Another method by which we can obtain a well-defined, finite number from infinitesimal quantities is to divide one such quantity by another.
We shall assume throughout that we are dealing with well-behaved functions, which means that you can plot the graph of such a function without lifting up your pencil, and you can do the same with each of the function's derivatives. So what is a function, and what is the derivative of a function?
A function  is a machine with an input and an output. Insert a number
is a machine with an input and an output. Insert a number  and out pops the number
and out pops the number  Rather confusingly, we sometimes think of
Rather confusingly, we sometimes think of  not as a machine that churns out numbers but as the number churned out when
not as a machine that churns out numbers but as the number churned out when  is inserted.
is inserted.

The (first) derivative  of
of  is a function that tells us how much
is a function that tells us how much  increases as
increases as  increases (starting from a given value of
increases (starting from a given value of  say
say  ) in the limit in which both the increase
) in the limit in which both the increase  in
in  and the corresponding increase
and the corresponding increase  in
in  (which of course may be negative) tend toward 0:
(which of course may be negative) tend toward 0:

The above diagrams illustrate this limit. The ratio  is the slope of the straight line through the black circles (that is, the
is the slope of the straight line through the black circles (that is, the  of the angle between the positive
of the angle between the positive  axis and the straight line, measured counterclockwise from the positive
axis and the straight line, measured counterclockwise from the positive  axis). As
axis). As  decreases, the black circle at
decreases, the black circle at  slides along the graph of
slides along the graph of  towards the black circle at
towards the black circle at  and the slope of the straight line through the circles increases. In the limit
and the slope of the straight line through the circles increases. In the limit  the straight line becomes a tangent on the graph of
the straight line becomes a tangent on the graph of  touching it at
touching it at  The slope of the tangent on
The slope of the tangent on  at
at  is what we mean by the slope of
is what we mean by the slope of  at
at 
So the first derivative  of
of  is the function that equals the slope of
is the function that equals the slope of  for every
for every  To differentiate a function
To differentiate a function  is to obtain its first derivative
is to obtain its first derivative  By differentiating
By differentiating  we obtain the second derivative
we obtain the second derivative  of
of  by differentiating
by differentiating  we obtain the third derivative
we obtain the third derivative  and so on.
and so on.
It is readily shown that if  is a number and
is a number and  and
and  are functions of
are functions of  then
then
 and
and 
A slightly more difficult problem is to differentiate the product  of two functions of
of two functions of  Think of
Think of  and
and  as the vertical and horizontal sides of a rectangle of area
as the vertical and horizontal sides of a rectangle of area  As
As  increases by
increases by  the product
the product  increases by the sum of the areas of the three white rectangles in this diagram:
increases by the sum of the areas of the three white rectangles in this diagram:
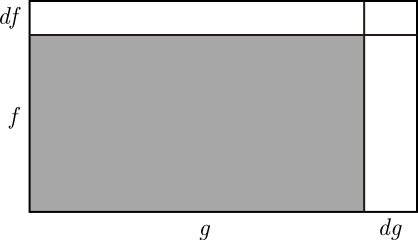
In other "words",

and thus

If we now take the limit in which  and, hence,
and, hence,  and
and  tend toward 0, the first two terms on the right-hand side tend toward
tend toward 0, the first two terms on the right-hand side tend toward  What about the third term? Because it is the product of an expression (either
What about the third term? Because it is the product of an expression (either  or
or  ) that tends toward 0 and an expression (either
) that tends toward 0 and an expression (either  or
or  ) that tends toward a finite number, it tends toward 0. The bottom line:
) that tends toward a finite number, it tends toward 0. The bottom line:

This is readily generalized to products of  functions. Here is a special case:
functions. Here is a special case:

Observe that there are  equal terms between the two equal signs. If the function
equal terms between the two equal signs. If the function  returns whatever you insert, this boils down to
returns whatever you insert, this boils down to

Now suppose that  is a function of
is a function of  and
and  is a function of
is a function of  An increase in
An increase in  by
by  causes an increase in
causes an increase in  by
by  and this in turn causes an increase in
and this in turn causes an increase in  by
by  Thus
Thus  In the limit
In the limit  the
the  becomes a
becomes a  :
:

We obtained  for integers
for integers  Obviously it also holds for
Obviously it also holds for  and
and 
- Show that it also holds for negative integers
 Hint: Use the product rule to calculate
Hint: Use the product rule to calculate 
- Show that
 Hint: Use the product rule to calculate
Hint: Use the product rule to calculate 
- Show that
 also holds for
also holds for  where
where  is a natural number.
is a natural number.
- Show that this equation also holds if
 is a rational number. Use
is a rational number. Use 
Since every real number is the limit of a sequence of rational numbers, we may now confidently proceed on the assumption that  holds for all real numbers
holds for all real numbers 




























































