A+ Certification/Exam Objectives/Hardware/Basics/Storage/Hard disk drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), commonly referred to as a hard drive, or hard disk, is a non-volatile storage device which stores digitally encoded data on rapidly rotating platters with magnetic surfaces. Strictly speaking, "drive" refers to a device distinct from its medium, such as a tape drive and its tape, or a floppy disk drive and its floppy disk. Early HDDs had removable media; however, an HDD today is typically a sealed unit (except for a filtered vent hole to equalize air pressure) with fixed media.
There are four main connection types for HDDs. These are:
- PATA - parallel ATA. (previously known as IDE or EIDE).
- SATA - serial ATA.
- SCSI - small computer system interface.
- External - hard drives that connect to an external port on the system.
Parallel ATA
[edit | edit source]
The parallel ATA (PATA) is a keyed 40-pin connection commonly in a form of a ribbon cable, with the first pin being marked by a red wire. Most cables give two connections for two potential hard drives. The later standard of PATA allowed for a total of 80 connections (2 per pin) for a faster transfer rate.
Hard drives connected by this system need to be set to either a Master or Slave using a removable jumper. In some cases, you may need to set the jumper to "Cable select" if the cable is designed in that fashion.
Mainboards normally have two PATA connections available, and support two devices on each connection. Expansion cards are available to allow additional hard drives within a computer.
Parallel ATA originally supported 16MB/s. Later versions of ATA increased the speed to 33, 66, 100, and 133MB/s.
Serial ATA
[edit | edit source]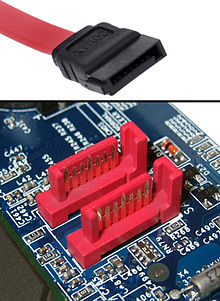
| This section is a stub. You can help Wikibooks by expanding it. |
Serial ATA hard drives use a small connector. Unlike Parallel ATA, only one hard drive per port is allowed.
Despite only having a few pins, Serial ATA is much faster than the predecessor. It allows data transfer starting at 1.5 Gbit/s (192MB/s), and can be as high as 6Gbit/s.
SCSI
[edit | edit source]| This section is a stub. You can help Wikibooks by expanding it. |
SCSI, or Small Computer System Interface, is a standard for attaching multiple devices onto a single connection chain. It normally allows 7 or 15 devices depending on the standard (not counting the SCSI controller itself.) It is mostly used in servers.
SCSI connection chains must be terminated - otherwise you will have undesirable interference preventing the devices from working.
External
[edit | edit source]| This section is a stub. You can help Wikibooks by expanding it. |
There are hard drives that connect to an external port on the computer, either due to their design, or because they are mounted in an external hard drive. The common connection types include Firewire and USB - both of these connections are described in more detail in the ports chapter.
