User:Psychofarm/asenapine
| |
Psychofarm/asenapine
| |
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
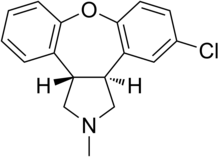
| (3aS,12bS)-5-Chloro-2,3,3a,12b-tetrahydro- 2-methyl-1H-dibenz[2,3:6,7]oxepino[4,5-c]pyrrole | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| ATC code | none |
| PubChem | |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | Template:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox atomTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBoxTemplate:OrganicBox |
| Mol. mass | 285.77 g/mol |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 35% sublingual |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Half life | 24 hours |
| Excretion | 50% in urine, 40% in feces |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. |
C(US) |
| Legal status |
Rx only |
| Routes | sublingual |
Asenapine (Saphris) is a new atypical antipsychotic developed for the treatment of schizophrenia and acute mania associated with bipolar disorder by Schering-Plough after its November 19, 2007 merge with Organon International. Development of the drug, through Phase III trials, began while Organon was still a part of Akzo Nobel.[1] Preliminary data indicate that it has minimal anticholinergic and cardiovascular side effects, as well as minimal weight gain. Over 3000 patients have participated in clinical trials of asenapine, and the FDA accepted the manufacturer's NDA on November 26, 2007 for standard review.[2]
Pharmacology
[edit | edit source]Asenapine shows high affinity (pKi) for numerous receptors, including the serotonin 5-HT1A (8.6), 5-HT1B (8.4), 5-HT2A (10.2), 5-HT2B (9.8), 5-HT2C (10.5), 5-HT5A (8.8), 5-HT6 (9.5), and 5-HT7 (9.9) receptors, the adrenergic α1 (8.9), α2A (8.9), α2B (9.5), and α2C (8.9) receptors, the dopamine D1 (8.9), D2 (8.9), D3 (9.4), and D4 (9.0) receptors, and the histamine H1 (9.0) and H2 (8.2) receptors.[3] It has much lower affinity (pKi < 5) for the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Asenapine behaves as an antagonist at all receptors.[3]
| receptor | affinity (pKi) [3] | affinity Ki (nM) [4] |
|---|---|---|
| serotonin: | ||
| 5-HT1A | 8.6 | 2.5 |
| 5-HT1B | 8.4 | 4.0 |
| 5-HT2A | 10.2 | 0.06 |
| 5-HT2B | 9.8 | 0.16 |
| 5-HT2C | 10.5 | 0.03 |
| 5-HT5 | 1.6 | |
| 5-HT5A | 8.8 | |
| 5-HT6 | 9.5 | 0.25 |
| 5-HT7 | 9.9 | 0.13 |
| adrenergic: | ||
| α1 | 8.9 | 1.2 |
| α2 | 1.2 | |
| α2A | 8.9 | |
| α2B | 9.5 | |
| α2C | 8.9 | |
| dopamine: | ||
| D1 | 8.9 | 1.4 |
| D2 | 8.9 | 1.3 |
| D3 | 9.4 | 0.42 |
| D4 | 9.0 | 1.1 |
| histamine: | ||
| H1 | 9.0 | 1.0 |
| H2 | 8.2 | 6.2 |
| acetylcholine: | ||
| muscarinic | <5 | 8128 |
Indications and usage
[edit | edit source]Asenapine has been approved by the FDA for the acute treatment of adults with schizophrenia and acute treatment of manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder with or without psychotic features in adults.[4]
Side effects
[edit | edit source]Common side effects: (incidence at least 5% or greater and at least twice that for placebo or greater than 10% regardless of placebo rate) Akathisia, oral hypothesia, somnolence, dizziness, extrapyramidal symptoms other than akathisia, weight gain, insomnia, headache
Uncommon side effects:
Rare side effects: Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (Combination of fever, muscle stiffness, faster breathing, sweating, reduced consciousness, and sudden change in blood pressure and heart rate.), tardive dyskinesia
References
[edit | edit source]- ↑ "Bipolar Disorder". Clinical Trials Update (Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News): pp. 52,55. 2007-06-15.
- ↑ Schering-Plough (2007-11-26). "Schering-Plough Announces Asenapine NDA Accepted for Filing by the U.S. FDA". Press release. http://www.schering-plough.com/news/news_article.aspx?reqid=1080771. Retrieved 2008-12-29.
- ↑ a b c Shahid M, Walker GB, Zorn SH, Wong EH. (2009). "Asenapine: a novel psychopharmacologic agent with a unique human receptor signature". J Psychopharmacol. 23 (1): 65–73. PMID 18308814.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ a b "Saphris (asenapine) prescribing information" (PDF). Schering Corporation. 2009-08-01. Retrieved 2009-09-05.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help)
External links
[edit | edit source]- Organon website
- Organon Continues With The Development Of Asenapine For Schizophrenia And Acute Mania Associated With Bipolar I Disorder
Template:Antipsychotics Template:Serotonergics Template:Dopaminergics
