User:LABoyd2/new import file 151111
import
[edit | edit source]Imports a file for use in the current OpenSCAD model. OpenSCAD currently supports import of DXF, OFF and STL (both ASCII and Binary) files.
NOTE: The file extension is used to determine which type.
OpenSCAD can export files as STL, OFF, AMF, DXF, SVG, CSG OR PNG(Image). These file types created by OpenSCAD, or others, can be imported as follows: STL, OFF and DXF are imported using import(). CSG can be imported using include<> or loaded like an SCAD file PNG can be imported using surface() There are open pull requests for SVG and AMF, which require a bit more work/testing. The file suffix is used to determine type.
Parameters
- <file>
- A string containing the path to the STL, OFF or DXF file.
- <convexity>
- An Integer. The convexity parameter specifies the maximum number of front sides (back sides) a ray intersecting the object might penetrate. This parameter is only needed for correctly displaying the object in OpenCSG preview mode and has no effect on the polyhedron rendering.
import("example012.stl", convexity=3);
import("D:\\Documents and Settings\\User\\My Documents\\Gear.stl", convexity=3);
(Windows users must "escape" the backslashes by writing them doubled.)
Convexity
[edit | edit source]This image shows a 2D shape with a convexity of 4, as the ray indicated in red crosses the 2D shape a maximum of 4 times. The convexity of a 3D shape would be determined in a similar way. Setting it to 10 should work fine for most cases.
Notes
[edit | edit source]In the latest version of OpenSCAD, import() is now used for importing both 2D (DXF for extrusion) and 3D (STL) files.
If you want to render the imported STL file later, you have to make sure that the STL file is "clean". This means that the mesh has to be manifold and should not contain holes nor self-intersections. If the STL is not clean, you might get errors like:
CGAL error in CGAL_Build_PolySet: CGAL ERROR: assertion violation! Expr: check_protocoll == 0 File: /home/don/openscad_deps/mxe/usr/i686-pc-mingw32/include/CGAL/Polyhedron_incremental_builder_3.h Line: 199
or
CGAL error in CGAL_Nef_polyhedron3(): CGAL ERROR: assertion violation! Expr: pe_prev->is_border() || !internal::Plane_constructor<Plane>::get_plane(pe_prev->facet(),pe_prev->facet()->plane()).is_degenerate() File: /home/don/openscad_deps/mxe/usr/i686-pc-mingw32/include/CGAL/Nef_3/polyhedron_3_to_nef_3.h Line: 253
In order to clean the STL file, you have the following options:
- use http://wiki.netfabb.com/Semi-Automatic_Repair_Options . This will repair the holes but not the self-intersections.
- use netfabb basic. This free software doesnt have the option to close holes nor can it fix the self-intersections
- use MeshLab, This free software can fix all the issues
Using MeshLab, you can do:
- Render - Show non Manif Edges
- Render - Show non Manif Vertices
- if found, use Filters - Selection - Select non Manifold Edges or Select non Manifold Vertices - Apply - Close. Then click button 'Delete the current set of selected vertices...' or check http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oDx0Tgy0UHo for an instruction video. The screen should show "0 non manifold edges", "0 non manifold vertices"
Next, you can click the icon 'Fill Hole', select all the holes and click Fill and then Accept. You might have to redo this action a few times.
Use File - Export Mesh to save the STL.
import_dxf
[edit | edit source]DEPRECATED: Will be removed in future releases. Use import() instead.
Read a DXF file and create a 2D shape.
linear_extrude(height = 5, center = true, convexity = 10) import_dxf(file = "example009.dxf", layer = "plate");
import_stl
[edit | edit source]DEPRECATED: Will be removed in future releases. Use import() instead.
Imports an STL file for use in the current OpenSCAD model
import_stl("example012.stl", convexity = 5);
Surface
[edit | edit source]Surface reads Heightmap information from text or image files. Surface can read PNG files.
Parameters
- file
- String. The path to the file containing the heightmap data.
- center
- Boolean. This determines the positioning of the generated object. If true, object is centered in X- and Y-axis. Otherwise, the object is placed in the positive quadrant. Defaults to false.
- invert
- Boolean. Inverts how the color values of imported images are translated into height values. This has no effect when importing text data files. Defaults to false. [Note: Requires version 2015.03]
- convexity
- Integer. The convexity parameter specifies the maximum number of front sides (back sides) a ray intersecting the object might penetrate. This parameter is only needed for correctly displaying the object in OpenCSG preview mode and has no effect on the final rendering.
Text file format
[edit | edit source]The format for text based heightmaps is a matrix of numbers that represent the height for a specific point. Rows are mapped to the Y-axis, columns to the X axis. The numbers must be separated by spaces or tabs. Empty lines and lines starting with a # character are ignored.
Images
[edit | edit source][Note: Requires version 2015.03]
Currently only PNG images are supported. Alpha channel information of the image is ignored and the height for the pixel is determined by converting the color value to Grayscale using the linear luminance for the sRGB color space (Y = 0.2126R + 0.7152G + 0.0722B). The gray scale values are scaled to be in the range 0 to 100.
Examples
[edit | edit source]Example 1:
//surface.scad surface(file = "surface.dat", center = true, convexity = 5); %translate([0,0,5])cube([10,10,10], center =true);
#surface.dat 10 9 8 7 6 5 5 5 5 5 9 8 7 6 6 4 3 2 1 0 8 7 6 6 4 3 2 1 0 0 7 6 6 4 3 2 1 0 0 0 6 6 4 3 2 1 1 0 0 0 6 6 3 2 1 1 1 0 0 0 6 6 2 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 6 6 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Result:
Example 2
// example010.dat generated using octave:
// d = (sin(1:0.2:10)' * cos(1:0.2:10)) * 10;
// save("example010.dat", "d");
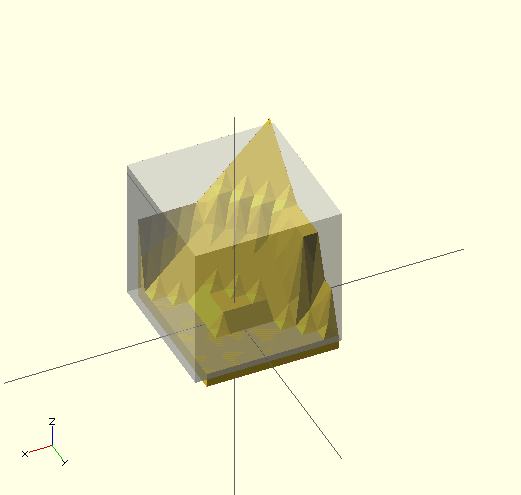
intersection() {
surface(file = "example010.dat", center = true, convexity = 5);
rotate(45, [0, 0, 1]) surface(file = "example010.dat", center = true, convexity = 5);
}
Example 3:
[Note: Requires version 2015.03]
// Example 3a scale([1, 1, 0.1]) surface(file = "smiley.png", center = true);
// Example 3b scale([1, 1, 0.1]) surface(file = "smiley.png", center = true, invert = true);