First Aid/Appendix A: Glossary
Appearance
First Aid
Introduction — Issues in Providing Care — Primary Assessment & Basic Life Support — Secondary Assessment — Circulatory Emergencies
Respiratory Emergencies — Soft Tissue Injuries — Bone & Joint Injuries — Environmental Illness & Injury
Medical Conditions & Poisoning — Advanced Topics — Appendices — Meta content
- Abrasion
- A superficial wound in which the topmost layers of the skin are scraped off
- ABCs
- Airway, breathing and circulation
- AED
- Automated External Defibrillator
- Airway
- The passages which transfer air from the outside environment to the lungs; the tracha, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli
- Artery
- A blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart; contains oxygen-rich, high-pressure blood in the systemic cardiorespiratory system
- Avulsion
- A tearing away of a section of skin from the layers of tissue beneath it
- Bystander
- Any person, trained or untrained, who assists in an emergency situation, but not as part of a duty of employment
- Capillary
- The smallest blood vessels in the body; the skin is rife with capillaries
- Carotid artery
- The main artery providing blood supply to the head.
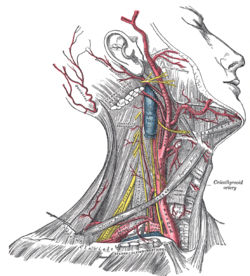
The carotid artery is the largest artery shown here; click for a larger version. - Causation
- Determination of whether the defendant's actions are causally linked to any harm
- Circulation
- The movement of blood throughout the body; performed by the heart
- Consciousness (level of)
- A state of awareness or lack thereof
- Consent
- A legal condition whereby a person can be said to have given consent based upon an appreciation and understanding of the facts and implications of an action
- CPR
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Cyanosis
- The bluish coloration of the skin due to the presence of deoxygenated blood near the skin surface; occurs when the oxygen saturation of arterial blood falls below 85%
- Defibrillation
- Delivering a therapeutic dose of electrical energy to the affected heart with a device called a defibrillator
- Diabetes
- a disease causing an inability to regulate the level of sugar (glucose) in the blood
- Distal
- The point on a limb furthest from its point of attachment to the body
- Duty of care
- A legal obligation imposed on an individual requiring that they exercise a reasonable standard of care while performing any acts that could foreseeably harm others
- EMS
- Emergency Medical System or Emergency Medical Services
- History
- One of the 3 parts of a secondary survey
- Hypoxia
- A condition in which insufficient oxygen reaches body tissue
- Incision
- A clean cut caused by a sharp-edged object
- Insulin
- a hormone that allows glucose to travel from the bloodstream into the cells
- Laceration
- Irregular wounds caused by a blunt impact to soft tissue which lies over hard tissue; tearing of skin
- Landmark
- The location of compressions; on the midline of the chest, even with the nipples
- Liability
- A legal doctrine that makes a person responsible for the damage and loss caused by their acts and omissions regardless of culpability; the requirements to prove liability are a)a duty of care exists b)the standard of care was breached c)causation exists
- Myocardial Infarction
- Heart attack; bleeding or blockage cuts off blood flow to part of the heart muscle
- Nailbed
- The tissue under the nail; pinching the nail and observing the blood return to the nailbed is a good test of circulation at that location
- Oedema (Edema)
- Swelling in the lower legs and ankles. Oedema is caused by a fluid build-up in the body.
- Proximal
- The point on a limb closest to its point of attachment to the body
- Puncture
- A wound caused by an object puncturing the skin
- Semi-prone position
- A position which keeps the tongue from obstructing the airway and allows any fluids to drain from the mouth (aka recovery position)
- Standard of Care
- The degree of prudence and caution required of an individual who is under a duty of care; the requirements of the standard are closely dependent on circumstances
- Tachycardia
- A rapid pulse generally a pulse over 100 at rest
- Vein
- A blood vessel that carries blood toward the heart; most veins carry low-oxygen blood

