -1 2 1 -1 2 1 -1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 3 -1 1 3 -1 1 3 -1 1 These are the little determinants with the -1 to the (n-1) factors and the value of the determinant is -9. The transposed matrix of cofactors is 2 -1 -3 1 -5 3 -5 -2 3 So the inverse is 2 -1 -3 -1/9 X 1 -5 3 -5 -2 3 Giving a solution 2 -1 -3 6 1 -1/9 X 1 -5 3 X 3 = -1 -5 -2 3 6 2This takes a long time to get all the signs right. Elimination by subtracting equations is MUCH easier. However as the computer cannot make sign mistakes it is not a problem when done by computer program.
The following determinant corresponds to an equation which is repeated three times giving an unsolvable set of simultaneous equations.
Matrix multiplication is not necessarily commutative, which in English means does not equal all the time. Multiplication may not even be possible in the case of rectangular rather than square matrices.
I will put a list of the properties and definitions of matrices in an appendix for reference through the later years of the course.
Determinants and the Eigenvalue problem
[edit | edit source]In 2nd year quantum chemistry you will come across this object:
You divide by and set to equal to get:
Expand this out and factorise it into two quadratic equations to give:
which can be solved using
Simultaneous equations as linear algebra
[edit | edit source]The above determinant is a special case of simultaneous equations which occurs all the time in chemistry, physics and engineering which looks like this:
This equation in matrix form is and the solution is .
This is a polynomial equation like the quartic above. As you know polynomial equations have as many solutions as the highest power of i.e. in this case . These solutions can be degenerate for example the orbitals in benzene are a degenerate pair because of the factorisation of the polynomial from the 6 Carbon-pz orbitals. In the 2nd year you may do a lab exercise where you make the benzene determinant and see that the polynomial is
from which the 6 solutions and the orbital picture are immediately obvious.
The use of matrix equations to solve arbitrarily large problems leads to a field of mathematics called linear algebra.
Matrices with complex numbers in them
[edit | edit source]Work out the quadratic equation from the 3 determinants
They are all the same! This exemplifies a deeper property of matrices which we will ignore for now other than to say that complex numbers allow you to calculate the same thing in different ways as well as being the only neat way to formulate some problems.
Differentiation
[edit | edit source]- ==Free web-based material from HEFCE==
There is a DVD on differentiation at Math Tutor.
The basic polynomial
[edit | edit source]The most basic kind of differentiation is:
There are two simple rules:
- The derivative of a function times a constant is just the same constant times the derivative.
- The derivative of a sum of functions is just the sum of the two derivatives.
To get higher derivatives such as the second derivative keep applying the same rules.
One of the big uses of differentiation is to find the stationary points of functions, the maxima and minima. If the function is smooth, (unlike a saw-tooth), these are easily located by solving equations where the first derivative is zero.
The chain rule
[edit | edit source]This is best illustrated by example: find given
Let and .
Now and
So using the chain rule we have
Differentiating a product
[edit | edit source]Notice when differentiating a product one generates two terms. (Terms are mathematical expression connected by a plus or minus.) An important point is that terms which represent physical quantities must have the same units and dimensions or must be pure dimensionless numbers. You cannot add 3 oranges to 2 pears to get 5 orangopears. Integration by parts also generates an extra term each time it is applied.
Differentiating a quotient
[edit | edit source]You use this to differentiate .
Problems
[edit | edit source]Differentiate with respect to
Notice we have .
Evaluate the inner brackets first.
Evaluate
a, b and c are constants. Differentiate with respect to .
Answers
[edit | edit source]Harder differentiation problems
[edit | edit source]Differentiate with respect to :
Differentiate with respect to
Differentiate with respect to
Evaluate
Using differentiation to check turning points
[edit | edit source]is the tangent or gradient. At a minimum is zero. This is also true at a maximum or an inflection point. The second gradient gives us the nature of the point. If is positive the turning point is a minimum and if it is negative a maximum. Most of the time we are interested in minima except in transition state theory.
If the equation of is plotted, is is possible to see that at there is a third kind of point, an inflection point, where both and are zero.
Plot between -4 and +3, in units of 1. (It will speed things up if you factorise it first. Then you will see there are 3 places where so you only need calculate 5 points.) By factorising you can see that this equation has 3 roots. Find the 2 turning points. (Differentiate once and find the roots of the quadratic equation using . This gives the position of the 2 turning points either side of zero. As the equation is only in it has 3 roots and 2 maxima / minima at the most therefore we have solved everything. Differentiate your quadratic again to get . Notice that the turning point to the left of zero is a maximum i.e. and the other is a minimum i.e. .
What is the solution and the turning point of .
Solve , by factorisation.
(The 3 roots are -3,0 and +2.
Solutions are and , i.e. -1.7863 and 1.1196.
There are 3 coincident solutions at , , at 0 so this is an inflection point.
The roots are 0, 1 and -1.
Integration
[edit | edit source]- ==Free Web Based Material from HEFCE==
There is a DVD on integration at Math Tutor.
The basic polynomial
[edit | edit source]This works fine for all powers except -1, for instance the integral of
is just
-1 is clearly going to be a special case because it involves an infinity when and goes to a steep spike as gets small. As you have learned earlier this integral is the natural logarithm of and the infinity exists because the log of zero is minus infinity and that of negative numbers is undefined.
The integration and differentiation of positive and negative powers
[edit | edit source]>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>Differentiation 1/3 x*x*x x*x 2x 2 0 0 0 0 1/3 x*x*x x*x 2x 2 ? ? ? ? Integration<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<< I(x) H(x) G(x) F(x) ln(x) 1/x -1/(x*x)
Here I, H, G and F are more complicated functions involving .You will be able to work them out easily when you have done more integration. The thing to notice is that the calculus of negative and positive powers is not symmetrical, essentially caused by the pole or singularity for at .
Logarithms
[edit | edit source]Logarithms were invented by Napier, a Scottish Laird, in the 17th-century. He made many inventions but his most enduring came from the necessity of doing the many long divisions and trigonometric calculations used in astronomy. The Royal Navy in later years devoted great time and expense to developing logarithm technology for the purposes of navigation, leading to the commissioning of the first mechanical stored program computer, which was theoretically sound but could not be made by Charles Babbage between 1833 and 1871.
The heart of the system is the observation of the properties of powers:
This means that if we have the inverse function of we can change a long division into a subtraction by looking up the exponents in a set of tables. Before the advent of calculators this was the way many calculations were done.
Napier initially used logs to the base for his calculations, but after a year or so he was visited by Briggs who suggested it would be more practical to use base 10. However base is necessary for the purposes of calculus and thermodynamics.
Integrating 1/x
[edit | edit source]This is true because is our function which reduces or grows at the rate of its own quantity.
This is our definition of a logarithm.
therefore
therefore
Integrating 1/x like things
[edit | edit source]Just as
so
therefore by the chain rule
therefore
Examples of this are:
or
and
As the integral of is so the differential of is so
is just a constant so so
This can also be done by the chain rule
What is interesting here is that the 5 has disappeared completely. The gradient of the log function is unaffected by a multiplier! This is a fundamental property of logs.
Some observations on infinity
[edit | edit source]Obviously is .
nd are undefined but sometimes a large number over a large number can have defined values. An example is the of 90 degrees, which you will remember has a large opposite over a large hypotenuse but in the limit of an infinitesimally thin triangle they become equal. Therefore the is 1.
Definite integrals (limits)
[edit | edit source]Remember how we do a definite integral
where is the indefinite integral of .
Here is an example where limits are used to calculate the 3 areas cut out by a quartic equation:
.
We see that is a solution so we can do a polynomial division:
x3 -x2 -2x ------------------- x-1 ) x4 -2x3 -x2 +2x x4 -x3 -------- -x3 -x2 -x3 +x2 ------- -2x2 +2x -2x2 +2x -------- 0So the equation is which factorises to
.
Integration by substitution
[edit | edit source]where .
Simple integration of trigonometric and exponential Functions
[edit | edit source]Answers
[edit | edit source]i.e. the integral of .
Integration by parts
[edit | edit source]This is done in many textbooks and Wikipedia. Their notation might be different to the one used here, which hopefully is the most clear. You derive the expression by taking the product rule and integrating it. You then make one of the into a product itself to produce the expression.
(all integration with respect to . Remember by
( gets differentiated.)
The important thing is that you have to integrate one expression of the product and differentiate the other. In the basic scheme you integrate the most complicated expression and differentiate the simplest. Each time you do this you generate a new term but the function being differentiated goes to zero and the integral is solved. The expression which goes to zero is .
The other common scheme is where the parts formula generates the expression you want on the right of the equals and there are no other integral signs. Then you can rearrange the equation and the integral is solved. This is obviously very useful for trig functions where ad infinitum.
also generates itself and is susceptible to the same treatment.
We now have our required integral on both sides of the equation so
Integration Problems
[edit | edit source]Integrate the following by parts with respect to.
Actually this one can be done quite elegantly by parts, to give a two term expression. Work this one out. Expanding the original integrand by Pascal's Triangle gives:
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 x + 7 x + 21 x + 35 x + 35 x + 21 x + 7 x + x
The two term integral expands to2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1/2 x + 7/3 x + 21/4 x + 7 x + 35/6 x + 3 x + 7/8 x + 1/9 x - 1/72
So one can see it is correct on a term by term basis.
If you integrate you will have to apply parts 7 times to get to become 1 thereby generating 8 terms:
7 6 5 4 3 -x cos(x) + 7 x sin(x) + 42 x cos(x) - 210 x sin(x) - 840 x cos(x) + 2 2520 x sin(x) + 5040 x cos(x) - 5040 sin(x) + c (Output from Maple.)Though it looks nasty there is quite a pattern to this, 7, 7x6,7x6x5 ------7! and sin, cos, -sin, -cos, sin, cos etc so it can easily be done by hand.
Differential equations
[edit | edit source]First order differential equations are covered in many textbooks. They are solved by integration. (First order equations have , second order equations have and .)
The arbitrary constant means another piece of information is needed for complete solution, as with the Newton's Law of Cooling and Half Life examples.
Provided all the s can be got to one side and the s to another the equation is separable.
This is the general solution.
Typical examples are:
by definition of logs.
(1)
(2)
(3)
This corresponds to:
The Schrödinger equation is a 2nd order differential equation e.g. for the particle in a box
It has taken many decades of work to produce computationally efficient solutions of this equation for polyatomic molecules. Essentially one expands in coefficients of the atomic orbitals. Then integrates to make a differential equation a set of numbers, integrals, in a matrix. Matrix algebra then finishes the job and finds a solution by solving the resultant simultaneous equations.
The calculus of trigonometric functions
[edit | edit source]There are many different ways of expressing the same thing in trig functions and very often successful integration depends on recognising a trig identity.
but could also be
(each with an integration constant!).
When applying calculus to these functions it is necessary to spot which is the simplest form for the current manipulation. For integration it often contains a product of a function with its derivative like where integration by substitution is possible.
Where a derivative can be spotted on the numerator and its integral below we will get a function. This is how we integrate .
We can see this function goes to infinity at as it should do.
Integration by rearrangement
[edit | edit source]Take for example:
Here there is no function producted in with the powers so we cannot use substitution. However there are the two trig identities
and
Using these we have
so we have two simple terms which we can integrate.
The Maclaurin series
[edit | edit source]We begin by making the assumption that a function can be approximated by an infinite power series in :
By differentiating and setting one gets
Sin, cos and can be expressed by this series approximation
Notice also works for negative .
When differentiated or integrated generates itself!
When differentiated generates .
By using series we can convert a complex function into a polynomial, and can use for small .
In actual fact the kind of approximation used inside computer programs is more like:
These have greater range but are much harder to develop and a bit fiddly on the calculator or to estimate by raw brain power.
We cannot expand this way because is
. However can be expanded.
Work out the series for .
Factorials
[edit | edit source]The factorials you have seen in series come from repeated differentiation. also has a statistical meaning as it is the number of unique ways you can arrange objects.
is 1 by definition, i.e. the number of different ways you can arrange 0 objects is 1.
In statistical thermodynamics you will come across many factorials in expressions such as:
Factorials rapidly get unreasonably large: 6! = 720, 8! = 40320 but 12! = 479001600 so we need to divide them out into reasonable numbers if possible, so for example .
Stirling's approximation
[edit | edit source]Also in statistical thermodynamics you will find Stirling's approximation:
This is proved and discussed in Atkins' Physical Chemistry.
How can you use series to estimate . Notice that the series for
converges extremely slowly. is much faster because the
denominator becomes large quickly.
Trigonometric power series
[edit | edit source]Remember that when you use and
that x must be in radians.....
Calculus revision
[edit | edit source]Problems
[edit | edit source]integrate x to the power of x with respect to x
- Differentiate , with respect to . (Hint - use the chain rule.)
- Differentiate . (Chain rule and product rule here.)
- Differentiate . (Hint - split it into a sum of logs first.)
- Integrate . (Hint - use integration by parts and take the expression to be differentiated as 1.)
Answers
[edit | edit source]- It is just . Bring a out of each term to simplify to .
- .
- - therefore it is 4 times the derivative of .
- You should get by 1 application of parts.
Some useful aspects of calculus
[edit | edit source]- ==Limits==
Many textbooks go through the proper theory of differentiation and integration by using limits. As chemists it is possible to live without knowing this so we might well not have it as an examinable topic. However here is how we differentiate sin from 1st principles.
As for small this expression is .
Similarly for
This is equal to .
Numerical differentiation
[edit | edit source]You may be aware that you can fit a quadratic to 3 points, a cubic to 4 points, a quartic to 5 etc. If you differentiate a function numerically by having two values of the function apart you get an approximation to by constructing a triangle and the gradient is the tangent. There is a forward triangle and a backward triangle depending on the sign of . These are the forward and backward differentiation approximations.
If however you have a central value with a either side you get the central difference formula which is equivalent to fitting a quadratic, and so is second order in the small value of giving high accuracy compared with drawing a tangent. It is possible to derive this formula by fitting a quadratic and differentiating it to give:
HCl r-0.02 sigma (iso) 32.606716 142.905788 -110.299071 HCl r-0.01 sigma (iso) 32.427188 142.364814 -109.937626 HCl r0 Total shielding: paramagnetic : diamagnetic sigma (iso) 32.249753 141.827855 -109.578102 HCl r+0.01 sigma (iso) 32.074384 141.294870 -109.220487 HCl r+0.02 sigma (iso) 31.901050 140.765819 -108.864769
This is calculated data for the shielding in ppm of the proton in HCl when the bondlength is stretched or compressed by 0.01 of an Angstrom (not the approved unit pm). The total shielding is the sum of two parts, the paramagnetic and the diamagnetic. Notice we have retained a lot of significant figures in this data, always necessary when doing numerical differentiation.
Exercise - use numerical differentiation to calculated and using a step of 0.01 and also with 0.02. Use 0.01 to calculate and
Numerical integration
[edit | edit source]Wikipedia has explanations of the Trapezium rule and Simpson's Rule. Later you will use computer programs which have more sophisticated versions of these rules called Gaussian quadratures inside them. You will only need to know about these if you do a numerical project later in the course. Chebyshev quadratures are another version of this procedure which are specially optimised for integrating noisy data coming from an experimental source. The mathematical derivation averages rather than amplifies the noise in a clever way.
Enzyme kinetics
[edit | edit source]Some mathematical examples applied to chemistry
[edit | edit source]- ==Variable names==
The ubiquitous is not always the variable as you will all know by now. One problem dealing with real applications is sorting out which symbols are the variables and which are constants. (If you look very carefully at professionally set equations in text books you should find that there are rules that constants are set in Roman type, i.e. straight letters and variables in italics. Do not rely on this as it is often ignored.)
Here are some examples where the variable is conventionally something other than .
- The Euler angles which are used in rotation are conventionally and not the more usual angle names and . The rotation matrix for the final twist in the commonest Euler definition therefore looks like
- The energy transitions in the hydrogen atom which give the Balmer series are given by the formula is just a single variable for the energy the tilde being a convention used by spectroscopists to say it is wavenumbers, (cm-1). The H subscript on has no mathematical meaning. It is the Rydberg constant and is therefore in Roman type. is known very accurately as 109,677.581 cm-1. It has actually been known for a substantial fraction of the class to make an error putting this fraction over a common denominator in examination conditions.
- In the theory of light is used for frequency and not surprisingly for time. Light is an oscillating electric and magnetic field therefore the cosine function is a very good way of describing it. You can also see here the use of complex numbers. Using the real axis of the Argand diagram for the electric field and the imaginary axis for the magnetic field is a very natural description mathematically and maps ideally onto the physical reality. Here we are integrating with respect to and , the operating frequency if it is a laser experiment is a constant, therefore it appears on the denominator in the integration. In this case we can see a physical interpretation for the integration constant. It will be a phase factor. If we were dealing with sunlight we might well be integrating a different function over in order to calculate all of the phenomenon which has different strengths at the different light frequencies. Our integration limits would either be from zero to infinity or perhaps over the range of energies which correspond to visible light.
- This example is a laser experiment called Second Harmonic Generation. There is an electric field , frequency and a property constant . is a fundamental constant. We have an intense monochromatic laser field fluctuating at the frequency , (i.e. a strong light beam from a big laser). Therefore the term contributes to the polarization. We know from trigonometric identities that can be represented as a cosine of the double angle Therefore the polarization is In this forest of subscripts and Greek letters the important point is that there are two terms contributing to the output coming from which multiplies the rest of the stuff. In summary we have is equal to where everything except the trig(t) and trig(2t) are to some extent unimportant for the phenomenon of doubling the frequency. and differ only in a phase shift so they represent the same physical phenomenon, i.e. light, which has phase. (One of the important properties of laser light is that it is coherent, i.e. it all has the same phase. This is fundamentally embedded in our mathematics.)
van der Waals Energy
[edit | edit source]The van der Waals energy between two inert gas atoms can be written simply as a function of
Notice that the term is positive corresponding to repulsion. The term is the attractive term and is negative corresponding to a reduction in energy. A and B are constants fitted to experimental numbers.
This function is very easy to both differentiate and integrate. Work these out. In a gas simulation you would use the derivative to calculate the forces on the atoms and would integrate Newton's equations to find out where the atoms will be next.
Another potential which is used is:
This has 1 more fittable constant. Integrate and differentiate this.
The is called a Lennard-Jones potential and is often expressed using the 2 parameters of an energy and a distance .
is an energy. Set the derivative of this to zero and find out where the van der Waals minimum is. Differentiate again and show that the derivative is positive, therefore the well is a minimum, not a turning point.
A diatomic potential energy surface
[edit | edit source]
Interaction energy of argon dimer. The long-range part is due to London dispersion forces In a diatomic molecule the energy is expanded as the bond stretches in a polynomial. We set . At the function is a minimum so there is no term.
Whatever function is chosen to provide the energy setting the 1st derivative to zero will be required to calculate . The 2nd and 3rd derivatives will then need to be evaluated to give the shape of the potential and hence the infra-red spectrum. is usually modelled by a very complicated function whose differentiation is not entered into lightly.
A one-dimensional metal
[edit | edit source]A one-dimensional metal is modelled by an infinite chain of atoms 150 picometres apart. If the metal is lithium each nucleus has charge 3 and its electrons are modelled by the function
which repeats every 150 pm. What constant must this function be multiplied by to ensure there are 3 electrons on each atom? (Hint... integrate between either and or -75pm and +75pm according to your equation. This integral is a dimensionless number equal to the number of electrons, so we will have to multiply by a normalisation constant.)
Here we have modelled the density of electrons. Later in the second year you will see electronic structure more accurately described by functions for each independent electron called orbitals. These are subject to rigorous mathematical requirements which means they are quite fun to calculate.
Kepler's Laws
[edit | edit source]Another physics problem but a good example of a log-log plot is the radius and time period relations of the planets.
This data is dimensionless because we have divided by the time / distance of the earth. We can take logs of both.
Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn r 0.3871 0.7233 1 1.524 5.203 9.539 T 0.2408 0.6152 1 1.881 11.86 29.46 Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn log10r -0.4122 0 0.9795 log10T -0.6184 0 1.4692 Try a least squares fit on your spreadsheet program. Using the Earth and Saturn data: (which is extremely bad laboratory practice, to usejust two points from a data set!)
so
so and
This is Kepler's 3rd law. If you use either a least squares fit gradient or the mercury to saturn data you get the same powers. We have got away with not using a full data set because the numbers given are unusually accurate and to some extent tautological, (remember the planets go round in ellipses not circles!).
Newton's law of cooling
[edit | edit source]is the excess temperature of a cooling body over room temperature (20oC say). The rate of cooling is proportional to the excess temperature.
This is a differential equation which we integrate with respect to to get
The water is heated to C and room temperature is C. At the beginning and , so
therefore
but
so
After 5 minutes the water has cooled to C.
so so
by the definition of logarithms. This gives the plot of an exponential decay between 80 and 20oC.
So after 10 minutes C. After 20 minutes C. After 30 minutes C.
Bacterial Growth
[edit | edit source]2 grams of an organism grows by 1/10 gram per day per gram.
This is a differential equation which is solved by integration thus
therefore
When we have 2 grams so
For the sample to double in mass
Half life calculations are similar but the exponent is negative.
Partial fractions for the 2nd order rate equation
[edit | edit source]In chemistry work you will probably be doing the 2nd order rate equation which requires partial fractions in order to do the integrals.
If you remember we have something like
Put the right-hand side over a common denominator
This gives
By setting x to 3 we get 1 = -B (B=-1). Setting x = 0 and B = -1
1 = 3A -2 (A=+1) Check 1 = 3 -x -2 +x true...Therefore
noting the sign changes on integrating 1/(2-x) not 1/x.
Tests and exams
[edit | edit source]- ==A possible final test with explanatory notes==
This test was once used to monitor the broad learning of university chemists at the end of the 1st year and is intended to check, somewhat lightly, a range of skills in only 50 minutes. It contains a mixture of what are perceived to be both easy and difficult questions so as to give the marker a good idea of the student's algebra skills and even whether they can do the infamous integration by parts.
(1) Solve the following equation for
It factorises with 3 and 5 so : therefore the roots are -5 and +3, not 5 and -3!
(2) Solve the following equation for
Divide by 2 and get .
This factorises with 2 and 5 so : therefore the roots are 5 and -2.
(3) Simplify
Firstly so it becomes .
(4) What is
64 = 8 x 8 so it also equals x i.e. is , therefore the answer is -6.
(5) Multiply the two complex numbers
These are complex conjugates so they are minus x i.e. plus 25 so the total is 34.
(6) Multiply the two complex numbers
The real part is -25 plus the . The cross terms make and so the imaginary part disappears.
(7) Differentiate with respect to :
Answer:
(8)
Answer:
(9)
Answer:
(10)
Expand out the difference of 2 squares first.....collect and multiply....then just differentiate term by term giving:
(11)
This needs the product rule.... Factor out the ....
(12)
This could be a chain rule problem.......
or you could take the power 2 out of the log and go straight to the same answer with a shorter version of the chain rule to:.
(13) Perform the following integrations:
must be converted to a double angle form as shown many times.... then all 3 bits are integrated giving .......
(14)
Apart from , which goes to , this is straightforward polynomial integration. Also there is a nasty trap in that two terms can be telescoped to .
(15) What is the equation corresponding to the determinant:
The first term is the second and the 3rd term zero. This adds up to .
(16) What is the general solution of the following differential equation:
where A is a constant..
.
(17) Integrate by parts:
Make the factor to be differentiated and apply the formula, taking care with the signs... .
(18)The Maclaurin series for which function begins with these terms?
It is ....
(19)Express
as partial fractions.
It is .....
(20) What is in terms of sin and cos
This is just Euler's equation.....
so one disappears to give ... .
50 Minute Test II
[edit | edit source](1) Simplify
(2)What is
(3) Solve the following equation for
(4) Solve the following equation for
(5) Multiply the two complex numbers
(6) Multiply the two complex numbers
(7) The Maclaurin series for which function begins with these terms?
(8) Differentiate with respect to :
(9)
(10)
where k is a constant.
(11)
where A is a constant.
(12)
(13)
(14) Perform the following integrations:
(15)
(16) What is the equation belonging to the determinant \begin{vmatrix} x & 0 & 0\\ 0 & x & i \\ 0 & i & x \\ \end{vmatrix} = 0</math>
(17) What is the general solution of the following differential equation:
(18) Integrate by any appropriate method:
(19) Express
as partial fractions.
(20) What is in terms of sin and cos.
50 Minute Test III
[edit | edit source](1) Solve the following equation for
(2) What is
(3) The Maclaurin series for which function begins with these terms?
---- (4) Differentiate with respect to :
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10) Multiply the two complex numbers
(11) Multiply the two complex numbers
(12) Perform the following integrations:
(13)
(14)
(15)
(16) Integrate by parts:
(17) What is the equation corresponding to the determinant:
(18) Express as partial fractions.
(19)What is the general solution of the following differential equation:
(20) What is in terms of sin and cos.
Further reading
[edit | edit source]- ==Further reading==
Books
[edit | edit source]- Paul Monk, Maths for Chemistry: A Chemist's Toolkit of Calculations, (Oxford, 2006), ISBN 978-0199277414.
- Bostock and Chandler, Core Maths for A-level, Third Edition, (Nelson Thornes, 2000), ISBN 978-0748755097.
- M. C. R. Cockett and G. Doggett, Maths for Chemists: Numbers, Functions and Calculus v. 1, (Royal Society of Chemistry, London, 2003), ISBN 978-0854046775
- M. C. R. Cockett and G. Doggett, Maths for Chemists: Power Series Complex Numbers and Linear Algebra v. 2, (Royal Society of Chemistry, London, 2003), ISBN 978-0854044955
- G. Currell and T. Dowman,Mathematics and Statistics for Science, (Wiley, 2005), ISBN 978-0470022290.
- Stephen K. Scott, Beginning Maths for Chemistry, (Oxford, 1995), ISBN 978-0198559306
- Peter Tebbutt, Basic Mathematics for Chemists, 2nd edition, (Wiley, 1994), ISBN 978-0471972839
Online resources
[edit | edit source]There is much useful free material relevant to this book, including downloadable DVDs, funded by the HEFCE Fund for the Development of Teaching & Learning and the Gatsby Technical Education Project in association with the Higher Education Academy at Math Tutor.
Discover Maths for Chemists from the Royal Society of Chemistry is a a one-stop site designed by chemists for chemists. This new free-to-use site brings together all the best resources to help you combine maths and chemistry.
Maths for Chemistry is an online resource providing interactive context-based resources which explain how various aspects of maths can be applied to chemistry. There are quizzes and downloadable files to check understanding.




































































![{\displaystyle -45.1(1.2[A]^{2}-57.9[A]+4.193)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7981e8b0121eda3e60c30bea17314ea9e22d75e2)













































































































































































































































































![{\displaystyle \int _{0}^{3}{(f(x))}={\left[F(x)\right]}_{0}^{3}=F(3)-F(0)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0b1cd525dbdb25e2da66823a62b3b7b3d704fed0)





![{\displaystyle \int _{a}^{b}{x^{4}-2x^{3}-x^{2}+2x}={\left[x^{5}/5-x^{4}/2-x^{3}/3+x^{2}\right]}_{a}^{b}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/32eb1b3fa3d860e7d58fecf62eb707f7e58bee9f)

















![{\displaystyle \int {UV}=U[{\rm {int}}]-\int {[{\rm {diff}}][{\rm {int}}]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c32b9184755e8a590b9c37008f3f3aeb899cdb41)
































































































































































































































































