Radiation Oncology/Hodgkin/Staging
Appearance
|
Front Page: Radiation Oncology | RTOG Trials |
|
|
Hodgkin's lymphoma: Main Page | Overview | Early stage | Advanced stage | Pediatric | Randomized | |
Lymphoma Staging
Staging
[edit | edit source]- Ann Arbor stage (1971)
- Stage I: Single nodal group; or single extranodal organ in the absence of lymph node involvement (IE)
- Stage II: Multiple nodal groups on same side of the diaphragm; involvement of single extranodal organ with regional lymph node involvement (IIE)
- Stage III: On both sides of the diaphragm; accompanied by extralymphatic extension (IIIE)
- Stage IV: Diffuse involvement of 1 or more extralymphatic organs; isolated extralymphatic organ involvement in the absence of adjacent regional LN involvement, but in conjunction with disease in distant sites. Stage IV includes any involvement of liver, bone marrow, lungs (other than direct extension from another site), or cerebrospinal fluid.
- Staging suffixes
- A and B classification:
- A: absence of constitutional "B" symptoms
- B: presence of constitutional "B" symptoms (see below)
- E: extralymphatic involvement (i.e. IIE)
- S: splenic involvement (i.e. IIIS)
- X: bulky mediastinal disease (i.e. IX). Defined as a ratio ≥ 1/3 of the maximum width of the mass on a PA chest X-ray and the maximum intrathoracic diameter
- A and B classification:
- B-symptoms: unexplained fever >38C / 100.4F, drenching night sweats, unexplained weight loss >10% of baseline weight in the past 6 months. Not included as B symptoms: pruritus, alcohol intolerance, fatigue
- "Classic" advanced disease: Stage III-B or IV.
- Cotswolds modification of Ann Arbor stage - PMID 2809679 (1989)
- Suffix X for bulky disease (nodes > 10cm, or mediastinal mass 1/3 of thoracic diameter or >10 cm)
- Subscript to indicate number of anatomic regions involved, e.g. II3; Stage III may be subdivided into III1 and III2: III1 (may involve splenic, hilar, celiac, or portal nodes) III2 (with para-aortic, iliac, or mesenteric nodes); staging should be identified as being clinical or pathologic
- Added categories of response to therapy (such as uncertain/unconfirmed CR, CRu)
- CRu - presence of an uncertain radiographic abnormality at the site of treated disease. This term was introduced because it is known that such abnormalities may persist for years without any sign of recurrence. Suspicious lesions should be biopsied
- Distinguishing extra-nodal disease from stage IV (guidelines):
- By site of origin: stomach, colon, brain, uterus--most likely extranodal; bone, lung--most likely Stage IV;
- Bone marrow, liver, pleural, or CSF involvement--always stage IV
- Number of lesions: one--extranodal; many or diffuse--stage IV
- Lugano Modification of Ann Arbor stage - PMID 25113753 (2014)
- For Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- A and B suffixes: Removed for NHL. Only used for HL.
- BM bx no longer indicated for routine staging of HL and most DLBCL
- Extranodal (E) designation is used only for limited extranodal disease in the absence of nodal involvement (IE) or in patients with Stage II disease and direct extension to a non-nodal site (IIE). E is not relevant to pts with advanced stage disease.
- X for bulky disease is no longer necessary (instead, a recording of the largest tumor diameter is required).
- Stage I: 1 node or a group of adjacent nodes
- Stage IE: single extranodal lesions without nodal involvement
- Stage II: 2 or more nodal groups on the same side of the diaphragm
- Stage IIE: Stage I or II by nodal extent with limited contiguous extranodal involvement
- Stage II bulky: Stage II as above with bulky disease
- Stage III: Nodes on both sides of the diaphragm; nodes above the diaphragm with spleen involvement
- Stage IV: Additional noncontiguous extralymphatic involvement
- Limited: Stage I-II non-bulky. Advanced: Stage III-IV. Stage II bulky disease may be treated as limited or advanced disease depending on histology and a number of prognostic factors.
Anatomy
[edit | edit source]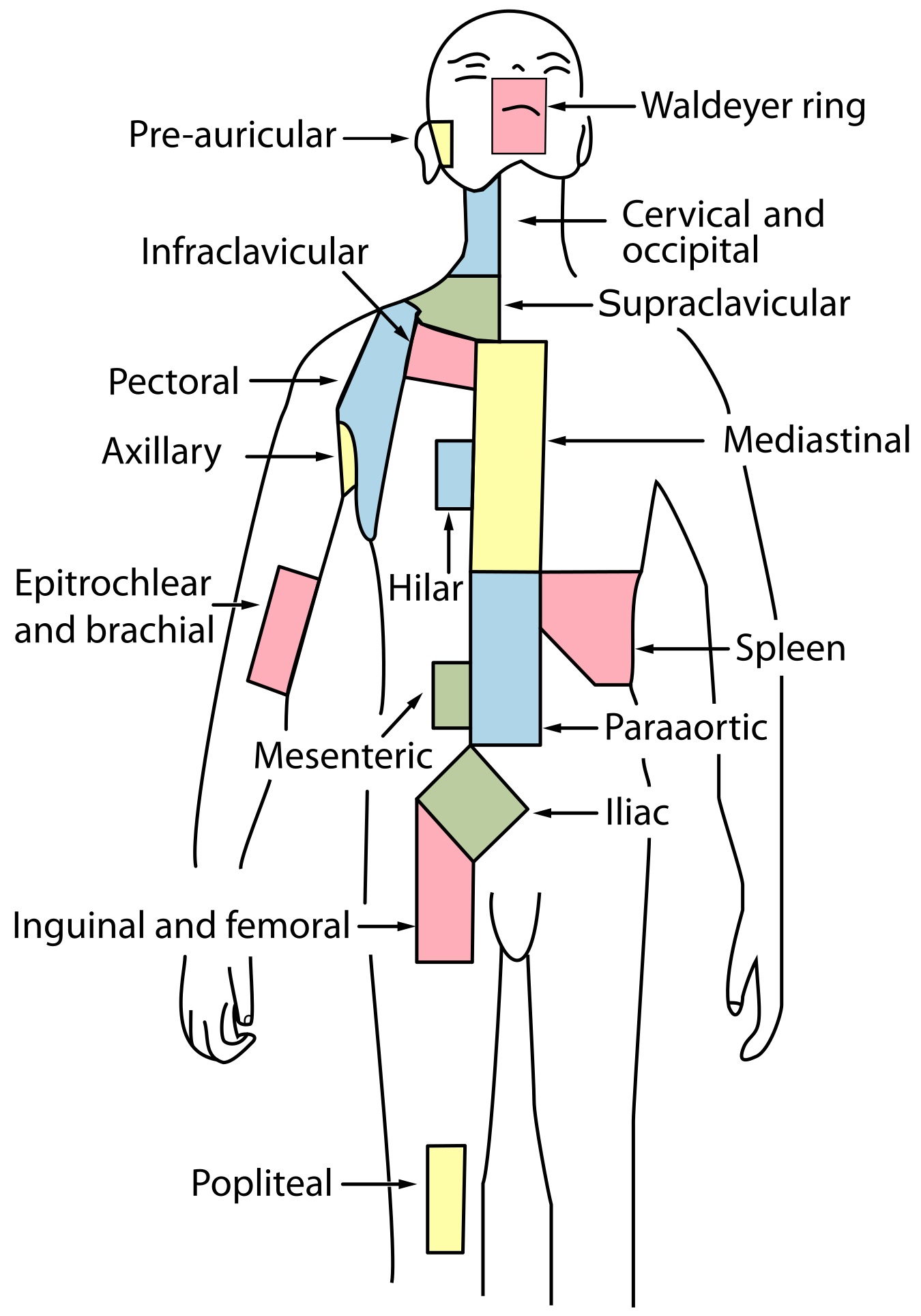
These are not to be taken as involved field diagrams.
Lymph node groups for staging: (bilateral counts as two sites)
From SEER.cancer.gov: Diagram of nodal areas Lymphatic chains
- Head and neck sites:
- Waldeyer's ring (includes palatine tonsils, lingual tonsil, adenoids)
- cervical (includes supraclavicular, occiptal, preauricular)
- Chest and upper extremity:
- Infraclavicular
- Axillary (and pectoral)
- Mediastinal
- Hilar
- Epitrochlear
- Abdomen and lower extremity:
- Spleen
- Paraaortic
- Mesenteric
- Iliac
- Inguinal / femoral
- Popliteal
Note that the supraclav area (especially the left) is considered contiguous to the para-aortics (via the thoracic duct).
